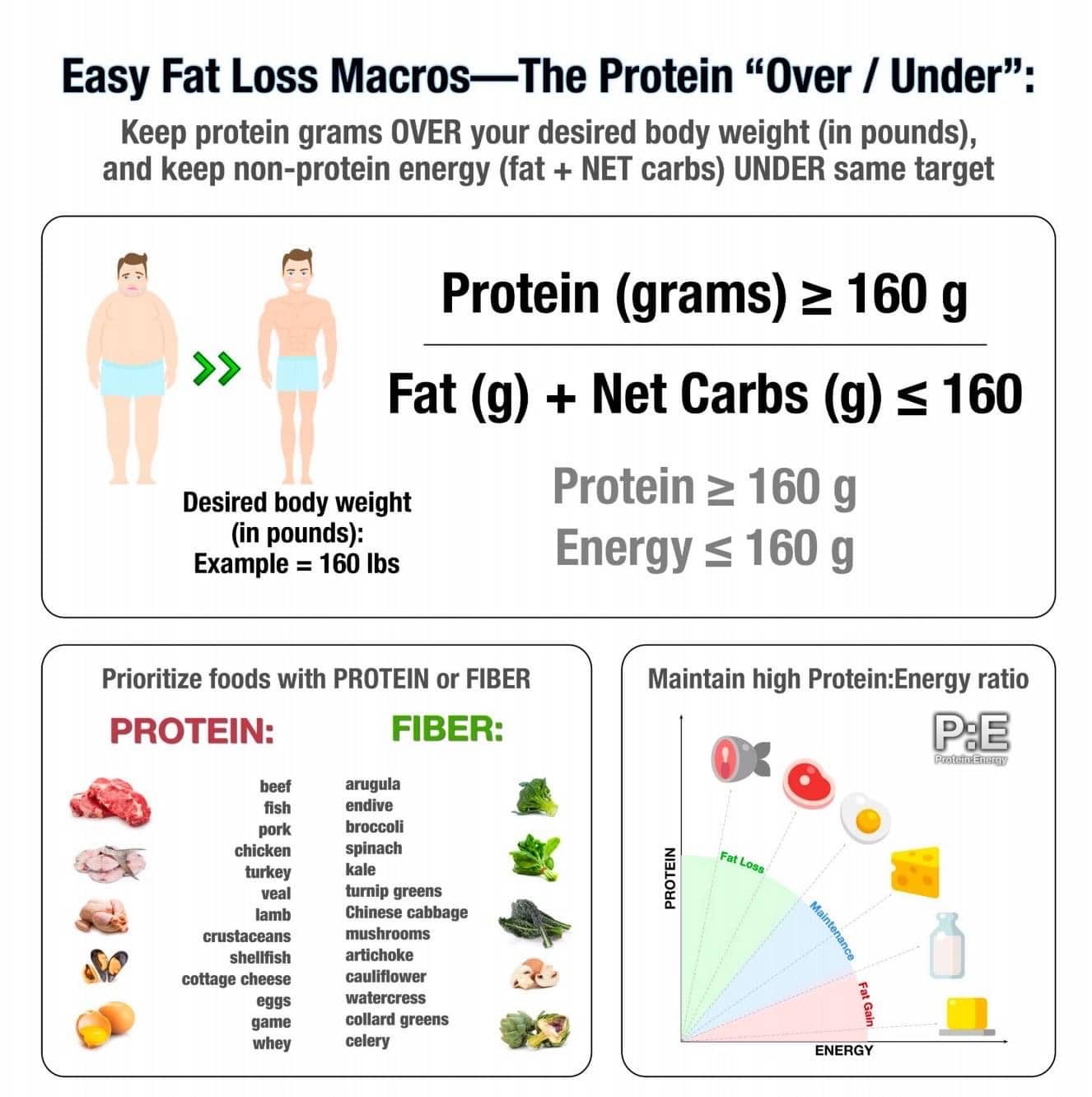
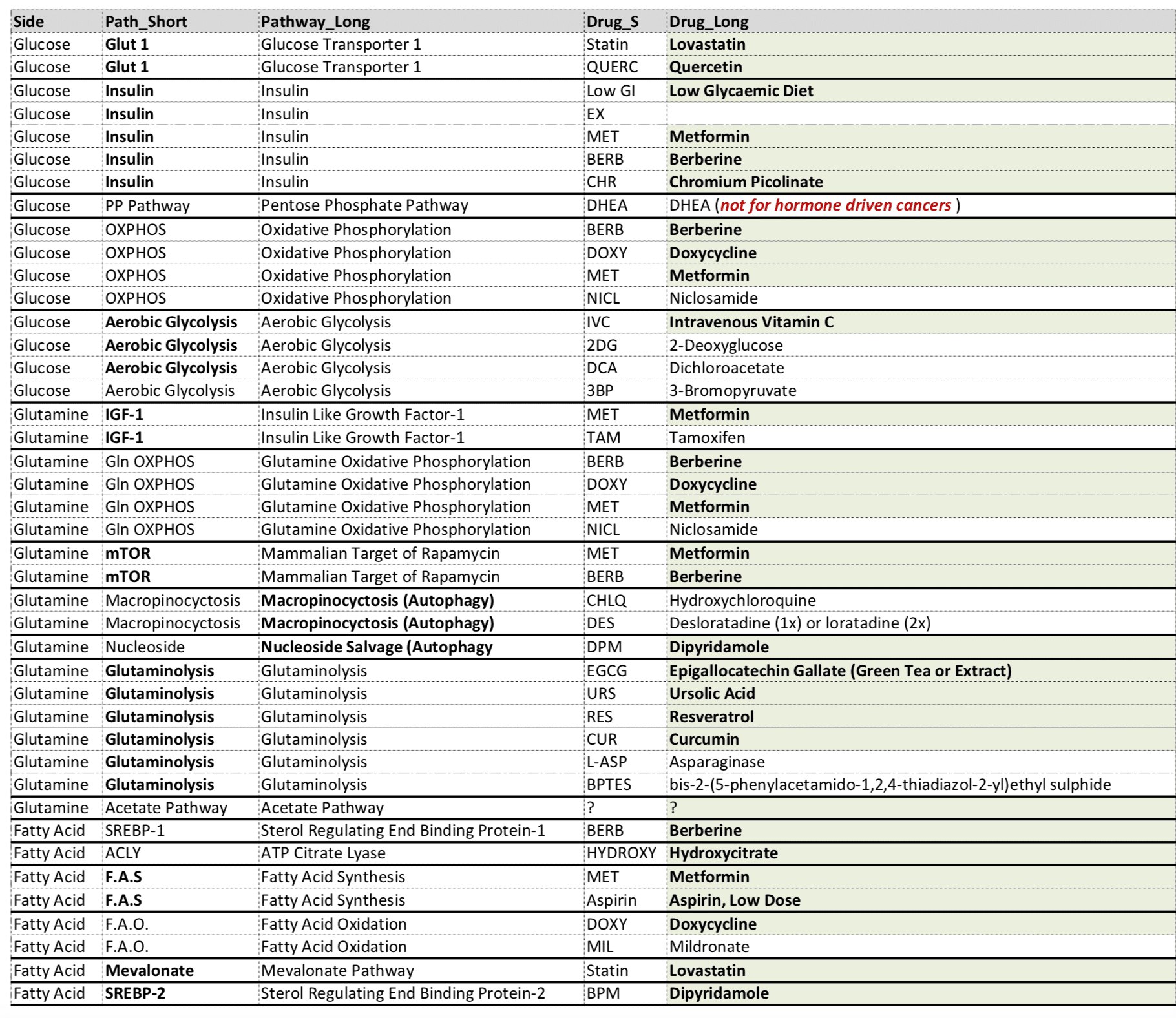
Calcium: Questions And Answers
Calcium is a common mineral in the body that is needed to help blood vessels, muscles, and nerves work to send signals from cell to cell, and to release hormones. The body stores most calcium in bones and teeth.
The main sources of calcium are in foods and dietary supplements. About one-third of dietary calcium comes from milk and milk products like cheese and yogurt. Vegetable sources include Chinese cabbage, kale, and broccoli. Foods may have calcium added, such as fruit juices and drinks, tofu, and cereals.
Most research about calcium and prostate cancer risk has studied calcium in the diet and not calcium in supplements.
For information on laboratory and animal studies done using calcium, see the Laboratory/Animal/Preclinical Studies section of the health professional version of Prostate Cancer, Nutrition, and Dietary Supplements.
Population studies
Clinical trials
Selenium: Questions And Answers
- Vitamin E and selenium.
Early results of SELECT reported in 2009 found no difference in the rate of prostate cancer among the 4 groups. In the selenium alone group, there was a slight increase in the rate of diabetes mellitus. Even though this change was not clearly shown to be due to the supplement, the men in the study were advised to stop taking the study supplements.
In 2014, further results of SELECT showed that selenium supplements in men with low selenium levels at the start of the trial had no effect on prostate cancer risk. However, selenium supplements in men who had high levels of selenium at the start of the trial increased the risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
A study of 1,434 men in SELECT suggested that changes in certain genes which control the way selenium is used by the body may have an effect on the risk of prostate cancer.
Several factors may have affected study results, including the dose of vitamin E and the form of selenium used. The authors concluded that men should avoid selenium at doses that are higher than the recommended dietary intake.
What You Can Do Now
Although fish oil is considered beneficial for your overall health, it isnt clear what kind of effect it may have on your prostate. Consult with your doctor before adding fish oil to your regimen.
Be sure to mention any family cancer history. This information will help your doctor determine whats best for your health profile.
If you decide to try fish oil, remember:
- The omega-3 fatty acids are what provide the health benefits.
- An average dose of omega-3s is 500 milligrams.
- A typical dose of fish oil may not provide the recommended amount of omega-3s.
You May Like: Does Incontinence Go Away After Prostate Surgery
Does Fish Oil Cause Prostate Cancer
I was very upset to read about the study showing that fish oil raises the risk of aggressive prostate cancer. Ive been taking omega-3 supplements for heart health but stopped when I heard the news about its effect on prostate cancer. Whats your take on the study?
Andrew Weil, M.D. |July 26, 2013
I know of no reason why you shouldnt resume taking your fish oil supplements. The study in question, from the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Wash., made headlines and snagged lots of sound bites, but much of the news coverage including that in medical publications did not accurately reflect the findings. Aside from the sensationalist way it was reported, the study itself has serious shortcomings.
As reported, the study found that men who had high concentrations of omega-3s in their blood had a risk of developing prostate cancer that was 43 percent higher than men who had the lowest blood levels of these fatty acids. Even more alarming was the finding that men with the highest blood levels of omega-3s had a 71 percent higher risk of aggressive, possibly fatal prostate cancer than those with the lowest levels. The study was published online on July 10, 2013, in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Andrew Weil, M.D.
In Vitro Cell Culture Experiment
PC3 and DU145 human prostate cancer cell lines were directly purchased from the ATCC and cultured in EMEM with 20% FBS . TRAMP-C2 cells were obtained from the ATCC and cultured in DMEM media 5% FBS added with 5% NUserum growth medium supplement , 0.03% insulin and 0.01 nmol/L dihydrotestosterone . All cell lines used in experiments were Mycoplasmas-free and regularly tested using PCR. Cells were cultured for 812 passages after been thawed. For cell proliferation assay 12,500 cells/well were seeded in 12-well plates. The day after, cells were treated with 6.12 and 12.5 mol/L MAGEPA and MAGAA along with HOSO and vehicle control . MAGDHA was used at 3 mol/L because cell death was observed at higher concentration. Proliferation was measured by cell count using Cytation-5 scanner plate . For spheroids assay, 1,500 cells were plated on agarose pre-coated 96-well plates to promote cellcell adhesion, plates were swirled and the next day each well contained a single spheroid mass. Tumor spheroid size was assessed via bright field imaging using Zeiss Axio Vert or Motic microscope. Spheroid diameter was measured every 48 hours and media changed at the same frequency. For the endothelial cell tube formation assay, immortalized human umbilical vein endothelial vascular cells cells, kindly provided by Dr. Olivier Barbier , were seeded on Matrigel . HUVECs were incubated with serum-free conditioned media from prostate cancer cells pretreated with MAGEPA or control HOSO.
You May Like: Henry Ford Hospital Prostate Cancer Treatment
Scientific Review Published In Advances In Nutrition Finds Despite Mounting Studies There Isnt Enough Strong Evidence
Consumers have been urged to increase their consumption of omega-3 fatty acids, with the promise of improved health outcomes. In particular, the results of many studies have suggested that omega-3 fatty acid intake may reduce your risk of many types of cancer. Despite these findings, the relationship between omega-3 fatty acid consumption and cancer remains controversial and unsettled.
Published in Advances in Nutrition, the international review journal of the American Society for Nutrition, Consumption of Fish and -3 Fatty Acids and Cancer Risk: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies sheds new light on the controversy. According to the authors of this scientific review, in studies of different types of cancer included in previously published meta-analyses, differences in types and doses of omega-3 fatty acids have affected the conclusions obtained and led to contradictory and inconsistent meta-analysis findings. A systematic approach to providing evidence is thus needed.
In order to determine whether or not omega-3 fatty acids prevent cancer with a high level of confidence, the authors have called for further studies to identify the actual effects of omega-3 fatty acids on cancer risks by using individual patient data meta-analyses.
Why You Should Take Krill Oil
The only problem is that a lot of Omega 3 supplements tend to use low-quality fish oils. These can become rancid and cause indigestion. Although they might be cheaper, they are less effective.
Krill Oil is, without a doubt, the best and most effective means of getting your dose of Omega 3. Its more potent, sourced from clean waters, meaning its unpolluted and more bioavailable.
If 70% of your fatty acid intake is not from Omega 3, you will suffer from high cholesterol levels, a higher risk of cancer, and even cardiovascular problems down the line. So finding a potent and effectively absorbed source of omega 3 is an integral part of your dietary supplements.
My Wild Antarctic Krill Oil is sourced from pure and unpolluted waters and as a result, does not need any processing, meaning it is Pure, Natural and Virgin pretty much its the best money can buy.
To find out more about my Wild Antarctic Krill Oil, .
Don’t Miss: What Is The Function Of Prostate Gland In Human Body
Modified Citrus Pectin: Questions And Answers
In This Section
Side effects that have been reported include itching, stomach upset, abdominalcramps, increased gas, and diarrhea.
The FDA has not approved the use of MCP as a treatment for cancer or any other medical condition.
MCP is available in the United States in food products and dietary supplements. The FDA does not approve dietary supplements as safe or effective. The company that makes the dietary supplements is responsible for making sure that they are safe and that the claims on the label are true and do not mislead the consumer. The way that supplements are made is not regulated by the FDA, so all batches and brands of MCP supplements may not be the same.
Prostate Cancer Risk And Omega
It is generally reassuring when we read health advice that contains a clear message, especially when the advice involves something pleasurable. For instance, eat dark chocolate, and wash it down with red wine . But confusion and consternation abound when research produces a mixed message that seems contrary to previous advice. After years of hearing that eating fatty fish or taking fish oil supplements was good for the heart, the eyes, and even mood, the public was puzzled this summer by a study that suggested a risk of prostate cancer in men with high levels of omega-3 fatty acids obtained from these sources.
Although conclusions in research are subject to change, in this instance, investigators not connected to the fish oil study complained that the headline-hungry media did not cover all of the facts. They also charged that the headlines were potentially harmful and that the findings were tainted by overreach. A closer look at the study is warranted.
Also Check: Prostate Md By 1md Reviews
Too Much Fish Oil Might Boost Prostate Cancer Risk
Often-fatal aggressive disease of particular concern
HealthDay Reporter
WEDNESDAY, July 10 — Eating a lot of oily fish or taking potent fish oil supplements may increase a man’s risk of developing prostate cancer, new research suggests.
Moreover, marine sources of omega-3 fatty acids may also raise the risk for aggressive prostate cancer, according to the study by scientists at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle.
“These anti-inflammatory omega-3s were associated with a 43 percent increased risk for prostate cancer overall, and a 71 percent increased risk in aggressive prostate cancer,” said study lead author Theodore Brasky, a research assistant professor at Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center in Columbus, who was at Hutchinson at the time of the study.
Aggressive prostatecancer is often fatal, he added.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish such as salmon, trout and fresh tuna and in fish oil capsules, are widely reputed to have health benefits because of their anti-inflammatory properties.
But this new research, published online July 11 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, confirms damaging evidence reported in two prior studies.
Just why are these omega-3 fatty acids associated with prostate cancer? “That’s the million dollar question,” Brasky said.
Oxidative stress plays a role in other cancers, Brasky said.
Show Sources
Patient Population And Eligibility Criteria
Inclusion criteria
Patients must be 18 or older, give informed consent and have chosen RP for treatment of a PCa with a Gleason score7.
Exclusion criteria
Patients are not eligible if they are intolerant or allergic to fish or sunflower seeds or if they have a diagnosis of bipolar disorder.
Washout period
Patients already taking omega-3 supplements can participate after a washout period of at least 8 weeks before randomization. Other dietary supplements must be stopped before randomization.
Don’t Miss: Malignant Neoplasm Of Prostate C61
Pomegranate: Questions And Answers
The pomegranate is a fruit grown in Asia and in the Mediterranean, East Indies, Africa, and the United States. Pomegranate has been used as medicine for hundreds of years.
The pomegranate is made up of the following:
Pomegranate fruit and juice may be taken as food, drink, or a dietary supplement.
For information on laboratory and animal studies done using pomegranate, see the Laboratory/Animal/Preclinical Studies section of the health professional version of Prostate Cancer, Nutrition, and Dietary Supplements.
In a 2015 study, 183 men with recurrentprostate cancer were randomly assigned to receive either pomegranate juice, pomegranate extract, or a placebo. The study found no difference in how fast the prostate-specific antigen level rose between the 3 groups. There is not enough evidence to know whether pomegranate can prevent or treat prostate cancer.
No serious side effects have been reported from the use of pomegranate.
Are Blood Levels Of Omega
Blog Post
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in U.S. men, with annual mortality of approximately 32,000. Nearly 175,000 new cases of prostate cancer are diagnosed in the U.S. per year.
Inflammation plays a role in many types of cancer, including prostate cancer. A number of variables such as obesity and diet have been shown to be related to inflammation. For example, long-chain polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory effects. These fatty acids, otherwise known as fish oils, are found mostly in fatty fish and dietary supplements and have also been shown to be beneficial for cardiovascular health. While most studies have not shown an association between fish oils and prostate cancer, there was one large study published in 2013 that did show an increased risk of prostate cancer, particularly more aggressive cancer, with increased blood levels of omega-3 fatty acids. Thus, the goal of the current study was to examine the relationship between baseline levels of omega-3 fatty acids and prostate cancer development in a sample of healthy men. A secondary goal of this study was to add our findings to an existing meta-analysis of similar studies.
Our main findings were as follows:
Conclusion
References
Help us guide the world to better health
You May Like: Is Surgery Best Option For Prostate Cancer
What Research Has Found About Omega
Two recent important studies on omega-3 fatty acids found that people who took omega-3 supplements did not have lower risks of having cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks or strokes.
The STRENGTH study looked at the effect of omega-3 fatty acid supplements in people who already had high risks of having cardiovascular events. This randomized trial included more than 13,000 people who were randomly assigned to take omega-3 supplements or a placebo. Between the two groups, there were no significant differences of major cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks or strokes, after three and a half years of follow- up. The authors concluded that their trial results did not support using omega-3 fatty acid supplements to reduce these risks.
Also, the DO-HEALTH clinical trial tested whether vitamin E, omega-3s, and/or strength-training exercises improved the health of more than 2,100 older adults. The study found that none of these interventions, including omega-3s, improved blood pressure, which is indicative of cardiovascular health.
Earlier studies also had similar findings. For example, in 2019 the VITAL study of supplements found that taking omega-3 supplements did not lead to lower risks of cardiovascular events. A 2018 analysis of clinical trials looked at data of nearly 78,000 patients with a history of heart disease, stroke, or diabetes and found no association between omega-3 fatty acids and a reduced risk of heart disease or major vascular events.
Qpcr And Western Blots
RNA extracted from the samples not analyzed by RNAseq was used to validate the expression of VEGFR2, Lrg1, Mmm2, Cd248, Plvap, DUSP1, Sfp1, Aplnr, c-Jun, and Sntb1 genes using the housekeeping gene b-actin as a reference gene. For HUVECs, the expression of VEGFR2, ANGPT2, and VWF was compared with reference genes GAPDH, b-actin, and 18S rRNA. Primers were ordered from Integrated DNA Technologies , qPCR reactions were prepared using Advanced qPCR mastermix and cDNA produced using the high-capacity cDNA reverse transcription Kit . The cycling conditions consisted of 1 cycle at 95°C during 5 minutes, followed by 40 three-segment cycles for amplification . Melting curve was performed at the end of PCR amplification to verify specificity. Experiments were run on CFX96 real-time system C1000 thermal cycler . For western blotting, total proteins were extracted using RIPA buffer and samples separated by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis before PDVF transfer and immunoblotting. Protein-bound membranes were incubated overnight with primary antibodies at 4°C, washed with TBS-T and secondary horseradish peroxidaseconjugated goat anti-rabbit or anti-mouse antibodies were incubated to perform ECL-based revelation of specific peptides. The primary antibodies were: Ang-2 , GAPDH , VEGFR-2 , b-Actin , and Flag .
Read Also: What Is The Test For Prostate Cancer Called
Quality Of Life And Psychosocial Functioning
PCa and its treatment are associated with significant psychological distress. Large-scale epidemiological studies on psychological disorders in the context of PCa are sparse. Nonetheless, in a study conducted by our team in 861 patients treated for PCa, we found that 17.0% exhibited clinical levels of depression, while 23.7% of the patients had clinical levels of anxiety . Moreover, we observed sexual difficulties, sleep impairments and fatigue in 70.5%, 31.9%, and 18.5% of the patients, respectively.
Epidemiological studies have shown associations between a greater annual fish intake and lower depression rates . A RCT conducted in medical students , comparing a 12-weeks LCn3 supplementation to a placebo, showed a 20% reduction of anxiety symptoms . A recent study found no significant effect of omega-3 supplementation on sleep quality , while a study of 633 breast cancer survivors showed that a higher intake of omega-6 relative to omega-3 was associated with a higher risk of fatigue . These questions remain to be investigated in PCa patients using a RCT.
