Getting A Prostate Biopsy
For some men, getting a prostate biopsy might be the best option, especially if the initial PSA level is high. A biopsy is a procedure in which small samples of the prostate are removed and then looked at under a microscope. This test is the only way to know for sure if a man has prostate cancer. If prostate cancer is found on a biopsy, this test can also help tell how likely it is that the cancer will grow and spread quickly.
For more details on the prostate biopsy and how it is done, see Tests to Diagnose and Stage Prostate Cancer.
For more information about the possible results of a prostate biopsy, see the Prostate Pathology section of our website.
Understanding Your Biopsy Results
A specialist doctor called pathologist looks at the prostate samples under a microspore. The results usually take about 2 to 4 weeks.
You might have a negative biopsy. This means that no cancer cells were found. Your doctor might recommend another biopsy even if the first was negative. They’ll discuss this with you. This is because in some cases biopsies can miss cancer.
A positive biopsy means that they have found cancer cells. A pathologist then grades each sample of prostate cancer cells based on how quickly they are likely to grow or how aggressive the cells look. You may hear this being called the Gleason score or Grade Group.
Doctors now use the Gleason score and other information to divide prostate cancer into 5 groups. This is called the Cambridge Prognostic Group .
It can be difficult to understand what the Gleason score, Grade Group and CPG mean in your situation. We have more information about this, and you can ask your doctor and specialist nurse if you have any questions.
If Screening Test Results Arent Normal
If you are screened for prostate cancer and your initial blood PSA level is higher than normal, it doesnt always mean that you have prostate cancer. Many men with higher than normal PSA levels do not have cancer. Still, further testing will be needed to help find out what is going on. Your doctor may advise one of these options:
- Waiting a while and having a second PSA test
- Getting another type of test to get a better idea of if you might have cancer
- Getting a prostate biopsy to find out if you have cancer
Its important to discuss your options, including their possible pros and cons, with your doctor to help you choose one you are comfortable with. Factors that might affect which option is best for you include:
- Your age and overall health
- The likelihood that you have prostate cancer
- Your own comfort level with waiting or getting further tests
If your initial PSA test was ordered by your primary care provider, you may be referred to a urologist for this discussion or for further testing.
Don’t Miss: Can You Ejaculate From Prostate
What Are The Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
Some of the greatest risk factors for prostate cancer include:
- Age. Prostate cancer is very rare in men younger than 40 years of age. In contrast, approximately 60% of prostate cancer cases occur in men that are older than 65.
- Race. African-American men tend to be at greater risk for prostate cancer compared to non-Hispanic whites, whereas Asian-Americans and Hispanic/Latino men are less susceptible to this disease.
- Location. Prostate cancer is most common in North America, Europe, Australia, and the Caribbean. It is rarer in Asia, Africa, and Central and South America. This may be because of more intensive screening procedures for the disease in certain countries, although lifestyle factors such as diet could also play a key role in the difference.
- Family history. In many cases, there is a strong hereditary factor associated with the emergence of prostate cancer. In fact, men who have a father or brother with prostate cancer have a much higher risk of developing it themselves.
Other possible risk factors could include a dairy-rich diet, obesity, smoking, and exposure to harmful chemicals.
Genetic Testing For Prostate Cancer
You may hear a lot about genetics or genomics. Both terms are related to genes and cell DNA, but they are different. These tests are being used to learn more about the DNA of cancer cells, and link DNA mutations with treatments. In the future, genetic testing may be the first step doctors take when diagnosing prostate cancer.
You May Like: How Long Can You Live With Gleason 7 Prostate Cancer
Recommended Reading: How To Know If You Have A Prostate
An Abnormal Psa Test: What Comes Next
If your PSA score is in the abnormal range, your doctor may recommend yourepeat the PSA test. If your levels are still high, your doctor mightrecommend one of the newer prostate cancer screening tests available today.
These tests can help better assess your risk for prostate cancer anddetermine whether a biopsy is necessary. Only a prostate biopsy candefinitively diagnose prostate cancer.
For individualized recommendations that suit you, ask your doctor about:
- What age you should start prostate cancer screening
- New blood, urine and imaging tests that are available
- Improved biopsy techniques, if applicable
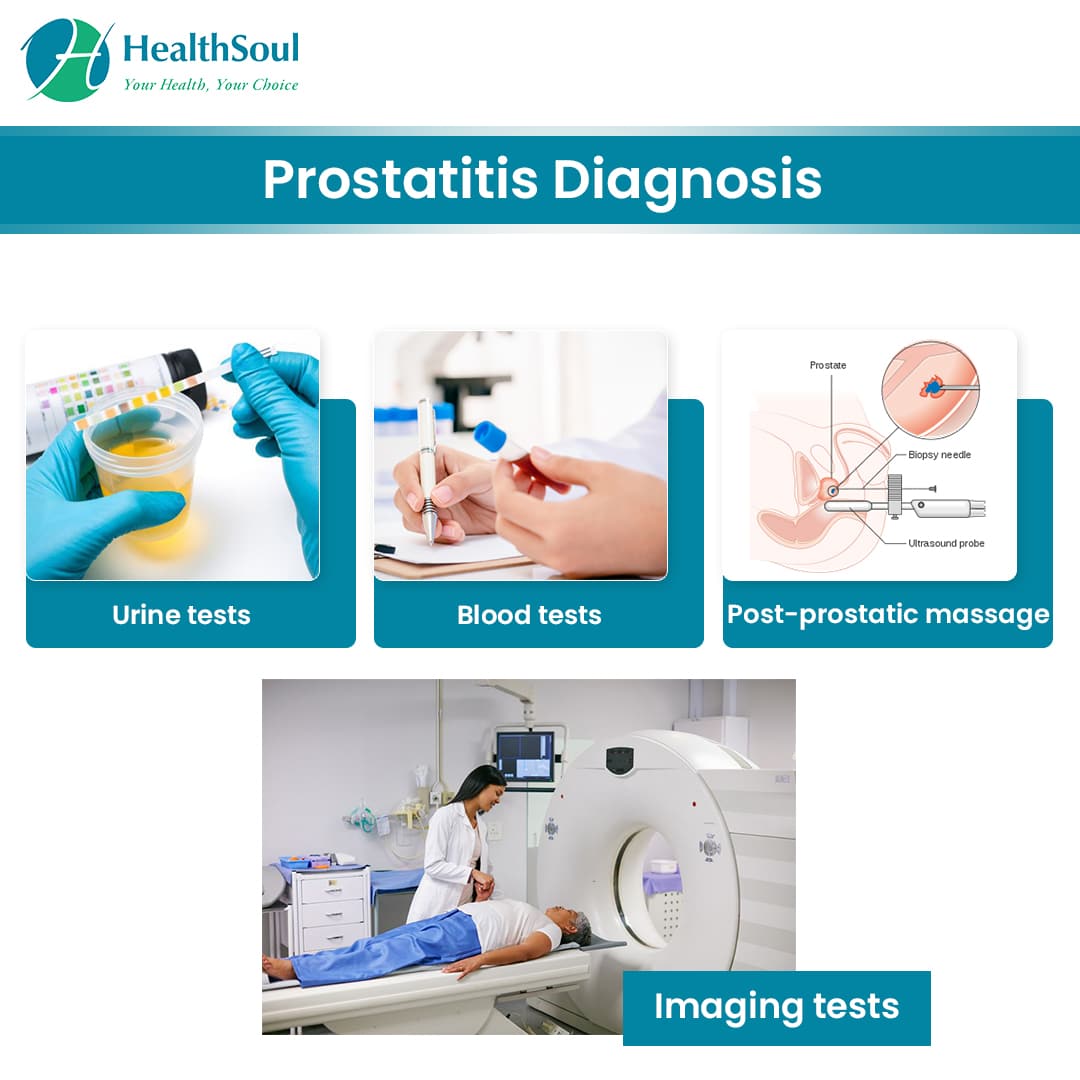
How Is Bph Diagnosed And Evaluated
Early diagnosis of BPH is important because if left untreated it can lead to urinary tract infections, bladder or kidney damage, bladder stones and incontinence. Distinguishing BPH from more serious diseases like prostate cancer is important.
Tests vary from patient to patient, but the following are the most common:
Also Check: Gleason Level 6 Prostate Cancer
Don’t Miss: What Age To Get Tested For Prostate Cancer
So Doc Which Grey Cup Did You Win
Do you need an annual prostate exam? Probably not. This mostly depends on your age and if youre high risk. You may not look forward to Prostate Cancer Awareness Month like you do the Grey Cup. Still, every year the September-long event does highlight a wide range of great tips for keeping your prostate and the rest of you healthy and getting a prostate exam tops the list if youre in a high-risk category. Oh, and doctors always remove their rings while performing the exams.
Also Check: Can You Remove A Prostate
What Should I Expect During A Prostate Exam
As mentioned above, there are two types of screenings that your healthcare provider may use to detect prostate cancer: a PSA blood test and a digital rectal exam . Research shows that the PSA blood test is more effective for detecting prostate cancer. However, the DRE can still find cancer in people with normal PSA levels. For this reason, many healthcare providers recommend both.
Neither test confirms you have prostate cancer, which is why theyre considered screening assessments rather than diagnostic tests.
PSA blood test
For this test, your healthcare provider simply draws a sample of your blood and sends it to a lab for analysis. The PSA blood test measures the amount of prostate-specific antigen in your blood.
There is no official cutoff score that can determine whether or not you have prostate cancer. Instead, the results are used as a gauge to determine if more testing is needed.
If you have a high PSA, you may need further testing such as a prostate biopsy, MRI or other lab tests to determine if prostate cancer may be present.
Digital rectal exam
During a DRE, your healthcare provider inserts a lubricated, gloved finger into your rectum. This way, they can feel your prostate to see if there are any lumps or bumps on the back portion of the gland .
Don’t Miss: Can Over Ejaculation Cause Prostate Problems
About Half Of Men Older Than 50 Have An Enlarged Prostate Here Are Some Of The Basic Facts You Need To Know About This Common Condition
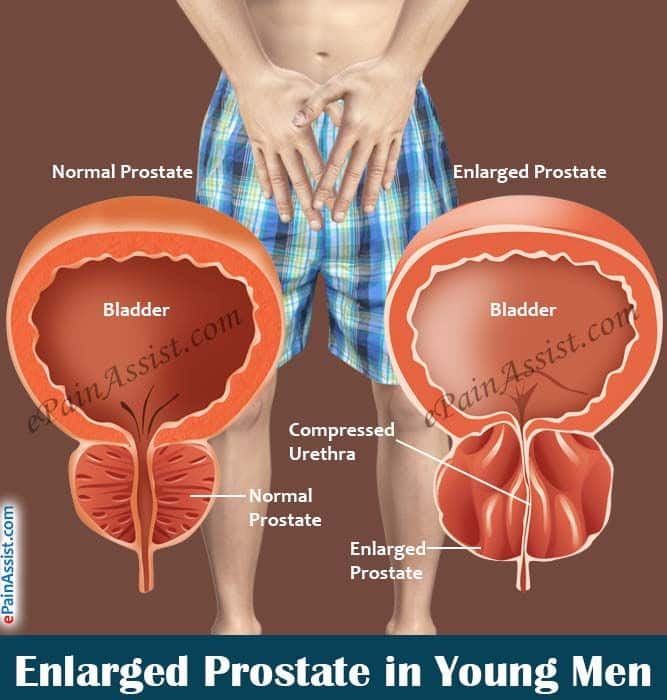
As men age, many experience prostate gland enlargement. This condition is known as benign prostatic hyperplasia .
The prostate gland surrounds the urethra, the hollow tube that carries urine out of the body. When the prostate gets bigger, it can squeeze or partially block the urethra, which leads to problems urinating.
BPH is quite common in older men. In fact, the condition impacts about 50% of men between the ages of 51 and 60. For men 80 and older, the prevalence of BPH is approximately 90%, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Prostate Cancer Screening Ages 55 To 69
This is the age range where men will benefit the most from screening.Thats because this is the time when:
- Men are most likely to get cancer
- Treatment makes the most sense, meaning when treatment benefits outweigh any potential risk of treatment side effects
Most men will get prostate cancer if they live long enough. Some prostatecancers are more aggressive others can be slow-growing. Doctors will takeyour age and other factors into consideration before weighing the risks andbenefits of treatment.
You should ask your doctor how often he or she recommends you get screened.For most men, every two to three years is enough.
Depending on the results of your first PSA test, your doctor may recommendyou get screened less frequently.
You May Like: Prostate Cancer Center Of New Jersey
Recommended Reading: How To Find Your Prostate
Tests Used To Check The Prostate
This first step lets your doctor hear and understand the “story” of your prostate concerns. You’ll be asked whether you have symptoms, how long you’ve had them, and how much they affect your lifestyle. Your personal medical history also includes any risk factors, pain, fever, or trouble passing urine. You may be asked to give a urine sample for testing.
See Your Doctor If You Have Symptoms
If you cant urinate at all, you should get medical help right away. Sometimes this problem happens suddenly to men after they take certain cold or allergy medicines.
You should see your doctor if you have one or more of these symptoms:
- a weak urine stream
- unable to empty your bladder completely
- urinating eight or more times a day
- urine that has an unusual color or smell
- waking often to urinate when you sleep
Recommended Reading: Support Group For Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer: Advancements In Screenings
You may know thatprostate canceris one of the most common cancer types in men. The good news is that thereare many treatment and management options, even if the cancer is caught ata later stage.
What you may not know: There are several options when it comes toprostate cancer screening. After considering multiple factors, your doctor may recommend theprostate-specific antigen test, and/or one of the newer screeningtests that are now available.
Johns Hopkins urologistChristian Pavlovich, M.D., explains what you should know.
What Is A Prostate Exam
A prostate exam is a screening method used to look for early signs of prostate cancer. In general, a prostate exam includes a PSA blood test and a digital rectal exam .
During the digital rectal exam portion, your healthcare provider carefully inserts their gloved finger into your rectum. This allows them to feel the edges and surface of your prostate gland to detect any potential abnormalities.
Read Also: Abdominal Pain After Prostate Surgery
Don’t Miss: Blood Test For Prostate Cancer Screening
Do Prostate Problems Cause Other Problems
Yes, a prostate problem may cause other problems, such as
- problems having sex
- feeling stressed due to chronic pain
- inflammation in areas near your prostate
Which problem you may get depends on the type of prostate problem you have. Other problems may vary from man to man for each type of prostate problem.
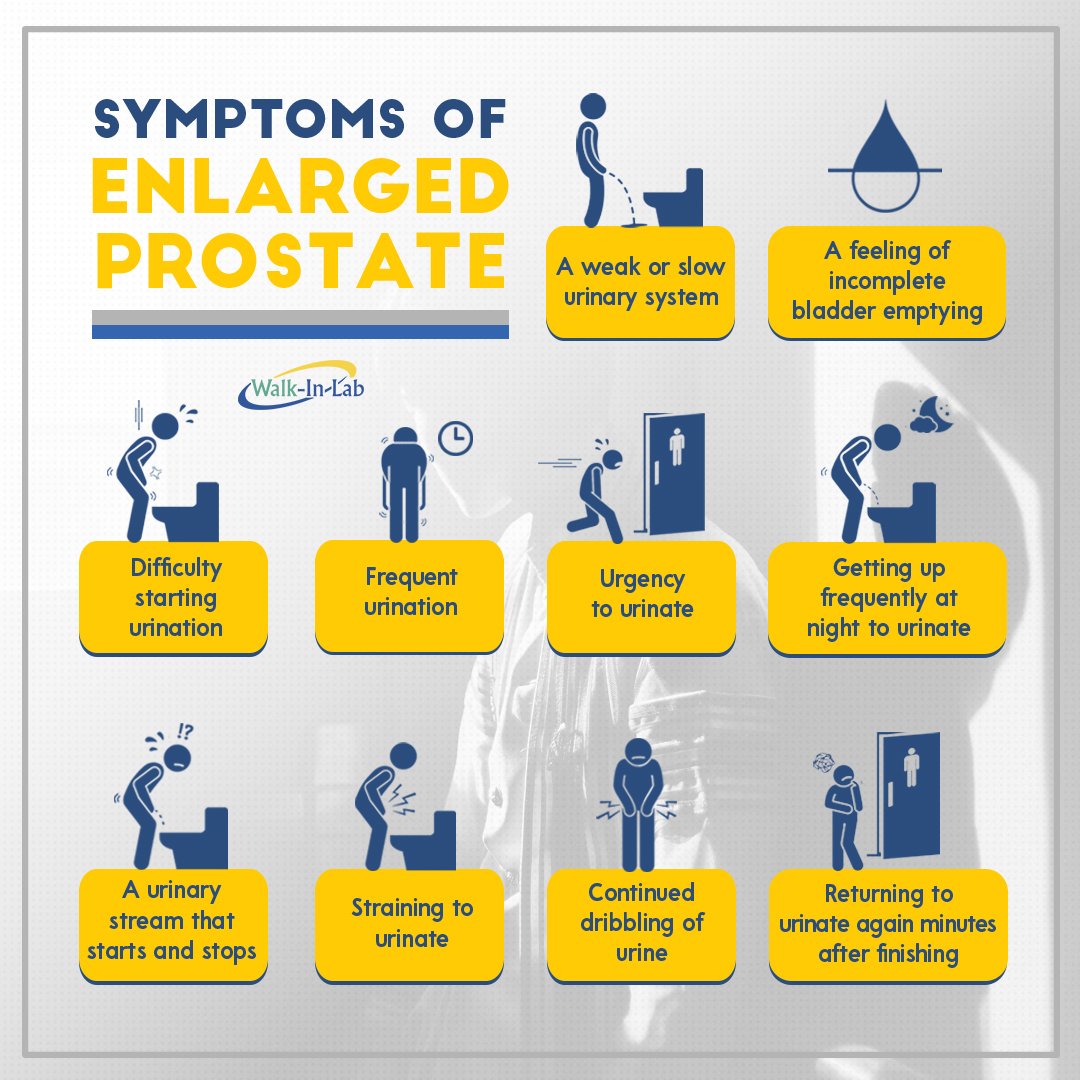
What Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia refers to an enlarged prostate gland. Although the prostate is about the size of a walnut in younger men, it can potentially get larger as men age. Though itâs mostly harmless, an enlarged prostate can contribute to uncomfortable or embarrassing urinary issues, and it may increase the risk of problems in the kidneys, bladder, and urinary tract. Some common symptoms include:
- A persistent or urgent need to urinate
- More instances of urinating at night
- A stream that has reduced pressure or frequently starts and stops
- Problems starting urination
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Feeling like the bladder isnât completely empty
BPH can typically be treated with medication or minimally invasive surgery .
Don’t Miss: Life Extension Ultra Prostate Formula
Tests To Diagnose And Stage Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancers are first found as a result of screening. Early prostate cancers usually dont cause symptoms, but more advanced cancers are sometimes first found because of symptoms they cause.
If prostate cancer is suspected based on results of screening tests or symptoms, tests will be needed to be sure. If youre seeing your primary care doctor, you might be referred to a urologist, a doctor who treats cancers of the genital and urinary tract, including the prostate.
The actual diagnosis of prostate cancer can only be made with a prostate biopsy .
On this page
Is The Psa Test Recommended For Prostate Cancer Screening
Beginning around 2008, as more was learned about both the benefits and harms of prostate cancer screening, a number of professional medical organizations began to caution against routine population screening with the PSA test. Most organizations recommend that individuals who are considering PSA screening first discuss the risks and benefits with their doctors.
Some organizations do recommend that men who are at higher risk of prostate cancer begin PSA screening at age 40 or 45. These include Black men, men with germline variants in BRCA2 , and men whose father or brother had prostate cancer.
In 2018, the United States Preventive Serves Task Force updated its recommendation statement for prostate cancer screening from a D to a C in men ages 55 to 69. The updated recommendation, which applies to the general population as well as those at increased risk due to race/ethnicity or family history, is as follows:
- For individuals ages 55 to 69 years, the decision to undergo periodic PSA-based screening for prostate cancer should be an individual one. Before making the decision, a person should discuss the potential benefits and harms of screening with their clinician and consider these in the context of their own values and preferences.
- PSA-based screening for prostate cancer is not recommended for individuals 70 years and older.
Recommended Reading: Does Finasteride Cause High Grade Prostate Cancer
What Is A Normal Psa Level
Your doctor may talk about a normal PSA level. Unlike some other blood tests, there is not one normal PSA level for everyone. The PSA level naturally gets higher as you get older and varies depending on the size of your prostate. The size of the prostate is different for each individual and the prostate gets bigger with age.
Your doctor will tell you what they think the normal level of PSA should be for you. They generally use these levels:
- A PSA level of up to 3 nanograms per millilitre of blood if you are in your 50s.
- A PSA level of up to 4ng/ml if you are in your 60s.
- A PSA level of up to 5ng/ml if you are in your 70s.
- There are no PSA level limits if you are aged 80 and over.
How Should I Prepare For The Exam
Your blood must be sent to a laboratory for analysis, so your PSA results wont be available immediately. Your doctor will let you know when they have the results.
The lab report will show the level of PSA in your blood as:
In addition to looking at the amount of PSA in your blood, your doctor will assess how quickly this number is changing. Many things can affect PSA, so test results require careful analysis by an expert. Your doctor will take all of your health information into account.
If you have an abnormal PSA test result, it doesnt mean you have prostate cancer. Most men with a high PSA level dont have prostate cancer. About of men who have a biopsy due to a high PSA level have prostate cancer.
Its also possible for men with prostate cancer to have normal DRE and PSA test results.
Recommended Reading: How To Shrink Prostate Naturally
What Are The Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Not everyone with prostate cancer has symptoms, so regular screening should be a part of your annual physical, starting at the age of 40-50. However, prostate symptoms should never be ignored and should be brought up to a physician.
Typical symptoms of prostate cancer, according to the Prostate Conditions Education Council , include:
- Frequent urination
- Weak urinary stream
Transrectal Ultrasound With Prostate Biopsy
Transrectal ultrasound is most often used to examine the prostate. In a transrectal ultrasound, the health care provider inserts a transducer slightly larger than a pen into the mans rectum next to the prostate. The ultrasound image shows the size of the prostate and any abnormal-looking areas, such as tumors. Transrectal ultrasound cannot definitively identify prostate cancer.
To determine whether a tumor is cancerous, the health care provider uses the transducer and ultrasound images to guide a needle to the tumor. The needle is then used to remove a few pieces of prostate tissue for examination with a microscope. This process, called biopsy, can reveal whether prostate cancer is present. A transrectal ultrasound with prostate biopsy is usually performed by a doctor in a health care providers office, outpatient center, or hospital with light sedation and local anesthesia. The biopsied prostate tissue is examined in a laboratory by a pathologista doctor who specializes in diagnosing diseases.
Read Also: Brca Therapy For Prostate Cancer
When Should You Get Tested
Prostate Cancer UK recommend PSA blood testing from age 45 and up for men who are at higher risk, and from 50 upward for men at normal levels of risk
Dr Rodgers said: Risk of prostate cancer is increased for people of African Carribean ethnicity and those with a family history of prostate cancer.
If you develop symptoms that suggest prostate enlargement, or your symptoms change over time then you should be discussing this with your doctor.
GETTY
Read Also: Prostate Removal Pros And Cons
