Is The Psa Test Recommended For Prostate Cancer Screening
Until about 2008, some doctors and professional organizations encouraged yearly PSA screening for men beginning at age 50. Some organizations recommended that men who are at higher risk of prostate cancer, including African-American men and men whose father or brother had prostate cancer, begin screening at age 40 or 45. However, as more was learned about both the benefits and harms of prostate cancer screening, a number of organizations began to caution against routine population screening. Most organizations recommend that men who are considering PSA screening first discuss the risks and benefits with their doctors.
Currently, Medicare provides coverage for an annual PSA test for all Medicare-eligible men age 50 and older. Many private insurers cover PSA screening as well.
Who Is At Risk For Advanced Prostate Cancer
The exact cause of prostate cancer isnt clear. Your risk of developing this particular cancer increases after you reach age 50.
Certain groups are more likely to develop aggressive forms of prostate cancer, including African-American men and men who carry certain inherited genetic mutations such as BRCA1, BRCA2, and HOXB13.
Most men with prostate cancer dont always have a family history of the disease. But having a father or brother with prostate cancer more than doubles your risk.
You May Like: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Should I Try A Clinical Trial
Researchers are actively conducting clinical trials to find better ways to treat metastatic prostate cancer and stop cancer spread. Many prostate cancer clinical trials focus on new therapies that target gene changes, as well as immunotherapies and chemotherapies.
Your doctor can help you determine if you might benefit from a clinical trial.
Donât Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Recommended Reading: Zinc Prostrate
About The Prostate And Prostate Cancer
The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system and produces fluid that mixes with semen during ejaculation to help sperm travel. The prostate is a walnut-sized, rubbery organ that surrounds the urethrathe urinary duct that carries urine from the bladder out of the bodyand sits directly below the bladder.
The prostate gland, which grows during puberty, is considered an organ and is made up of several dozen lobules or saclike glands, held together with connective prostate tissue and muscle between them. The glands are called exocrine glands, because they secrete liquid to outside the body.
An enlarged prostate, called benign prostatic hyperplasia , is common in men over the age of 40 and may obstruct the urinary tract. The abnormal prostate cell growth in BPH is not cancerous and doesnt increase your risk of getting prostate cancer. However, symptoms for BPH and prostate cancer can be similar.
A condition called prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia , where prostate gland cells look abnormal when examined under a microscope, may be connected to an increased risk of prostate cancer. Prostate cancer is often caught by a doctor performing a digital rectal exam , through a prostate-specific antigen blood test, through a prostate biopsy or with a CT scan.
Another condition, prostatitis, is the inflammation of the prostate. While not cancerous, it may cause higher PSA levels in the blood.
Metastatic Hormone Sensitive Prostate Cancer
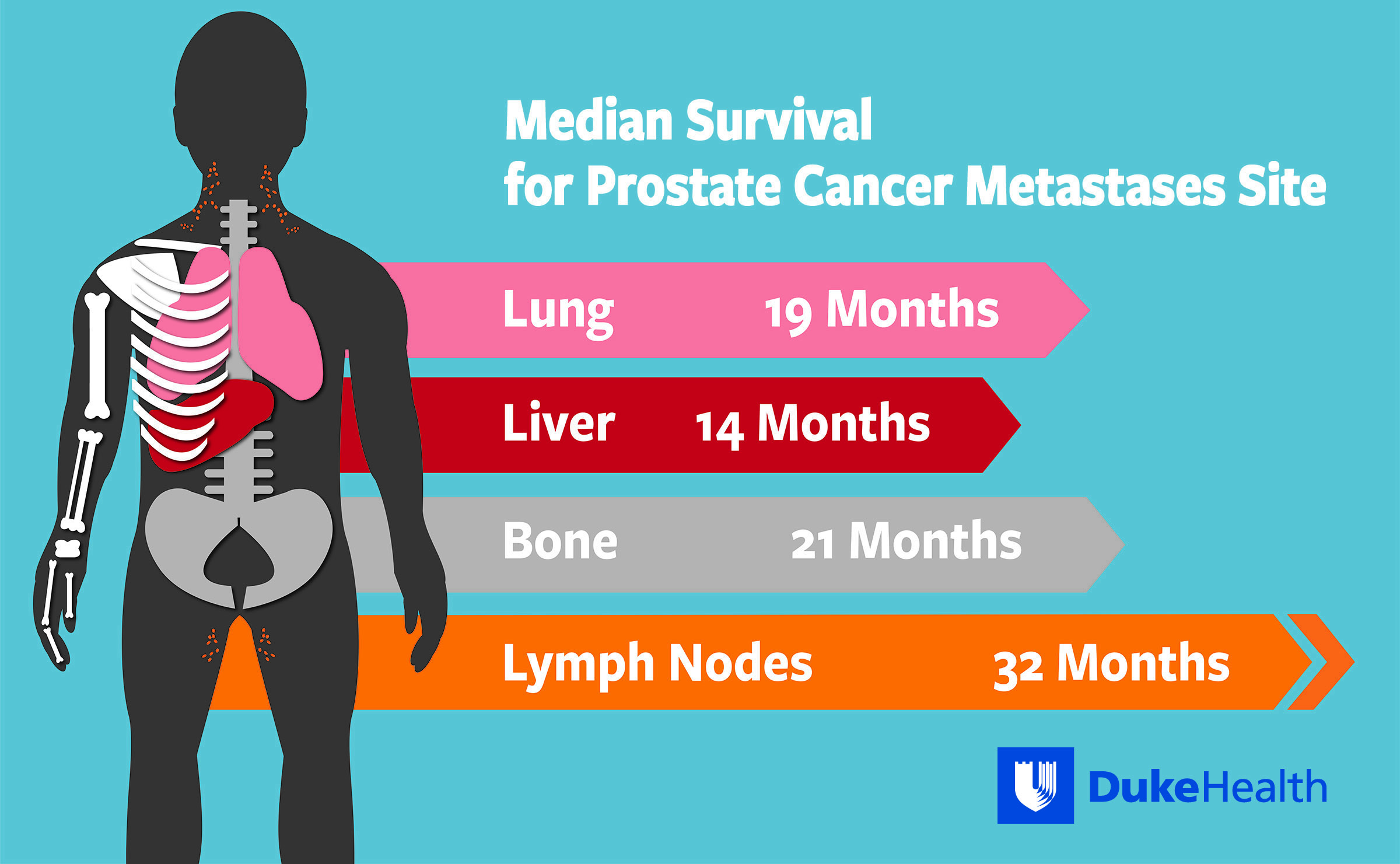
This form of prostate cancer can be an initial diagnosis but more often refers to cases where surgeries or other initial treatments to remove tumors from the prostate havent succeeded in stopping its progression.
Notably, too, these cases are defined by metastasis, meaning it has started to spread to other structures in the body, such as bones or the lymph nodes. However, the development of castration resistance is part of the eventual and expected progression of the diseaseeven while on ADT.
Read Also: Do Females Have Prostate
Risk Of Prostate Cancer
About 1 man in 8 will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during his lifetime.
Prostate cancer is more likely to develop in older men and in non-Hispanic Black men. About 6 cases in 10 are diagnosed in men who are 65 or older, and it is rare in men under 40. The average age of men at diagnosis is about 66.
How Fast Does Prostate Cancer Spread To The Bones
Early detection can catch prostate cancer even before there are any symptoms. Some types of prostate cancer grow very slowly.
There are four main stages of prostate cancer. Within each stage, the cancer is graded based on factors like the size of tumor, prostate-specific antigen level, and other clinical signs.
If the cancer has spread to the bones, its considered to be the most advanced, or stage 4.
Newer lab tests look at the genes inside cancer cells. This can provide more information on how quickly the prostate cancer may progress.
Theres also a grading system known as the Gleason system, which assigns the cancer into a grade group based on how closely it resembles normal tissue.
During the biopsy to diagnose prostate cancer, the cells are closely examined. The more abnormal cells that are in the biopsy sample, the higher the Gleason score and grade group.
When more abnormal cells are present, the cancer is more likely to spread quickly.
Also Check: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
In Five Years A Major Treatment Shift
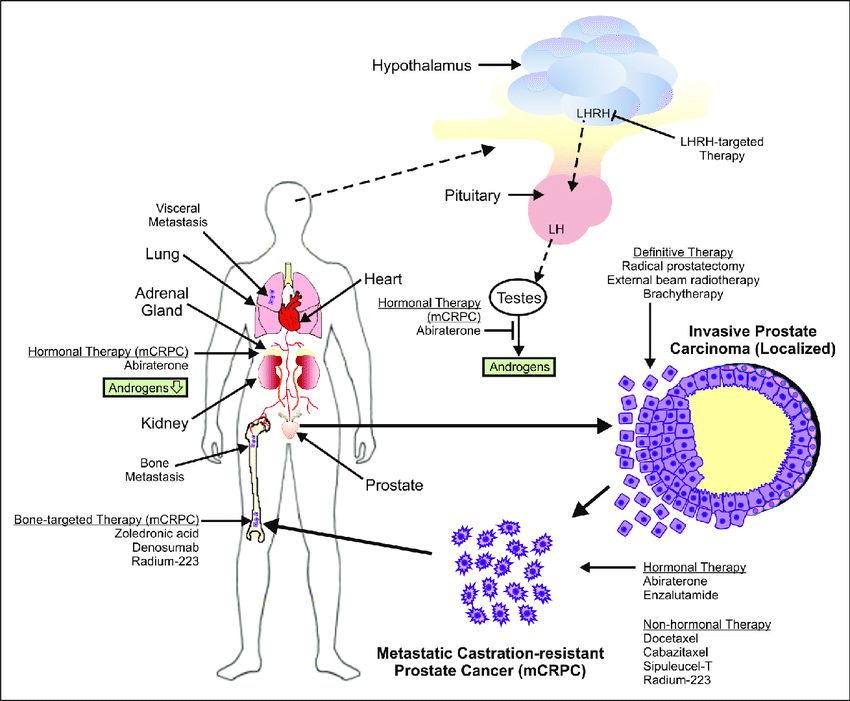
In men diagnosed with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, the cancer is typically driven to grow and spread by androgens that are produced largely in the testes. For many years, treatments that block androgen production have been a mainstay for men initially diagnosed with metastatic prostate cancer.
Starting in 2014, that began to change after a large clinical trial showed that adding the chemotherapy drug docetaxel to ADT improved how long men with hormone-responsive disease lived. Shortly after, another clinical trial showed that adding abiraterone to ADT also improved survival in these men, although primarily in men with many metastatic tumors, known as high-volume disease.
However, docetaxel, which works by directly killing cancer cells, can have substantial side effects, and some patients arent healthy enough to tolerate it. And abirateronewhich blocks androgen production throughout the bodycan also cause side effects, including those that affect the liver. It also has to be given in combination with the steroid prednisone, which carries its own toxicity.
Doing so, Dr. Chi said during a presentation of the TITAN data at the ASCO meeting, might help stave off the typically inevitable development of hormone-resistant cancer, which is more difficult to treat and a key driver of prostate cancer deaths.
What Is My Outlook
If youre diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer, you may want to know how well your treatment is likely to control your cancer and for how long it will control it. This is sometimes called your outlook or prognosis. But not all men will want to know this.
While it isnt possible to cure advanced prostate cancer, treatments can help keep it under control, often for several years. Treatments will also help manage any symptoms, such as pain.
No one can tell you exactly what your outlook will be, as it will depend on many things such as where the cancer has spread to, how quickly it has spread, and how well you respond to treatment. Some men may not respond well to one treatment, but may respond better to another. And when your first treatment stops working, there are other treatments available to help keep the cancer under control for longer. Speak to your doctor about your own situation and any questions or concerns you have.
You May Like: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Symptoms of metastatic prostate cancer vary depending on where the secondary cancer develops. Up to 90% of the time, prostate cancer spreads to bones. Bone mets often form in the ribs, spine, pelvis, arms, and legs.
Bone mets can cause chronic pain in the affected area, as well as bone fractures and spinal compressions. You may experience:
-
arthritis-like pain
-
numbness or weakness
-
pain that worsens or doesnt get better when resting
Bone mets can also raise blood calcium to dangerous levels. Too much calcium in the blood can affect brain and heart function. You may feel confused, lethargic, or experience heart palpitations.
Dont Miss: Will A Prostate Infection Cure Itself
What Are Next Steps
Bone metastasis have a profound effect on the long-term outlook for prostate cancer. But its important to remember that the numbers are only statistics.
The good news is that life expectancy for advanced prostate cancer continues to increase. New treatments and therapies offer both longer life and better quality of life. Speak to your doctor about your treatment options and long-term outlook.
Everyones cancer experience is different. You may find support through sharing your treatment plan with friends and family. Or you can turn to local community groups or online forums like Male Care for advice and reassurance.
Read Also: Urinozinc Prostate Formula Plus With Beta-sitosterol
Clues In Diet And Lifestyle
To clarify the prognosis for a tumor, HSPH researchers are homing in on other factors that might affect susceptibility to prostate cancer, especially the aggressive form of the disease. Edward Giovannucci, professor of nutrition and epidemiology, recently looked at nine diet and lifestyle factors. He found that smoking, obesity, and lack of physical activity raise the risk of developing a more virulent cancer. According to Giovannucci, The question is whether there are two types of prostate canceran aggressive and nonaggressive formor whether certain factors cause a nonaggressive form to become more aggressive. Evidence provided by HSPH researchers suggests that an increase in insulin in the bloodstream, caused by obesity and physical inactivity, may encourage tumor growth.
Other investigations have linked dietary factors to the disease. A 2011 study by HSPH research associate Kathryn Wilson, together with Mucci and Giovannucci, professor of nutrition and epidemiology Meir Stampfer, and other colleagues, found that men who drank coffee had a notably lower risk of aggressive prostate cancer. Those who consumed six cups or more a day were 20 percent less likely to develop any form of the disease, and 60 percent less likely to develop a lethal disease those who consumed one to three cups a day showed no difference in developing any form of the disease, but had a 30 percent lower risk of developing a lethal form.
Survival By Disease Recurrence
If a man develops an elevated PSA level after cancer surgery, then the disease is viewed as recurrent.
The number of lymph nodes at the time of prostatectomy can influence the risk of recurrence. One study suggests the removal of a large number of nodes is associated with an improvement in odds of recurrence, but this doesnt appear to impact overall survival.
But disease recurrence doesnt always influence survival times. If a recurrence does occur, the 15-year survival rate at the time of diagnosis may be as high as 94% in those with low-risk recurrence.
The main factors influencing survival rates are:
- The Gleason score
- The PSA doubling time
- Whether the recurrence occurred within three years or after three years
A recurrence that occurs within three years reduces survival rates by anywhere from 15 to 20%and even more, if the doubling time is short.
Recommended Reading: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
You May Like: Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis Osteoblastic
Prediction Of Metastatic Prostate Cancer By Prostate
-
Roles Formal analysis, Writing review & editing
Affiliations Department of Surgical Sciences, Uppsala University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden, Department of Mathematics, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
- Hans Garmo,
Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing review & editing
Affiliations Department of Surgical Sciences, Uppsala University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden, Kings College London, School of Medicine, Division of Cancer Studies, Cancer Epidemiology Group, London, United Kingdom
-
Roles Data curation, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Department of Urology, Ryhov Hospital, Jönköping, Sweden
-
Affiliation Department of Surgical Sciences, Uppsala University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden
- Hans David Ulmert,
Roles Writing review & editing
Affiliations University of California Los Angeles, Department of Molecular and Medical Pharmacology, Los Angeles, CA, United States of America, Ahmanson Translational Imaging Division, David Geffen UCLA School of Medicine, Los Angeles, CA, United States of America, Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, David Geffen UCLA School of Medicine, Los Angeles, CA, United States of America
-
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Resources, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Department of Surgical Sciences, Uppsala University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden
Advanced Prostate Cancer Webinars
The treatment and management of advanced prostate cancer continues to evolve. Hear from Dr. Alicia Morgans and Col. Paul Taylor a Stage IV prostate cancer patient as they discuss current treatments, managing side effects, and clinical trials in this December 2017 webinar.
Other webinars on relevant topics, such as clinical trials and bone health, in our webinar library
Watch our collection of educational videos on prostate cancer, featuring experts, patients, caregivers, and survivors speaking on a variety of issues relating to advanced prostate cancer, including bone health, treatment options, and the possibility of recurrence.
You May Like: Urinozinc Prostate Plus
Screening For Prostate Cancer
There are no tests available with sufficient accuracy to screen populations of men for early signs of prostate cancer. However, early detection and treatment can significantly improve prostate cancer survival.
The test most commonly used to aid early detection of prostate cancer is the prostate specific antigen blood test. This is not a diagnostic test as it can only indicate changes in the prostate. If you are concerned about prostate cancer you should talk to your doctor and make an informed choice about whether to have one of the tests designed to find early signs of prostate cancer, in view of the potential risks and benefits.
There are no proven measures to prevent prostate cancer.
Prognosis For Prostate Cancer
It is not possible for a doctor to predict the exact course of a disease, as it will depend on each person’s individual circumstances. However, your doctor may give you a prognosis, the likely outcome of the disease, based on the type of prostate cancer you have, the test results, the rate of tumour growth, as well as your age, fitness and medical history.
Prostate cancer often grows slowly and even more aggressive types tend to grow more slowly than other types of cancer. If diagnosed early, prostate cancer has one of the highest five year survival rates.
Recommended Reading: What Happens To The Prostate Later In Life
What Is Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer develops when abnormal cells in the prostate gland grow in an uncontrolled way, forming a malignant tumour.
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed in men in Australia and the third most common cause of cancer death. It is estimated that 18,110 new cases of prostate cancer will be diagnosed in Australia in 2021. One in 6 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer by the age of 85. It is more common in older men, with over 63% of cases diagnosed in men over 65 years of age.
Early prostate cancer refers to cancer cells that have grown but do not appear to have spread beyond the prostate.
There are two stages of advanced prostate cancer:
- locally advanced prostate cancer where the cancer has spread outside the prostate to nearby parts of the body or glands close to the prostate
- metastatic prostate cancer where the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body.
The five year survival rate for prostate cancer is 95%.
How Common Is Prostate Cancer
About one in nine men will receive a prostate cancer diagnosis during his lifetime. Prostate cancer is second only to skin cancer as the most common cancer affecting males. Close to 200,000 American men receive a diagnosis of prostate cancer every year. There are many successful treatments and some men dont need treatment at all. Still, approximately 33,000 men die from the disease every year.
Also Check: Drugs Used To Treat Bph
What Causes Prostate Cancer
The exact cause of prostate cancer is not known. The tumor arises from cells with abnormal deoxyribonucleic acid changes in the prostate. These abnormal cells rapidly grow and divide, invading surrounding structures and can spread to other parts of the body .
Risk factors
There are certain factors that can increase the risk of prostate cancer. These include
- Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases with age and is most commonly seen after the age of 50.
- Race: African American men have a higher risk of prostate cancer than men of other ethnicities. Cancer in African Americans is also more likely to be aggressive.
- Family history: If a blood relative has prostate cancer, it increases the risk as well. Having a family history of genes that increase the risk of breast cancer or a very strong family history of breast cancer also increases the risk of developing prostate cancer.
- Obesity: Obese people have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer, which is also more likely to be aggressive and recurrent despite treatment.
Bladder And Urinary Troubles
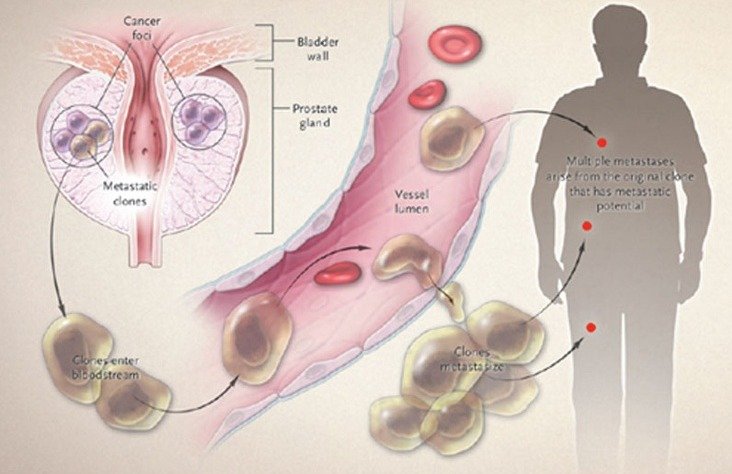
A prostate tumor that has grown significantly in size may start to press on your bladder and urethra. The urethra is the passage the carries urine from your bladder out of your body. If the tumor is pressing on your urethra, you might have trouble passing urine.
One of the common areas for prostate cancer to spread to is the bladder, because the two organs are close. This can cause additional problems with urination and bladder function.
Some symptoms your bladder and urethra are being affected by cancer include:
- urinating more frequently
- getting up in the middle of the night to pee
- having blood in your urine or semen
- feeling like you have to urinate often and not actually passing anything
Its not as common, but prostate cancer can also spread to your bowel. The cancer first spreads to the rectum, which is the part of your bowel closest to the prostate gland.
Symptoms of cancer thats spread to the bowels include:
- stomach pain
Read Also: How Do You Treat Prostate Cancer
Recommended Reading: Tamsulosin Retrograde Ejaculation
