Risk Of Prostate Cancer
About 1 man in 8 will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during his lifetime.
Prostate cancer is more likely to develop in older men and in non-Hispanic Black men. About 6 cases in 10 are diagnosed in men who are 65 or older, and it is rare in men under 40. The average age of men at diagnosis is about 66.
Understanding Prostate Cancers Progression
To determine the appropriate treatment, doctors need to know how far the cancer has progressed, or its stage. A pathologist, the doctor trained in analyzing cells taken during a prostate biopsy, will provide two starting pointsthe cancers grade and Gleason score.
- Cancer grade: When the pathologist looks at prostate cancer cells, the most common type of cells will get a grade of 3 to 5. The area of cancer cells in the prostate will also be graded. The higher the grade, the more abnormal the cells.
- Gleason score: The two grades will be added together to get a Gleason score. This score tells doctors how likely the cancer is to grow and spread.
After a biopsy confirms prostate cancer, the patient may undergo additional tests to see whether it has spread through the blood or lymph nodes to other parts of the body. These tests are usually imaging studies and may include a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or computed tomography scan.
Recommended Reading: What Is Perineural Invasion
Grade And Risk Category
The biopsy results will show the grade of the cancer. This is a score that describes how quickly the cancer may grow or spread.
For many years, the Gleason scoring system has been used to grade the tissue taken during a biopsy. If you have prostate cancer, youll have a Gleason score between 6 and 10. A new system has been introduced to replace the Gleason system. Known as the International Society of Urological Pathologists Grade Group system, this grades prostate cancer from 1 to 5 .
Risk of progression
Based on the stage, grade and your PSA level before the biopsy, localised prostate cancer will be classified as having a low, intermediate or high risk of growing and spreading. This is known as the risk of progression. The risk category helps guide management and treatment.
Grading prostate cancer
| High risk. The cancer is likely to grow aggressive. |
You May Like: How To Decalcify The Prostate
Treatments To Help Manage Symptoms
Advanced prostate cancer can cause symptoms, such as bone pain. Speak to your doctor or nurse if you have symptoms there are treatments available to help manage them. The treatments above may help to delay or relieve some symptoms. There are also specific treatments to help manage symptoms you may hear these called palliative treatments. They include:
This is the team of health professionals involved in your care. It is likely to include:
- a specialist nurse
The Symptoms Of Delirium Are A Lot Like Symptoms Of Depression And Dementia
Early symptoms of delirium are like symptoms of depression and dementia. Delirium that causes the patient to be inactive may appear to be depression. Delirium and dementia both cause problems with memory, thinking, and judgment. Dementia may be caused by a number of medical conditions, including Alzheimer disease. Differences in the symptoms of delirium and dementia include the following:
- Patients with delirium often show changes in how alert or aware they are. Patients who have dementia usually stay alert and aware until the dementia becomes very advanced.
- Delirium occurs suddenly . Dementia appears gradually and gets worse over time.
Older patients with cancer may have both dementia and delirium. This can make it hard for the doctor to diagnose the problem. If treatment for delirium is given and the symptoms continue, then the diagnosis is more likely dementia. Checking the patients health and symptoms over time can help diagnose delirium and dementia.
You May Like: Perineural Invasion Present
Read Also: Fiducial Marker Prostate
What Are The Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
The most important factors that increase the risk of prostate cancer are African American race, a family history of prostate cancer, and increasing age. Black men have a 60% higher risk of prostate cancer than white men and are approximately twice as likely to die of prostate cancer. People with a family history of prostate cancer are at increased risk, and having more than one family member with prostate cancer increases the risk further. Older men have a higher risk of prostate cancer than younger men, with more than 50% of all diagnoses occurring after the age of 65 and 97% occurring after the age of 50. There are also certain genetic syndromes that increase the risk of prostate cancer such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations and, as new evidence is suggesting, Lynch Syndrome .
Dont Miss: Is Viagra Good For Enlarged Prostate
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates
Answering the question of how curable is prostate cancer? first requires understanding what doctors mean when they refer to curability. Regardless of the type of cancer, doctors consider cancer cured when a patient remains cancer-free for a specified period after treatment. The higher the number of patients who stay cancer-free for five years or longer, the higher the curability of that particular disease.
Prostate cancer, therefore, has one of the highest curability rates of all types of cancer, thanks in large part to early detection standards and advances in treatment, such as the stereotactic body radiation therapy offered by Pasadena CyberKnife. When the cancer is detected in the early local or regional stages that is, before the cancer has spread or when it has only spread to limited areas in the pelvic regions the five-year survival rate is nearly 100 percent.
Survival rates decline significantly when cancer is detected at later stages however, the good news is that only about five percent of men are diagnosed after the cancer has become widespread throughout the body. In short, more than 90 percent of men who are diagnosed with prostate cancer live for five years or longer after treatment, making it one of the most curable forms of cancer.
Recommended Reading: Prostatic Neoplasms
What Are Prostate Cancer Treatment Side Effects
Some prostate cancer treatments can affect the bladder, erectile nerves and sphincter muscle, which controls urination. Potential problems include:
- Incontinence: Some men experience urinary incontinence. You may leak urine when you cough or laugh, or you may feel an urgent need to use the bathroom even when your bladder isnt full. This problem can improve over the first six to 12 months without treatment.
- Erectile dysfunction : Surgery, radiation and other treatments can damage the erectile nerves and affect your ability to get or maintain an erection. Some men regain erectile function within a year or two . In the meantime, medications like sildenafil or tadalafil can help by increasing blood flow to the penis.
- Infertility: Treatments can affect your ability to produce or ejaculate sperm, resulting in male infertility. If you think you might want children in the future, you can preserve sperm in a sperm bank before you start treatments. After treatments, you may undergo sperm extraction. This procedure involves removing sperm directly from testicular tissue and implanting it into a womans uterus.
Biology Of Circulating Tumor Cells
Figure 3 Circulating tumor cells in prostate cancer patients. Early metastatic features within PCa cells can be induced under stress conditions e.g. hypoxia, immune attack, or therapeutic pressure. In response to TGF-, Wnt or IL-6 PCa cells undergo EMT to gain motility and invasiveness. PCa cells intravasate into blood vessels either passively throughout leaky vessel walls or actively via trans-endothelial migration. Prostate CTCs circulate either as single cells, CTC cluster, or coated with platelets, neutrophils or macrophages shielding immune attack and reducing shear stress. CD45-EpCAM+ CTCs are a heterogeneous population differing in, e.g. the expression of androgen receptor splice variants, TMPRSS2-ERG status or loss of tumor suppressors PTEN, RB1, and TP53 recapitulating local tumor heterogeneity, influencing metastatic capacity and indicating therapy response.
Also Check: How To Shrink Prostate Mayo Clinic Naturally
Clinical Application Of Circulating Tumor Cell
While EpCAM-based CTC enumeration methods may miss CTC subpopulation with low EpCAM expression, there are attempts to apply additional markers for CTC detection to increase sensitivity and specificity or apply label-free methods such as microfiltration, density gradient centrifugation or dielectrophoretic techniques . Putative prostate CTC markers include e.g. EMT phenotype , the tyrosine kinase cMET , the immune checkpoint marker PD-L1 , telomerase activity and the TMPRSS2-ERG translocation . The applicable additional marker would enable the monitoring of therapy resistance in real-time and may recapitulate tumor heterogeneity within the blood. Another putative prostate CTC marker is the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 , but detection level was demonstrated to be higher in metastatic patients compared to local disease . Promising results were also obtained with the cytological ISET test in combination with prostate-specific marker PSA and prostein . Within this observational study, 20 men with diagnosed PCa were analyzed with a mean CTC count of 6.5 CTCs per 7.5 ml blood . Interestingly, in patients without previously diagnosed PCa ISET-CTC-based screening demonstrated a predictive value of 99% compared to 25% with the standard PSA-based test method within patients receiving PSMA-PET-imaging later on.
Table 2 Summary of completed clinical trials applying enumeration of circulating tumor cells in PCa patients either as primary or secondary endpoint.
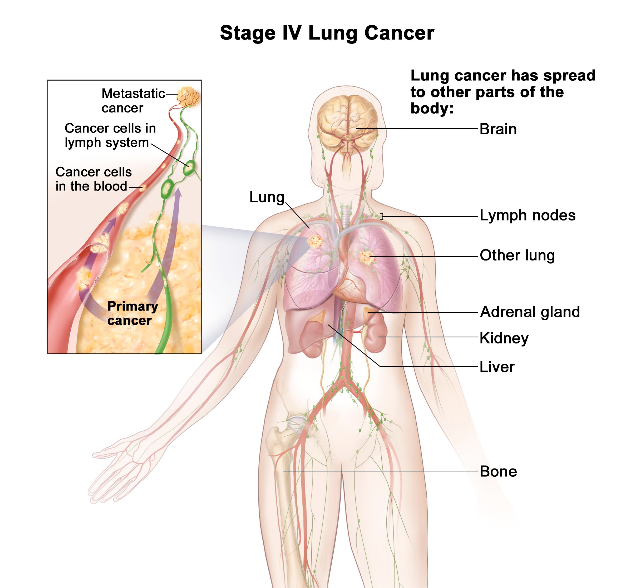
Bone Metastases: Symptoms And Relation To Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men, with 1 in 9 men diagnosed with it during their lifetime. Despite its high occurrence, when caught early, prostate cancer often can be treated successfully. Most prostate cancers are a type called adenocarcinomas, which are very slow growingso much so that aggressive treatment of this type of cancer may be unnecessary.
However, thats not true in all cases. Some prostate cancers, while rarer, grow rapidly and can metastasize or spread to bones, including the hip, spine, pelvis and other organs. The more the cancer spreads, the more challenging it is to treat, and is considered advanced prostate cancer.
Even if prostate cancer travels to your bones, it is not considered bone cancer. Rather, it is still considered prostate cancer because that was the original location of the disease development.
Also Check: How Long Can You Stay On Lupron For Prostate Cancer
Imaging Of Metastasis Status In Prostate Cancer Patients
The screening for PSA level in the serum of patients was introduced in the late 1980s and enabled a dramatic increase in early PCa detection . On the other hand, PSA is not solely a PCa-specific biomarker and, as such, leads to overdiagnosis and overtreatment of clinically insignificant cases, representing a significant burden for patients . Moreover, absolute PSA level does not always correlate with prognosis . Therefore, more specific and sensitive PSA-based values like PSA density , PSA velocity , free-to-total PSA , and PSA doubling time are seen as options with stronger predictive value. For example, PSADT is defined as the length of time for two-fold PSA level increase. A PSADT < 6 months is strongly associated with metastatic disease, increased PCa mortality , and relapse . Nonetheless, the reported benefit of PSADT in PCa management did not enter clinical routine and some studies even reported discrepant results indicating that further studies are required to determine the reliability of PSADT and other available biomarkers .
Symptoms Of Advanced Prostate Cancer
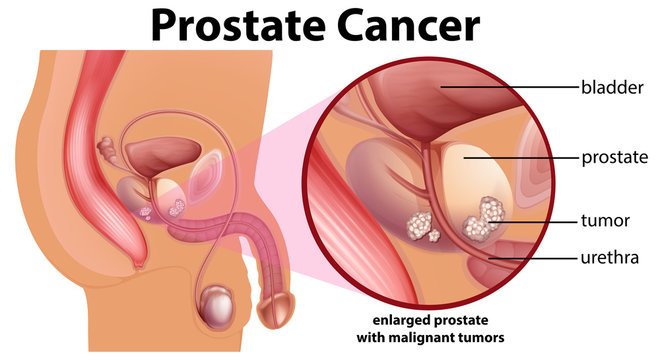
If you are worried about prostate cancer, we have more information about the signs and symptoms.
Symptoms of prostate cancer may not develop for many years. The symptoms of advanced prostate cancer may be caused by an enlarged prostate. Or symptoms may be a sign of secondary cancer, where the cancer has spread to another part of the body.
See also
You May Like: Does Cialis Shrink An Enlarged Prostate
Recommended Reading: How Are Fiducial Markers Placed In The Prostate
Delirium Is A Confused Mental State That Can Occur In Patients Who Have Cancer
Delirium is a confused mental state that can occur in patients who have cancer, especially advanced cancer. Patients with delirium have problems with the following:
- Attention.
There are three types of delirium:
- Hypoactive: The patient is not active and seems sleepy, tired, or depressed.
- Hyperactive: The patient is restless or agitated.
- Mixed: The patient changes back and forth between being hypoactive and hyperactive.
Also Check: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computers clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
Read Also: Seminal Vesicle Massage
Second Cancers After Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer survivors can be affected by a number of health problems, but often a major concern is facing cancer again. Cancer that comes back after treatment is called a recurrence. But some cancer survivors may develop a new, unrelated cancer later. This is called a second cancer.
Unfortunately, being treated for prostate cancer doesnt mean you cant get another cancer. Men who have had prostate cancer can still get the same types of cancers that other men get. In fact, they might be at higher risk for certain types of cancer.
Men who have had prostate cancer can get any type of second cancer, but they have an increased risk of certain cancers, including:
This risk is probably related to the dose of radiation. Newer methods of giving radiation therapy may have different effects on the risks of a second cancer. Because these methods are newer, the long-term effects have not been studied as well.
Recommended Reading: How To Stimulate A Mans Prostate
What Does It Mean When There Are Different Core Samples With Different Gleason Scores
Cores may be samples from different areas of the same tumor or different tumors in the prostate. Because the grade may vary within the same tumor or between different tumors, different samples taken from your prostate may have different Gleason scores. Typically, the highest Gleason score will be the one used by your doctor for predicting your prognosis and deciding on treatment options.
Read Also: Prostate Medical Definition
Clues In Diet And Lifestyle
To clarify the prognosis for a tumor, HSPH researchers are homing in on other factors that might affect susceptibility to prostate cancer, especially the aggressive form of the disease. Edward Giovannucci, professor of nutrition and epidemiology, recently looked at nine diet and lifestyle factors. He found that smoking, obesity, and lack of physical activity raise the risk of developing a more virulent cancer. According to Giovannucci, The question is whether there are two types of prostate canceran aggressive and nonaggressive formor whether certain factors cause a nonaggressive form to become more aggressive. Evidence provided by HSPH researchers suggests that an increase in insulin in the bloodstream, caused by obesity and physical inactivity, may encourage tumor growth.
Other investigations have linked dietary factors to the disease. A 2011 study by HSPH research associate Kathryn Wilson, together with Mucci and Giovannucci, professor of nutrition and epidemiology Meir Stampfer, and other colleagues, found that men who drank coffee had a notably lower risk of aggressive prostate cancer. Those who consumed six cups or more a day were 20 percent less likely to develop any form of the disease, and 60 percent less likely to develop a lethal disease those who consumed one to three cups a day showed no difference in developing any form of the disease, but had a 30 percent lower risk of developing a lethal form.
Clinical Features And Imaging
Taken as a group, primary and secondary prostatic leukemia/lymphoma most commonly presents in the seventh decade. Primary prostatic lymphomas, which tend to be high grade on the basis of a large series, usually present with symptoms of a large prostatic mass, including obstructive symptoms and hematuria. Digital rectal examination findings usually are abnormal, showing a diffusely enlarged or nodular prostate in the majority of cases. Serum prostate-specific antigen usually is not elevated .
Secondary prostatic leukemia/lymphoma is often discovered incidental to a diagnosis of prostatic adenocarcinoma. Symptoms at presentation may thus be intermixed with those of prostate cancer and include elevated serum PSA . Secondary prostatic leukemia/lymphoma may also present with obstructive symptoms.
The differential diagnosis for prostatic tumors that have the appearance of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas is wide, including the following :
- High-grade neoplasms
The differential diagnosis for prostate leukemia/lymphoma also includes the following non-neoplastic processes:
- Benign chronic inflammation with follcular hyperplasia
- Granulomatous prostatitis
Read Also: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Also Check: Fiducial Marker Placement Prostate
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
Screenings are the most effective way to catch prostate cancer early. If you are at average cancer risk, youll probably have your first prostate screening at age 55. Your healthcare provider may start testing earlier if you have a family history of the disease or are Black. Screening is generally stopped after age 70, but may be continued in certain circumstances.
Screening tests for prostate cancer include:
- Digital rectal exam: Your provider inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum and feels the prostate gland, which sits in front of the rectum. Bumps or hard areas could indicate cancer.
- Prostate-specific antigen blood test: The prostate gland makes a protein called protein-specific antigen . Elevated PSA levels may indicate cancer. Levels also rise if you have BPH or prostatitis.
- Biopsy: A needle biopsy to sample tissue for cancer cells is the only sure way to diagnose prostate cancer. During an MRI-guided prostate biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging technology provides detailed images of the prostate.
