How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
A biopsy is when a small piece of tissue is removed from the prostate and looked at under a microscope.
A biopsy is a procedure that can be used to diagnose prostate cancer. A biopsy is when a small piece of tissue is removed from the prostate and looked at under a microscope to see if there are cancer cells.
A Gleason score is determined when the biopsy tissue is looked at under the microscope. If there is a cancer, the score indicates how likely it is to spread. The score ranges from 2 to 10. The lower the score, the less likely it is that the cancer will spread.
A biopsy is the main tool for diagnosing prostate cancer, but a doctor can use other tools to help make sure the biopsy is made in the right place. For example, doctors may use transrectal ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging to help guide the biopsy. With transrectal ultrasound, a probe the size of a finger is inserted into the rectum and high-energy sound waves are bounced off the prostate to create a picture of the prostate called a sonogram. MRI uses magnets and radio waves to produce images on a computer. MRI does not use any radiation.
Medical History And Physical Exam
If your doctor suspects you might have prostate cancer, you will be asked about symptoms you are having, such as any urinary or sexual problems, and how long you have had them. You might also be asked about possible risk factors, including your family history.
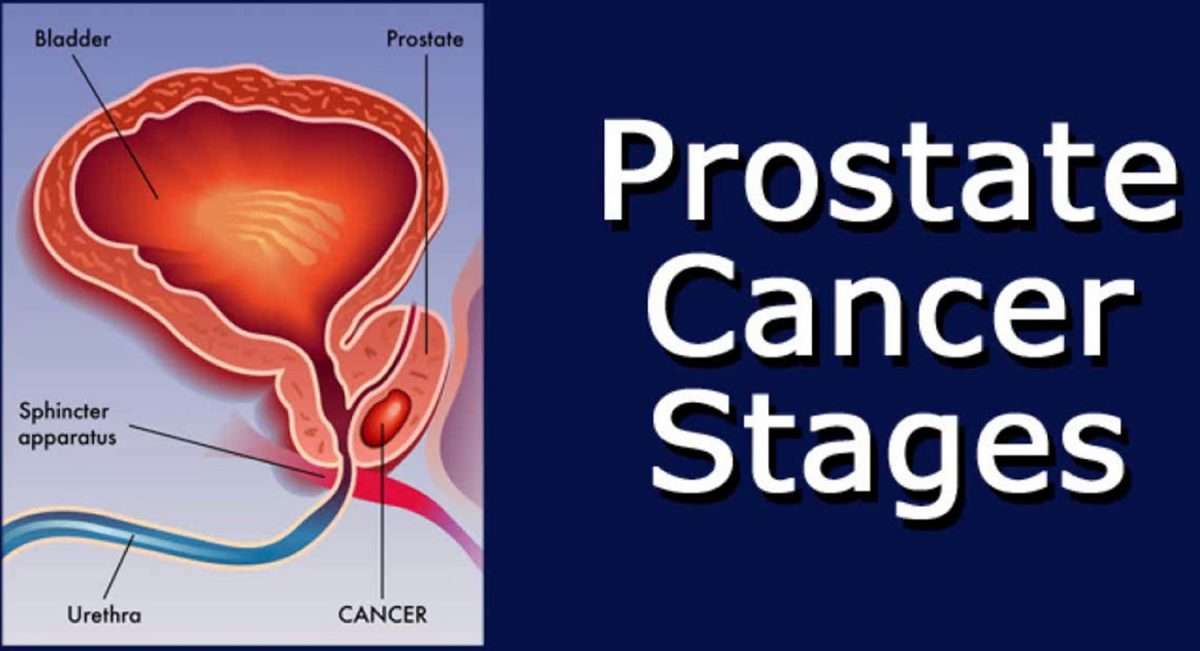
Your doctor will also examine you. This might include a digital rectal exam , during which the doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum to feel for any bumps or hard areas on the prostate that might be cancer. If you do have cancer, the DRE can sometimes help tell if its only on one side of the prostate, if its on both sides, or if its likely to have spread beyond the prostate to nearby tissues. Your doctor may also examine other areas of your body.
After the exam, your doctor might then order some tests.
What If My Test Results Are Abnormal
If the results of early detection tests like the PSA test or the digital rectal exam suggest that you might have prostate cancer, your doctor will conduct further testing. The PSA may be repeated, or you may be sent to a specialist for more tests such as a transrectal ultrasound and a prostate biopsy.
In a prostate biopsy, a tissue sample is taken from your prostate. Cancer can only be diagnosed with a tissue sample.
In addition to a PSA test, DRE , and a biopsy, research has yielded additional tests that can detect if cancer is present, and if so, how aggressive that cancer might be:
- Phi
- The Prostate Health Index combines three blood tests that give a more accurate Phi Score, which gives accurate information based on a high PSA to better determine the probability of finding cancer during a biopsy.
Also Check: What Is A Prostate Exam
Benefits Of Psa Screening
The benefits of PSA screening merit careful consideration while developing an approach to prostate cancer screening. It is also important to emphasize that the benefits of PSA based screening for prostate cancer may not be representative of prostate cancer screening in general. While there are several potential tests that could be applied in screening for prostate cancer, almost all currently available data pertain to the use of PSA with or without DRE. As a primary screening test, there is no evidence that DRE is beneficial, but DRE in men referred for an elevated PSA may be a useful secondary test.
Prostate cancer specific mortality was the primary endpoint for both the ERSPC and the PLCO trials. However, one cannot ignore the benefits of earlier detection through screening in decreasing the risk of metastatic disease.54 The incidence of metastatic disease at presentation has declined by approximately three-fourths in the US since the advent of PSA screening. Further, in data from the ERSPC, the cumulative risk of metastatic disease at 9 to 11 years of follow-up was 31% to 33% lower in the screened arm compared to the control arm.7,18 The Goteborg arm of the trial demonstrated a 56% reduction in risk of metastatic disease.17 Most of this reduction in metastatic disease was seen in cancers detected at the time of diagnosis in the screened arm and not following diagnosis. This reduction is more pronounced with longer follow-up.
More Articles From This Issue

When a man has an enlarged prostate, the first step is usually a screening test known as a PSA , which measures the level of a specific protein produced by cells of the prostate gland, says Dr. Mitchell Benson, a urologist with ColumbiaDoctors, the faculty practice of Columbia University Irving Medical Center, and Chief of Urologic Oncology at New-York Presbyterian Lawrence Hospital in Bronxville. PSA levels may be elevated in men and, if high enough, might indicate the possibility of prostate cancer and the need for a biopsy.
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among American men and is caused by the uncontrollable growth of cells in the prostate gland. Only a biopsy can diagnose prostate cancer and if so, determine whether the cancer is likely to be slow-growing or aggressive. Slow-growing prostate cancer can often just be watched, a process we now call active surveillance, says Dr. Benson. Most men in this category never advance to the need for treatment. In fact, there are men who, at very ripe old ages, pass away from natural causes, and yet are found to have lived with undiagnosed prostate cancer. But aggressive prostate cancer is something quite different and requires aggressive treatment.
Also Check: What Is Bipolar Transurethral Resection Of The Prostate
Does Early Prostate Cancer Screening Do More Harm Than Good
Dec. 14, 2021 — Itâs a question that has divided menâs health experts for years: Should healthy men, with no symptoms or family history of prostate cancer, get a prostate specific antigen test and treatment right away if a tumor is found?
Menâs health experts and cancer specialists say the continuing back-and-forth on PSA testing and active surveillance has deepened widespread confusion for men with questions about what to do.
Proponents of routine PSA testing say it is the best screening tool in oncologistsâ arsenals for catching prostate cancer early, when it is most treatable.
But opponents argue that it prompts many newly diagnosed men to seek invasive treatments that can cause impotence and incontinence, although up to 80% have low-risk tumors that will never be life-threatening. For them, they say, the best option is âactive surveillance,â where doctors monitor patients closely for signs their cancer is advancing before treating it.
This fall, the influential National Comprehensive Cancer Network reignited the debate, recommending active surveillance, surgery, or radiation for men newly diagnosed with prostate cancer as a result of PSA testing — giving equal weight to all three approaches.
After a firestorm of criticism, the NCCN reversed course and now recommends that âmost menâ with low-risk prostate cancer be managed through active surveillance as the âpreferredâ first treatment option over surgery and radiation.
Further Testing For Advanced Cancer
If there’s a significant chance the cancer has spread from your prostate to other parts of the body, further tests may be recommended.
These include:
- an MRI scan, CT scan or PET scan these scans build a detailed picture of the inside of your body
- an isotope bone scan, which can tell if the cancer has spread to your bones a small amount of radiation dye is injected into the vein and then collects in parts of the bone where there are any abnormalities
Also Check: How To Cure Prostate Cancer Natural Way
How Is The Psa Used After Diagnosis
PSA is the primary tool for screeningthat is, testing of healthy men without symptoms. Once the diagnosis of prostate cancer is confirmed by biopsy, PSA is also routinely used for risk assessment, active surveillance in men with low-risk cancer who elect this approach, and post-treatment monitoring. Your doctor will use the PSA test as one of many guides to indicate whether treatment is working and, down the line, whether the cancer recurs.
Tests To Diagnose And Stage Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancers are first found as a result of screening. Early prostate cancers usually dont cause symptoms, but more advanced cancers are sometimes first found because of symptoms they cause.
If prostate cancer is suspected based on results of screening tests or symptoms, tests will be needed to be sure. If youre seeing your primary care doctor, you might be referred to a urologist, a doctor who treats cancers of the genital and urinary tract, including the prostate.
The actual diagnosis of prostate cancer can only be made with a prostate biopsy .
On this page
Recommended Reading: How Do You Die From Prostate Cancer
Screening For Prostate Cancer
At UCSF, we believe in testing men so they know if they have prostate cancer, but that doesn’t mean every man diagnosed should have aggressive treatment. Screening is the only way to detect high-risk, potentially life-threatening prostate cancer early, while it can still be cured.
Most prostate cancers in the U.S. are identified through the following screening tests:
- Prostate-specific antigen . This simple blood test checks levels of prostate-specific antigen, a protein produced by prostate cells. The higher the PSA level, the more likely prostate cancer is present. But PSA elevations can also occur in benign conditions, most commonly benign prostatic hyperplasia, in which the prostate enlarges, as occurs in most men over their lifetime.
- Digital rectal exam . For this physical examination, your doctor inserts a lubricated gloved finger into your rectum to feel for any irregular or abnormally firm areas. While most prostate cancers are detected by PSA screening, some cancers produce little PSA but are detected by DRE.
In some circumstances, your doctor may order a repeat PSA or other tests to help determine whether a benign condition led to an elevated PSA. These tests may include:
- Free PSA
- MyProstateRisk
- Multiparametric MRI
An MRI exam of the prostate is helpful and can allow for a more targeted biopsy.
Warning Signs Of Prostate Cancer
One of the challenges of prostate cancer is that it often doesnt present symptoms that alert men to its presence, particularly in the early stages. But the Urology Care Foundation notes that there may be some warning signs that you have problems related to your prostate, including the following:
If you get screened for prostate cancer, there are additional warning signs based on how the prostate gland cells look under a microscope, notes the American Cancer Society. Cells that may be concerning will exhibit some level of what is known as prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia . These cells may exhibit low-grade PIN, in which something is slightly off with the cells, or high-grade PIN, when they show clear abnormalities.
Under a microscope, prostate gland cells may also exhibit what is known as proliferative inflammatory atrophy . PIA indicates cells that are smaller than normal and show some signs of inflammation. These cells may be worth additional monitoring because they could develop high-grade PIN and ultimately prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Happens After Prostate Surgery
Use In Men Who Might Have Prostate Cancer
The PSA blood test is used mainly to screen for prostate cancer in men without symptoms. Its also one of the first tests done in men who have symptoms that might be caused by prostate cancer.
PSA in the blood is measured in units called nanograms per milliliter . The chance of having prostate cancer goes up as the PSA level goes up, but there is no set cutoff point that can tell for sure if a man does or doesnt have prostate cancer. Many doctors use a PSA cutoff point of 4 ng/mL or higher when deciding if a man might need further testing, while others might recommend it starting at a lower level, such as 2.5 or 3.
- Most men without prostate cancer have PSA levels under 4 ng/mL of blood. Still, a level below 4 is not a guarantee that a man doesnt have cancer.
- Men with a PSA level between 4 and 10 have about a 1 in 4 chance of having prostate cancer.
- If the PSA is more than 10, the chance of having prostate cancer is over 50%.
If your PSA level is high, you might need further tests to look for prostate cancer.
To learn more about how the PSA test is used to look for cancer, including factors that can affect PSA levels, special types of PSA tests, and what the next steps might be if you have an abnormal PSA level, see Screening Tests for Prostate Cancer.
Causes Of Early Prostate Cancer
Certain things called risk factors may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer. If you are Black, you have a much higher risk of developing prostate cancer. You are also more likely to develop it at a younger age. Having a strong family history of prostate cancer is also a risk factor.
We have more information about the risk factors of prostate cancer.
Related Stories & Media
You usually start by seeing your GP to have your symptoms checked. Your GP usually arranges some tests. The first tests used to diagnose prostate cancer are:
- Rectal Examination
The doctor gently inserts a gloved finger into your back passage . The rectum is close to the prostate gland so your doctor can feel for anything unusual in the prostate. A rectal examination test is quick and it should not be painful. It is also sometimes called Digital Rectal Examination .
- PSA test
The PSA test is a blood test to measure the level of prostate-specific antigen in your blood. Prostate cancer often causes a raised level of PSA. But different things such as non-cancerous prostate conditions and getting older can also increase your PSA.
If your PSA level is raised or your rectal examination is unusual your GP refers you to a specialist doctor . Your GP may test your PSA level again if it is raised but your prostate feels normal.
Recommended Reading: Can You Have Sex After Prostate Cancer
Genetic Testing For Some Men With Prostate Cancer
Some doctors now recommend that some men with prostate cancer be tested to look for certain inherited gene changes. This includes men in whom a family cancer syndrome is suspected, as well as men with prostate cancer that has certain high-risk features or that has spread to other parts of the body. Talk to your doctor about the possible pros, cons, and limitations of such testing.
Gleason Prostate Cancer Score
1960s as a way to measure how aggressive your prostate cancer may be.
A pathologist determines your Gleason score by looking at a biopsy of your prostate tissue under a microscope. They grade the cells in the biopsy on a scale of 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are healthy prostate, whereas grade 5 cells are highly mutated and dont resemble healthy cells at all.
The pathologist will calculate your Gleason score by adding together the number of the most prevalent type of cell in the sample and the second most prevalent type of cell.
For example, if the most common cell grade in your sample is 4 and the second most common is 4, you would have a score of 8.
A Gleason score of 6 is considered low-grade cancer, 7 is intermediate, and 8 to 10 is high-grade cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Age Should You Get Prostate Checked
What Is A Dangerous Psa Level
PSA levels are measured as a number of nanograms in each milliliter of fluid tested. This is written as ng/mL.
- PSA level 2.5 ng/mL or lower: This is a normal PSA level for those under age 60, but in some cases, prostate cancer may still be present.
- PSA level between 2.5 and 4 ng/mL: This is a normal PSA level for most people.
- PSA level between 4 and 10 ng/mL: This indicates that prostate cancer might be present. At this level, there is about a 25% chance that you have prostate cancer.
- PSA level 10 ng/mL or above: There is a 50 percent chance that prostate cancer is present. The higher the PSA rises above 10 ng/mL, the greater the chance that you have prostate cancer.
Your doctor may also monitor your PSA velocity, or doubling time, which means recording your baseline PSA the level at your very first PSA test and seeing how fast the PSA level increases over time. Rapid increases in PSA readings can suggest cancer. If your PSA is slightly high, you and your doctor may decide to keep an eye on your levels on a regular basis to look for any change in the PSA velocity.
