> > > This Simple Morning Test Will Fix Your Prostate
Another type of prostate issue is chronic prostatitis, or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. This condition causes pain in the lower back and groin area, and may cause urinary retention. Symptoms include leaking and discomfort. In severe cases, a catheter may be required to relieve the symptoms. If the problem is unresponsive to other treatments, your doctor may suggest a surgical procedure. If these do not work, your symptoms could progress and become chronic.
An acute bacterial infection can cause a burning sensation. Inflammation of the prostate can affect the bladder and result in discomfort and other symptoms. This is the most common urinary tract problem in men under 50, and the third most common in men over 65. The symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are similar to those of CPPS. Patients may experience a fever or chills as a result of the infection.
You May Like: Can Prostate Cancer Spread To Testicles
Life After Prostate Removal
Categories:Cancer Survivorship,Prostate Cancer,Survivorship & Side Effects
For many men with prostate cancer, prostate removal is never needed because the cancer is often slow-growing and managed with non-surgical treatments. But, if the cancer has grown beyond the prostate, the oncologist may recommend prostate removal surgery, also called a prostatectomy. If you are going to have prostate removal surgery, this information can help you in your discussion with the doctors.
Donât Miss: How Painful Is A Biopsy Of The Prostate
What Is The Prostate Gland
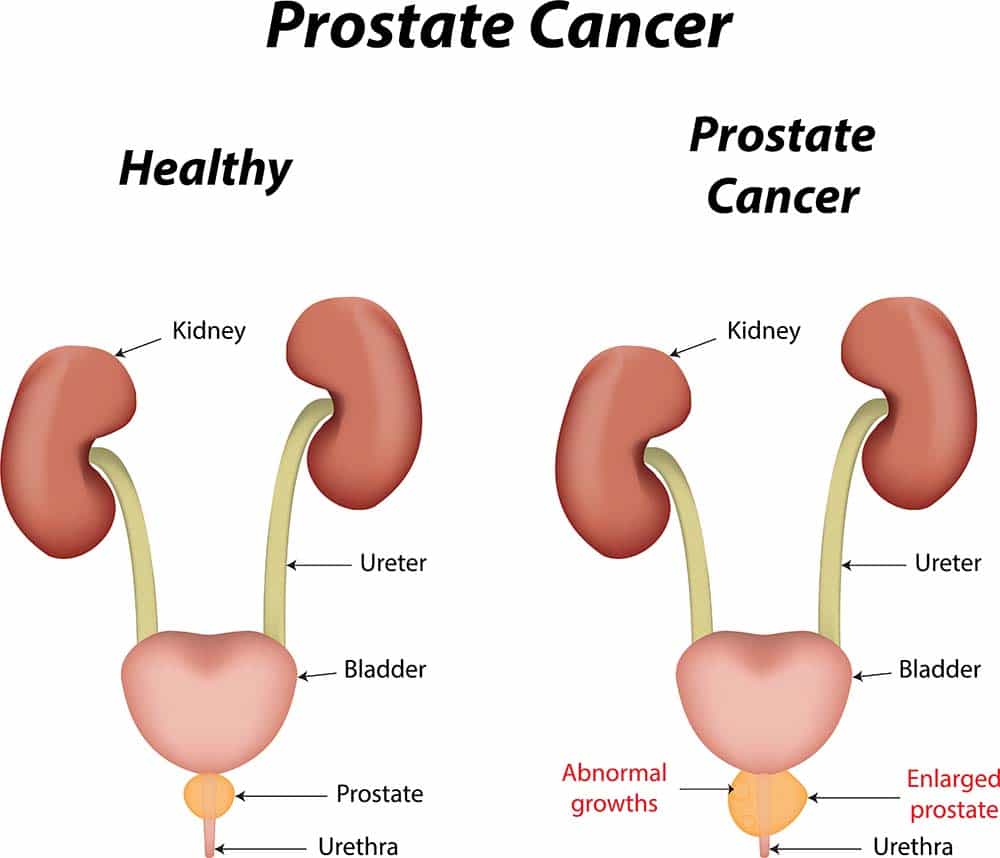
The prostate gland is about the size of a walnut and surrounds the neck ofa man’s bladder and urethrathe tube that carries urine from the bladder.It’s partly muscular and partly glandular, with ducts opening into theprostatic portion of the urethra. It’s made up of three lobes, a centerlobe with one lobe on each side.
Researchers don’t know all the functions of the prostate gland. However,the prostate gland plays an important role in both sexual and urinaryfunction. It’s common for the prostate gland to become enlarged as a manages, and it’s also likely for a man to encounter some type of prostateproblem in his lifetime.
Many common problems that don’t require a radical prostatectomy areassociated with the prostate gland. These problems may occur in men of allages and include:
Cancer of the prostate is a common and serious health concern. According tothe American Cancer Society, prostate cancer is the most common form ofcancer in men older than age 50, and the third leading cause of death fromcancer.
There are different ways to achieve the goal of removing the prostate glandwhen there’s cancer. Methods of performing prostatectomy include:
Don’t Miss: What Age To Get Prostate Checked
Prostate Cancer Surgery Should Be Individualized To Each Patient
Not every prostate cancer can be treated with a single-port approach or retzius-sparing surgery, but there are other choices. We have a large and expanding repertoire of treatment options that allow us to personalize treatment to each patients needs, says Dr. Sprenkle.
The potential options include several different surgical approaches and robots, as well as the alternative of radiation therapy, which uses high-energy rays or particles to kill cancer cells, delivered in precisely targeted external beam treatments or an implanted radioactive seed. For small tumors, another approach is focal therapy, a term for noninvasive techniques for eliminating the tumors while leaving the prostate gland itself intact.
“Patients come to my office concerned about the potential side effects of surgerythey are afraid they will become incontinent or have erectile dysfunction, says Isaac Kim, MD, PhD, MBA, professor and chair of the Department of Urology at Yale School of Medicine.
The best candidates for single-port surgery are men whose cancer is classified as favorable intermediate risk, Dr. Sprenkle says. He wouldnt recommend it for men with unfavorable intermediate or high-risk cancer, because the approach doesnt provide easy access for pelvic lymph node dissection to assess whether the cancer has spread.
Some simply favor other approaches, Dr. Sprenkle says.
The Purpose Of Prostate Surgery
Prostate cancer surgery, or radical prostatectomy, is a procedure conventional medicine praises for curing prostate cancer.
It has been performed for many years and was regarded as the gold standard of prostate cancer treatment. However, few studies compare its efficacy to other techniques.
Most men diagnosed with prostate cancer today are typically diagnosed with Gleason 6 cancer levels. But, according to many experts, this diagnosis may not be cancer! According to Mark Scholz, MD, a board-certified oncologist and expert on prostate cancer:
Misuse of the term cancer has tragic implications. Real cancer requires action and aggressive medical intervention with the goal of saving a life. But consider the potential havoc created by telling someone they have cancer when it is untrue. This dreadful calamity is occurring to 100,000 men every year in the United States with men who undergo a needle biopsy and are told they have prostate cancer with a grade of Gleason 6.
The impact of this is quite profound. Most prostate cancer diagnosed today falls into this Gleason 6. If it is not cancer, thousands of men have had aggressive treatment for cancer they dont really have.
Aggressive treatment, usually a complete surgical removal of the prostate , is the typical result. This leaves the patient to suffer from its side effects for the rest of their life.
You May Like: Can A Enlarged Prostate Be Reduced
What Is A Radical Prostatectomy
Surgery to remove the prostate to treat prostate cancer is called a radical prostatectomy. The aim of surgery is to remove all of the cancer cells.
It is usually done when the cancer is contained in the prostate and has not spread to the surrounding area.
A prostatectomy may sometimes be done to treat locally advanced prostate cancer. But usually, this operation is not possible. This is because the surgeon would not be able to remove all the cancer cells that have spread outside the prostate. Other types of surgery, such as transurethral resection of the prostate , can help with the symptoms of locally advanced prostate cancer.
A prostatectomy is a big operation and may not be suitable for everyone. Your doctor can tell you whether it is suitable or if a different treatment may be best for you.
See also
When You Might Have A Radical Prostatectomy
Your doctor might recommend a radical prostatectomy if:
- your cancer hasn’t spread outside the prostate gland. This is localised prostate cancer
- your cancer has broken through the covering of the prostate and spread to the area just outside the prostate gland. This is locally advanced prostate cancer
- you are well enough to have this operation
The aim of a radical prostatectomy operation is to cure prostate cancer.
Read Also: Mri Images Of Prostate Cancer
Most Prostate Surgeries Are Now Done Robotically
In the U.S., about 95% of prostate surgeries are performed robotically, with the surgeon sitting apart from the patient at a control console, watching progress on a high-definition monitor while controlling the robot remotely. The robot translates the surgeons hand movements into precise micro-movements, making it easy for them to manipulate a tiny camera and surgical instruments with greater range of motion than they could with their hands.
Robotic procedures are done with the patient under general anesthesia and take two hours or more to complete. The possibility of side effects is a concern with any type of prostatectomyeven with the aid of a robotthe main ones being an inability to control urine after surgery, and difficulty having or maintaining an erection. There are several different types of robotic surgeries, and each one comes with its own set of benefits.
What Are The Side Effects
The most common side effects of surgery are leaking urine and problems with getting or keeping an erection .
Your risk of getting these side effects depends on your overall health and age, how far the cancer has spread in and around the prostate and how likely it is to grow, and your surgeons skill and experience.
Read Also: How Effective Is Hormone Treatment For Prostate Cancer
Surgically Removing The Prostate Gland
A radical prostatectomy is the surgical removal of your prostate gland. This treatment is an option for curing prostate cancer that has not spread beyond the prostate or has not spread very far.
Like any operation, this surgery carries some risks, such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
In extremely rare cases, problems arising after surgery can be fatal.
It’s possible that prostate cancer can come back again after treatment. Your doctor should be able to explain the risk of your cancer coming back after treatment, based on things like your PSA level and the stage of your cancer.
Studies have shown that radiotherapy after prostate removal surgery may increase the chances of a cure, although research is still being carried out into when it should be used after surgery.
You may want to ask your doctors about storing a sperm sample before the operation so it can be used later for in vitro fertilisation .
Caring For The Incision
You will be able to take a shower the second day after your surgery. You may continue to have some discharge at the drain site for three to five days. Once you leave the hospital, the key words on caring for the drain site and incisions are clean and dry. Showering once a day and gently patting the area with a clean towel should be sufficient.
Recommended Reading: What Is Psma In Prostate Cancer
Loss Of Bladder Control
You may have some light dribbling or trouble controlling your bladder after a radical prostatectomy. This is known as urinary incontinence or urinary leakage. You may need to use a pad to manage urinary leakage for some days or weeks after the operation. Bladder control usually improves in a few weeks but it can take up to a year after the surgery. For about 5% of people, incontinence is ongoing and may need an operation to fix. In rare cases, incontinence may be permanent.
For help managing these problems, see Urinary problems.
Donât Miss: Show Me A Picture Of A Manâs Prostate
What You Need To Know About The Prostate Removing The Prostate Due To Cancer
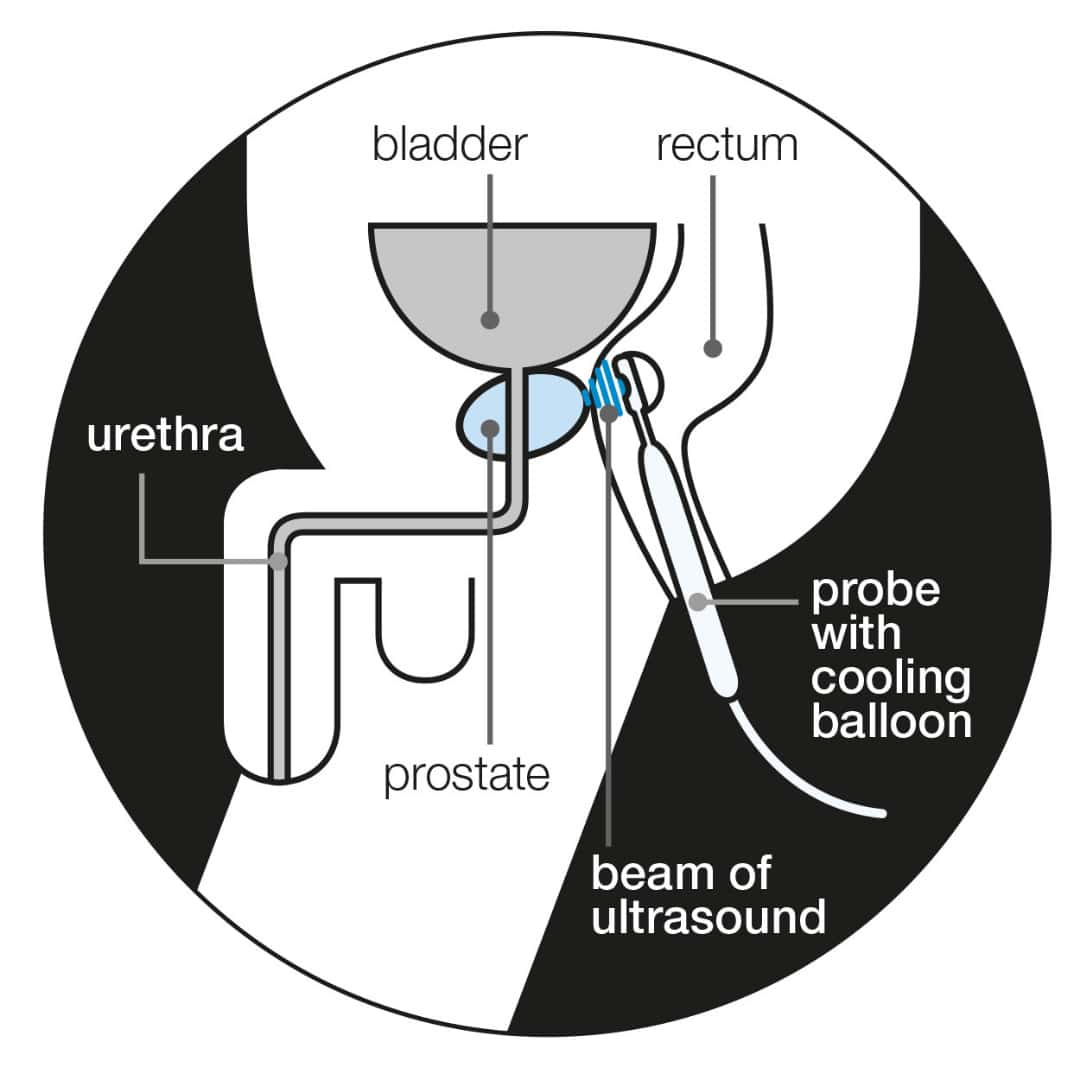
A enlarged prostate can also cause blockages in the urethra. A blocked urethra can also damage the kidneys. A patient suffering from an enlargement of the prostate may have pain in his lower abdomen and genitals. If pain is present, a digital rectal examination will reveal hard areas. A doctor may prescribe surgery or perform an endoscopic procedure. If the enlarged prostate is not completely removed, it will shrink.
While the size of an enlarged prostate will influence the extent of urinary symptoms, men may experience a range of urinary symptoms. Some men have minimal or no symptoms at all. Some men will have a very enlarged prostate, whereas others will have a mild enlargement. Generally, the symptoms can stabilize over time. Some men may have an enlarged prostate but not notice it. If they have an enlarged colon, their physician can perform a TURP procedure.
Also Check: Most Common Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Recommended Reading: Greenlight Laser Vaporization Of The Prostate Is Performed
How We Approach Prostate Cancer Treatment At Ctca
When you come to CTCA for a diagnostic consultation or second opinion, your case is reviewed by a multidisciplinary team of genitourinary cancer experts before you arrive for your first appointment. This care team may include a medical oncologist, a urologist or urologic oncologist and a radiation oncologist.
If we determine you need additional diagnostic evaluations, such as imaging or genomic testing, we schedule those procedures for you before your arrival.
Well also schedule appointments for you with our integrative care providers, who work to prevent and manage side effects of cancer and its treatment.
Together, we develop a treatment plan thats based on your unique needsusually within two to three days. Our goal is to give you and your caregivers a clear understanding of your options to empower you to make an informed decision about your care.
At CTCA, we strive to treat our patients as we would want our own loved ones to be treated: with compassion, dignity and respect. Its the basis of our foundation, and we call it the Mother Standard® of care.
How Prostate Cancer Is Treated
In cancer care, different types of doctorsincluding medical oncologists, surgeons, and radiation oncologistsoften work together to create an overall treatment plan that may combine different types of treatments to treat the cancer. This is called a multidisciplinary team. Cancer care teams include a variety of other health care professionals, such as palliative care experts, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, oncology nurses, social workers, pharmacists, counselors, dietitians, physical therapists, and others.
The common types of treatments used for prostate cancer are described below. Your care plan may also include treatment for symptoms and side effects, an important part of cancer care.
Treatment options and recommendations depend on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, possible side effects, and the patients preferences and overall health.
Cancer treatment can affect older adults in different ways. More information on the specific effects of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy on older patients can be found another section of this website.
Because most prostate cancers are found in the early stages when they are growing slowly, you usually do not have to rush to make treatment decisions. During this time, it is important to talk with your doctor about the risks and benefits of all your treatment options and when treatment should begin. This discussion should also address the current state of the cancer:
Don’t Miss: Genetic Testing Of Prostate Biopsy
If Treatment Does Not Work
Recovery from cancer is not always possible. If the cancer cannot be cured or controlled, the disease may be called advanced or terminal.
This diagnosis is stressful, and for some people, advanced cancer may be difficult to discuss. However, it is important to have open and honest conversations with your health care team to express your feelings, preferences, and concerns. The health care team has special skills, experience, and knowledge to support patients and their families and is there to help. Making sure a person is physically comfortable, free from pain, and emotionally supported is extremely important.
People who have advanced cancer and who are expected to live less than 6 months may want to consider hospice care. Hospice care is designed to provide the best possible quality of life for people who are near the end of life. You and your family are encouraged to talk with the health care team about hospice care options, which include hospice care at home, a special hospice center, or other health care locations. Nursing care and special equipment, including a hospital bed, can make staying at home a workable option for many families. Learn more about advanced cancer care planning.
After the death of a loved one, many people need support to help them cope with the loss. Learn more about grief and loss.
What Will I Learn By Reading This
When you have treatment for your prostate cancer, you may have erectile dysfunction also known as impotence. Erectile dysfunction is a very common side effect . Side effects from prostate cancer treatment are different from one man to the next. They may also be different from one treatment to the next. Some men have no erectile dysfunction. The good news is that there are ways to deal with erectile dysfunction. In this booklet you will learn:
- What erectile dysfunction is
- Why prostate cancer treatment can cause erectile dysfunction
- What can be done about erectile dysfunction
- How erectile dysfunction may affect your sex life
- What your partner can expect
It is important for you to learn how to deal with erectile dysfunction so that you can continue to have a satisfying intimate relationship.
Recommended Reading: External Prostate Massage For Prostatitis
Also Check: What Happens In Prostate Cancer
Prostatectomy: What To Expect During Surgery And Recovery
If youve been diagnosed withprostate cancer, your doctor will consider many factors before recommending the besttreatment. For many men, that may mean a prostatectomy. In this surgery,doctors remove the entire prostate.
The Johns Hopkins Hospital performs more of these procedures than almostanywhere else in the world. One of the most common questions they hear frompatients: What should I expect after surgery?
Johns Hopkins urologistMohamad Allaf, M.D., explains the surgery and recovery.
Who Should Undergo Radical Prostatectomy
Men younger than age 75 with limited prostate cancer who are expected to live at least 10 more years tend to get the most benefit from radical prostatectomy.
Before performing radical prostatectomy, doctors first try to establish that the prostate cancer has not spread beyond the prostate. The statistical risk of spread can be determined from tables comparing the results of a biopsy and PSA levels. Further testing for spread, if needed, can include CT scans, bone scans, MRI scans, and ultrasound.
If it appears that the prostate cancer has not spread, a surgeon may first offer other options besides surgery. These can include radiation therapy, hormone therapy, or simply observing the prostate cancer over time, since many prostate cancers grow slowly. Depending on how high the risk of cancer spread, pelvic lymph node dissection may be considered, as well.
Recommended Reading: How Serious Is Prostate Surgery
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Prostate Surgery
Advantages
- Surgery will completely remove the cancer if it is only in the prostate gland.
- The prostate can be removed and be fully analysed and staged in the laboratory.
- The success of the treatment can be easily assessed by PSA testing.
- If the PSA were to rise after surgery you would still be able to get other treatments like radiotherapy or hormone treatment.
Disadvantages
It involves a general anaesthetic and the usual risks you would expect with surgery, like the risk of bleeding, infection and blood clots.
- You will have to stay in hospital for a few days.
- You may get side-effects afterwards like problems with erections and urinary incontinence.
- Recovery takes around 6 weeks.
