Why Do Prostate Cancer Treatments Cause Urinary Incontinence
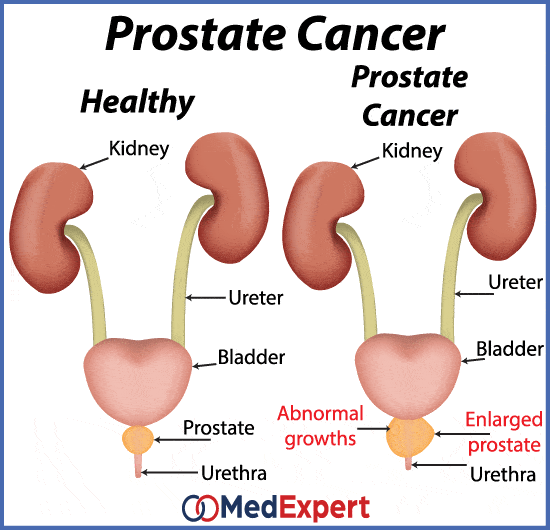
It helps to know a bit about how the bladder holds urine. When urine is emptied into the bladder from the kidneys, it is stored inside the bladder until you have the urge to urinate. The bladder is a hollow, muscular, balloon-shaped organ. Urine flows out of the bladder, and leaves the body through a tube called the urethra. Urination happens when the muscles in the wall of the bladder contract, forcing urine out of the bladder. At the same time, muscles that surround the urethra relax and allow the flow of urine. The prostate gland surrounds the urethra. Because an enlarged prostate gland can obstruct the urethra, it can cause urination retention or other problems with urination.
Removing the prostate through surgery or destroying it through radiation can disrupt the way the bladder holds urine and can result in urine leakage. Radiation can decrease the capacity of the bladder and cause spasms that force urine out. Surgery can, at times, damage the nerves that help control bladder function.
Dont Miss: Are Utis A Sign Of Bladder Cancer
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if bladder cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually bladder cancer cells. The disease is metastatic bladder cancer, not bone cancer.
What Screening Tests Are Used For Bladder Cancer
It is not standard to screen for bladder cancer. Bladder cancer screening may be used in people who are considered high risk. If you have a history of bladder cancer, a history of a birth defect of the bladder, or have been exposed to certain chemicals at work, you may be considered high-risk. You should ask your provider if screening tests are right for you.
Testing the urine for blood, abnormal cells, and tumor markers can help find some bladder cancers early but the results vary. Not all bladder cancers are found, and some people may have changes in their urine but do not have bladder cancer. These tests can be used in those who already have signs of bladder cancer or if the cancer has returned. However, more research is needed to determine how useful testing the urine is as a screening test.
Don’t Miss: Best Treatment For Ed After Prostate Surgery
Bladder Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Bladder
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys. There are two kidneys, one on each side of the backbone, above the waist. Tiny tubules in the kidneys filter and clean the blood. They take out waste products and make urine. The urine passes from each kidney through a long tube called a ureter into the bladder. The bladder holds the urine until it passes through the urethra and leaves the body.
There are three types of bladder cancer that begin in cells in the lining of the bladder. These cancers are named for the type of cells that become malignant :
- Transitional cell carcinoma: Cancer that begins in cells in the innermost tissue layer of the bladder. These cells are able to stretch when the bladder is full and shrink when it is emptied. Most bladder cancers begin in the transitional cells. Transitional cell carcinoma can be low-grade or high-grade:
- Low-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment, but rarely spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder or to other parts of the body.
- High-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment and often spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder, to other parts of the body, and to lymph nodes. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer are due to high-grade disease.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information:
What Are The Treatment Options For Bladder Cancer
There are four types of treatment for patients with bladder cancer. These include:
Sometimes, combinations of these treatments will be used.
Surgical options
Surgery is a common treatment option for bladder cancer. The type of surgery chosen will depend on the stage of the cancer.
- Transurethral resection of the bladder is used most often for early stage disease . It is done under general or spinal anesthesia. In this procedure, a special telescope called a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. The tumor is then trimmed away with the resectoscope, using a wire loop, and the raw surface of the bladder is then fulgurated .
- Partial cystectomy is the removal of a section of the bladder. At times, it is used for a single tumor that invades the bladder wall in only one region of the bladder. This type of surgery retains most of the bladder. Chemotherapy or radiation therapy is often used in combination. Only a minority of patients will qualify for this bladder-sparing procedure.
- Radical cystectomy is complete removal of the bladder. It is used for more extensive cancers and those that have spread beyond the bladder .
Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy
Read Also: Proton Therapy For Prostate Cancer In Florida
How Can You Get Tested For Prostate Cancer And Prostatitis
Digital rectal exam . For both conditions, your doctor may perform this exam. Theyâll use a glove and lubricant to insert their finger into your rectum. Your doctor can examine your prostate this way. If they notice any abnormal features in the texture, shape, or size of your prostate, they might suggest more tests.
Blood tests. They also may do blood tests for either prostate cancer or prostatitis. These measure prostate specific antigen , a natural substance that your prostate makes. High levels might mean that you have prostatitis, prostate cancer, or benign prostatic hyperplasia .
If you are at risk for cancer, your health care provider may order a blood test to check your PSA level. But if you have a prostate infection, your PSA can be falsely raised. Because of this, doctors are careful about how they read your PSA test results
For prostatitis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms and do a physical exam on you to check for prostatitis. They may also do a few different tests. These might include:
Urinalysis. This test checks your pee for bacteria and UTIs.
Cystoscopy. A cystoscopy looks for other urinary tract issues. It canât diagnose prostatitis, but it can help find what other things may cause your symptoms. Your doctor will use a cystoscope to look inside your urethra and bladder.
Read Also: Turbt Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Despite This Pancreatic Cancer Is Among The Deadliest Types Of Cancer Which Is Why Its Extremely Important To Know And Recogni
In fact, most people donât even know what it does. When malignant cancer cells form and grow within a personâs breast tissue, breast cancer occurs. Although it is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in american women, breast cancer can impact people of all genders. It may grow slowly and itâs typically treatable. The pancreas is a bodily organ that few people think about. Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer diagnosed in men. The pancreas is located behind the stomach, so having pancreatic cancer doesnât involve a palpable mass that you can feel. If breast cancer is diagnosed at an early enough stage, itâs treatable. Being armed with information is vital to begin the fight. Find the information you need today. Here are 10 more facts about prostate cancer. Breast cancer is the second most common cancer found in women after skin cancer but that doesnât mean men arenât at risk as well. But hearing the words can still be scary.
Recommended Reading: Best Foods For Prostate Cancer Prevention
What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is often grouped into four stages, with stages III and IV being more advanced prostate cancer.
- Early Stage | Stages I & II: The tumor has not spread beyond the prostate.
- Locally Advanced | Stage III: Cancer has spread outside the prostate but only to nearby tissues.
- Advanced | Stage IV: Cancer has spread outside the prostate to other parts such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver or lungs.
When an early stage prostate cancer is found, it may be treated or placed on surveillance . Advanced prostate cancer is not curable, but there are many ways to treat it. Treatment can help slow advanced prostate cancer progression.
There are several types of advanced prostate cancer, including:
Biochemical Recurrence
With biochemical recurrence, the prostate-specific antigen level has risen after treatment using surgery or radiation, with no other sign of cancer.
Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Non-Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone treatment and is only found in the prostate. This is found by a rise in the PSA level, while the testosterone level stays low. Imaging tests do not show signs the cancer has spread.
Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Read Also: How Do You Treat A Bladder Infection
Prostatitis Vs Prostate Cancer Symptoms And Signs
- Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland the four types are acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome, and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis.
- Prostate cancer develops when abnormal prostate gland cells multiply without control and may metastasize to other organs.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a noncancerous condition where normal prostate gland cells keep multiplying, thereby increasing the size of the prostate.
- Prostatitis usually does not lead to death, but prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in men, even though it is a slow-moving disease.
- Most men with early prostate cancer have no symptoms or signs symptoms and signs appear when the cancer becomes large enough to cause urinary blockage. Prostatitis, in contrast, usually appears with symptoms such as urinary frequency, urgency and/or pain with urination and possibly, some type of sexual dysfunction.
- Prostate cancer, when it produces signs and symptoms, may produce one or more of the following symptoms or signs that may also be seen in patients with prostatitis or BPH:
Also Check: How To Relax The Bladder Naturally
You May Like: Signs Of Late Stage Prostate Cancer
The Initial Causes Difference Between Enlarged Prostate And Cancer
One of the first symptoms of prostate issues is pain or tenderness in the groin or lower back. This can be the result of a noncancerous condition called enlarged prostatic tissue, or it could be an infection of the bladder. In either case, its important to see a doctor as soon as possible. If youre suffering from prostate pain, you may want to consider reducing your caffeine intake.
Another symptom of a potentially enlarged prostate is difficulty starting a stream of urine, leaking, or dribbling. These symptoms are not serious, but theyre still alarming. Most men put up with an enlarged prostate for years before seeking medical attention, but they typically seek treatment as soon as they notice symptoms. Even if you dont have symptoms, its worth getting checked to determine if you have any prostate issues.
If you experience nightly bathroom runs, you may be experiencing an enlarged prostate. You may be having difficulty starting a stream of urine, or you may even be dribbling or leaking during the day. These problems arent life-threatening, but can become a nuisance. You should not ignore these signs and seek treatment as soon as you notice them. If you feel any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
The Basics Of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer occurs when the cells in the prostate, a male reproductive gland, begin to grow out of control and develop into cancerous cells.
Nearly all prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas, which grow from the gland cells and grow slowly.
You May Like: Does Cranberry Juice Help Bladder Problems
Don’t Miss: Prostate Cancer And Leg Swelling
Bladder Cancer: What You Need To Know
Bladder Cancer is most common in men over the age of 60. There are two broad categories of bladder cancer based on what symptoms you may be experiencing, including:
- Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Approximately 70 percent of patients have non-muscle invasive cancer
- Muscle-Invasive And Advanced Bladder Cancer Between 20 percent and 25 percent of bladder cancer cases are muscle-invasive
Treatment Options for Bladder Cancer
We know processing this information and planning treatment can be difficult. Our doctors are here to help make you to feel at ease throughout the treatment process. Here are some things you can expect with the different treatment options. If the cancer has spread into the bladder wall or outside the bladder, treatment may include:
- Cystectomy With Urinary Diversion In men, the bladder and prostate are identified, dissected and removed. Surrounding lymph nodes are removed to assess the extent or spread of the cancer.
- Chemotherapy A systemic treatment in which drugs are given throughout the entire body. Its designed to kill cancer cells. Typically, it is administered intravenously .
- Radiation Therapy with Chemotherapy Radiation uses high-energy x-rays to destroy cancer cells. The addition of systemic chemotherapy makes cancer cells more vulnerable to the killing effects of radiation. Radiation therapy is also used to relieve symptoms of advanced bladder.
Bph And Other Conditions
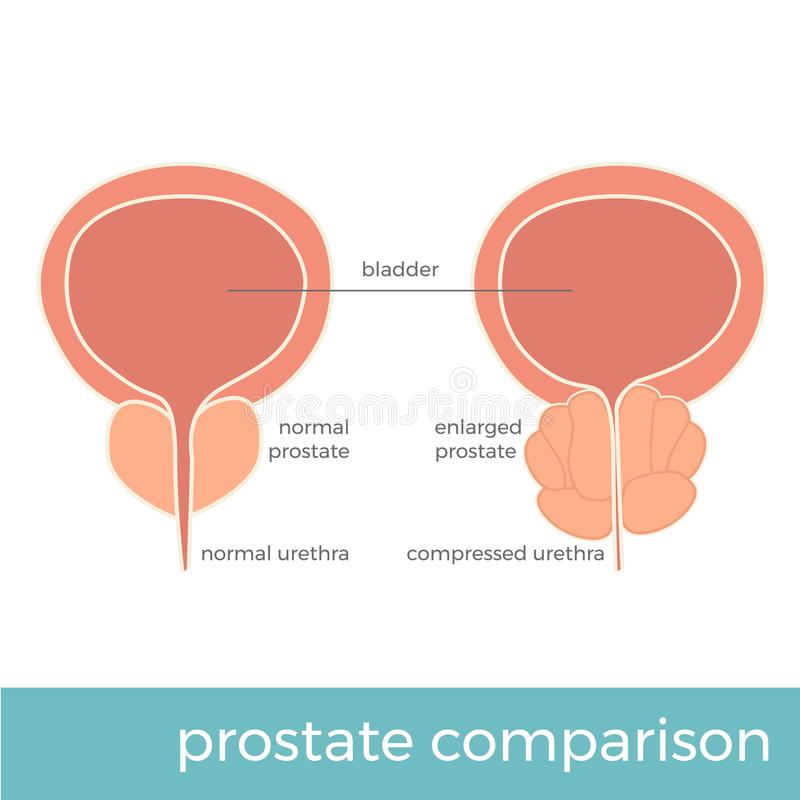
There are other conditions that affect the prostate that can have similar symptoms as prostate cancer. Those conditions include benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatitis. BPH is a noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland caused by aging, testosterone and genetics.
BPH is not cancer but has similar symptoms.
Another condition is prostatitis, an inflammation of the prostate gland that occurs from bacterial infection. Roughly half of all men will be affected by prostatitis during their lives.
Recommended Reading: What Causes A Swollen Prostate
How Does The Robot
Sexual dysfunction following the RALP tends to be severe and difficult to treat. The RALP procedure can cause sexual dysfunction for the following several reasons:
- The RALP can damage the cavernosal nerves that are vital to the erection.
- The RALP can produce urinary incontinence. Leakage of urine can decrease libido and interfere with overall sexual function.
The Top 7 Signs Of Advanced Prostate Cancer
In the early stages, you may not notice any symptoms related to prostate cancer. This is why screenings are important. Symptoms can sometimes be noticed for the first time when the cancer advances.
Advanced prostate cancer, also called metastatic cancer, means the cancer has spread to other areas of your body beyond your prostate gland. The most common areas for prostate cancer to spread are your bladder, rectum, and bones. It can also spread to your lymph nodes, liver, lungs, and other body tissues.
Whether youve just been diagnosed or youre in treatment, its also important to know the signs of advanced cancer. Cancer can behave differently depending on your genetics, so not every person will experience the same symptoms in the same way.
Read on to learn more about the seven top symptoms of advanced prostate cancer and how to spot them.
You May Like: How Do They Diagnose Bladder Cancer
Don’t Miss: Prostate Cancer Treatment In Charlotte Nc
What Are The Risks Of Bladder Cancer
No single factor is directly connected to bladder cancer, but factors that can increase the risk include:
- Age: Bladder cancer typically affects people age 55 and older.
- Smoking: Carcinogens from tobacco smoke come in contact with the lining of the bladder. Smokers are three times as likely as non-smokers to get bladder cancer.
- Family history: There is evidence that bladder cancer may have a genetic component.
- Industrial chemicals: Chemicals known as aromatic amines are often used in the dye industry. Workers who have daily exposure to them, such as painters, machinists and hairdressers, may be at a higher risk for bladder cancer.
- Drinking contaminated water: This includes water that has been treated with chlorine or drinking water with a naturally high level of arsenic, which occurs in many rural communities in the United States,.
- Taking certain herb: Supplements such as Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb, sometimes used for weight loss has been linked to higher rates of bladder cancer.
Is A Cystoscopy Painful
You may feel discomfort when the cystoscope goes into the urethra and bladder. Youâll probably feel a strong need to pee when your bladder gets full. You may feel a slight pinch if the doctor takes a biopsy.
After the procedure, your urethra may be sore and it might burn when you pee for a day or two.
Recommended Reading: What Does A Swollen Prostate Feel Like
Treatment Of Proximal Urethral Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of proximal urethral cancer or urethral cancer that affects the entire urethra is different for men and women.
For women, treatment may include the following:
- Radiation therapy followed by surgery .
For men, treatment may include the following:
- Radiation therapy or radiation therapy and chemotherapy, followed by surgery .
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
