> > > This Simple Morning Test Will Fix Your Prostate
Another type of prostate issue is chronic prostatitis, or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. This condition causes pain in the lower back and groin area, and may cause urinary retention. Symptoms include leaking and discomfort. In severe cases, a catheter may be required to relieve the symptoms. If the problem is unresponsive to other treatments, your doctor may suggest a surgical procedure. If these do not work, your symptoms could progress and become chronic.
An acute bacterial infection can cause a burning sensation. Inflammation of the prostate can affect the bladder and result in discomfort and other symptoms. This is the most common urinary tract problem in men under 50, and the third most common in men over 65. The symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are similar to those of CPPS. Patients may experience a fever or chills as a result of the infection.
A bacterial infection can also lead to prostate issues. Acute bacterial infections can be hard to treat. Some men with a bacterial infection may need to take antibiotics to prevent or treat symptoms. Symptoms of the disease include fever and chills, pain in the lower back and the tip of the penis. Some men may have blood in the urine, frequent urination, and blood in the urine. If you suffer from acute bacterial prostatitis, a medical professional should be able to prescribe you the appropriate treatments to prevent the disease.
Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial Risk Calculator Version 20
Disclaimer
The original Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial Prostate Cancer Risk Calculator posted in 2006 was developed based upon 5519 men in the placebo group of the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial. All of these 5519 men initially had a prostate-specific antigen value less than or equal to 3.0 ng/ml and were followed for seven years with annual PSA and digital rectal examination . If PSA exceeded 4.0 ng/ml or if an abnormal DRE was noted, a biopsy was recommended. After seven years, all men were recommended to have a prostate biopsy, regardless of PSA or DRE findings. PSA, family history, DRE findings, and history of a prior negative prostate biopsy provided independent predictive value to the calculation of risk of a biopsy that showed presence of cancer.
The results of the PCPTRC may not apply to different groups of individuals. As about 80% of men had a prostate biopsy with six cores, if more than six cores are obtained at biopsy, a greater risk of cancer may be expected. Most men in this study were white and results may be different with other ethnicities or races. The calculator is in principle only applicable to men under the following restrictions:
- Age 55 or older
- No previous diagnosis of prostate cancer
- DRE and PSA results less than 1 year old
The Future Of Diagnostic Risk Assessment
As many of the above calculators offer good potential to aid in the diagnostic pathway for PCA, the choice and use of which calculator needs to be determined by the clinical setting in which it is to be used and the wider full head to head comparisons can often be difficult to evaluate. There remains an important issue in terms of the error inherent in defining the gold standard of diagnosis, i.e. all the calculators above relied on the TRUS biopsy as being definitive but this is known to have error rates as high as 30 %. Hence, the new paradigm is how these calculators will perform in an optimally investigated population .
Perhaps leading the way in terms of evaluating the use of risk calculators in a near population-based community setting, recent work in Sweden has been undertaken to investigate the clinical advantages of using a combined risk assessment to reduce the over diagnosis of low-grade tumours and the study results are expected to be published soon. It is likely that the study will be able to demonstrate in a setting of wide-scale population-based screening the sorts of advantages seen in previous more constrained clinic-based evaluations. The Swedish research team are looking to continue their evaluations to include advances in biopsy procedures including MRI guided biopsies.
Table 1 Emerging biomarkers for characterising the risk to the individual from their particular cancer
Recommended Reading: How Long Is Recovery From Prostate Surgery
Psa And Prostate Cancer Risk
For the study, Roobol and colleagues examined the value of PSA combined with digital rectal exam findings, prostate size, previous prostate biopsy results, family history of prostate cancer, and age at diagnosis in predicting the future risk of prostate cancer among 5,176 men in the Netherlands. The men had an initial screening to assess all of these risk factors and a second screening four years later.
The researchers found that PSA level was the strongest predictor of future prostate cancer risk. Men with PSA levels of 1.5 or higher were seven times more likely to develop prostate cancer over the next four years than those men whose PSA scores were below that level.
Importantly, for any given PSA level, the other factors further modified this risk, Roobol says. A family history of prostate cancer elevated a man’s future cancer risk, while a previous negative biopsy and increasing prostate size lowered risk.
For example, a man with a PSA of 1.3 and no previous negative biopsy, a positive family history, and a smaller-than-average prostate size had a 5% chance of developing prostate cancer within four years.
In contrast, a man with a previous negative biopsy, no family history, and a large prostate could have a PSA of up to 4.0 before he would have a 5% risk of prostate cancer within four years.
Experts Discuss Addition Of West
We actually found that our calculator held up pretty well at different risk thresholds, especially when compared to the PCPT in terms of maintaining the same number of missed cancers, but cutting the number of biopsies that were not necessary nearly in half, says Neil Mistry, MD, MPH.
In this video, Neil Mistry, MD, MPH, and Adam B. Murphy, MD, MBA, MSCI, discuss the abstract, West-African ancestry can aid prediction of high-grade prostate cancer in Black-tailored risk calculator, which was presented at the North Central Section of the AUA Annual Meeting in Chicago, Illinois. Mistry is a urology resident and Murphy is an assistant professor of urology and preventive medicine at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago.
Related Content:
You May Like: What To Eat When You Have Prostate Cancer
> > > 1 Bedtime Hack To Pee Like A Bull
An enlarged prostate can also be the cause of other problems. If the enlarged prostate is causing symptoms, the best treatment would be a natural remedy. In the meantime, there are treatments for a wide range of conditions that cause a man to experience pain. A common surgical procedure involves an electric loop, laser, or electro-stimulation. The procedure is a safe and effective option for treating enlarged or symptomatic BPH.
> > > One Crazy Prostate Trick All Men Over 40 Should Try
Symptomatic treatment of an enlarged prostate usually involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables may be the best option if you suffer from chronic urination. It will help the body adjust to the increased size of the prostate. Also, taking regular urination intervals will help retrain the bladder to function properly. Inactivity also contributes to urine retention, and cold temperatures can increase the urge to urinate.
Invasive treatment of enlarged prostate includes medication that relieves the pressure on the urethra and bladder. However, if the condition is severe, it may require surgical intervention. If treatment is not successful, the enlarged prostate can become a potentially life-threatening disease. As the hormone levels in the body change, the enlarged prostate can lead to various complications, including urinary retention and even cancer. This is why it is critical to see a doctor for further evaluation.
A physician can recommend a number of treatments to address an enlarged prostate. An enlarged prostate will require surgery to relieve the symptoms. In most cases, surgical treatment for an enlargement of the penis is enough. Moreover, a doctor may recommend a course of treatment based on symptoms. A TURP procedure is not painful and requires less recovery time than open surgery. The recovery period will be shorter and less traumatic.
Also Check: Is A Prostate Exam Necessary
New Way To Predict Prostate Cancer Risk
Personalized Risk Calculator May Help Identify Men at High Risk for Prostate Cancer
Feb. 25, 2009 — For the first time, researchers say they have developed a tool that can help predict a man’s future risk of developing prostate cancer.
The personalized risk calculator combines prostate-specific antigen test results with additional prostate cancer risk factors, including previous prostate biopsy results, family history of prostate cancer, and prostate size.
“Doctors use PSA to determine whether a man currently has prostate cancer. But the idea of using a combination of baseline PSA levels and specific, known risk factors to give a longer-term view about prostate cancer risk is a new concept that we hope will become part of standard practice,” says researcher Monique Roobol, PhD, an epidemiologist in urologic oncology at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
“Assessing future risk of prostate cancer is important for identifying men who are candidates for more frequent screening,” she tells WebMD.
“If future risk is high, you may want to consider the use of drugs that have been shown to reduce the risk of developing prostate cancer,” Roobol says.
Patient Cohort And Sample Collection
The study cohort consisted of 436 Caucasian Irish men referred for a TRUS biopsy on the basis of an elevated PSA and/or abnormal DRE between April 2012 and June 2016. Blood samples were collected in a serum separator tube prior to biopsy and processed within 3 h of collection. Samples were centrifuged at 1500×g for 15 min at room temperature. Serum was removed and stored at 80 °C until further analysis. Patients were classified as either biopsy-negative or biopsy-positive and further sub-divided into low-grade and high-grade disease. The clinicopathologic details of the cohort are summarised in Table .
Table 1 Clinical Features of the Patient Cohort.
Sample collection and processing were ethically approved by the St James Hospital and Mater Misericordiae University Hospital ethics committees. The patient information leaflet and consent form were written and constructed in line with best practice and the EU Data protection Directive and Data protection Acts 1988 and 2018 and approved by the two ethics committees. All patients gave written informed consent agreeing to participate in the study. All steps were carried out in accordance with national guidelines and regulations.
Also Check: How To Cure Prostate Stones
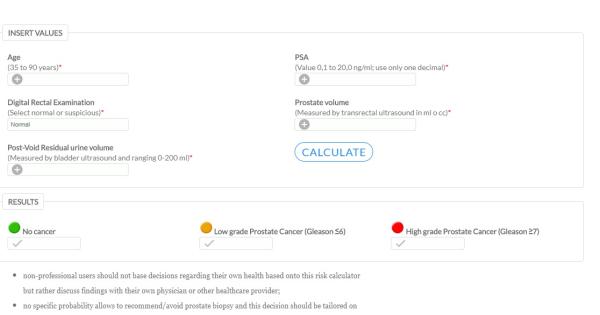
The Pcpt Prostate Cancer Risk Calculator
The Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial prostate cancer risk calculator was the first online prostate cancer risk assessment tool to allow a man to assess his risk for prostate cancer in consultation with his primary care physician.
This tool was developed by Thompson et al., based on data developed from 5,519 men in the placebo group of the PCPT trial who went on to have a biopsy after final completion of the therapy stage of the trial.
In addition to PSA and DRE results, the nomogram is based on knowledge of the following patient characteristics: any prior biopsy data, age, family history of prostate cancer, and ethnicity.
At this time, this nomogram is considered to be the standard nomogram for assessment of risk for prostate cancer. The more recent Sunnybrook nomogram is based on additional data, but has yet to be validated.
A plug and play version of the PCPT prostate cancer risk calculator is available on the University of Texas Health Sciences Center web site. If you want to use the calculator, all you need to do is enter the following data:
- Your prostate specific antigen level
- Your ethnic background
What You Need To Know About The Prostate Next
The main purpose of the prostate is to produce semen, a milky fluid that sperm swims in. During puberty, the body produces semen in a large number of cases, including enlarged prostate. This fluid causes the prostate to swell and cause a number of bladder-related symptoms. This is why the prostate is important to the body. It can be caused by many factors, including infection and inflammation.
A enlarged prostate can also cause blockages in the urethra. A blocked urethra can also damage the kidneys. A patient suffering from an enlargement of the prostate may have pain in his lower abdomen and genitals. If pain is present, a digital rectal examination will reveal hard areas. A doctor may prescribe surgery or perform an endoscopic procedure. If the enlarged prostate is not completely removed, it will shrink.
While the size of an enlarged prostate will influence the extent of urinary symptoms, men may experience a range of urinary symptoms. Some men have minimal or no symptoms at all. Some men will have a very enlarged prostate, whereas others will have a mild enlargement. Generally, the symptoms can stabilize over time. Some men may have an enlarged prostate but not notice it. If they have an enlarged colon, their physician can perform a TURP procedure.
You May Like: What Does Swollen Prostate Mean
Inflammation Of The Prostate
Some studies have suggested that prostatitis may be linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer, but other studies have not found such a link. Inflammation is often seen in samples of prostate tissue that also contain cancer. The link between the two is not yet clear, and this is an active area of research.
Prostate Cancer Risk Calculator To Add Genetic Data

Dr. Robert Nam.
Every year, 24,000 Canadian men are diagnosed with prostate cancer. How can we better identify which men are at higher risk for the disease and which men will develop more aggressive forms. How can we be more proactive in our treatment? Is it necessary to treat all forms of prostate cancer? Or is it best to employ an active monitoring strategy? There are no easy answers.
Enter Dr. Robert Nam, head of genitourinary cancer care at the Odette Cancer Centre. Predicting which men are at risk of prostate cancer, and whether that cancer is likely to be slow-growing or aggressive, is the focus of his research.
The tool developed at Sunnybrook to calculate those risks has been shown to be remarkably effective. In fact, the Sunnybrook Prostate Risk Calculator, borne out of basic science and biomarker research, has greater accuracy than a similar tool used widely in the U.S., resulting in Dr. Nams team being recognized as a world leader in this area.
Now, the latest research on genetics, biopsy and treatment outcomes is being integrated into the Prostate Risk Calculator: Next Generation. Last year, Prostate Cancer UK awarded Dr. Nam a large grant to research and build on the existing screening tool. He heads an international consortium to develop the new iteration.
This program aims to reduce overtreatment of clinically insignificant prostate cancer while providing the option of treatment if, over time, the patient becomes higher risk.
You May Like: Are There Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer Risk Factors
A risk factor is anything that raises your risk of getting a disease such as cancer. Different cancers have different risk factors. Some risk factors, like smoking, can be changed. Others, like a persons age or family history, cant be changed.
But having a risk factor, or even several, does not mean that you will get the disease. Many people with one or more risk factors never get cancer, while others who get cancer may have had few or no known risk factors.
Researchers have found several factors that might affect a mans risk of getting prostate cancer.
The Initial Causes Next
One of the first symptoms of prostate issues is pain or tenderness in the groin or lower back. This can be the result of a noncancerous condition called enlarged prostatic tissue, or it could be an infection of the bladder. In either case, its important to see a doctor as soon as possible. If youre suffering from prostate pain, you may want to consider reducing your caffeine intake.
Another symptom of a potentially enlarged prostate is difficulty starting a stream of urine, leaking, or dribbling. These symptoms are not serious, but theyre still alarming. Most men put up with an enlarged prostate for years before seeking medical attention, but they typically seek treatment as soon as they notice symptoms. Even if you dont have symptoms, its worth getting checked to determine if you have any prostate issues.
If you experience nightly bathroom runs, you may be experiencing an enlarged prostate. You may be having difficulty starting a stream of urine, or you may even be dribbling or leaking during the day. These problems arent life-threatening, but can become a nuisance. You should not ignore these signs and seek treatment as soon as you notice them. If you feel any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Recommended Reading: Can You Milk Your Prostate
> > > All Natural Technique Fixes Enlarged Prostate Watch Here< <
Surgical procedures to remove the diseased prostate are usually necessary. Surgical procedures are not always necessary. If the disease is caused by bacterial infections, a doctor can treat the symptoms using alpha-blockers or surgery. Physical therapy, relaxation exercises, and warm baths are all recommended. A physician may also prescribe antibiotics to cure the infection. A bacterial infection can also cause a recurrence of the condition.
An enlarged prostate can be uncomfortable for both men and women. Some of the symptoms of an enlarged male reproductive organ include a weakened urine stream, urgent need to urinate, and urinary tract infections. BPH can also cause damage to the kidneys. A sudden inability to urinate can be life-threatening, as it can lead to bladder and kidney damage. Unfortunately, most men with enlarged prostrates put up with the symptoms for years before they seek treatment. However, many of the men with symptoms finally decide to go to a doctor for proper gynecological evaluation and to begin enlarged prostatic therapy.
