Family History And Genes
Your risk of prostate cancer is higher if you have a close relative, such as a brother or father, who has had prostate cancer.
Some inherited genes can increase your risk of prostate cancer. These inherited genes are rare and account for only a small number of prostate cancers.
The risk increases by up to 5 times in men with the gene BRCA2. And the risk might increase with the BRCA1 gene. These genes also cause breast and ovarian cancers.
Men with a rare syndrome called Lynch syndrome have a higher chance of developing prostate cancer and some other cancers. A change in one of the genes that fixes mistakes in DNA causes this syndrome eg. MSH2 and MLH1 genes.
Researchers are looking into other genes that might also increase the risk of prostate cancer.
Whos At Risk For Prostate Cancer
All men are at risk of having prostate cancer. About one man in nine will be diagnosed with it during their lifetime, but only one in 39 will die of this disease. About 80% of men who reach age 80 have cancer cells in their prostate. Besides being male, there are other things that contribute to the risk.
Ways To Lower Your Risk Of Developing Prostate Cancer
While there is no ironclad way to ensure that you wont get prostate cancer, there are things you can do to reduce your risk. Many of these suggestions may help reduce the chance of developing other cancers too.
- Eat more fruits, vegetables, and legumes . Eat whole grains instead of white bread and white pasta. Cooked tomatoes, cruciferous vegetables , and soy-based foods seem especially helpful.
- Replace some red meats in your diet with chicken and fish, especially fish with good fats like salmon.
- Get more active. Begin exercising and try to lose weight if youre overweight. Walking is an easy way to become active.
- Stop smoking. Consider using a smoking cessation program or buddy up with a friend so that you both can quit smoking.
- Medication. Research shows that medications used to treat BPH, also known as prostate gland enlargement, may help reduce your risk for prostate cancer. Talk to your doctor about finasteride and dutasteride to determine if one of these medications may be right for you.
- Avoid excessive calcium. Dont take more than 1,200 mg per day.
- Consider Vitamin D. Men who live north of 40 degrees latitude experience the highest death rate from prostate cancer. This adverse effect appears to be caused by decreased sunlight during the winter months. Ask your doctor if taking Vitamin D is appropriate for you.
You May Like: When Should You Get Prostate Exam
Can Drinking Cause Prostate Cancer
No. Alcohol use can increase the risk for many types of cancer, but prostate cancer is not on this list.
Prostate cancer treatment: The care you need is one call away
Your multidisciplinary team will work with you to develop a personalized plan to treat your prostate cancer in a way that fits your individual needs and goals.
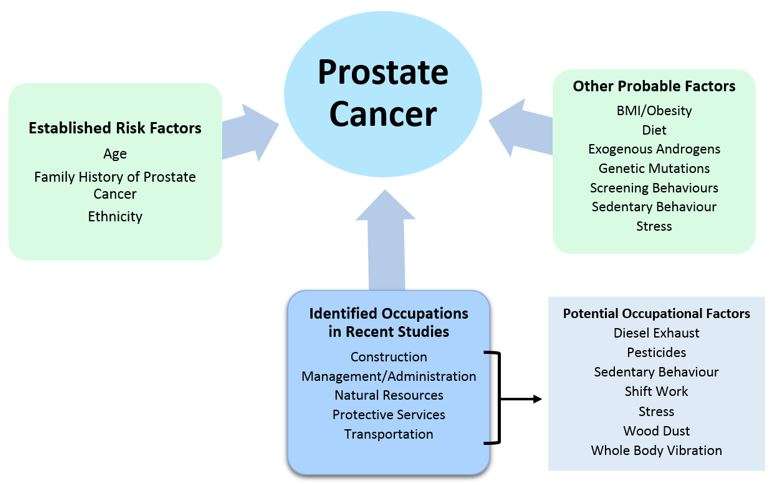
Established Risk Factors: Age Race And Family History
The only risk factors for prostate cancer that can be considered established are age, race/ethnicity, and family history. Study of age-specific incidence curves reveals that prostate cancer risk begins to rise sharply after age 55 years and peaks at age 7074, declining slightly thereafter. Autopsy studies confirm that prostate cancer has a long induction period, and that many men have incipient lesions in their 20s and 30s.2 As Figure 1 shows, the risk of prostate cancer is approximately 60% higher in African Americans than in whites. Mortality among African Americans is approximately double that of whites. Conflicting data exist as to whether this mortality difference is explained entirely by differences in socioeconomic status variables and stage at diagnosis, or whether an inherent difference exists between these racial/ethnic groups in the underlying biology of prostate cancer. It should be emphasized that biological explanations for these risk differences could involve genetic factors, environmental factors, or, more likely, an interaction between the two.
Also Check: Are Tomatoes Good For Prostate Health
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Screening and Prevention Editorial Board. PDQ Prostate Cancer Prevention. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
The Following Risk Factors May Increase The Risk Of Prostate Cancer:
Age
Prostate cancer is rare in men younger than 50 years of age. The chance of developing prostate cancer increases as men get older.
Family history of prostate cancer
A man whose father, brother, or son has had prostate cancer has a higher-than-average risk of prostate cancer.
Race
Prostate cancer occurs more often in African American men than in White men. African American men with prostate cancer are more likely to die from the disease than White men with prostate cancer.
Hormones
The prostate needs male hormones to work the way it should. The main male sex hormone is testosterone. Testosterone helps the body develop and maintain male sex characteristics.
Testosterone is changed into dihydrotestosterone by an enzyme in the body. DHT is important for normal prostate growth but can also cause the prostate to get bigger and may play a part in the development of prostate cancer.
Vitamin E
The Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial found that vitamin E taken alone increased the risk of prostate cancer. The risk continued even after the men stopped taking vitamin E.
Folic acid
Dairy and calcium
A diet high in dairy foods and calcium may cause a small increase in the risk of prostate cancer.
Recommended Reading: Can Young Men Get Prostate Cancer
Can Lack Of Sex Cause Prostate Cancer
Lack of sex is not known to cause prostate cancer. But, as noted, there is some evidence that frequent ejaculation, whether through masturbation or sex, may confer some protection against this cancer. Researchers are still trying to understand the exact biologic mechanisms that give rise to prostate cancer.
Prostate Cancer Prevention Patient Version
On This Page
Cancerprevention is action taken to lower the chance of getting cancer. By preventing cancer, the number of new cases of cancer in a group or population is lowered. Hopefully, this will lower the number of deaths caused by cancer.
To prevent new cancers from starting, scientists look at risk factors and protective factors. Anything that increases your chance of developing cancer is called a cancer risk factor anything that decreases your chance of developing cancer is called a cancer protective factor.
Some risk factors for cancer can be avoided, but many cannot. For example, both smoking and inheriting certain genes are risk factors for some types of cancer, but only smoking can be avoided. Regular exercise and a healthy diet may be protective factors for some types of cancer. Avoiding risk factors and increasing protective factors may lower your risk but it does not mean that you will not get cancer.
Different ways to prevent cancer are being studied.
Also Check: Where Does Prostate Cancer Spread To Bones
Risks For Prostate Cancer
Certain behaviours, substances or conditions can affect your risk, or chance, of developing cancer. Some things increase your risk and some things decrease it. Most cancers are the result of many risks. But sometimes cancer develops in people who don’t have any risks.
The risk for prostate cancer increases as men get older. The chance of being diagnosed with prostate cancer is greater after age 50. Prostate cancer is most often diagnosed in men in their 60s.
The following can increase your risk for prostate cancer. Most of these risks cannot be changed.
The Following Protective Factors May Decrease The Risk Of Prostate Cancer:
Folate
Folate is a kind of vitamin B that occurs naturally in some foods, such as green vegetables, beans and orange juice. Folic acid is a man-made form of folate that is found in vitamin supplements and fortified foods, such as whole-grain breads and cereals. A 10-year study showed that the risk of prostate cancer was lower in men who had enough folate in their diets. However, the risk of prostate cancer was increased in men who took 1 milligram supplements of folic acid.
Finasteride and Dutasteride
Finasteride and dutasteride are drugs used to lower the amount of male sex hormones made by the body. These drugs block the enzyme that changes testosterone into dihydrotestosterone . Higher than normal levels of DHT may play a part in developing prostate cancer. Taking finasteride or dutasteride has been shown to lower the risk for prostate cancer, but it is not known if these drugs lower the risk of death from prostate cancer.
Read Also: Does Medicare Cover Hormone Therapy For Prostate Cancer
Cancer Prevention Clinical Trials Are Used To Study Ways To Prevent Cancer
Cancer prevention clinical trials are used to study ways to lower the risk of developing certain types of cancer. Some cancer prevention trials are conducted with healthy people who have not had cancer but who have an increased risk for cancer. Other prevention trials are conducted with people who have had cancer and are trying to prevent another cancer of the same type or to lower their chance of developing a new type of cancer. Other trials are done with healthy volunteers who are not known to have any risk factors for cancer.
The purpose of some cancer prevention clinical trials is to find out whether actions people take can prevent cancer. These may include eating fruits and vegetables, exercising, quitting smoking, or taking certain medicines, vitamins, minerals, or food supplements.
What Causes Prostate Cancer

Like all types of cancer, the exact cause of prostate cancer isnt easy to determine. In many cases, multiple factors may be involved, including genetics and exposure to environmental toxins, like certain chemicals or radiation.
Ultimately, mutations in your DNA, or genetic material, lead to the growth of cancerous cells. These mutations cause cells in your prostate to start growing uncontrollably and abnormally. Abnormal or cancerous cells continue to grow and divide until a tumor develops. If you have an aggressive type of prostate cancer, the cells may metastasize, or leave the original tumor site and spread to other parts of your body.
Some risk factors may affect your chances of developing prostate cancer, including your:
- family history
Read more: 9 tips to prevent prostate cancer »
You May Like: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
Trends In Incidence And Mortality
Age-adjusted incidence and mortality of prostate cancer in the United States, 19731999 .
In the United States, the risk of dying from prostate cancer began to decline measurably in 1994, for the first time since statistics have been kept, and mortality has continued to decline at an average annual rate of about 2% to 3%. Reasons for this decline are beyond the scope of this article, but a contribution of PSA screening appears to be very likely.1
Prostate Cancer Screening Recommendations
Talk to your doctor about your personal history and family history to determine what screening recommendation is best for you. The American Cancer Society recommends:
- Age 50for men at average risk
- Age 45for men at high risk including African-Americans and men with a first-degree relative diagnosed with prostate cancer before age 65
- Age 40for men at the highest risk men who have more than one first-degree relative with prostate cancer at a younger age
Recommended Reading: When To Get Prostate Cancer Screening
Prostate Cancer Is The Second Most Common Cancer Among Men In The United States
Prostate cancer is most common in older men. In the U.S., about one out of every 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer. Most men diagnosed with prostate cancer do not die of it.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information about prostate cancer:
- Avoiding risk factors and increasing protective factors may help prevent cancer.
- The following risk factors may increase the risk of prostate cancer:
- Age
- Family history of prostate cancer
- Race
Does Undergoing A Vasectomy Cause Prostate Cancer
The link between prostate cancer and vasectomy is controversial. A 2020 study in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute suggests that undergoing a vasectomy may result in a small increased risk of prostate cancer that persists for at least three decades, regardless of the age at vasectomy. However, other studies have not found this to be true and more research is needed, according to the American Cancer Society.
Also Check: Where Does Prostate Cancer Tend To Metastasize To
Things You Should Know About Risk Factors For Cancer:
- Risk factors can increase a person’s risk, but they do not necessarily cause the disease.
- Some people with 1 or more risk factors never develop cancer. Other people can develop cancer and have no risk factors. Some risk factors are very well-known. But there is ongoing research about risk factors for many types of cancer.
- Some risk factors, such as family history, may not be in your control. But others may be things you can change.
Knowing the risk factors can help you make choices that might lower your risk. For example, if an unhealthy diet is a risk factor, you may choose to eat healthy foods. If excess weight is a risk factor, your health care provider may check your weight or help you lose weight.
What Age Does Prostate Cancer Risk Increase Risk Factors
Prostate cancer risk increases with age, especially after age 50. Most prostate cancers are diagnosed between the ages of 65-69. Prostate cancer is rare before age 40, although it can still happen.
Men aged 65 years and older account for about two-thirds of all prostate cancer cases. However, as you get older, the disease becomes less aggressive, especially at about age 70.
If you are older than 45 and have a high risk of prostate cancer due to a family history of the disease or other factors, or if you are older than 50 and worried about prostate cancer, talk to your doctor about prostate cancer screenings.
You May Like: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Good For Prostate Cancer
Understand Your Prostate Cancer Risk Factors
Researchers continue to study what causesprostate cancer. They do know that genes play a role in the development and progression of the disease, especially:
- Oncogenes. Genes that help cells grow, divide and stay alive.
- Tumor suppressor genes. Genes that control cell growth, repair mistakes in DNA and cause cells to die at the right time.
Genetic mutations that keep oncogenes active or inactivate tumor suppressor genes can be prostate cancer causes. Both make cells grow out of control.
Gene mutations can be inherited or acquired.
Inflammation Of The Prostate
Some studies have suggested that prostatitis may be linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer, but other studies have not found such a link. Inflammation is often seen in samples of prostate tissue that also contain cancer. The link between the two is not yet clear, and this is an active area of research.
You May Like: Where’s Your Prostate Located
Consult A Doctor To Learn More About Your Risk Factors
We offer you access to New Jerseys largest network of cancer specialists. If you are concerned about your prostate health or are experiencing any of the prostate cancer symptoms mentioned above, make an appointment with one of our expert urologists or oncologists today.
To contact one of New Jerseys best prostate cancer specialists call
What Are The Odds You Will Get Prostate Cancer
What are Prostate Cancer Risk Factors? One man in six will get prostate cancer. But which men and why? What makes some men predisposed to prostate cancer, while others are never diagnosed? Age, race, lifestyle, family history, where you live, and what you eat can be risk factors. Having one or more of the risk factors described on this page is not a guarantee that you will get prostate cancer, but it does mean your chances of developing prostate cancer are higher.
What are Prostate Cancer Risk Factors? One man in six will get prostate cancer. But which men and why? What makes some men predisposed to prostate cancer, while others are never diagnosed? Age, race, lifestyle, family history, where you live, and what you eat can be risk factors. Having one or more of the risk factors described on this page is not a guarantee that you will get prostate cancer, but it does mean your chances of developing prostate cancer are higher.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Prostate Cancer
