How The Prostate Changes As You Age
Because the prostate gland tends to grow larger with age, it may squeeze the urethra and cause problems in passing urine. Sometimes men in their 30s and 40s may begin to have these urinary symptoms and need medical attention. For others, symptoms aren’t noticed until much later in life. An infection or a tumor can also make the prostate larger. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have any of the urinary symptoms listed below.
Tell your doctor if you have these urinary symptoms:
- Are passing urine more during the day
- Have an urgent need to pass urine
- Have less urine flow
- Feel burning when you pass urine
- Need to get up many times during the night to pass urine
Growing older raises your risk of prostate problems. The three most common prostate problems are inflammation , enlarged prostate , and prostate cancer.
One change does not lead to another. For example, having prostatitis or an enlarged prostate does not increase your risk of prostate cancer. It is also possible for you to have more than one condition at the same time.
What Are Prostate Cancer Treatment Side Effects
Some prostate cancer treatments can affect the bladder, erectile nerves and sphincter muscle, which controls urination. Potential problems include:
- Incontinence: Some men experience urinary incontinence. You may leak urine when you cough or laugh, or you may feel an urgent need to use the bathroom even when your bladder isnt full. This problem can improve over the first six to 12 months without treatment.
- Erectile dysfunction : Surgery, radiation and other treatments can damage the erectile nerves and affect your ability to get or maintain an erection. Some men regain erectile function within a year or two . In the meantime, medications like sildenafil or tadalafil can help by increasing blood flow to the penis.
- Infertility: Treatments can affect your ability to produce or ejaculate sperm, resulting in male infertility. If you think you might want children in the future, you can preserve sperm in a sperm bank before you start treatments. After treatments, you may undergo sperm extraction. This procedure involves removing sperm directly from testicular tissue and implanting it into a womans uterus.
What Are The Potential Complications
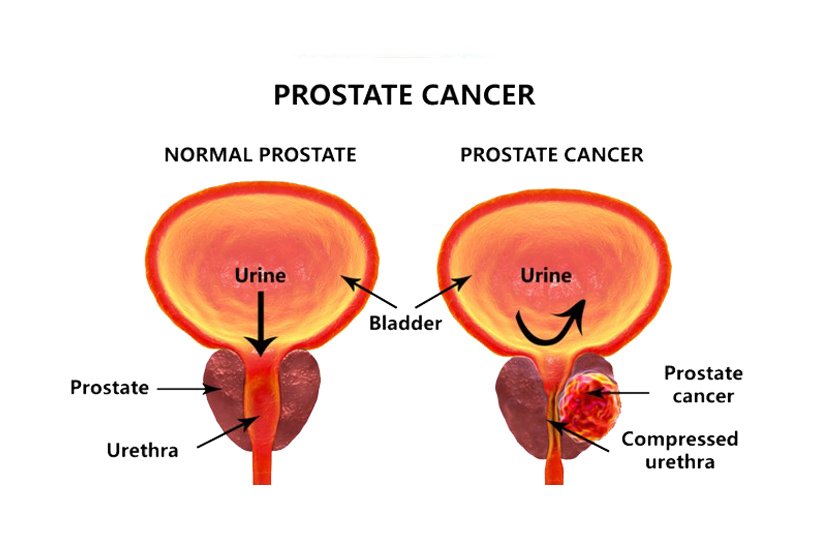
Prostate cancer and treatment can lead to problems with urination as well as erectile dysfunction.
If stage 2 prostate cancer spreads outside the prostate, it can reach nearby tissues, the lymph system, or bloodstream. From there, it can metastasize to distant sites. Later-stage prostate cancer is difficult to treat and can be life-threatening.
Donât Miss: External Prostate Massage Prostatitis
Read Also: What Is The Definition Of Prostate Gland
Current Psa Screening Recommendations
PSA-based screening refers to testing healthy men without symptoms.
Until recently, physician societies disagreed on screening recommendations, but with the publication of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Guideline in May 2018, all the major physician groups are broadly in agreement, including the American College of Physicians , the American Cancer Society , American Urological Association , and American Society of Clinical Oncology :
- They advise supporting men so that they make informed decisions about screening that reflect their personal preferences and values.
- Routine screening is not recommended in men between ages 40 and 54 of average risk.
- For men ages 55 to 69 years, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force concluded with moderate certainty that the net benefit of PSA-based screening is small for some men, making the decision up to the judgment of the physician and the values of the patient.”
- For men 70 years and older, they recommend against routine screening because the expected harms are thought to outweigh the benefits.
- Your doctor should not screen you unless you express a preference for it.
- A discussion of the benefits and harms of screening should include a family history of prostate cancer, race or ethnicity, any medical conditions that affect your overall health and lifespan, and your values about risk and benefit.
- If you have less than a 10-year life expectancy, screening is not recommended.
What Are The 4 Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer Stages T2a: The tumor has invaded one-half of one side of the prostate. T2b: The tumor has spread to more than one-half of one side of the prostate, but not to both sides. T2c: The cancer has invaded both sides of the prostate.
You May Like: Can Retrograde Ejaculation Be Fixed
Are Prostate Problems Always A Sign Of Prostate Cancer
Not all growths in the prostate are cancerous, and not all prostate problems indicate cancer. Other conditions that cause similar prostate cancer symptoms include:
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia : At some point, almost every man will develop benign prostatic hyperplasia . This condition enlarges the prostate gland but doesnt increase cancer risk. The swollen gland squeezes the urethra and blocks the flow of semen and urine. Medications, and sometimes surgery, can help.
- Prostatitis: Men younger than 50 are more prone to prostatitis, inflammation and swelling of the prostate gland. Bacterial infections are often the cause. Treatments include antibiotics or other medications.
Can Prostate Cancer Treatment Affect Your Quality Of Life
Your age and overall health will make a difference in how treatment may affect your quality of life. Any health problems you have before youre treated, especially urinary, bowel or sexual function problems, will affect how you recover. Both surgery and radiation can cause urinary incontinence or impotence .
You May Like: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Prostate Cancer Treatment Options: What Are They
Prostate cancer is, most often, a slow-growing cancer.
For some men, prostate cancer causes no symptoms or long-term issues, so treatment isn’t necessary.
In these cases, doctors may recommend active surveillance. That is, they’ll keep an eye on the development of the tumor using various tools and tests, including:
- Digital rectal exams
- Transrectal ultrasounds
- Prostate biopsies
Men who require treatment for their condition are most often treated with surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, or a combination of these modalities.
Looking For More Survivorship Resources
For more information about cancer survivorship, explore these related items. Please note that these links will take you to other sections of Cancer.Net:
-
ASCO Answers Cancer Survivorship Guide:Get this 44-page booklet that helps people transition into life after treatment. It includes blank treatment summary and survivorship care plan forms. The free booklet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
-
Cancer.Net Patient Education Video:View a short video led by an ASCO expert that provides information about what comes after finishing treatment.
-
Survivorship Resources: Cancer.Net offers an entire area of this website with resources to help survivors, including those in different age groups.
The next section offers Questions to Ask the Health Care Team to help start conversations with your cancer care team. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
This is the end of Cancer.Nets Guide to Prostate Cancer. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Va Disability Rating For Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer Stages: What You Need To Know
There are four prostate cancer stages, which refer to how quickly and how far the cancer has spread.
The stages are based on guidelines set by the American Joint Committee on Cancer .
To determine your prostate cancer stage, your doctor will perform a number of tests, including:
- Digital rectal exam, in which your prostate is felt for abnormalities
- A blood test to measure the amount of PSA that’s circulating in your body
- A biopsy to extract cancerous tissue and grade how likely it will spread based on its appearance compared with normal prostate tissue
- Various imaging tests, such as computerized tomography and magnetic resonance imaging scans
- Bone scans to look for cancerous cells in bone
What Are Prostate Cancer Survival Rates By Stage
Staging evaluation is essential for the planning of treatment for prostate cancer.
- A basic staging evaluation includes the patient examination, blood tests, and the prostate biopsy including ultrasound images of the prostate.
- Further testing and calculations may be performed to best estimate a patient’s prognosis and help the doctor and patient decide upon treatment options.
Prognosis refers to the likelihood that the cancer can be cured by treatment, and what the patient’s life expectancy is likely to be as a consequence of having had a prostate cancer diagnosis.
If a cancer is cured, your life expectancy is what it would have been had you never been diagnosed with prostate cancer. If the cancer cannot be cured due to it recurring in distant locations as metastases, or recurs either locally or in an area no longer able to be treated in a curative manner, then estimates can be made of what is likely to be your survival based again on group statistics for people who have been in the same situation.
Nomograms are charts or computer-based tools that use complex math from analysis of many patients’ treatment results.
The prognosis for prostate cancer varies widely, and depends on many factors, including the age and health of the patient, the stage of the tumor when it was diagnosed, the aggressiveness of the tumor, and the cancer’s responsiveness to treatment, among other factors.
Recommended Reading: What Happens To The Prostate Later In Life
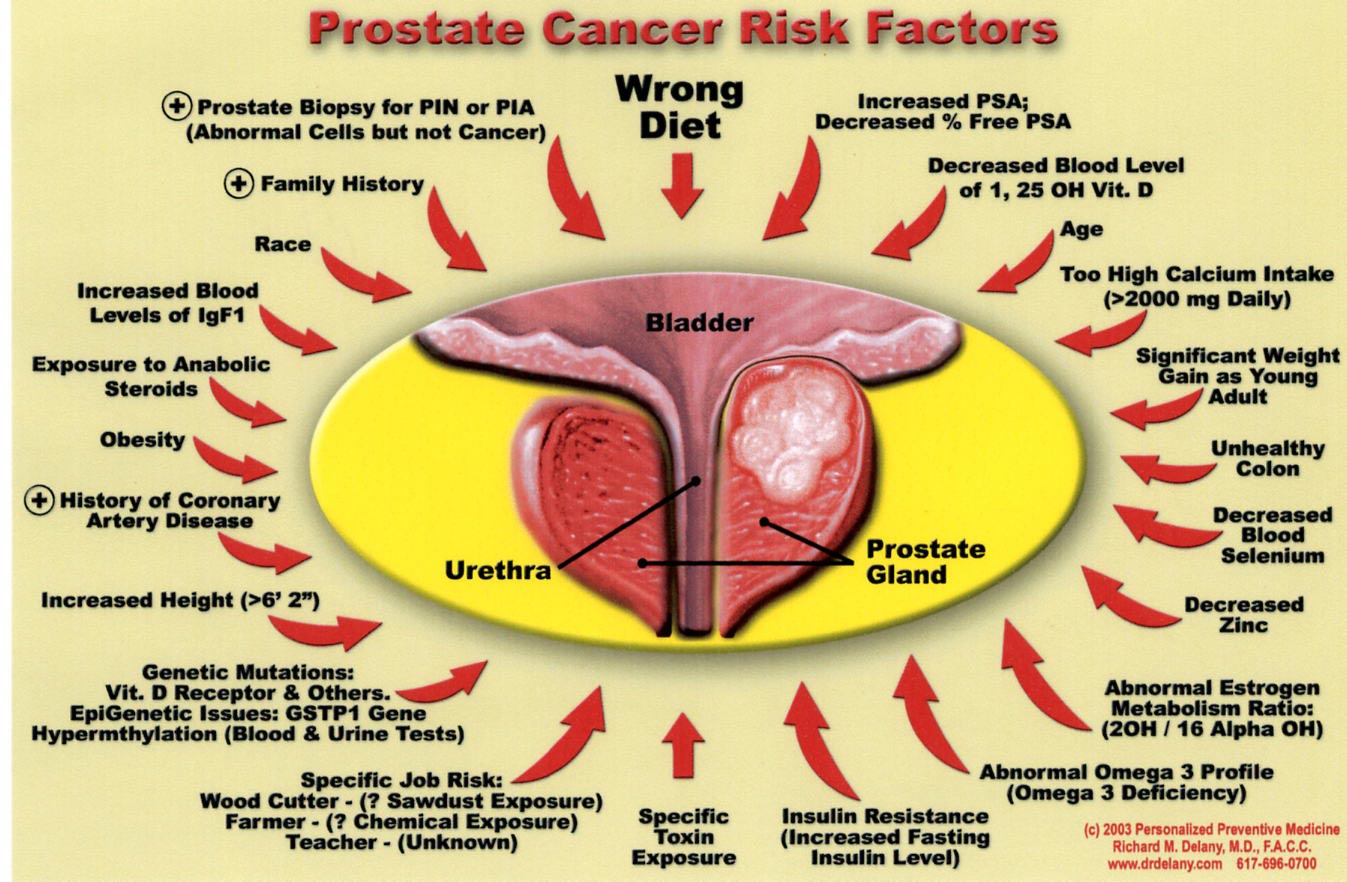
What Causes Prostate Cancer And Am I At Risk
Every man is at risk for prostate cancer as he ages. Although prostate cancer can affect younger men, about 6 out of 10 cases are diagnosed in men over the age of 65. The average age of diagnosis is 66. After non-melanoma skin cancer, prostate is the most common cancer diagnosed in men in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates there will be 248,530 new cases of prostate cancer each year.
Although there are several known risk factors for getting prostate cancer, no one knows exactly why one man gets it and another doesn’t. Some important risk factors for prostate cancer are:
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have prostate cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get prostate cancer?
- What is my Gleason score? What is my Grade Group? What do these numbers mean for me?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the prostate gland?
- What is the best treatment for the stage of prostate cancer I have?
- If I choose active surveillance, what can I expect? What signs of cancer should I look out for?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Is my family at risk for developing prostate cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Prostate cancer is a common cancer that affects males. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and remain in the prostate gland. For a small number, the disease can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. Men with slow-growing prostate cancers may choose active surveillance. With this approach, you can postpone, and sometimes completely forego, treatments. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for you based on your Gleason score and Group Grade.
Also Check: What Are Symptoms Of Prostate Issues
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
What Tests Detect Prostate Cancer Early
Because prostate cancer cant necessarily be detected at home, its a good idea to learn about the tests that provide early detection 2 . Keep in mind that these tests cant decipher whether or not you have prostate cancer and, following the test, your doctor will most likely suggest a prostate biopsy. If youre wondering how to check for prostate cancer at home, your best bet is to leave it to your health care professional.
Also Check: Do Girls Have Prostates
How Can I Prevent Prostate Cancer
The best way to try and prevent prostate cancer is to modify the risk factors for prostate cancer that you have control over. Eat a low-fat diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables and low in animal fats. It is always a good idea to maintain a healthy weight, get plenty of exercise and not to smoke or to quit smoking.
Don’t Miss: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
Data Extraction And Quality Assessment
The information extracted from the studies were as follows: characteristics of study: the authors name, publication year, country, study design , the definition of csPCa patient characteristics: patient number, patient age, biopsy-naïve , location of lesions, PSA levels, prostate volume, prostate-specific antigen density and imaging characteristics: coil, the b values of DWI sequence, magnetic field strength, and the description of the reference standard. When multiple readers provided each result independently, we used the average value because the interobserver agreement of studies included was generally favorable. True and false positive and true and false negative from included studies were extracted to compute sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio , negative likelihood ratio , diagnostic odds ratios and area under the curves .
We applied the revised instrument for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies tool to assess the quality of the included studies by RevMan software . The risks of bias were also scored, such as patient selection and index texts.
You May Like: How To Tell Prostate Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
In most cases, prostate cancer causes no symptoms.
In rare cases, men may experience certain symptoms when they have advanced prostate cancer. However, these symptoms are also present in many men who do not have cancer, so it is best to discuss them with a doctor before jumping to any conclusions. Some of these symptoms can include difficulty emptying the bladder, blood in the urine, and bone pains.
Don’t Miss: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
How Prostate Cancer Develops
However, sometimes something goes wrong within prostate cells, and cancer develops.
In general, cancer is a condition in which a normal cell becomes abnormal and starts to grow and/or reproduce uncontrollably without having the signals or brakes that stop typical cell growth. Prostate cancer occurs when a normal prostate cell begins to grow out of control. In many cases, prostate cancer is a slow-growing cancer that does not spread beyond the prostate gland before the time of diagnosis.
Once prostate cancer forms, it feeds on androgens and uses them as fuel for growth. This is why one of the backbones of treatment for men, especially with advanced prostate cancer, is to lower a mans androgen levels with drugs collectively termed hormone therapy.
Not all prostate cancer cells are alike. Prostate cancers that are composed of very abnormal cells are much more likely to both divide quickly and spread, or metastasize, from the prostate to other regions of the body. Often, prostate cancer spreads first to tissues that are near the prostate, including the seminal vesicles and nearby lymph nodes.
Researchers have identified various biological and genetic subtypes of prostate cancer. Although these subtypes are typically not yet used to guide treatment recommendations, they are the subject of active research funded by the Prostate Cancer Foundation.
Help support PCFs research into causes and treatments of prostate cancer: Donate Today!
Also Check: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
Types Of Imaging Studies
If your doctor suspects your cancer might be spreading, they will likely order more imaging tests. A common imaging workup may include a bone scan and a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. An MRI might be done as well. Some research centers are also using magnetic MRIs or PET scans to further refine the staging of prostate cancer.
Prostate Cancer Doctor Discussion Guide
Get our printable guide for your next doctorâs appointment to help you ask the right questions.
You May Like: Prostate Definition Medical
Possible Side Effects Of Chemotherapy
Chemo drugs attack cells that are dividing quickly, which is why they work against cancer cells. But other cells in the body, such as those in the bone marrow , the lining of the mouth and intestines, and the hair follicles, also divide quickly. These cells can also be affected by chemo, which can lead to side effects.
The side effects of chemo depend on the type and dose of drugs given and how long they are taken. Some common side effects can include:
- Increased chance of infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Fatigue
These side effects usually go away once treatment is finished. There are often ways to lessen these side effects. For example, drugs can be given to help prevent or reduce nausea and vomiting.
Along with the risks above, some side effects are seen more often with certain chemo drugs. For example:
- Docetaxel and cabazitaxel sometimes cause severe allergic reactions. Medicines are given before each treatment to help prevent this. These drugs can also damage nerves , which can cause numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the hands or feet.
- Mitoxantrone can, very rarely, cause leukemia several years later.
- Estramustine carries an increased risk of blood clots.
If you notice any side effects while getting chemo report them to your cancer care team so that they can be treated promptly. In some cases, the doses of the chemo drugs may need to be reduced or treatment may need to be delayed or stopped to prevent the effects from getting worse.
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
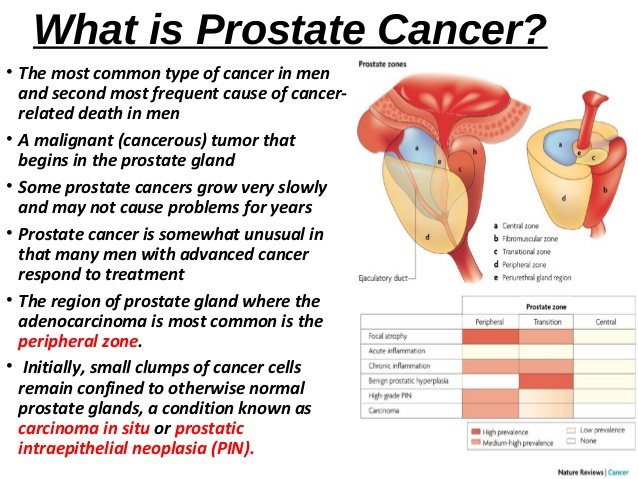
A biopsy is when a small piece of tissue is removed from the prostate and looked at under a microscope.
A biopsy is a procedure that can be used to diagnose prostate cancer. A biopsy is when a small piece of tissue is removed from the prostate and looked at under a microscope to see if there are cancer cells.
A Gleason score is determined when the biopsy tissue is looked at under the microscope. If there is a cancer, the score indicates how likely it is to spread. The score ranges from 2 to 10. The lower the score, the less likely it is that the cancer will spread.
A biopsy is the main tool for diagnosing prostate cancer, but a doctor can use other tools to help make sure the biopsy is made in the right place. For example, doctors may use transrectal ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging to help guide the biopsy. With transrectal ultrasound, a probe the size of a finger is inserted into the rectum and high-energy sound waves are bounced off the prostate to create a picture of the prostate called a sonogram. MRI uses magnets and radio waves to produce images on a computer. MRI does not use any radiation.
Read Also: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Prostate
