Figure 2 Why Understaging May Occur
When the prostate is removed, a pathologist examines slices of the gland for evidence of cancer. A. Under a microscope, the pathologist can distinguish tiny tumors, consisting of clumps of visibly abnormal cells. B. With current imaging technology, it is not yet possible for a pathologist to identify micrometastases individual cancer cells shed from the primary tumor that have gone on to seed adjacent tissue. In this image, for example, cancer cells have already penetrated the capsule and migrated to adjacent tissue, even beyond the margin of tissue removed during surgery.
Individual prostate cancer cells can spread to more remote areas of the body in three ways . Whats more, they can do so without being detected with our current technology, essentially escaping under the radar. So its always possible even if you are diagnosed with early-stage prostate cancer that the cancer has already spread and will manifest in the coming years. How likely is it that an early-stage prostate cancer will become active without treatment? A small study provides some clues .
Followup By Primary Care Physicians
The American Cancer Society has released evidence- and expert-based guidelines for the management of prostate cancer survivors by primary care physicians , a response to the fact that as the number of men surviving prostate cancer has increased, reliance on PCPs for their care has grown as well. The guidelines address promotion of healthy lifestyles, surveillance for disease recurrence, screening for second primary cancers, and evaluation and management of adverse physical and psychosocial effects caused by the disease and its treatment. Recommendations include the following :
Lutetium Lu 177 Vipivotide Tetraxetan
Lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan is indicated for the treatment of men with prostate-specific membrane antigen -positive, metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer who have been treated with androgen receptor pathway inhibition and taxane-based chemotherapy. It is a radioligand therapeutic agent. The active moiety is the radionuclide lutetium-177, which is linked to a moiety that binds to PSMA, a transmembrane protein expressed in prostate cancer, including mCRPC. Upon binding to PSMA-expressing cells, the lutetium-177 delivers beta-minus radiation to the cells, as well as to surrounding cells, inducing DNA damage that can lead to cell death.
Approval was based on the phase 3 VISION trial. Compared with patients receiving standard care , patients who received lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan plus standard care had significantly prolonged imaging-based progression-free survival and overall survival .
Also Check: Does Flomax Reduce Prostate Size
Table 1 Why A Low Psa Does Not Mean You Are Cancer
The Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial included a provision that men randomized to receive placebo undergo a prostate biopsy at the end of the study, even if they had normal PSA levels and digital rectal exams. To their surprise, investigators found that many of these men had prostate cancer in some cases, high-grade prostate cancer.
PSA level 13 *Note: A PSA level over 4.0 ng/ml traditionally triggers a biopsy. Adapted with permission from I.M. Thompson, et al. Prevalence of Prostate Cancer Among Men with a Prostate-Specific Antigen Level 4.0 ng per Milliliter. New England Journal of Medicine, May 27, 2004, Table 2.
This study inadvertently provided evidence not only that prostate cancer occurs more often than once believed, but also that PSA levels may not be a reliable indicator of which cancers are most aggressive. Both findings add weight to the growing consensus that many prostate tumors currently being detected may not need to have been diagnosed or treated in the first place.
Radiation Therapy In Metastatic Disease
In a study of men with newly diagnosed metastatic prostate cancer, treatment with prostate radiation and ADT led to substantially longer survival compared with treatment with ADT alone. In the study, which included 6,382 men, combination therapy yield superior median survival and 5-year overall survival .
In patients with metastatic prostate cancer, radiation is also applied for palliative purposes. It is used in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer with painful bone metastases, in patients at risk for fracture, and in patients with impending spinal cord compression.
A meta-analysis of the use of radioisotopes to relieve pain from bone metastases found that over 1-6 months, pain may be reduced without an increase in analgesic use however, severe effects such as leukocytopenia and thrombocytopenia frequently surface.
Radium-223 dichloride , formerly alpharadin, is an alpha particleemitting radioactive therapeutic agent that was approved by the FDA in 2013 for use in men with CRPC, symptomatic bone metastases, and no known visceral metastatic disease. Approval was based on the multinational ALSYMPCA trial , which is the first randomized phase III trial to demonstrate improved survival of CRPC with a bone-seeking radioisotope.
Recommended Reading: What Age Should You Get Prostate Checked
Disease Progression And Mortality In Patients With Gleason Score 910 Prostate Cancer
- JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association
Youve saved your first item
You can find your saved items on your dashboard, in the saved tab.
Youve recommended your first item
Your recommendations help us improve our content suggestions for you and other PracticeUpdate members.
Youve subscribed to your first topic alert
What does that mean?
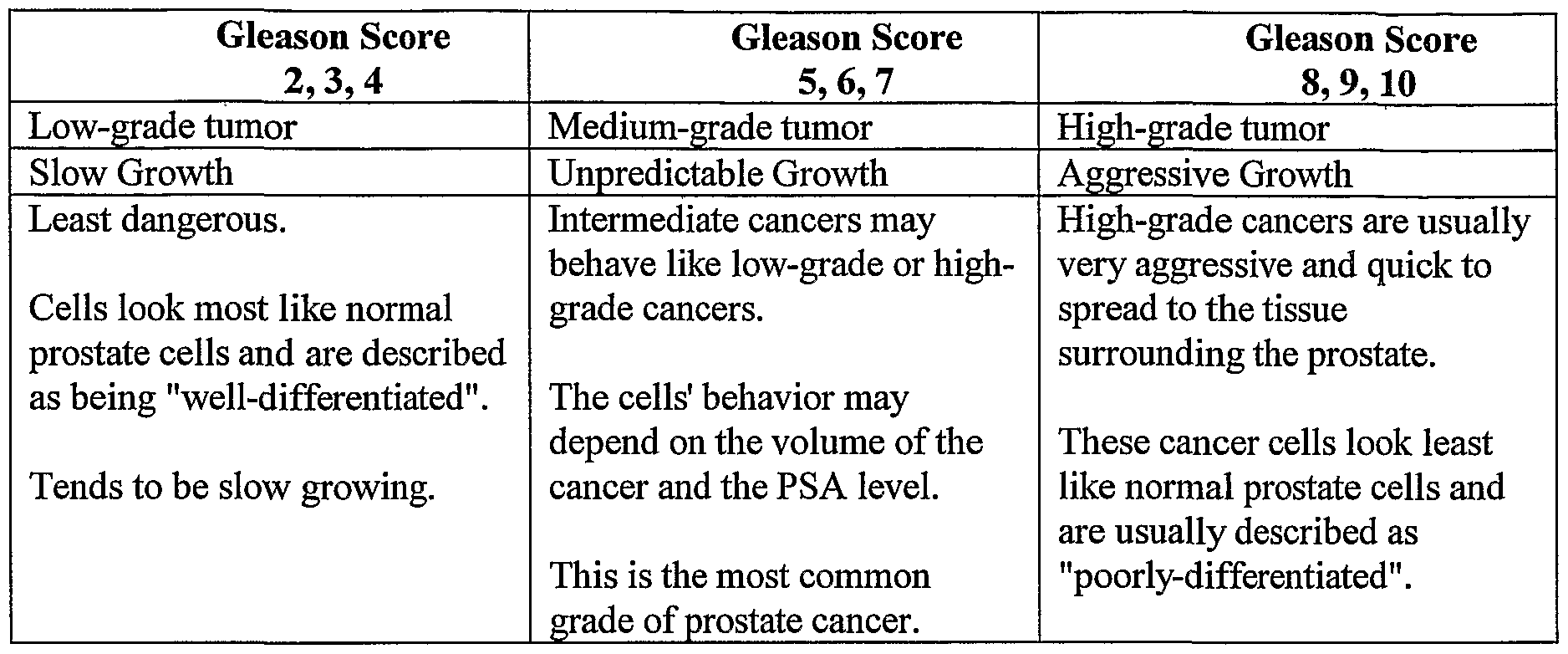
What Is A Gleason Score
If you have prostate cancer, your Gleason score is one factor healthcare providers consider to develop your treatment plan.
Your score reflects what providers learned about your cancer after examining tissue samples from your prostate cancer biopsy. They looked for patterns of normal and abnormal cells, noting where your cells look more like cancerous cells and where they look more like healthy cells.
Then they graded each piece of the pattern on a 3 to 5 scale. Pattern pieces with cancer cells that look like healthy cells were graded low. Pieces with cancer cells that don’t look like healthy cells get high grades.
Providers add those scores to set an overall Gleason score between 6 and 10. They might refine their analysis by classifying your cells by group, with Gleason scores listed in grade groups 1 to 5.
Recommended Reading: Prostate Bed Radiation Side Effects
Use In Men Who Might Have Prostate Cancer
The PSA blood test is used mainly to screen for prostate cancer in men without symptoms. Its also one of the first tests done in men who have symptoms that might be caused by prostate cancer.
PSA in the blood is measured in units called nanograms per milliliter . The chance of having prostate cancer goes up as the PSA level goes up, but there is no set cutoff point that can tell for sure if a man does or doesnt have prostate cancer. Many doctors use a PSA cutoff point of 4 ng/mL or higher when deciding if a man might need further testing, while others might recommend it starting at a lower level, such as 2.5 or 3.
- Most men without prostate cancer have PSA levels under 4 ng/mL of blood. Still, a level below 4 is not a guarantee that a man doesnt have cancer.
- Men with a PSA level between 4 and 10 have about a 1 in 4 chance of having prostate cancer.
- If the PSA is more than 10, the chance of having prostate cancer is over 50%.
If your PSA level is high, you might need further tests to look for prostate cancer.
To learn more about how the PSA test is used to look for cancer, including factors that can affect PSA levels, special types of PSA tests, and what the next steps might be if you have an abnormal PSA level, see Screening Tests for Prostate Cancer.
Positron Emission Tomography Scan
A PET scan is similar to a bone scan, in that a slightly radioactive substance is injected into the blood, which can then be detected with a special camera. But PET scans use different tracers that collect mainly in cancer cells. The most common tracer for standard PET scans is FDG, which is a type of sugar. Unfortunately, this type of PET scan isnt very useful in finding prostate cancer cells in the body.
However, newer tracers, such as fluciclovine F18, sodium fluoride F18, and choline C11, have been found to be better at detecting prostate cancer cells.
Other newer tracers, such as Ga 68 PSMA-11, 18F-DCFPyl , and Ga 68 gozetotide , attach to prostate-specific membrane antigen , a protein that is often found in large amounts on prostate cancer cells. Tests using these types of tracers are sometimes referred to as PSMA PET scans.
These newer types of PET scans are most often used if its not clear if prostate cancer has spread. For example, one of these tests might be done if the results of a bone scan arent clear, or if a man has a rising PSA level after initial treatment but its not clear where the cancer is in the body. PSMA PET scans can also be used to help determine if the cancer can be treated with a radiopharmaceutical that targets PSMA.
Doctors are still learning about the best ways to use these newer types of PET scans, and some of them might not be available yet in all imaging centers.
Don’t Miss: Is Ejaculation Healthy For The Prostate
How Prostate Cancer Is Treated
In cancer care, different types of doctorsincluding medical oncologists, surgeons, and radiation oncologistsoften work together to create an overall treatment plan that may combine different types of treatments to treat the cancer. This is called a multidisciplinary team. Cancer care teams include a variety of other health care professionals, such as palliative care experts, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, oncology nurses, social workers, pharmacists, counselors, dietitians, physical therapists, and others.
The common types of treatments used for prostate cancer are described below. Your care plan may also include treatment for symptoms and side effects, an important part of cancer care.
Treatment options and recommendations depend on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, possible side effects, and the patients preferences and overall health.
Cancer treatment can affect older adults in different ways. More information on the specific effects of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy on older patients can be found another section of this website.
Because most prostate cancers are found in the early stages when they are growing slowly, you usually do not have to rush to make treatment decisions. During this time, it is important to talk with your doctor about the risks and benefits of all your treatment options and when treatment should begin. This discussion should also address the current state of the cancer:
What Is A Normal Gleason Score For Prostate Cancer
Your Gleason score doesn’t rank potential ranges like ranges set for elevated PSA tests. Instead, providers break Gleason scores into three categories:
- Gleason 6 or lower: The cells look similar to healthy cells, which is called well differentiated.
- Gleason 7: The cells look somewhat similar to healthy cells, which is called moderately differentiated.
- Gleason 8, 9 or 10: The cells look very different from healthy cells, which is called poorly differentiated or undifferentiated.
What are grade groups?
Healthcare providers established grade groups to clarify the Gleason score system. Those grade groups are:
- Grade Group 1 = Gleason 6 .
- Grade Group 2 = Gleason 3+4=7.
- Grade Group 3 = Gleason 4+3=7.
- Grade Group 4 = Gleason 8.
- Grade Group 5 = Gleason 9-10.
Recommended Reading: How Far Inside Is The Prostate
When Is Brachytherapy Alone The Right Choice
For some patients with disease that is confined to the prostate and not too aggressive , brachytherapy alone is a good option. It is also convenient for the patient as it is done in an outpatient setting and most people can get back to work within a few days.
But brachytherapy is not right for everyone. For some patients with less-aggressive disease, a watch-and-wait approach would be preferred. At MSK, our philosophy is that when the disease is caught very early, it is very appropriate to do active surveillance and hold off on treatment.
This philosophy applies to patients with a low PSA level, or nonaggressive disease as reflected by a Gleason score of 6 with evidence of cancer in only a few of the biopsy samples and no evidence from the MRI of a significant amount of disease. There are also very select patients with Gleason 7 disease who may be candidates for active surveillance.
Natural History Of The Disease
Several studies reported in the literature provide insights into the natural history of high-grade prostate cancer in a 70-year-old man. Albertsen and associates6 examined the survival of men 6575 years of age who had clinically localized prostate cancer, comparing those treated with hormonal therapy with aged-matched, untreated controls. The survival expectancy for men with Gleason 810 adenocarcinoma of the prostate treated with hormonal therapy was 68 years less than that for controls. If one assumes that hormonal therapy does not extend survival, then the difference in survival between the hormonally-treated group versus the control group represents the impact of high-grade, clinically localized prostate cancer on survival.
You May Like: How Long Does A Prostate Mri Scan Take
What Tests Check For Prostate Cancer
Common tests to check for prostate cancer include:
- Digital rectal exam: Your doctor inserts a finger into your rectum and touches your prostate gland. The doctor feels the shape of the prostate gland and checks for any hard spots.
- PSA blood test: This blood test tells how much PSA is in your blood. Many men with prostate cancer have PSA levels that are higher than normal or that have gotten higher over time.
- A high PSA level does not always mean a man has prostate cancer. As men get older, their prostate gland may grow larger over time. This growth, and other health conditions, can cause a high PSA level in men who do not have prostate cancer.
If the test results are not normal, your doctor may recommend more tests, such as a biopsy. During a biopsy, the doctor uses a needle to take out a tiny piece or pieces of the prostate gland. An ultrasound probe may be used to guide the needle. Another doctor called a pathologist looks at the tissue under a microscope to check for cancer cells.
Note
Radiation As Adjuvant Or Salvage Therapy After Surgery
Several randomized trials have evaluated the use of adjuvant radiation therapy to the prostatic bed following surgery for patients at high risk of recurrence . Those include EORTC 22911, SWOG 8794, ARO 96-02/AUO AP 09/95, and FinnProstataX, as well as the ongoing RAVES, GETUG-AFU 17, and RADICALS-RT studies. Recent research has further highlighted the role of early salvage radiation therapy with concomitant ADT for those with biochemical recurrence after prostatectomy, to avoid overtreatment associated with adjuvant radiotherapy. This is reflected in the current AUA/ASTRO guidelines.
You May Like: What Causes Enlarged Prostate At Young Age
When Further Treatment Is Needed
While prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment have improved significantly in recent years, the cancer can still recur. Thats why it is essential that you and your doctor continue to monitor your PSA on a quarterly basis for some period of time, no matter how successful your treatment seems to be. Patients usually can consider a number of treatment options to treat or control recurrent cancer. Choosing among them requires a new decision-making process.
Recommended Reading: Vaccine Treatment For Prostate Cancer
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of prostate cancer is 90%, it means that men who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as men who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Don’t Miss: How To Find My Prostate
What Are The Benefits Of A Prostate Mri
The MRI scan can help find a cancer of the prostate gland, especially if you have elevated or rising PSA.
If a cancer has already been found, the MRI images can show whether it has spread outside the prostate gland or not. This can have a very important impact on whether or not you have treatment, and if so, which type of treatment you receive.
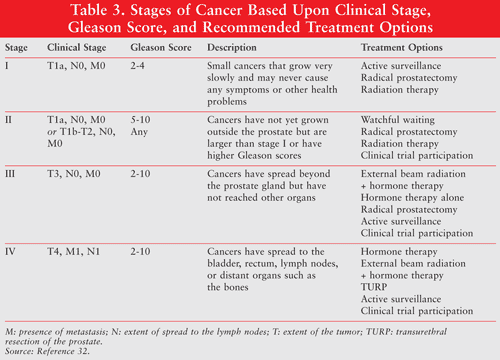
What Is A Grade Group
In 2014, the International Society of Urological Pathology released supplementary guidance and a revised prostate cancer grading system, called the Grade Groups.
The Grade Group system is simpler, with just five grades, 1 through 5.
*Risk Groups are defined by the Grade Group of the cancer and other measures, including PSA, clinical tumor stage , PSA density, and number of positive biopsy cores.
Many hospitals report both the Gleason score and the Grade Group, but there may be hospitals that still report only the old Gleason system.
You May Like: How To Tell If Prostate Is Enlarged
What Is The Normal Gleason Score
Theoretically, Gleason scores range from 2-10. However, since Dr. Gleasons original classification, pathologists almost never assign scores 2-5, and Gleason scores assigned will range from 6 to 10, with 6 being the lowest grade cancer.
Otherwise, is a Gleason score of 9 a death sentence?
Not all men with Gleason 8-10 disease are going to do badly after treatment. There is a perception among a lot of patients especially when they get diagnosed that having a high Gleason score of 8, 9, or 10 is essentially a death sentence, regardless of how they get treated. This is not actually the case at all.
Although, is Gleason score the same as PSA? A Gleason score of 8 or higher, accompanied by a PSA level of higher than 20 ng/ml and a more advanced tumor stage, signifies a high risk of advancing cancer. In high-risk cases, the prostate cancer tissue looks very different from normal tissue.
So too, what is a Gleason score of 7 mean?
A Gleason score of 7 is a medium-grade cancer, and a score of 8, 9, or 10 is a high-grade cancer. A lower-grade cancer grows more slowly and is less likely to spread than a high-grade cancer.
What if prostate biopsy is positive?
If prostate cancer is found on a biopsy, it will be assigned a grade. The grade of the cancer is based on how abnormal the cancer looks under the microscope. Higher grade cancers look more abnormal, and are more likely to grow and spread quickly.
28 Related Questions Answered
