What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. Advanced prostate cancer occurs when it has spread, or metastasized, from the prostate to other areas of the body.
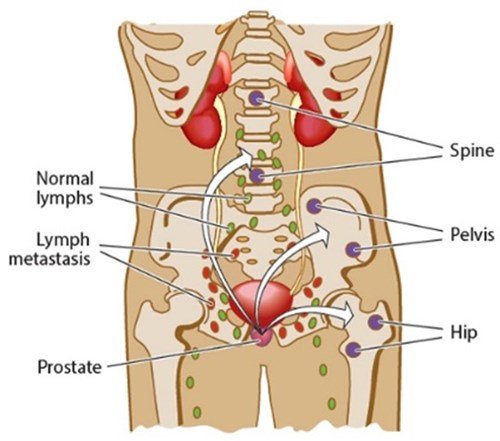
Cancer spreads when cells break off from the original tumor and invade nearby tissue. This is called localized metastasis. Cancer can spread directly into nearby tissues or through the lymphatic system to distant parts of the body. When this happens, its called metastatic disease or prostate cancer with metastasis to a certain body part or organ system.
New tumors can grow in any organ, but prostate cancer is most likely to spread to the:
Stage 4 prostate cancer occurs when the prostate cancer has already spread to distant organs or tissues at the time of diagnosis. Most of the time, doctors diagnose prostate cancer at an earlier stage. Its generally a slow-growing cancer, but it can spread or it can come back, or recur, after treatment.
When cancer is confined to the prostate, many men have no symptoms. Others have trouble urinating or notice blood in their urine.
Metastatic cancer can cause generalized symptoms such as:
Other symptoms of advanced prostate cancer depend on where it has spread and how big the tumors are:
What Is The Outlook
No cure is available for stage 4 prostate cancer. Your healthcare team will work with you to help control the cancer for as long as possible while maintaining a good quality of life.
Your outlook will depend on how fast the cancer is spreading and how well you respond to therapies.
With treatment, you can live for many years with metastatic prostate cancer.
Stages Of Prostate Cancer
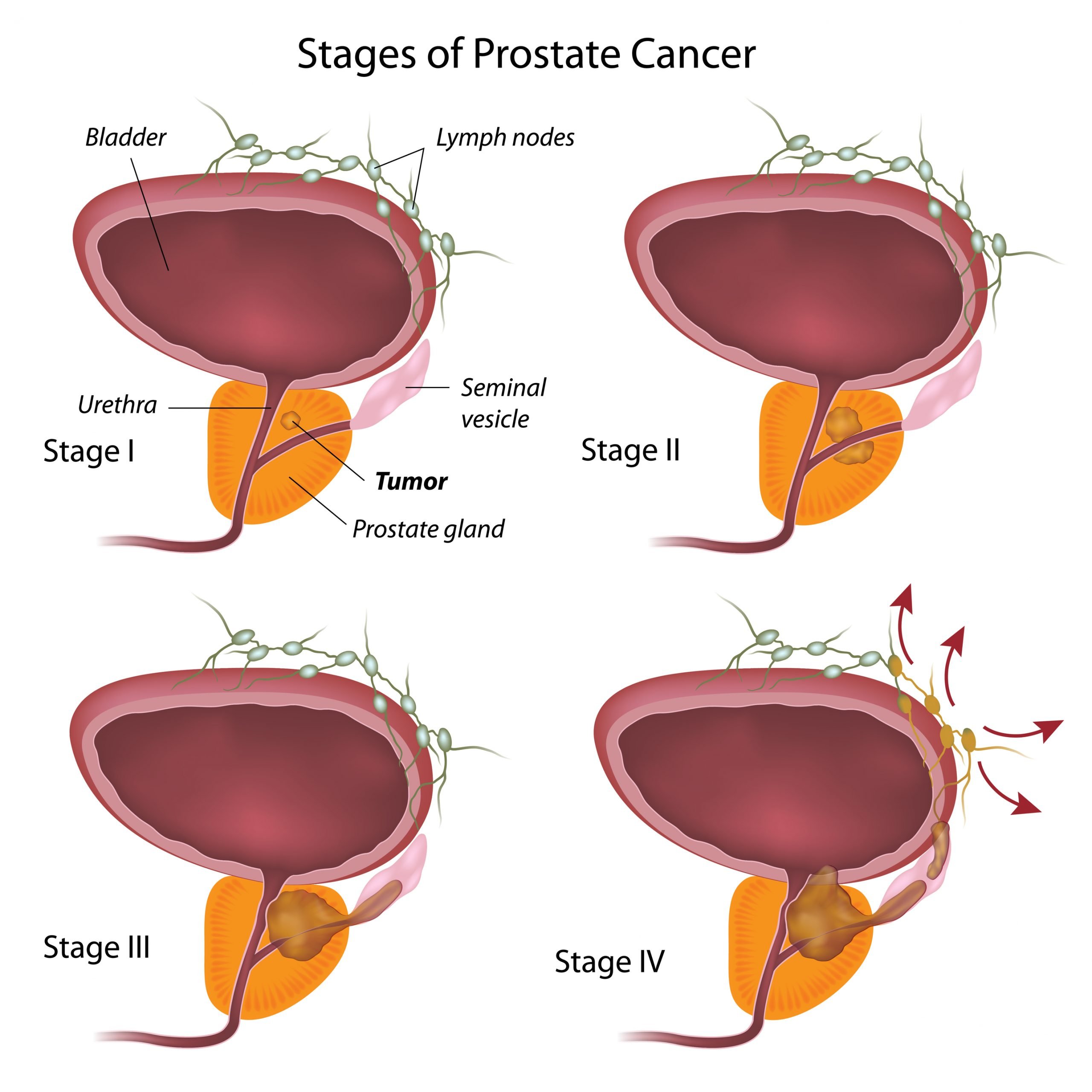
In order to determine the stage of a patients prostate cancer, most doctors start by using the TNM staging system, which helps describe different aspects of the cancers growth.
- T the T category measures the size and extent of the Tumor
- N the N category measures whether and how far the cancer has spread to the Lymph Nodes
- M the M category whether the cancer has spread to other organs in the body (a process called Metastasis
The score for each of these categories is determined based on a pre-determined set of criteria. Your doctor cannot feel or see the tumor with a score of T1. A score of T3 means that the tumor has begun to grow outside of the prostate.
After calculating the TNM categories, doctors will combine the TNM score with the patients Gleason score and PSA levels assigning of a specific stage to the patients cancer.
Prostate cancer prognosis and survival rates can help give patients an idea of their chances of surviving the disease based on the stage and time of diagnosis. While some patients may find this information helpful, others may not want to know.
Also Check: How Many Prostate Glands Do Males Have
Survival Of Prostate Cancer
Survival depends on many factors. No one can tell you exactly how long you will live.
Below are general statistics based on large groups of people. Remember, they cant tell you what will happen in your individual case.
Survival for prostate cancer is generally good, particularly if you are diagnosed early.
Survival By Disease Progression
The extent prostate cancer has progressed can influence survival rates.
Prostate-specific antigen is a protein produced by cells of the prostate gland by normal and malignant cells. In men with prostate cancer, blood levels of PSA are often elevated.
Doctors can use PSA as a marker to better understand the progression of prostate cancer and the resulting prognosis.
One way doctors assess the progression of the disease is through PSA doubling time. This refers to the number of months it takes for PSA to double.
One study suggests a short doubling time means a poorer prognosis for patients with stage IV prostate cancer. Median survival was 16.5 months for those with a PSA doubling time lower than 45 days compared with 26 months for patients with a longer PSA doubling time.
Whether or not the cancer has metastasized and spread to other areas of the body outside the prostate can also influence survival. In distant or stage IV prostate cancer, when cancer has spread from the prostate to other organs like the liver or lungs, the five-year survival rate is 31% compared with localized cancer, which has a five-year survival rate of nearly 100%.
Don’t Miss: Can The Prostate Be Removed
Stage Iv Prostate Cancer Prognosis
Prostate cancers detected at the distant stage have an average five-year survival rate of 28 percent, which is much lower than local and regional cancers of the prostate. This average survival rate represents stage IV prostate cancers that have metastasized beyond nearby areas to lymph nodes, organs or bones in other parts of the body.
Survival By Disease Recurrence
If a man develops an elevated PSA level after cancer surgery, then the disease is viewed as recurrent.
The number of lymph nodes at the time of prostatectomy can influence the risk of recurrence. One study suggests the removal of a large number of nodes is associated with an improvement in odds of recurrence, but this doesnt appear to impact overall survival.
But disease recurrence doesnt always influence survival times. If a recurrence does occur, the 15-year survival rate at the time of diagnosis may be as high as 94% in those with low-risk recurrence.
The main factors influencing survival rates are:
- The Gleason score
- The PSA doubling time
- Whether the recurrence occurred within three years or after three years
A recurrence that occurs within three years reduces survival rates by anywhere from 15 to 20%and even more, if the doubling time is short.
Also Check: Is Coffee Bad For Your Prostate
Recommended Reading: Can Prostate Cancer Come Back After Radiation
Peer Review And Document Approval
An integral part of the guideline development process at the AUA is external peer review. The AUA conducted a thorough peer review process to ensure that the document was reviewed by experts in the diagnosis and management of Advanced Prostate Cancer. In addition to reviewers from the AUA PGC, Science and Quality Council , and Board of Directors , the document was reviewed by representatives from ASTRO, SUO, and ASCO as well as external content experts. Additionally, a call for reviewers was placed on the AUA website from December 2-16, 2019 to allow any additional interested parties to request a copy of the document for review. The guideline was also sent to the Urology Care Foundation and representation from prostate cancer advocacy to open the document further to the patient perspective. The draft guideline document was distributed to 96 peer reviewers. All peer review comments were blinded and sent to the Panel for review. In total, 44 reviewers provided comments, including 34 external reviewers. At the end of the peer review process, a total of 522 comments were received. Following comment discussion, the Panel revised the draft as needed. Once finalized, the guideline was submitted for approval to the AUA PGC, SQC, and BOD as well as the governing bodies of ASTRO and SUO for final approval.
What Is My Outlook
If youre diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer, you may want to know how well your treatment is likely to control your cancer and for how long it will control it. This is sometimes called your outlook or prognosis. But not all men will want to know this.
While it isnt possible to cure advanced prostate cancer, treatments can help keep it under control, often for several years. Treatments will also help manage any symptoms, such as pain.
No one can tell you exactly what your outlook will be, as it will depend on many things such as where the cancer has spread to, how quickly it has spread, and how well you respond to treatment. Some men may not respond well to one treatment, but may respond better to another. And when your first treatment stops working, there are other treatments available to help keep the cancer under control for longer. Speak to your doctor about your own situation and any questions or concerns you have.
Read Also: Vitamin C Prostate Cancer Treatment
Intermittent Versus Continuous Therapy
The common complications of androgen deprivation therapy include sexual dysfunction, mood disturbance, change in body composition and osteoporosis.2,3 In view of these adverse effects intermittent dosing has been considered. This is a period of androgen deprivation therapy followed by a break until disease progression, if a good response was attained. The optimal duration of androgen deprivation therapy is fairly arbitrary as the studies have looked into various periods ranging from three months to three years.
In patients with PSA relapse only , intermittent therapy has been shown to be non-inferior to continuous dosing. There was also a better quality of life with intermittent dosing.4
In patients with objective metastases, intermittent androgen deprivation therapy had numerically worse outcomes than continuous treatment, but the study was statistically inconclusive. There was less sexual dysfunction and better mental health in the intermittent group, but this effect disappeared by 15 months when most people were back on continuous treatment.5 If short-term quality of life is important, even at the risk of possible worse survival, intermittent therapy is a reasonable approach.
Staging And Grading Of Advanced Prostate Cancer
The stage of a cancer describes its size and how far it has spread, based on your test results. Doctors often use the TNM staging system or a number staging system.
A doctor decides the grade by how the cancer cells look under the microscope. This gives an idea of how quickly the cancer might grow or spread. You and your doctors can then talk about the best treatment choices for you.
Recommended Reading: Can Enlarged Prostate Cause Back Pain
Managing Bone Pain And Weakness
Symptoms like nausea, hot flashes, and pain can usually be relieved with medication. Some people find that complimentary treatments like acupuncture or massage help manage side effects.
Your doctor may also recommend orthopedic surgery to stabilize your bones, relieve pain, and help prevent bone fractures.
What Are Next Steps
Bone metastasis have a profound effect on the long-term outlook for prostate cancer. But its important to remember that the numbers are only statistics.
The good news is that life expectancy for advanced prostate cancer continues to increase. New treatments and therapies offer both longer life and better quality of life. Speak to your doctor about your treatment options and long-term outlook.
Everyones cancer experience is different. You may find support through sharing your treatment plan with friends and family. Or you can turn to local community groups or online forums like Male Care for advice and reassurance.
Read Also: Can Men Have Sex After Prostate Cancer
Biochemical Recurrence Without Metastatic Disease After Exhaustion Of Local Treatment Options
Prognosis
4. Clinicians should inform patients with PSA recurrence after exhaustion of local therapy regarding the risk of developing metastatic disease and follow such patients with serial PSA measurements and clinical evaluation. Clinicians may consider radiographic assessments based on overall PSA and PSA kinetics.
5. In patients with PSA recurrence after exhaustion of local therapy who are at higher risk for the development of metastases , clinicians should perform periodic staging evaluations consisting of cross-sectional imaging and technetium bone scan.
6. Clinicians may utilize novel PET-CT scans in patients with PSA recurrence after failure of local therapy as an alternative to conventional imaging or in the setting of negative conventional imaging.
Treatment
7. For patients with a rising PSA after failure of local therapy and no demonstrated metastatic disease by conventional imaging, clinicians should offer observation or clinical trial enrollment.
8. ADT should not be routinely initiated in this population . However, if ADT is initiated in the absence of metastatic disease, intermittent ADT may be offered in lieu of continuous ADT.
What Are Prostate Cancer Survival Rates By Stage
Staging evaluation is essential for the planning of treatment for prostate cancer.
- A basic staging evaluation includes the patient examination, blood tests, and the prostate biopsy including ultrasound images of the prostate.
- Further testing and calculations may be performed to best estimate a patients prognosis and help the doctor and patient decide upon treatment options.
Prognosis refers to the likelihood that cancer can be cured by treatment, and what the patients life expectancy is likely to be as a consequence of having had a prostate cancer diagnosis.
If cancer is cured, your life expectancy is what it would have been had you never been diagnosed with prostate cancer. If cancer cannot be cured due to it recurring in distant locations as metastases, or recurs either locally or in an area no longer able to be treated in a curative manner, then estimates can be made of what is likely to be your survival-based again on group statistics for people who have been in the same situation.
Nomograms are charts or computer-based tools that use complex math from the analysis of many patients treatment results.
The prognosis for prostate cancer varies widely and depends on many factors, including the age and health of the patient, the stage of the tumor when it was diagnosed, the aggressiveness of the tumor, and cancers responsiveness to treatment, among other factors.
The 5 and 10-year survival rate of prostate cancer chart
| Stage and 5-Year Survival |
|---|
Read Also: What Does Your Prostate Do
Symptoms Of Advanced Prostate Cancer
If you are worried about prostate cancer, we have more information about the signs and symptoms.
Symptoms of prostate cancer may not develop for many years. The symptoms of advanced prostate cancer may be caused by an enlarged prostate. Or symptoms may be a sign of secondary cancer, where the cancer has spread to another part of the body.
See also
Improvements In Life Expectancy
A decade ago, a man with metastatic prostate cancer would typically have a life expectancy of two to three years. Today, life expectancy for men with the same advanced disease is likely to be five to six years. In the UK the survival rate for men with stage 4 prostate cancer is approximately 50%, meaning that 50 out of every 100 men will survive their cancer for 5 years or more after they are diagnosed with stage 4 prostate cancer*. There is now a much broader range of chemotherapy drugs available for men with advanced disease with greater efficacy . We also have better treatments to control the symptoms of advanced prostate cancer, such as pain from metastases. In this section, we consider in more detail the different treatments that are available and evidence for their effectiveness.
Read Also: What Happens In A Prostate Exam
When Is The Right Time To Use Hospice Care
Many people believe that hospice care is only appropriate in the last days or weeks of life. Yet Medicare states that it can be used as much as 6 months before death is anticipated. And those who have lost loved ones say that they wish they had called in hospice care sooner.
Research has shown that patients and families who use hospice services report a higher quality of life than those who dont. Hospice care offers many helpful services, including medical care, counseling, and respite care. People usually qualify for hospice when their doctor signs a statement saying that patients with their type and stage of disease, on average, arent likely to survive beyond 6 months. More information about hospice can be found below in the Related Resources section of this fact sheet.
Determination Of Evidence Strength
Based on assessments of the domains described above, the methodology team graded the strength of evidence for each intervention as high, moderate, low, or very low. Randomized controlled trials of interventions start as high strength of evidence and are graded down based on the presence and severity of shortcomings in each domain. A high grade indicates high confidence that the evidence reflects the true effect and that further research is very unlikely to change confidence in the estimate of effect. A moderate grade indicates moderate confidence that the evidence reflects the true effect and further research may change the estimate. A low grade indicates low confidence that the evidence reflects the true effect and further research is likely to change the confidence in the estimate of effect and could increase the confidence in the estimate. A very low grade indicates evidence either is unavailable or is too limited to permit any conclusion due to extreme study limitations, inconsistency, imprecision, or reporting bias.
The AUA employs a three-tiered strength of evidence system to underpin evidence-based guideline statements. In short, high certainty by GRADE translates to AUA A-category strength of evidence, moderate to B, and both low and very low to C.
| Table 1: Strength of Evidence Definitions | |
|---|---|
| AUA Strength of Evidence Category | GRADE Certainty Rating |
Also Check: Does Enlarged Prostate Cause High Psa Levels
What Is Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer is most often used to describe cancers that cannot be cured. This means cancers that wont totally go away and stay away completely with treatment. However, some types of advanced cancer can be controlled over a long period of time and are thought of as an ongoing illness.
Even if advanced cancer cant be cured, treatment can sometimes:
- Shrink the cancer
- Help relieve symptoms
- Help you live longer
For some people, the cancer may already be advanced when they first learn they have the disease. For others, the cancer may not become advanced until years after it was first diagnosed.
Advanced cancers can be locally advanced or metastatic.
Locally advanced means that cancer has grown outside the body part it started in but has not yet spread to other parts of the body. For example, some cancers that start in the brain may be considered advanced because of their large size or closeness to important organs or blood vessels. This can make them life-threatening even though they havent spread to other parts of the body. But other locally advanced cancers, such as some prostate cancers, may be cured.
Metastatic cancers have spread from where they started to other parts of the body. Cancers that have spread are often thought of as advanced when they cant be cured or controlled with treatment. Not all metastatic cancers are advanced cancers. Some cancers, such as testicular cancer, can spread to other parts of the body and still be very curable.
