How Common Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
BPH is the most common prostate problem in men. Almost all men will develop some enlargement of the prostate as they grow older. By age 60, 50% of men will have some signs of BPH; by age 85, 90% of men will have signs of the condition. About half of these men will develop symptoms that need to be treated.
Enlarged Prostate Signs And Symptoms
The prostate is located right underneath the bladder, and surrounds part of the urethra. There are usually no symptoms at the start, even after the prostate has started to enlarge. The first sign of benign prostate hypertrophy is usually problems with urinating. This is because the enlarged prostate is squeezing and narrowing the urethra and may push against the bladder and bladder muscles. This means that men might feel the need to urinate even though their bladder isnt at all full. The constant pressure can also weaken the bladder muscles. As a result, the bladder can no longer empty itself completely. The pressure on the urethra may prevent urine from flowing out normally, too.
In some men, the symptoms are mild and dont need treatment. In others, they can be very troublesome.
The symptoms of benign prostate hypertrophy can include:
- difficulty starting to pee
- dribbling of urine at the end of peeing
- bladder infections
Occasionally, benign prostate hypertrophy interferes with your ability to have sex, causing impotence or painful orgasms.
Leaking urine can happen when you feel a sudden need to pee and cant stop some pee leaking out before you get to a toilet. This is called urge incontinence.
Leaking urine can also happen when you strain, for example when you cough, sneeze or lift a heavy object. This is stress incontinence.
The most common form of leaking is when a small amount of urine dribbles into your underwear after peeing.
Signs of enlarged prostate:
Various Treatments For Enlarged Prostate
Before opting for treatment, your doctor will do a few tests to see if the prostate enlargement is severe. If your condition isnt good, the doctor will recommend the following treatments. Along with the disease, the doctor will consider your prostate size, age, health, and if you suffer from any other medical conditions.
- Alpha-Blockers for BPH.;The doctor will recommend this to loosen the bladder neck muscles and its fiber in the prostate. When the power is relaxed, it is easier to pee, and there will be an increase in urination. You will not pee frequently. It is effective after two days of taking the alpha-blocker. Some of the alpha-blockers are Hytrin, Uroxatral, Flomax, Rapaflo, and Cardura.
- 5- Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors for BPH.;It is one of the ways on;how to shrink the prostate.;It blocks hormones that grow the prostate glands, thus reducing the prostate size. There are two types of 5- alpha-reductase inhibitors, namely Avodart and Proscar. These inhibitors are effective after three to six months.
- TUNA Treatment. TUNA is a short form of transurethral needle ablation and is one of the trusted;prostate enlargement home remedies. This treatment procedure uses two needles, which carry high-frequency radio waves that inflame a particular region in the prostate. The treatment allows men to have good urine flow and decreases the BPH symptoms. You can do the treatment at home; the doctor will use an anesthetic to prevent burning sensation.
Read Also: Does Cialis Shrink The Prostate
How Is Benign Prostate Enlargement Diagnosed
If your GP suspects that you have an enlarged prostate, youll be asked to complete a questionnaire to assess your symptoms.
Each question has five possible answers that carry a score, and your overall score indicates the severity of your symptoms.
Your GP will also want to rule out other conditions that cause similar symptoms to prostate enlargement.;
You may have a number of standard tests, such as urine tests, plus some more specific tests, such as a;blood test that measures PSA.
You May Like: Does Cialis Shrink The Prostate
Medications For Enlarged Prostate

There are two main classes of pharmaceuticals that work to alleviate enlarged prostate symptoms: alpha blockers and alpha reductase inhibitors
-
Alpha Blockers. Alpha blockers relax the smooth muscle around the bladder neck and within the urethra.
-
Inhibitors. Inhibitors stop the conversion of the male hormone testosterone to DHT to reduce the prostate’s size, eliminating blockage.
Dont be surprised if your physician prescribes a combination of the two medications, as they have been shown to work more effectively together than alone. The downside is that combination therapy may increase the likelihood of experiencing side effects from the medications. Be sure to work with your doctor to assess the benefits and costs before starting on combination therapy.
Don’t Miss: Prostatitis Symptoms Mayo
When To Contact A Medical Professional
- Less urine than usual
- Back, side, or abdominal pain
- Blood or pus in your urine
Also call if:
- Your bladder does not feel completely empty after you urinate.
- You take medicines that may cause urinary problems, such as diuretics, antihistamines, antidepressants, or sedatives. DO NOT stop or change your medicines without talking to your provider.
- You have tried self-care steps for 2 months and symptoms have not improved.
What Are Additional Tests For Detecting Prostate Problems
If the DRE or the PSA blood test indicates a problem may exist, the health care provider may order additional tests, including urinalysis, urodynamic tests, cystoscopy, abdominal ultrasound, transrectal ultrasound with prostate biopsy, and imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging or computerized tomography scan.
Recommended Reading: Swollen Prostate Constipation
Tests Used To Check The Prostate
This first step lets your doctor hear and understand the “story” of your prostate concerns. You’ll be asked whether you have symptoms, how long you’ve had them, and how much they affect your lifestyle. Your personal medical history also includes any risk factors, pain, fever, or trouble passing urine. You may be asked to give a urine sample for testing.
Diagnosis And Management Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
JONATHAN L. EDWARDS, MD, Barberton Citizens’ Hospital, Barberton, Ohio
Am Fam Physician.;2008;May;15;77:1403-1410.
;Patient information: See related handout on benign prostatic hyperplasia, written by the author of this article.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a common condition in older men. Histologically, it is characterized by the presence of discrete nodules in the periurethral zone of the prostate gland.1 Clinical manifestations of BPH are caused by extrinsic compression of the prostatic urethra leading to impaired voiding. Chronic inability to completely empty the bladder may cause bladder distension with hypertrophy and instability of the detrusor muscle. Some patients with BPH present with hematuria. Because the severity of symptoms does not correlate with the degree of hyperplasia, and other conditions can cause similar symptoms, the clinical syndrome that often accompanies BPH has been described as lower urinary tract symptoms.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Men with suspected BPH can be evaluated with a validated questionnaire to quantify symptom severity.
BPH = benign prostatic hyperplasia.
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence; B = inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence; C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, see page 1360 or .
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
You May Like: Enlarged Prostate Sexuality
Do Prostatitis And Bph Cause Pain
Both BPH and prostatitis may cause pain. However, if BPH causes pain, it usually occurs with urination .
Prostatitis may cause painful urination, painful ejaculations, and generalized groin/abdominal pain. Prostatitis pain may be more constant and may be due to the inflammation of the prostatic tissue and/or adjacent tissues. Experts point out that often the source of pain from prostatitis is unclear.
What Is An Enlarged Prostate In Dogs
Prostate disease, usually in the form of an enlarged prostate, is also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia . It may give you some relief to know that its often caused by normal aging of the prostate, which becomes larger as your dog gets older. Youll know if your dog is affected because it can cause discomfort or difficulty when he pees or poops.
The canine prostate gland is inside the pelvis, behind the bladder and below the rectum. It reaches maturity by the time hes two years old. The prostate produces fluid for urine production and helps control ejaculation. It surrounds the urethra which carries urine from the bladder out through the penis. If it becomes enlarged or swells around part of the urethra it may cause dribbling, frequent accidents and other signs of urinary incontinence. A tumor in the prostate, a urinary tract infection or a urethral obstruction cause similar symptoms.
RELATED:;Ways to manage your dogs urinary incontinence
Also Check: Is Viagra Good For Enlarged Prostate
What Tests Might I Have At The Hospital
If youre given an appointment with a hospital specialist, they may do some of the tests you had at the GP surgery again. You may also have other tests, including the following.
Symptom questionnaire
You might be asked to fill in a short questionnaire about your symptoms. This is called the International Prostate Symptom Score and is used to see how bad your symptoms are and how much they are bothering you.
Urine flow test
Youll be asked to urinate into a machine that measures the speed of your urine flow. Men with an enlarged prostate usually have a slower flow than other men. You’ll need a full bladder for the test. The doctor or nurse will tell you how much to drink before you have the test. They may also ask you not to urinate for two to three hours before the test.
Ultrasound scan
This shows how much urine your bladder can hold, and if it is emptying properly. You may have the scan straight after the urine flow test to see how much urine is left in your bladder after you urinate. You may also have an ultrasound scan to look at your kidneys.
What Causes Prostatitis Vs Bph
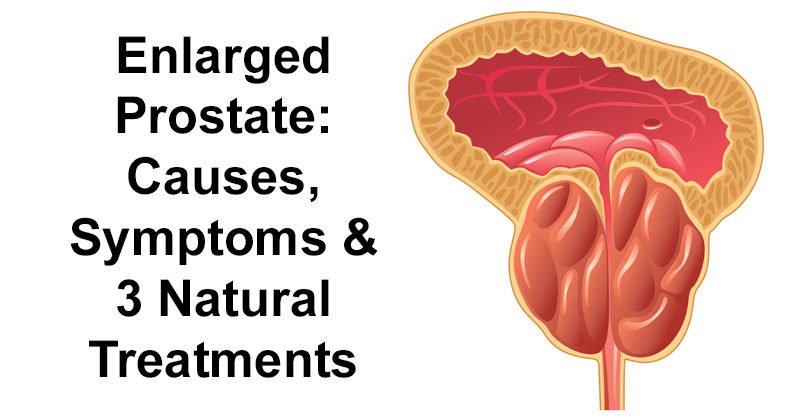
The cause of BPH or enlarged prostate is by benign growth that enlarges the prostate gland. Researchers do not know exactly what causes the gland to enlarge, but they have speculated that it might be related to hormonal changes as men age.
In men under the age of 35, the most common type of prostatitis is acute bacterial prostatitis, while in older patients non-bacterial prostatitis is the most common type. There are four types or syndromes of prostatitis.
- Type I – Acute bacterial prostatitis
- Type II – Chronic bacterial prostatitis
- Type III Chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Type IV is asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis.
The cause of acute bacterial prostatitis is by bacteria that may be present in the urethra and then infect the prostate gland. Chronic bacterial prostatitis occurs because of inadequate treatment or because of a structural/functional problem in the urinary tract. Researchers and doctors do not completely understand the cause of chronic prostatitis, but it is speculated that the cause may be initiated by neurological injury and/or related to infection.
You May Like: Can Prostatitis Go Away On Its Own
What Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia , or benign prostatic hypertrophy, is an enlargement of the prostate, a walnut-sized gland that forms part of the male reproductive system. During ejaculation, the prostate secretes fluid into the urethra, the narrow tube that runs through the center of the prostate. When a man urinates, the bladder;squeezes urine out through the urethra.
As a man ages, the prostate can become enlarged. Because it surrounds the urethra right at the bladder exit, the prostate may squeeze or pinch the urethra as it gets larger over time. This may cause difficulty with urination such as a slow stream, the need to strain, increased frequency, urgency to urinate, incomplete emptying of the bladder, and intermittent flow or dribbling.
BPH is the most common disorder of the prostate gland and the most common diagnosis by urologists;for males between the ages of 45 and 74. More than half of men in their sixties and as many as 90 percent in their seventies and eighties have some symptoms of BPH.
Although research has yet to pinpoint a specific cause for BPH, theories focus on hormones and related substances like dihydrotestosterone , a testosterone derivative in the prostate that may encourage the growth of cells.
Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
Some risk factors have been linked to prostate cancer. A risk factor is something that can raise your chance of developing a disease. Having one or more risk factors doesn’t mean that you will get prostate cancer. It just means that your risk of the disease is greater.
- Age. Men who are 50 or older have a higher risk of prostate cancer.
- Race. African-American men have the highest risk of prostate cancerâthe disease tends to start at younger ages and grows faster than in men of other races. After African-American men, prostate cancer is most common among white men, followed by Hispanic and Native American men. Asian-American men have the lowest rates of prostate cancer.
- Family history. Men whose fathers or brothers have had prostate cancer have a 2 to 3 times higher risk of prostate cancer than men who do not have a family history of the disease. A man who has 3 immediate family members with prostate cancer has about 10 times the risk of a man who does not have a family history of prostate cancer. The younger a man’s relatives are when they have prostate cancer, the greater his risk for developing the disease. Prostate cancer risk also appears to be slightly higher for men from families with a history of breast cancer.
- Diet. The risk of prostate cancer may be higher for men who eat high-fat diets.
Also Check: External Prostate Massage For Prostatitis
Using Medication To Reduce Symptoms
Treating Benign Prostate Enlargement
Treatment for an enlarged prostate is determined by the severity of your symptoms.
If you have mild to moderate;symptoms, you won’t receive any immediate medical treatment, but you’ll have regular check-ups to carefully monitor your prostate.
You’ll probably also be advised to make;lifestyle changes, such as limiting your caffeine and;alcohol intake, and exercising regularly,;to see if they improve your symptoms.
As well as;lifestyle changes, medication is usually recommended to treat moderate to severe symptoms of benign prostate enlargement.;Finasteride and dutasteride are medications;that are commonly used. They block the effects of a hormone called dihydrotestosterone on the prostate gland, which can reduce the size of the prostate and improve associated symptoms.
Alpha blockers may also be prescribed. They help to relax your bladder muscles, making it easier to pass urine. Tamsulosin and alfuzosin are two alpha blockers commonly used to treat benign prostate enlargement.
Surgery is usually only recommended for moderate to severe symptoms of benign prostate enlargement that have failed to respond to medication.
Read more about treating benign prostate enlargement
You May Like: Does Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
How Are Prostate Problems Diagnosed
To diagnose prostate problems, the health care provider will perform a digital rectal exam . The health care provider will also ask the patient
- when the problem began and how often it occurs
- what symptoms are present
- whether he has a history of recurrent urinary tract infections
- what medications he takes, both prescription and those bought over the counter
- the amount of fluid he typically drinks each day
- whether he consumes caffeine and alcohol
- about his general medical history, including any major illnesses or surgeries
Answers to these questions will help the health care provider identify the problem or determine what medical tests are needed. Diagnosing BPH may require a series of medical exams and tests.
Tests To Diagnose And Stage Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancers are first found as a result of screening. Early prostate cancers usually dont cause symptoms, but more advanced cancers are sometimes first found because of symptoms they cause.
If prostate cancer is suspected based on results of screening tests or symptoms, tests will be needed to be sure. If youre seeing your primary care doctor, you might be referred to a urologist, a doctor who treats cancers of the genital and urinary tract, including the prostate.
The actual diagnosis of prostate cancer can only be made with a prostate biopsy .
On this page
You May Like: What Happens If Prostate Cancer Goes Untreated
How To Reduce Prostate Size
This article was medically reviewed by . Dr. Litza is a board certified Family Medicine Physician in Wisconsin. She is a practicing Physician and taught as a Clinical Professor for 13 years, after receiving her MD from the University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health in 1998.There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 65,131 times.
The prostate gland is a part of the male reproductive system that can enlarge with age, putting uncomfortable pressure on the urethra. This can cause urinary difficulties, urinary tract infections , and even bladder stones. By making lifestyle changes and using medication, most men can reduce their urinary troubles. A few men, though, may need to consider minimally invasive or traditional surgery options to feel their best.
