What Are Prostate Cancer Treatment Side Effects
Some prostate cancer treatments can affect the bladder, erectile nerves and sphincter muscle, which controls urination. Potential problems include:
- Incontinence: Some men experience urinary incontinence. You may leak urine when you cough or laugh, or you may feel an urgent need to use the bathroom even when your bladder isnt full. This problem can improve over the first six to 12 months without treatment.
- Erectile dysfunction : Surgery, radiation and other treatments can damage the erectile nerves and affect your ability to get or maintain an erection. Some men regain erectile function within a year or two . In the meantime, medications like sildenafil or tadalafil can help by increasing blood flow to the penis.
- Infertility: Treatments can affect your ability to produce or ejaculate sperm, resulting in male infertility. If you think you might want children in the future, you can preserve sperm in a sperm bank before you start treatments. After treatments, you may undergo sperm extraction. This procedure involves removing sperm directly from testicular tissue and implanting it into a womans uterus.
What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Your healthcare provider uses the Gleason score and Grade Groups to stage prostate cancer based on its projected aggressiveness. To get this information, the pathologist:
- Assigns a grade to each type of cell in your sample. Cells are graded on a scale of three to five . Samples that test in the one to two range are considered normal tissue.
- Adds together the two most common grades to get your Gleason score .
- Uses the Gleason score to place you into a Grade Group ranging from one to five. A Gleason score of six puts you in Grade Group 1 . A score of nine or higher puts you in Grade Group five . Samples with a higher portion of more aggressive cells receive a higher Grade Group.
Testing Is Easy But Timing Is Inconclusive
You can be tested for prostate cancer in the doctors office with a digital rectal exam and a blood test.
Speak to Louisiana Healthcare Associates Urology Division;about your individual situation and when you should begin testing. If you have higher than average risk you may want to begin testing at age 40.
Also Check: Can An Enlarged Prostate Lead To Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Early-stage prostate cancer rarely causes symptoms. These problems may occur as the disease progresses:
- Frequent, sometimes urgent, need to urinate, especially at night.
- Weak urine flow or flow that starts and stops.
- Painful urination .
- Painful ejaculation and erectile dysfunction .
- Blood in semen or urine.
- Lower back pain, hip pain and chest pain.
- Leg or feet numbness.
Both Us And Global Data

The new study is based on US data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program and on global data from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation’s Global Burden of Disease resource. Findings in the new study encompass North, South, and Central America , Europe, Asia, and Africa.
From 1990 to 2017, prostate cancer incidence in three age groups has “steadily increased” in all four study regions, the authors report.
Notably, the mortality rate of prostate cancer in these age groups did not mimic the incidence trend in any of these regions, having decreased or remained stable. There were some exceptions for 2016 and 2017, the most recent years of available data, during which the death rate increased in some regions and age groups.
There are a lot of unknowns about the incidence increase of prostate cancer in young men including its cause, say the authors.
They cite a long list of possible reasons for the increase, some linked to observational evidence and some not. One associated factor in the US will be familiar to observers of prostate cancer trends: prostate-specific antigen testing.
The authors point to a recent study that found that from 2000 through 2015 in the US, 2% of men aged 30 to 39 and 5% to 6% of those aged 40 to 49 years who had health insurance were screened with PSA tests, “contrary to all existing practice guidelines.” :S155)
What is certain to the researchers is that young American men with prostate cancer have dire survival rates.
Recommended Reading: When To Get A Prostate Biopsy
What You Should Know About Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer is the second most common cancer in men.
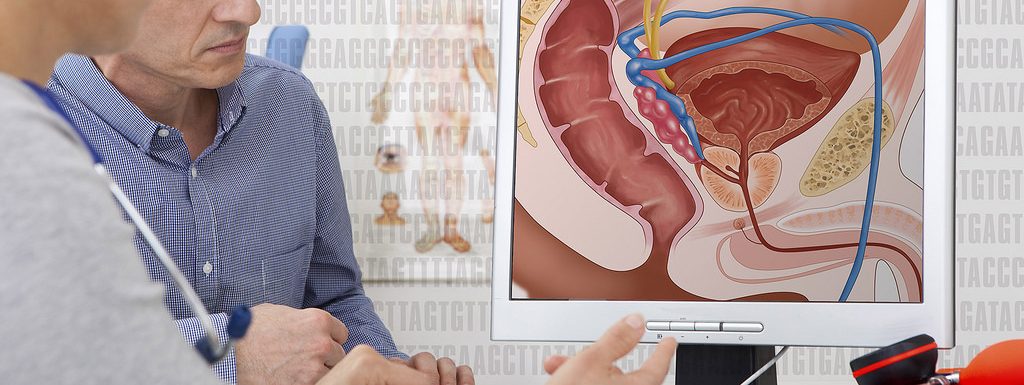
The cancer begins when cells in the prostate, a gland found below the bladder and in front of the rectum, begin to grow uncontrollably.
When a male is young, the prostate gland is around the size of a walnut. However, the size of the prostate increases with age.
Most prostate cancer cases grow slowly, allowing for successful treatment options and a low mortality rate. More than two million men in the United States are prostate cancer survivors.
However, the danger comes when men do not recognize their symptoms or delay seeing a doctor.
What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Prostate Cancer
Because prostate cancer tends to grow slowly, most men die from something other than the disease. Early detection is key to better outcomes. Almost all men 97% to 98% diagnosed with localized cancer that hasnt spread outside of the prostate live at least five years after diagnosis. When metastatic cancer has spread outside of the gland, one-third of men continue to survive after five years.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can You Take Hormone Therapy For Prostate Cancer
Are Prostate Problems Always A Sign Of Prostate Cancer
Not all growths in the prostate are cancerous, and not all prostate problems indicate cancer. Other conditions that cause similar prostate cancer symptoms include:
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia : At some point, almost every man will develop benign prostatic hyperplasia . This condition enlarges the prostate gland but doesnt increase cancer risk. The swollen gland squeezes the urethra and blocks the flow of semen and urine. Medications, and sometimes surgery, can help.
- Prostatitis: Men younger than 50 are more prone to prostatitis, inflammation and swelling of the prostate gland. Bacterial infections are often the cause. Treatments include antibiotics or other medications.
Masturbation And Prostate Cancer Risk
Masturbation Frequency Linked to Prostate Risk in 20s, Protection in 50s
Jan. 27, 2009 — Frequent masturbation in young men is linked to higher risk of early prostate cancer, but it lowers prostate cancer risk for men in their 50s, a study shows.
High levels of male sex hormones, or androgens, may increase a man’s risk of prostate cancer. But different studies of this question, done in different ways, have reached different conclusions.
To look at the question in a new way, a team of researchers at England’s University of Nottingham looked at whether men with more intense sex drives were at higher risk of prostate cancer.
Polyxeni Dimitropoulou, PhD; Rosalind Eeles, PhD, FRCP; and Kenneth R. Muir, PhD, obtained detailed sexual histories from 840 men. About half the men got prostate cancer by age 60, and about half did not have cancer.
The findings were surprising. Sexual intercourse did not affect prostate cancer risk. But frequent masturbation did — in different ways, at different times of life.
“Frequent masturbation during men’s 20s and 30s increased their risk of prostate cancer,” Dimitropoulou tells WebMD. “But men in their 50s who masturbated frequently had decreased risk.”
Of course, masturbation frequency is relative.
For men in their 50s, “frequent masturbation” was one or more times per week. Compared to same-age men who reported never masturbating, 50-something frequent masturbators had a 70% lower risk of prostate cancer.
Read Also: How Accurate Is Mri In Diagnosing Prostate Cancer
Inflammation Of The Prostate
Some studies have suggested that prostatitis may be linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer, but other studies have not found such a link. Inflammation is often seen in samples of prostate tissue that also contain cancer. The link between the two is not yet clear, and this is an active area of research.
Your Risk For Prostate Cancer
The greatest risk factors for developing prostate cancer are increasing age, family history, ethnicity, and diet. Do any of the following describe you?
- I am older than 50
- I have a family history of prostate cancer
- I am African-American
If you answered yes to any of these, then you may be at higher risk of prostate cancer. However, not having any of these risk factors does not mean you are immune. Unfortunately, all men are at risk for prostate cancer. Keep reading to learn more about your risk and what steps you can take.
Read Also: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have prostate cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get prostate cancer?
- What is my Gleason score? What is my Grade Group? What do these numbers mean for me?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the prostate gland?
- What is the best treatment for the stage of prostate cancer I have?
- If I choose active surveillance, what can I expect? What signs of cancer should I look out for?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Is my family at risk for developing prostate cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Prostate cancer is a common cancer that affects males. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and remain in the prostate gland. For a small number, the disease can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. Men with slow-growing prostate cancers may choose active surveillance. With this approach, you can postpone, and sometimes completely forego, treatments. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for you based on your Gleason score and Group Grade.
Natural Remedies For Enlarged Prostate In Young Men
While appropriate medical attention is an absolute necessity in treating enlarged prostate, there are quite a few natural remedies that one can try to control symptoms of enlarged prostate in y9oung men. These home remedies are:
Time Voids: It is quite an effective natural remedy to control the symptoms of enlarged prostate. Even if you do not feel an urge to void try going to the bathroom every half an hour to try to void. This will not only control urinary urgency but will also release pressure from the bladder and urethra quite significantly.
Void Whenever the Need Arises: Do not try to control the urge for urination. This causes extra stress to the bladder and urethra especially in cases of enlarged prostate. Thus, voiding whenever you feel the urge to do so is a natural remedy to control urinary urgency due to enlarged prostate in young men.
Drink Plenty of Water: Drinking lot of water eliminates bacteria from the urethra and also soothes the bladder and hence is quite an effective natural remedy for controlling the symptoms of enlarged prostate in young men.
Exercise Regularly: This is also quite an effective natural remedy for enlarged prostate. It not only eases the pressure in the urethra but also helps with symptoms of Enlarged Prostate in young men. The best exercise for this condition is known as the Kegel exercise. This exercise goes a long way in calming down the inflammation of the prostate gland and treat enlarged prostate in young men.
Also Read:
You May Like: Will A Blood Test Show Prostate Cancer
Impact Of Age On Treatment
The rising number of men diagnosed with prostate cancer is a result of increasing life expectancy as well as the current practice of screening by prostate-specific antigen blood tests. Besides PSA and Gleason score, age is considered a key prognostic factor in treatment decision making. Although organ-confined disease can be cured by radical prostatectomy and full-dose local radiation therapy, treatment options for advanced- stage disease remain palliative. They include active surveillance, or watchful waiting, early versus delayed hormonal therapy to control disease progression, and continuous or intermittent androgen deprivation. Observational studies of older men with early stage disease have suggested conservative management as a viable option.,
Chodak and associates evaluated 828 men who were managed expectantly in a series of nonrandomized trials. Median follow-up was approximately 6.5 years. Patients with poorly differentiated cancers had a 10-fold increased risk of death from prostate cancer as compared with men showing highly differentiated prostate cancer. A 5-year disease-specific survival of only 34% was found in men with poorly differentiated prostate cancer. In contrast a 5-year disease-specific survival of 87% was described in men with well-or moderately differentiated cancers.
How Early Onset Prostate Cancer Is Different
Doctors think the type of prostate cancer you get when youâre younger may be different from prostate cancer with a later onset and are doing research to learn more.
If you get a prostate cancer diagnosis when youâre younger, itâs more likely to be in a more advanced stage. Youâre also more likely to have a lower rate of survival than middle-aged men and older men would.
In the U.S., the average 5-year survival rate for prostate cancer is between 95% and 100% for men ages 40-80.
For younger men, the 5-year survival rate is lower. For men ages 25-34, itâs 80%. For men ages 20-29, itâs 50%. For men ages 15-25, itâs 30%.
Don’t Miss: Is Turmeric Good For Prostate
Watchful Waiting And Active Surveillance
Watchful waiting is an adequate approach in patients who are at low risk of death from prostate cancer because of their limited life expectancy due to severe comorbidities., Watchful waiting resulted in similar overall survival when compared with radical prostatectomy, but disease-specific survival was better in patients who had undergone surgery. For some patients it turns out to be hard to persist on a watchful waiting policy, and many men drop out and seek active treatment within several years, mostly when PSA elevation is noted.
Active surveillance is a novel and fascinating approach to distinguish between patients who are at higher risk and need active therapy and patients who are at low risk for disease progression., This approach avoids the risks of therapy while allowing early detection of those patients who are prone to progress. In these high-risk individuals, delayed active treatment is offered. Periodic monitoring of the PSA serum level, digital rectal exam, and repeated prostate biopsies are performed in patients who are on active surveillance, and active therapy is started when predefined threshold values are reached. This concept makes it possible to offer curative treatment to individuals who are at high risk for disease progression as indicated by active surveillance parameters.
Why Is Prostate Cancer Rising Among Young Men
Scientists aren’t certain while incidents of prostate cancer are rising among young men. However, some increase in cases may be caused by number of cases that are documented because of increased access to screening. Additionally, scientists are seeing a correlation between boys who are growing taller than their peers and this may be lead to an increased risk of prostate cancer later in life as well.;
Other theories for why prostate cancer is becoming more common among young men include social and environmental factors. Cancers as a whole are increasingly common among young men due to obesity, lack of physical activity, exposure to chemical substances, and in some cases sexually transmitted infections such as HPV.
Don’t Miss: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
Risk Factors In Young Patients
Early-onset prostate cancer is similar to breast cancer and endometrial cancer in one way. When patients are diagnosed at a younger age, a hereditary pattern is more likely. Thus, among the risk factors listed above, the most important in these patients is a family history.
Actually, a study found that family history is particularly relevant in men under 65 years. After 65 years, it may not increase the risk as much . These younger patients have a higher risk of genetic variants that increase the aggressiveness.
This increase in genetic burden is recorded in the scientific literature but is quite difficult to study. In the future, it will be very useful to know which genes are particularly risky. This would allow us to screen young patients with prostate cancer to see if they have these defective genes. If they do, they are at a notably higher risk and need to undergo aggressive treatment right away. However, this sounds very good in theory. Cancer is not as easy to manage and understand.
One of the few genes currently identified is a small change in the gene HOXB13. This gene encodes a transcription factor that modulates cell growth. In a mutant HOXB13 gene, cells start to divide rapidly independent from androgen stimulation. Patients with this defective gene are more likely to develop cancer at an early age .
What Are The Symptoms Of Enlarged Prostate In Young Men
The symptoms of enlarged prostate in young men may begin with difficulty with urination in the early stages of the disease condition and if not appropriately diagnosed and promptly treated different types of complications may arise based on the extent of the inflammation and the severity of the condition. Enlarged prostate in young men may not be evident clearly but gradually advances over a period of time which may be months to years before an individual can actually feel the symptoms. Some of the common symptoms which may point towards an enlarged prostate in young men are:
Poor Urinary Stream: An individual with an Enlarged Prostate will have symptoms of poor urinary stream. This is due to the urethra being strangled by the Enlarged Prostate. Not only will the individual have a poor urinary stream, he will also feel that he has not completely emptied the bladder and will also have pain with urination.Incomplete Bladder Emptying: Since Enlarged Prostate causes the urethra to get strangled and under a lot of pressure not all the urine that is collected in the bladder is able to flow through the urethra resulting in incomplete voiding. This results in an individual to go to the bathroom more times than normal and still have a sensation that he has not completely emptied the bladder.
Pain with Urination: Enlarged Prostate causes pain when urination and is a common symptom of this condition.
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Prostate Cancer Without Treatment
