How To Do Active Surveillance Right
After a diagnosis of low-risk prostate cancer, you may be presented with a range of treatment options. Considering the slow progress of most prostate cancer, active surveillance is a reasonable choice for many men. Even if you live a long time after your diagnosis, your cancer may;neverbecome aggressive and cause harm. Often, low-risk prostate cancer hardly progresses at all, even over decades.
If you choose to go the active surveillance route, do it the smart way.;Dr. Hu recommends that for the first two years after your diagnosis
- Get a PSA test every six months.
- Have an office visit that includes a digital exam every six months.
- Within the first two years after diagnosis, get at least one follow-up biopsy as well as magnetic resonance imaging and precision medicine tests to reduce the risk of missing more aggressive cancer.
What happens next depends on those first two years. If it looks like your cancer is stable and not progressing, your doctor may suggest less frequent follow-ups. But if there is evidence that the cancer is becoming more aggressive, then you can decide;at that time;whether radiation, surgery, hormone therapy or some combination of these treatments is right for you. You may never need treatment, but if you do, youll get it when its still highly effective.
Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
Some risk factors have been linked to prostate cancer. A risk factor is something that can raise your chance of developing a disease. Having one or more risk factors doesn’t mean that you will get prostate cancer. It just means that your risk of the disease is greater.
- Age. Men who are 50 or older have a higher risk of prostate cancer.
- Race. African-American men have the highest risk of prostate cancerâthe disease tends to start at younger ages and grows faster than in men of other races. After African-American men, prostate cancer is most common among white men, followed by Hispanic and Native American men. Asian-American men have the lowest rates of prostate cancer.
- Family history. Men whose fathers or brothers have had prostate cancer have a 2 to 3 times higher risk of prostate cancer than men who do not have a family history of the disease. A man who has 3 immediate family members with prostate cancer has about 10 times the risk of a man who does not have a family history of prostate cancer. The younger a man’s relatives are when they have prostate cancer, the greater his risk for developing the disease. Prostate cancer risk also appears to be slightly higher for men from families with a history of breast cancer.
- Diet. The risk of prostate cancer may be higher for men who eat high-fat diets.
What About Trans People
People assigned male at birth can develop prostate cancer whether they remain male or not.
Trans women who use hormone therapy such as estrogenmay have a lower risk, but the risk is still present.
Anyone assigned male at birth should speak to their doctor about screening for prostate cancer.
Knowing the stage of prostate cancer can help a person understand what to expect, and it will inform decisions about treatment. We list the stages below:
Stage 0: Precancerous cells are present, but they only affect a small area and are slow growing.
Localized : Cancer is only present in the prostate gland. Effective treatment is possible at this stage.
Regional : Cancer has spread to nearby tissues.
Distant : Cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs or bones.
If a male has symptoms that may indicate prostate cancer, the doctor will likely:
- ask about symptoms
- ask about personal and medical history
- conduct a blood test to assess PSA levels
- carry out a urine test to look for other biomarkers
- carry out a physical examination, which may include a digital rectal exam
During a DRE, the doctor will check manually for any abnormalities of the prostate with their finger.
Learn more about prostate exams here.
Also Check: Prostate Cancer Ruined My Marriage
What Are Male Sex Hormones
Hormones are substances that are made by glands in the body. Hormones circulate in the bloodstream and control the actions of certain cells or organs.
Androgens are a class of hormones that control the development and maintenance of male characteristics. The most abundant androgens in men are testosterone and dihydrotestosterone .;
Androgens are required for normal growth and function of the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system that helps make semen. Androgens are also necessary for prostate cancers;to grow. Androgens promote the growth of both normal and cancerous prostate cells by binding to and activating the androgen receptor, a protein that is expressed in prostate cells . Once activated, the androgen receptor stimulates the expression of specific genes that cause prostate cells to grow .
Almost all testosterone is produced in the testicles; a small amount is produced by the adrenal glands. Although prostate cells do not normally make testosterone, some prostate cancer cells acquire the ability to do so .
Risk Factors In Aggressive Vs Slow
![Prostate Cancer: Facts and Statistics [Infographic] Prostate Cancer: Facts and Statistics [Infographic]](https://img.healthyprostateclub.com/wp-content/uploads/prostate-cancer-facts-and-statistics-infographic.jpeg)
In the past few years, weve learned that prostate cancer really is several diseases with different causes. More aggressive and fatal cancers likely have different underlying causes than slow-growing tumors.
For example, while smoking has not been thought to be a risk factor for low-risk prostate cancer, it may be a risk factor for aggressive prostate cancer. Likewise, lack of vegetables in the diet is linked to a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer, but not to low-risk prostate cancer.
Body mass index, a measure of obesity, is not linked to being diagnosed with prostate cancer overall. In fact, obese men may have a relatively lower PSA levels than non-obese men due to dilution of the PSA in a larger blood volume. However, obese men are more likely to have aggressive disease.
Other risk factors for aggressive prostate cancer include:
- Tall height
- Lack of exercise and a sedentary lifestyle
- High calcium intake
- Agent Orange exposure
Research in the past few years has shown that diet modification might decrease the chances of developing prostate cancer, reduce the likelihood of having a prostate cancer recurrence, or help slow the progression of the disease. You can learn more about how dietary and lifestyle changes can affect the risk of prostate cancer development and progression in PCFs Health and Wellness: Living with Prostate Cancer guide.
Don’t Miss: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
Tests Used To Check The Prostate
This first step lets your doctor hear and understand the “story” of your prostate concerns. You’ll be asked whether you have symptoms, how long you’ve had them, and how much they affect your lifestyle. Your personal medical history also includes any risk factors, pain, fever, or trouble passing urine. You may be asked to give a urine sample for testing.
What If I Am Diagnosed With Prostate Cancer
Many people have been where you are standing. Dont lose hope. More than 3.1 million American men have been diagnosed with prostate cancer and are alive today.
The first thing you should consider doing is to find out about the specifics of your cancer. You should know your stage and grade .
From there you can find out what treatment options you want to pursue, if any. Talk to your doctors. Choose a healthcare team of different specialists, or consult a second opinion. You can also do your own research, or talk to men who have been in your position. Many of our advocates are patients and survivors; hear their stories at the;video library. Or head to the rest of our website to start some research.
Determining who needs treatment for prostate cancer has evolved with new options to diagnose aggressive vs. indolent disease.;Check out our infographic with more information on what genomic and advanced tests are available based on a mans individual cancer.
Learn
Recommended Reading: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
You May Like: Prostatitis Symptoms Mayo
Why Are Black Men More At Risk
It is a health disparity that needs to be addressed. Considerable money, time, and effort have gone into studies in men of European ancestry; it is time for a large-scale effort devoted to men of African ancestry.
Christopher Haiman, ScD,Professor of Preventive Medicine at Keck School of Medicine.
1. Genetics
According to a study published in Cancer Discovery, there may be a genetic reason behind black men experiencing a more aggressive form of prostate cancer.
2. Lack of PSA tests
PSA refers to the amount of protein prostate-specific antigen in your blood. According to experts, high levels of PSA are associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. Therefore, its important for men to get the test done.
Unfortunately,; black men are significantly;less likely;than white;men;to use early detection screening tools, like;prostate-specific antigen;;testing;for;prostate;cancer .
3. Racial bias
A study published in the Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities found that previous bias and fear of black men likely resulted in them not getting the same healthcare as white male patients.
Additionally, another study found that black men diagnosed with early-stage prostate cancer were less likely than white men to receive any type of treatment for that cancer.
What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?
According to the Cancer Treatment Centers of America, the following signs may indicate that you have prostate cancer;
How can black men protect themselves?
2. Exercise
Risk Factors You Cant Control
Age: The risk of developing prostate cancer increases with age. One in 10,000 men younger than 40 will be diagnosed with prostate cancer, but one in 15 men in their 60s will be diagnosed with the disease.
Family history: Being born with a gene mutation is one of the unavoidable risks of prostate cancer. Two of them include the BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations. BRCA and other inherited mutations, including HOXB13 and DNA mismatch repair genes, may explain why prostate cancer runs in families. Having a father or brother with prostate cancer may double a mans risk, especially if that relative was diagnosed before age 55.
Hormones: The level of male sex hormones, called androgens, may be higher in some men than others. Higher levels of androgensmainly testosteronehave been linked to a higher risk of prostate cancer. Men who use testosterone therapy are at a higher risk of developing prostate cancer, as an increase in testosterone stimulates the growth of the prostate gland.
Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia : This condition may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer. PIN is a condition in which prostate gland cells look abnormal when examined with a microscope. Its not necessarily linked with any symptoms. Nearly half of men will be diagnosed with PIN before age 50.
Race: Studies show that African-American men are about 70 percent more likely to develop prostate cancer in their lifetime than Caucasian or Hispanic men.
You May Like: Enlarged Prostate Sexuality
Do Not Stuff Yourself
The Japanese enjoy a long life expectancy, and the highest percentage of centenarians in the world is found in Okinawa. If you want to learn how to live to 100, follow the eating style of people who live there. They have a practice of eating until they are only 80 percent full. This makes good sense because it takes 20 minutes for the brain to receive the signal from your stomach that it is full. Stop eating before you feel full. Over time, not cleaning your plate adds up to weight loss.
Screenings Can Lead To High Costs
The cost for a PSA test is fairly lowabout $40.
If your result is abnormal, the costs start adding up. Your doctor will usually refer you to a urologist for a biopsy. Costs may include:
- A consultation fee .
- An ultrasound fee .
- Additional professional fees .
- Biopsy fees .
If the biopsy causes problems, there are more costs. You might also have hospital costs.
You May Like: What Happens If Prostate Cancer Goes Untreated
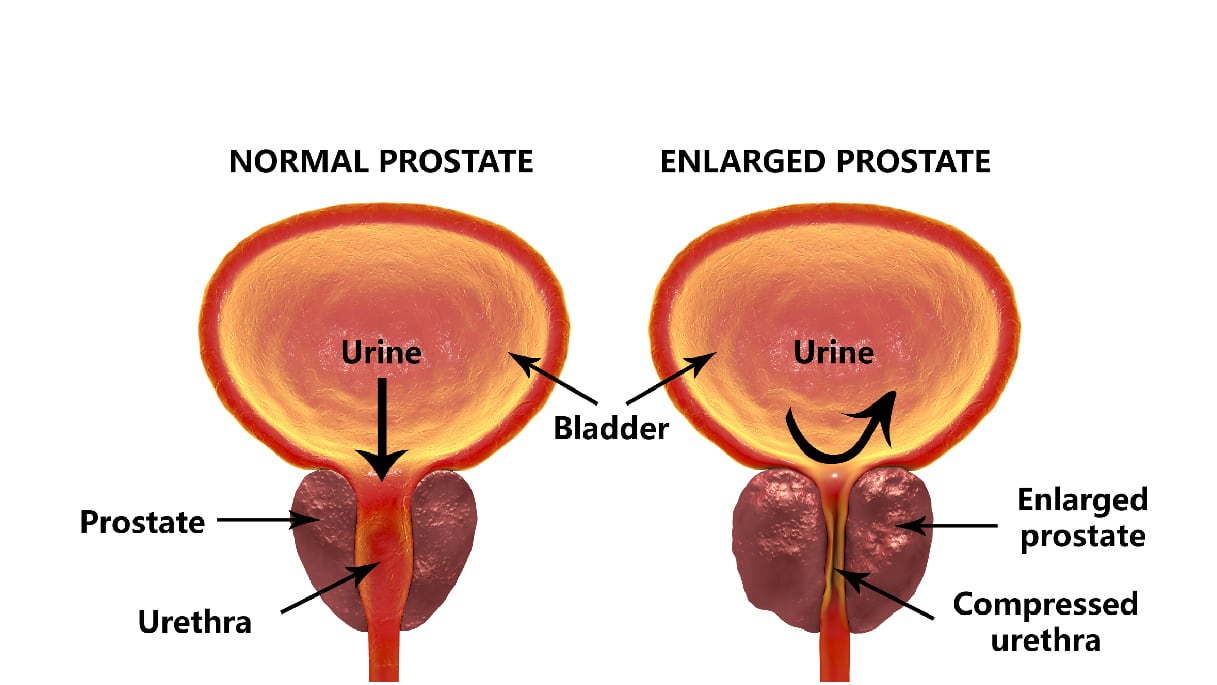
How Are Prostate Problems Treated
Treatment depends on which kind of prostate problem you develop.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia needs treatment only if the urinary symptoms become bothersome. BPH often responds to drugs that either:
- Relieve the tension around the urethra
- Reduce the size of the prostate itself
The FDA is revising labels on several BPH drugs — Proscar, Avodart, and Jalyn — to include a warning that the drugs may be linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer.
If medication does not relieve the symptoms, surgery may be required. Several herbs showed promise as treatment for BPH in some studies, but results are incomplete or conflicting. These include saw palmetto, beta-sitosterol, and Pygeum africanum.
Prostate cancer treatment is complex. When designing a prostate cancer treatment plan, doctors consider a man’s age, overall health, and how aggressive or widespread the prostate cancer is. All men’s cancer is unique, and their treatment will be unique. Some treatment options include:
- No treatment
Should I Get Screened For Prostate Cancer
This video helps men understand their prostate cancer screening options.
In 2018, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force made the following recommendations about prostate cancer screeningexternal icon
- Men who are 55 to 69 years old should make individual decisions about being screened for prostate cancer with a prostate specific antigen test.
- Before making a decision, men should talk to their doctor about the benefits and harms of screening for prostate cancer, including the benefits and harms of other tests and treatment.
- Men who are 70 years old and older should not be screened for prostate cancer routinely.
This recommendation applies to men who
- Are at average risk for prostate cancer.
- Are at increased risk for prostate cancer.
Donât Miss: Can Bph Cause Constipation
Read Also: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
What Is Screening For Prostate Cancer
Some men get a PSA test to screen for prostate cancer. Talk to your doctor, learn what is involved, and decide if a PSA test is right for you.
Cancer screeningexternal icon means looking for cancer before it causes symptoms. The goal of screening for prostate cancer is to find cancers that may be at high risk for spreading if not treated, and to find them early before they spread.
If you are thinking about being screened, learn about the possible benefits and harms of screening, diagnosis, and treatment, and talk to your doctor about your personal risk factors.
There is no standard test to screen for prostate cancer. Two tests that are commonly used to screen for prostate cancer are described below.
Black Men Both Get And Die From Prostate Cancer At A Higher Rate The Reasons Are Complex And Unclear
Black men are 50% more likely to develop prostate cancer in their lifetime and twice as likely to die from the disease, Dr. Kantoff says.
It is difficult to untangle the various factors that might affect the risk and outcome of prostate cancer, Dr. Kantoff explains. Prostate cancer in Blacks tends to have biological characteristics associated with more aggressive disease, he says. There is evidence suggesting that this is partly related to inherited genetic factors.
He points out that in addition to differences in tumor biology, the higher risk may be tied to disparities in environment and behavior. This could include social stress or more exposure to cancer-causing pollutants. Smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise, which can cause obesity, may also have effects. Disparities in outcome could be affected by differences in when the cancer is diagnosed and how the men are treated after diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: What Happens To The Prostate Later In Life
Why Is Obesity A Risk Factor In Prostate Cancer
Overweight men are less likely to be diagnosed with early prostate cancer.
Due to this, the researchers point out that the risk association with obesity may not be accurate.
Obesity can hinder detection of the disease because overweight men tend to have larger prostates.
lus, the report states that they have lower concentrations of prostate specific antigens.
Am I At Risk Of Prostate Cancer
In the UK, about 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime. We don’t know exactly what causes prostate cancer but there are some things that may mean you are more likely to get it these are called risk factors.
There are three main risk factors for getting prostate cancer, which are things you can’t change. These are:;
If you have any of these risk factors or if you have any;symptoms, speak to your GP. They can talk to you about your risk, and about the;tests;that are used to diagnose prostate cancer. You can also get in touch with;our Specialist Nurses, who can help you understand your risk of prostate cancer.
Read Also: Does Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
Men With Prostate Cancer Could Be Cured In One Week: Patients Could Be Treated With Just Two Sessions Of Radiotherapy
- Typically prostate cancer is treated with roughly 20 radiation doses a month
- But researchers found that the radiation can be safely given in 5 big doses;
- Doctors are this week set to treat the first patient as part of a trial looking into whether it is safe to give radiotherapy in two large doses
08:40 EDT, 19 September 2021 | Updated: 09:22 EDT, 19 September 2021
Prostate cancer patients could be cured in just one week instead of a month with targeted high-dose radiotherapy sessions.;;
Doctors at the;London Royal Marsden hospital are this week set to treat the first patient as part of a trial looking into whether it is safe to give radiotherapy in two large doses instead of lots of smaller doses.;;
Earlier this month researchers from the hospitals NHS Foundation Trust and The Institute of Cancer Research found that the typical amount of radiation to treat prostate cancer delivered in small doses over about 20 sessions in a month could be safely given in just five big doses in just one or two weeks.;
The trials leader and;consultant clinical oncologist at the Royal Marsden and the Institute of Cancer Research in London , Dr Alison Tree, told The Times;that working age men could come in, get cured, get on with their normal lives and forget about their cancer completely.;
There are nearly 50,000 diagnoses of prostate cancer each year, making it the most common form of cancer among British men.;
We are so much more precise that we dont hit much of the healthy tissue now.;
