Herbal Combinations For The Prostate Gland
Another good herbal combination for the prostate is PS II. This formulation for overall prostate health contains eleven herbsincluding saw palmetto. This prostate formula has been used to reduce swelling, inflammation, and muscle spasms in the urinary tract. PS II is often helpful for inflammations of the prostate that are not due to BPH. For men who have some of the urinary symptoms of BPH, but are under 40 and/or have been told by their doctors that their prostate is not enlarged, this formulation may prove the most helpful. In fact, any man with prostate concerns might want to try this formulation first, since it is relatively inexpensive and when it works it usually gives quick results. If an improvement is not noticed by the time the first or second bottle is finished, a switch to the “Men’s Formula” mentioned above might be considered.
Description Of The Urinary System
The urinary system works with the lungs, skin and intestines to maintain the balance of chemicals and water in the body. Adults eliminate about 27 to 68 fluid ounces per day based on typical daily fluid intake of 68 ounces , National Institutes of Health . Other factors in urinary system function include fluid lost through perspiring and breathing. In addition, certain types of medications, such as diuretics that are sometimes used to treat high blood pressure, can also affect the amount of urine a person produces and eliminates. Some beverages, such as coffee and alcohol, can also cause increased urination in some people.
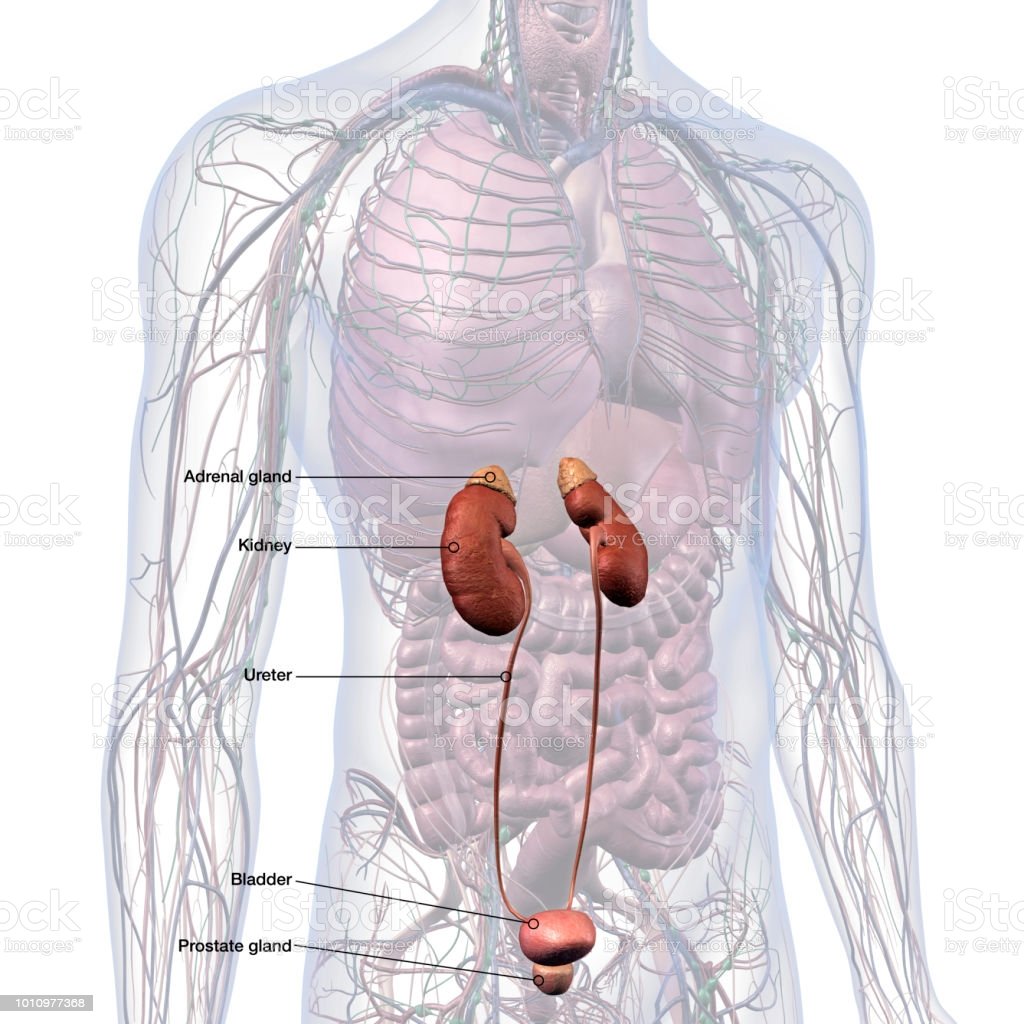
The primary organs of the urinary system are the kidneys, which are bean-shaped organs that are located just below the rib cage in the middle of the back. The kidneys remove urea waste product formed by the breakdown of proteins from the blood through small filtering units called nephrons, according to the Cleveland Clinic. Each nephron consists of a ball formed of small blood capillaries, called a glomerulus, and a small tube called a renal tubule. Urea, together with water and other waste substances, forms the urine as it passes through the nephrons and down the renal tubules of the kidney.
From the kidneys, urine travels down two thin tubes, called ureters, to the bladder. The ureters are about 8 to 10 inches long , according to the Cleveland Clinic.
How Can You Naturally Improve Urinary Symptoms
If you are experiencing urinary symptoms and discomfort due to the conditions described above, there are simple strategies to improve bladder control and reduce pain.
These strategies usually revolve around lifestyle modifications, behavior therapies, and physiotherapy. They are safe, effective, inexpensive, and can work alongside other treatment methods such as surgery.
You can take the following steps to improve symptoms:
Read Also: What Happens If You Have Prostate Cancer
What Is The Genitourinary System
The different parts of the urinary system in the body are somewhat similar in males and females. People of both genders have kidneys which process waste. They possess lines from the kidneys to the bladder, which are called ureters. In men and women, urine ultimately passes through the urethra, but this is where the differences really begin.
The urethra feeds through the shaft of the penis in men, but in women it is located near the opening of the vagina. In both male and female anatomy this tube from the bladder is still the means by which urine leaves the body. Location is a little different and somewhat defines why certain physical problems with the urinary tract are more likely to be associated with a specific gender.
It is easy to understand close proximity of the two systems when thinking about parts of the body like the urethra. It passes through the penis and is very close to the vagina, and these are vital parts of the reproductive system. Yet, unlike the relative similarities in the urinary system between genders, there is significant difference in what makes up male and female reproductive anatomy.
Aging Changes In The Kidneys And Bladder
The kidneys filter the blood and help remove wastes and extra fluid from the body. The kidneys also help control the body’s chemical balance.
The kidneys are part of the urinary system, which includes the ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Muscle changes and changes in the reproductive system can affect bladder control.
AGING CHANGES AND THEIR EFFECTS ON THE KIDNEYS AND BLADDER
As you age, your kidneys and bladder change. This can affect their function.
Changes in the kidneys that occur with age:
- Amount of kidney tissue decreases and kidney function diminishes.
- Number of filtering units decreases. Nephrons filter waste material from the blood.
- Blood vessels supplying the kidneys can become hardened. This causes the kidneys to filter blood more slowly.
Changes in the bladder:
- The bladder wall changes. The elastic tissue becomes stiffer and the bladder becomes less stretchy. The bladder cannot hold as much urine as before.
- The bladder muscles weaken.
- The urethra can become partially or totally blocked. In women, this can be due to weakened muscles that cause the bladder or vagina to fall out of position . In men, the urethra can become blocked by an enlarged prostate gland.
In a healthy aging person, kidney function declines very slowly. Illness, medicines, and other conditions can significantly degrade kidney function.
COMMON PROBLEMS
Aging increases the risk of kidney and bladder problems such as:
You May Like: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Effects Of Aging On The Urinary Tract
, MD, Duke Comprehensive Kidney Stone Center
As people age, a number of changes happen throughout the genitourinary tract Overview of the Urinary Tract Normally, a person has two kidneys. The rest of the urinary tract consists of the following: Two ureters The bladder (an expandable muscular… read more .
Nephrons: The Functional Unit
Nephrons take a simple filtrate of the blood and modify it into urine. Many changes take place in the different parts of the nephron before urine is created for disposal. The term forming urine will be used hereafter to describe the filtrate as it is modified into true urine. The principal task of the nephron population is to balance the plasma to homeostatic set points and excrete potential toxins in the urine. They do this by accomplishing three principle functionsfiltration, reabsorption, and secretion. They also have additional secondary functions that exert control in three areas: blood pressure , red blood cell production , and calcium absorption .
Also Check: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
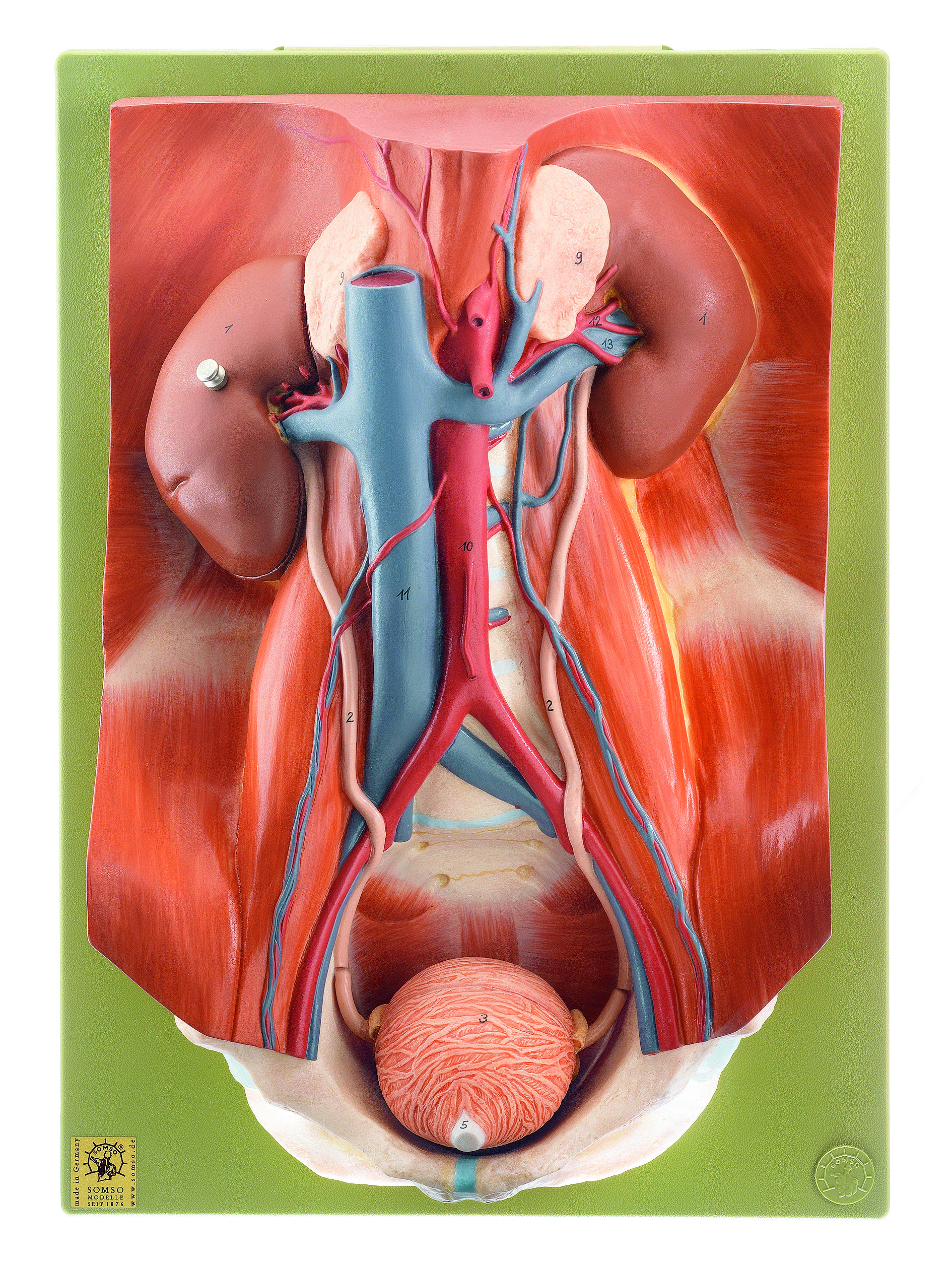
Blood And Lymph Supply
The bladder receives blood by the vesical arteries and drained into a network of vesical veins. The superior vesical artery supplies blood to the upper part of the bladder. The lower part of the bladder is supplied by the inferior vesical artery, both of which are branches of the internal iliac arteries. In females, the uterine and vaginal arteries provide additional blood supply. Venous drainage begins in a network of small vessels on the lower lateral surfaces of the bladder, which coalesce and travel with the lateral ligaments of the bladder into the internal iliac veins.
The lymph drained from the bladder begins in a series of networks throughout the mucosal, muscular and serosal layers. These then form three sets of vessels: one set near the trigone draining the bottom of the bladder one set draining the top of the bladder and another set draining the outer undersurface of the bladder. The majority of these vessels drain into the external iliac lymph nodes.
What Happens During A Urine Flow Test
A urine flow test may be done on an outpatient basis. This means you willgo home the same day. Or it may be done as part of your hospital stay.Procedures may vary depending on your condition and your healthcareprovider’s practices.
Generally, a urine flow test follows this process:
Recommended Reading: How Long Should You Take Lupron For Prostate Cancer
Common Symptoms Of Urological Diseases
Urology is a science that deals with the urinary tract. This means that the signs and symptoms caused by urological disease are usually related to your urinary system.
The following are some of the symptoms of urology that indicate you need to consult a urologist.
- bloody urine ,
- changes in urine color and odor,
- nausea and vomiting, as well
- impotence.
There are some symptoms that may not be mentioned and can be caused by urological diseases. If you have further questions, consult with your doctor to find the right solution for you.
What Is Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is the reduction of bladder control over time, leading to a sudden uncontrolled need for urination or leaking due to strain. Like other urinary problems, prostate conditions increase the risk of urinary incontinence.
This condition can also develop after procedures to treat prostate conditions such as radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy. The severity of leakage depends on the extent of the underlying cause. It can vary from a single drop to total emptying of the bladder.
Further, there are different types of urinary incontinence, including:
- Stress urinary incontinence is the leaking of urine due to pressure around the abdomen. In affected individuals, events like coughing, laughing, and exercise can increase abdominal pressure and urine loss.
- Urge urinary incontinence is the urgent need to urinate without any bladder control, leading to leaking of urine before reaching the restroom. It is caused by overactive bladder or uncontrolled bladder contraction.
- Overflow incontinence is the inability to empty the bladder, causing urine to leak completely. Men with an enlarged prostate or treatment-related injury to the bladder or urethra may experience overflow incontinence.
- Total incontinence is the complete lack of bladder function. Here the bladder cannot store any urine, leading to constant urination or frequent leaking.
Also Check: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
Ejaculation Physiology Anatomy And Dysfunction
Ejaculation is a complex process comprised of two phases: emission followed by expulsion. Following emission, during which time semen collects in the prostatic urethra, the bulbar urethra rapidly distends. Distension of the bulbar urethra triggers the expulsive phase of ejaculation, at which time the semen is rapidly propelled along the penile urethra by contraction of the bulbocavernosus muscle . Closure of the internal urethral sphincter is crucial to antegrade ejaculation, preventing retrograde flow of semen into the bladder.
The complex process of emission and expulsion is coordinated by sympathetic efferent fibers . Spinal cord injuries, as well as peripheral neuropathies, including iatrogenic injury during retroperitoneal and pelvic surgery, can result in partial or complete bladder neck dysfunction . Once bladder neck dysfunction occurs and retrograde ejaculation is noted, medical treatment can be offered to return antegrade flow during expulsion. Other patients may suffer from delayed or complete absence of ejaculation, while the last group of patients may have premature ejaculation .
Dianne M. Creasy, Robert E. Chapin, in, 2013
Inflammation Of The Prostate Gland
Bacteria sometimes cause prostatitis . More commonly, the underlying cause is uncertain. Consult your doctor promptly if you experience:
- fever
- pain in the groin
- urgent and frequent urination.
Treatment with antibiotics is essential for acute bacterial prostatitis. Admission to hospital is often necessary and, as with chronic bacterial prostatitis, specific antibacterial drugs are required for a long time.
Also Check: How Long Should You Take Lupron For Prostate Cancer
The Female Urethra Is Shorter Than The Male Urethra
Urine produced in the kidneys passes through the ureters, collects in the bladder, and is then excreted through the urethra. In females, the urethra is narrow and about 4 cm long, significantly shorter than in males. It extends from the bladder neck to the external urethral orifice in the vestibule of the vagina.
Male Internal Genital Organs
The ductus deferens which transports spermatozoa to the urethra starts at the inferior pole of the testis as a continuation of the epididymis. It passes through the inguinal canal and the deep inguinal ring before reaching the posterior surface of the bladder. The dilatation just before its termination is the ampulla of the vas deferens. The ductus terminates by joining the duct of the seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct. The ejaculatory ducts open into the prostatic part of the urethra.
The seminal vesicles secrete the bulk of the seminal fluid. Rarely the seminal vesicle may become infected and the tenderness may be felt during rectal examination. Normal seminal vesicles are not palpable per rectum.
Prostate gland
The prostate lies below the bladder. The urethra and the two ejaculatory ducts pass through the prostate. The ejaculatory ducts drain into the prostatic part of the urethra. The prostate has a base and an apex the base, which is the upper surface, is fused with the bladder neck and the blunt apex projects downwards. The posterior surface of the prostate has a groove which is normally felt on rectal examination. When the prostate enlarges this groove disappears. Veins of the prostate drain into the prostatic venous plexus around the gland. This in turn is connected to the vertebral venous plexuses . There are no valves in these connections. Malignant tumours of the prostate spread through these veins into the vertebral column.
Recommended Reading: Does Cialis Shrink An Enlarged Prostate
What Causes Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The cause of benign prostatic hyperplasia is not well understood however, it occurs mainly in older men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia does not develop in men whose testicles were removed before puberty. For this reason, some researchers believe factors related to aging and the testicles may cause benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Throughout their lives, men produce testosterone, a male hormone, and small amounts of estrogen, a female hormone. As men age, the amount of active testosterone in their blood decreases, which leaves a higher proportion of estrogen. Scientific studies have suggested that benign prostatic hyperplasia may occur because the higher proportion of estrogen within the prostate increases the activity of substances that promote prostate cell growth.
Another theory focuses on dihydrotestosterone , a male hormone that plays a role in prostate development and growth. Some research has indicated that even with a drop in blood testosterone levels, older men continue to produce and accumulate high levels of DHT in the prostate. This accumulation of DHT may encourage prostate cells to continue to grow. Scientists have noted that men who do not produce DHT do not develop benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Penis And Penile Urethra
The penile urethra runs through the penis, within the corpus spongiosum. The urethra exits distally through the glans penis, within which it becomes the fossa navicularis . The opening of the urethra on the tip of the glans penis is the urethral meatus. Further information can be found in the Penile Anatomy article. See the image below.
You May Like: What Is The Definition Of Prostate Gland
What Are The Symptoms Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia may include
- urinary frequencyurination eight or more times a day
- urinary urgencythe inability to delay urination
- trouble starting a urine stream
- a weak or an interrupted urine stream
- dribbling at the end of urination
- nocturiafrequent urination during periods of sleep
- urinary incontinencethe accidental loss of urine
- pain after ejaculation or during urination
- urine that has an unusual color or smell
Symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia most often come from
- a blocked urethra
- a bladder that is overworked from trying to pass urine through the blockage
The size of the prostate does not always determine the severity of the blockage or symptoms. Some men with greatly enlarged prostates have little blockage and few symptoms, while other men who have minimally enlarged prostates have greater blockage and more symptoms. Less than half of all men with benign prostatic hyperplasia have lower urinary tract symptoms.3
How Do I Get Ready For A Urine Flow Test
- Your healthcare provider will explain the procedure and you can ask questions.
- Generally, no prior preparation, such as fasting is needed.
- You may be told to drink about 4 glasses of water several hours before the test to be sure that your bladder is full. Don’t empty your bladder before arriving for the procedure.
- If you are pregnant or think you may be, tell your healthcare provider.
- Make sure your healthcare provider has a list of all medicines , herbs, vitamins, and supplements that you are taking.
Based on your health condition, your healthcare provider may request otherspecific preparation.
Read Also: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
Side View Of The Prostate
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is just in front of the rectum. The urethra runs through the center of the prostate, from the bladder to the penis, letting urine flow out of the body.
The prostate secretes fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. During ejaculation, the prostate squeezes this fluid into the urethra, and itâs expelled with sperm as semen.
The vasa deferentia bring sperm from the testes to the seminal vesicles. The seminal vesicles contribute fluid to semen during ejaculation.
