Anemia In Cancer Patients
Kiran Panesar, BPharmS , MRPharmS, RPh, CPhConsultant Pharmacist and Freelance Medical WriterOrlando, Florida
US Pharm
ABSTRACT:Anemia is a common complication inpatients with cancer. It can be caused by either the tumor itself or thechemotherapeutic regimen used. The severity and prevalence of thecondition varies based on a number of factors. Treatment is aimed atincreasing the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, reducing fatigue,and improving the patients overall quality of life.Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, iron supplementation, and red bloodcell transfusions have all been recommended in different settings. Whilethese have proven beneficial in some patients, the optimal therapeuticmodality is yet to be established.
Recent Update In The Pathogenesis And Treatment Of Chemotherapy And Cancer Induced Anemia
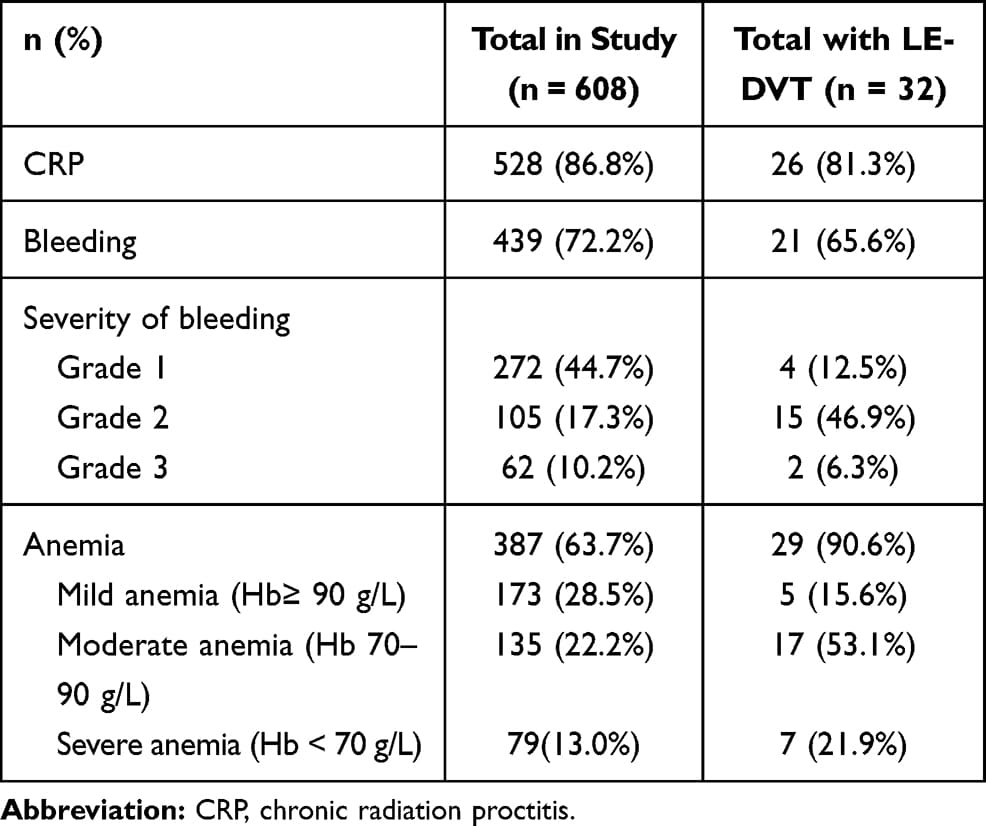
Cancer and chemotherapy-induced anemia is relatively common but underdiagnosed.
-
Anemia in cancer patients can negatively impact their quality of life and may worsen their prognosis and response to treatment particularly when radiation therapy is planned.
-
Blood transfusion can be offered in severe and symptomatic patients.
-
ESA should be avoided when cure is the goal in treating cancer patients, specially so if baseline Hb is above 1012gm/dL.
-
Cancer, along with chronic infections and inflammation, may increase the production of hepcidin which may result in poor utilization of iron creating a state of functional iron deficiency.
-
Intravenous third-generation iron formulations are safe and can be utilized in the treatment of both absolute and functional iron deficiency states.
During Watchful Waiting Or Active Surveillance
If you choose observation or active surveillance, your PSA level will be monitored closely to help decide if the cancer is growing and if treatment should be considered.
Your doctor will watch your PSA level and how quickly it is rising. Not all doctors agree on exactly what PSA level might require further action . Again, talk to your doctor so you understand what change in your PSA might be considered cause for concern.
Don’t Miss: Us Task Force Prostate Cancer Screening
Following Psa Levels During And After Prostate Cancer Treatment
A mans prostate-specific antigen blood level is often a good indicator of how effective treatment is or has been. Generally speaking, your PSA level should get very low after treatment. But PSA results arent always reliable, and sometimes doctors arent sure what they mean.
Before starting treatment, you might want to ask your doctor what your PSA level is expected to be during and after treatment, and what levels might cause concern. Its important to know that the PSA level is only one part of the overall picture. Other factors can also play a role in determining if cancer is still there, if it is growing, or if it has come back.
Its also important to know that PSA levels can sometimes fluctuate a bit on their own, even during or after treatment, so they may not always be a sign of what is actually happening with your cancer. Understandably, many men being treated for prostate cancer are very concerned about even very small changes in their PSA levels. The PSA level is an important tool to monitor the cancer, but not every rise in PSA means that the cancer is growing and requires treatment right away. To help limit unnecessary anxiety, be sure you understand what change in your PSA level might concern your doctor.
Salvage Radiotherapy And Androgen Deprivation Therapy
GETUG-AFU 16 was the first randomized trial comparing SRT vs. SRT and short ADT as salvage treatment for biochemical recurrent prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy and was presented in abstract form at the American Association of Clinical Oncology 2015 Annual Meeting. The trial randomized 743 patients most of them having high intermediate risk features . The 5-year PFS was 62.1% vs. 79.6% for SRT and SRT+ADT, respectively . The 5-year OS was 94.8% for RT vs. 96.2% for SRT+ADT . Cause of death was progressive disease in 2.1% of the patients on SRT arm vs. 0.8% in the SRT+ADT arm. Acute toxicities occurred more frequently in SRT+ADT arm . This trial will require longer follow-up to see if the benefits observed in progression-free survival translate into the same OS benefit .
Don’t Miss: Can Prostate Cancer Be Cured
Radiation Therapy: What It Is
This therapy, also known as radiotherapy, is a cancer treatment procedure that uses high doses of radiation to kill cancerous cells and shrink the tumor as well. At low doses, this procedure is used as an x-ray.
This therapy can be internal or external or both form. For external beam, a machine that is outside your body aims at the cancerous cells. For internal therapy, the radiations are placed inside your body inside or near the cancer.
For radiotherapy for prostate cancer, high-energy rays are used to kill the cancer cells. This treatment procedure does not cause pain. However, it may result in various side effects that might cause pain and make you feel uncomfortable. The good thing is that there are numerous ways to manage radiotherapy side effects with the help of your radiation oncologist.
Types Of Aplastic Anemia
There are two types of aplastic anemia:
- Acquired aplastic anemia: This type can be triggered by a virus, medication, toxic chemicals, or cancer treatments such as radiation or chemotherapy.
- Inherited aplastic anemia: This is caused by a genetic defect, and it can increase a persons risk of developing leukemia and other cancers.
You May Like: Prognosis For Metastatic Prostate Cancer
How Is Anemia Diagnosed
A diagnosis of anemia can be made through a complete blood count laboratory test that measures your hemoglobin level and other characteristics of your red blood cells, including their size. To determine what is causing the anemia, a number of other tests can be performed, including blood chemistry tests, a bone marrow exam, and test of your stool to check for internal bleeding.
Another test that can diagnose iron-deficiency anemia is serum ferritin level. Ferritin is a protein that stores iron. Low levels of ferritin lead to iron-deficiency anemia. Elevated levels of ferritin, on the other hand, are often found in patients with conditions that cause the body to absorb too much iron, such as hemochromatosis. Elevated levels of ferritin can also be due to inflammation. High levels of ferritin have been found in patients with some forms of cancer, such as lymphoma, cervical, and breast cancer, and high serum ferritin levels are associated with poor survival in some cancers.
Remove Devices From Your Skin
The manufacturer recommends taking these devices off your skin before your simulation or treatment:
- Continuous glucose monitor
If you use one of these, ask your radiation oncologist if you need to take it off. If you do, make sure to bring an extra device to put on after your simulation or treatment.
While your device is off, you may not be sure how to manage your glucose . Ask the healthcare provider who manages your diabetes care. Make sure to do this before your simulation or treatment appointment.
You May Like: Cold Medicine For Enlarged Prostate
Other Professionals Who Can Help
Your doctor, nurse or GP can refer you to these professionals.
- Physiotherapists can help with mobility and provide exercises to help improve fitness or ease pain. This can help you stay independent for longer.
- Counsellors, psychologists or psychotherapists can help you and your family work through any difficult feelings and find ways of coping. Many hospitals have counsellors or psychologists who specialise in helping people with cancer. You can also get free counselling on the NHS without a referral from your GP. Visit nhs.uk/counselling to find out more.
- Dietitians can give you advice about healthy eating, which might help with fatigue and staying a healthy weight. They can also help if you are losing weight or having problems eating.
- Occupational therapists can provide advice and access to equipment and adaptations to help with daily life. For example, help with dressing, eating, bathing or using the stairs.
- Social services, including social workers, can provide practical and financial advice and access to emotional support. They can give you advice about practical issues such as arranging for someone to support you at home. Whats available varies from place to place. Your GP, hospital doctor or nurse might be able to refer you to some services. The telephone number for your local social service department will be in the phonebook under the name of your local authority, on their website and at the town hall.
Prevalence Of Anemia In Radiation Oncology
Radiation oncologists often “inherit” anemia that has developed from surgical blood loss, myelotoxic chemotherapy, and/or advanced disease. The prevalence of anemia among patients presenting for radiation therapy is not well documented, but it is generally believed that a substantial proportion of these patients do become anemic. A recent literature review revealed a relatively high incidence of mild-to-moderate anemia in patients receiving single-agent or combination chemotherapy for nonmyeloid malignancies. A similar assessment in the radiation oncology setting is not available.
An ongoing retrospective study at the Beth Israel Medical Center is assessing the prevalence of anemia immediately prior to and during radiation therapy. We are performing this study through random chart sampling of patients who had received radiation therapy since December 1996. As of June 1999, a total of 574 patients were evaluable, with a relatively even distribution of cancers of the prostate , breast , head/neck , colon/rectum , lung/bronchus , and uterine cervix . The overall prevalence of anemia at presentation for radiation therapy was approximately 41% . At completion of radiation therapy, 43% of men and 63% of women had anemia , which usually was of mild-to-moderate severity .
You May Like: How To Find The Prostate Gland Externally
Your Gp Practice Nurse And District Nurse
Your GP, practice nurse, and district or community nurse will work with other health professionals to co-ordinate your care and offer you support and advice. They can also refer you to local services. They can visit you in your home and also help support your family. They might also care for you if you go into a nursing home or hospice.
Worsening Anemia Signals Poorer Outcomes In Men Treated For Advanced Prostate Cancer

Researchers from the Oregon Health & Science University Cancer Institute and Southwest Oncology Group have identified a new method of determining how men with advanced prostate cancer will respond to treatment. They found that worsening anemia during the first three months of hormonal therapy for prostate cancer that has spread predicts shorter survival and earlier relapse.
These results suggest that by monitoring anemia during the first three months of treatment, we can provide men with a better idea of how well they will fare, said principal investigator Tomasz Beer, M.D., director of the prostate cancer research program in the OHSU Cancer Institute. Beer presented results of this study at the 101st Annual Meeting of the American Urological Association in Atlanta on Tues., May 23.
Researchers also found that race alone was not a strong predictor of survival or disease progression. However, they found that men with the same hemoglobin levels before treatment experienced significantly different overall and progression-free survival depending on whether they were black or white. Hemoglobin levels in the blood are measured to monitor anemia. Lower levels of hemoglobin are considered anemic.
Overall, researchers found that anemic blacks fare worse than anemic whites and that blacks with high baseline hemoglobin fare better than whites with similar hemoglobin levels.
This study was funded by the National Cancer Institute.
Recommended Reading: Can A Swollen Prostate Affect Bowel Movements
Anemia And Colon Cancer
Colon cancer is caused by abnormal growth of cells in the large intestine . These cells can form tumors on or inside blood vessels in the colon that carry red blood cells.
Many people with colon cancer and bloody stool, as well as weakness and fatigue linked to their anemia. Iron deficiency anemia may be the first sign of colon cancer in some patients.
How May My Anemia Be Treated
During your chemotherapy treatment your doctor will ask you to have blood tests. These blood tests tell your doctor how your body is doing. When you have a blood test, a nurse or technician will take a small amount of blood from your arm with a needle. The blood tests will tell your doctor if your red blood cell count is low. If your red blood cell count is too low, your doctor may stop your chemotherapy until your red blood cell count is higher. The good news is that anemia caused by your chemotherapy is treatable.
Your doctor may give you medications to treat your anemia. Your doctor may also order a blood transfusion for your anemia. A blood transfusion is when you are given red blood cells donated by another person. The blood that you are given is tested to make sure that it is healthy. When you have a blood transfusion a bag of blood is given to you through an I.V. . A blood transfusion will help your body until it can make more red blood cells.
You May Like: Does Prostate Md Really Work
Analysis Of Missing Data
Table shows the reasons for nonresponse to the 5-year survey by treatment group. Overall, statistically significantly fewer men in the external beam radiotherapy group than in the radical prostatectomy group completed the 5-year survey . However, differences between treatment groups in the specific reasons for nonresponse were relatively small for example, 7% of radical prostatectomy patients had died compared with 11% of external beam radiotherapy patients. Refusal was the leading reason for nonresponse.
We further evaluated the possible effects of differential response levels by age at diagnosis on our reported outcomes by performing a last value forward analysis on urinary, bowel, sexual, and general health outcomes. We used data from the 2-year survey or from the 12- or 6-month surveys to estimate outcomes at 5 years after diagnosis. The impact of estimating outcomes on the reported comparisons was negligible.
Also Check: How To Shrink Prostate Mayo Clinic Naturally
What Are The Different Types Of Radiation Treatments
Radiation therapy uses concentrated doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and reduce the size of tumors. Depending on the type of cancer present in the body, one of two types of radiation therapy may be used.
External beam radiation therapy uses a large machine to send radiation into the specific area containing cancer. The radiation machine never touches the body, but it does move around to deliver radiation into precise parts of the body. External beam radiation is the most common type of treatment for many cancers.
Internal radiation therapy, on the other hand, uses a solid or liquid radiation source to physically deliver radiation inside the body. If a solid source of radiation is used, it only targets a specific part of the body for localized treatment, especially for cancers of the head, neck, breast, cervix, prostate, and eye. If a liquid source of radiation is used, its considered a systemic therapy that travels through the blood into tissues throughout the entire body.
Radiation therapy is often used in conjunction with other treatments or surgeries to target cancer in the most strategic way possible. Its often used to make surgery easier by shrinking the size of the tumor beforehand. Radiation therapy is even used during surgery to go straight into cancer cells without passing through the skin.
Recommended Reading: Multiple Myeloma And Prostate Cancer
What Are The Types Of Radiation Therapy Used For Prostate Cancer
Radiationtherapy for prostate cancer can be divided into two main categories.
Externalbeam radiation :Using a machine outside the body, beams of radiation are focused on theprostate gland. This can help relieve symptoms such as pain while limiting thedamage to the tissues surrounding the prostate.
The 4methods of external beam radiation are:
- Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy
- Stereotactic body radiation therapy
- Proton beam radiation therapy
Brachytherapy:Small radioactive pellets are inserted into the prostate, each one about thesize of a grain of rice. About 100 pellets are used to limit the damage tosurrounding tissues and organs. Brachytherapy is most often used forearly-stage cases and is sometimes combined with EBRT. The pellets can eitherbe inserted for a couple of days for high dosages or a few months for lowdosage depending on the patients overall status.
Radiotherapy Effects On Your Blood
Radiotherapy sometimes slows down the cells in the bone marrow that make your blood cells.
This is more likely if you’re having treatment to a large area of your body. Or having treatment to your:
Having chemotherapy with radiotherapy can make the effects on the bone marrow worse. You have blood tests before your chemotherapy to check your blood count.
You May Like: Can You Still Have Sex With No Prostate
Proton Beam Radiation Therapy
Proton beam therapy focuses beams of protons instead of x-rays on the cancer. Unlike x-rays, which release energy both before and after they hit their target, protons cause little damage to tissues they pass through and release their energy only after traveling a certain distance. This means that proton beam radiation can, in theory, deliver more radiation to the prostate while doing less damage to nearby normal tissues. Proton beam radiation can be aimed with techniques similar to 3D-CRT and IMRT.
Although in theory proton beam therapy might be more effective than using x-rays, so far studies have not shown if this is true. Right now, proton beam therapy is not widely available. The machines needed to make protons are very expensive, and they arent available in many centers in the United States. Proton beam radiation might not be covered by all insurance companies at this time.
Urinary And Bowel Changes
Radiation therapy can cause permanent urinary and bowel changes. Many people dont notice any changes or have any symptoms. However, some people have late side effects.
Late side effects may be similar to the ones you had during treatment. Theres a very small chance you may develop other side effects. For example:
- The opening of your bladder may become narrower.
- You may lose your ability to control your bladder.
- You may have blood in your urine.
- You may have bleeding from your rectum.
- Your rectum may be injured.
These side effects are rare. They may come and go over time or be persistent and chronic. Your healthcare team will help you manage them.
Even if you dont develop any late side effects, remember that the tissues in your bladder and rectum were affected by your radiation therapy. Call your radiation oncologist if you:
- Have any new urinary, bladder, or bowel symptoms.
- Need to have a colonoscopy. Avoid having a colonoscopy for the first year after radiation therapy.
- Need any type of urological or rectal procedure.
Read Also: What Is Stage 5 Prostate Cancer
