Understanding Prostate Cancers Progression
To determine the appropriate treatment, doctors need to know how far the cancer has progressed, or its stage. A pathologist, the doctor trained in analyzing cells taken during a prostate biopsy, will provide two starting pointsthe cancers grade and Gleason score.
- Cancer grade: When the pathologist looks at prostate cancer cells, the most common type of cells will get a grade of 3 to 5. The area of cancer cells in the prostate will also be graded. The higher the grade, the more abnormal the cells.
- Gleason score: The two grades will be added together to get a Gleason score. This score tells doctors how likely the cancer is to grow and spread.
After a biopsy confirms prostate cancer, the patient may undergo additional tests to see whether it has spread through the blood or lymph nodes to other parts of the body. These tests are usually imaging studies and may include a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or computed tomography scan.
What Are The Damico Risk Categories
The DAmico system provides an estimate of the risk of recurrence at five years after treatment. This system is one of the most widely used for risk assessment. It combines the PSA, Gleason score, and the clinical stage to create low, intermediate, and high risk categories. The higher the risk category, the higher the chance of recurrence is five years after treatment.
The DAmico risk categories are below. If one factor is putting you in a lower category but another is putting you in a higher category, then the higher category takes precedent.
Diagnosis Of Prostate Cancer
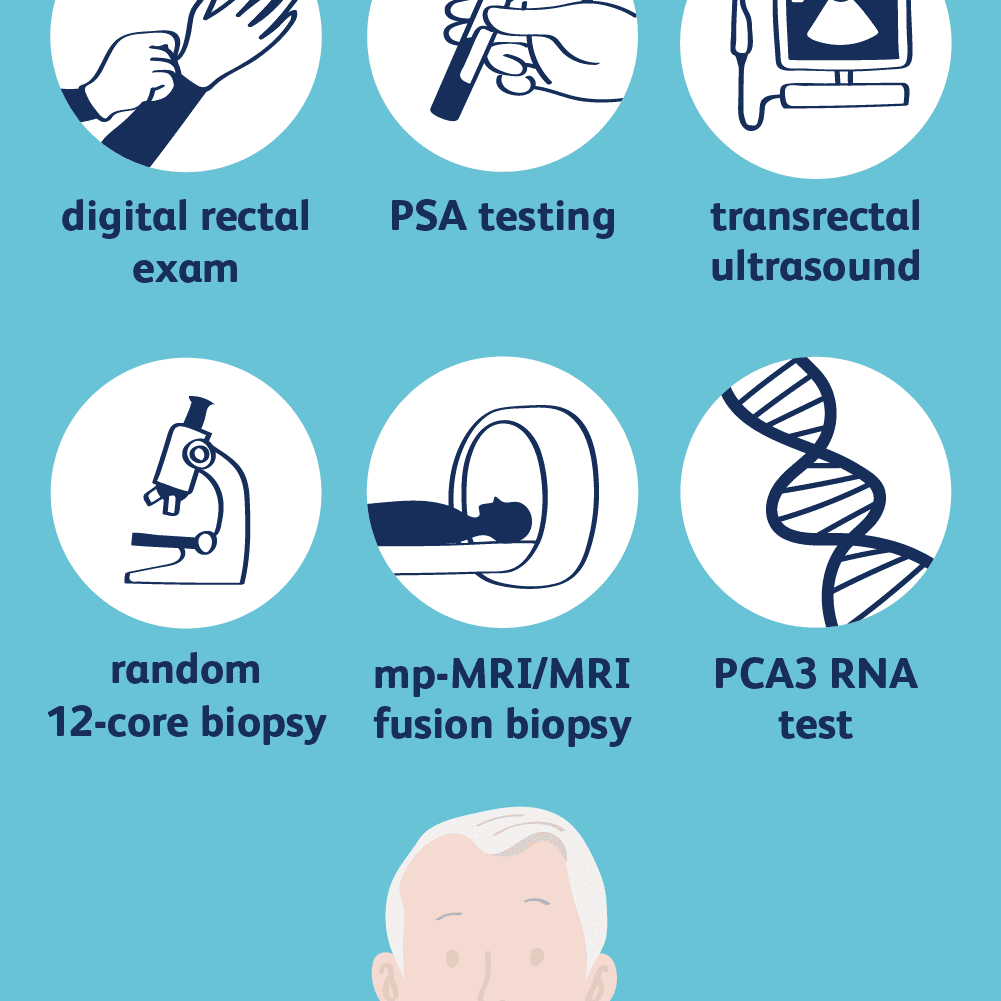
When a digital rectal exam or a PSA test reveal abnormal results, the next step is further testing to determine whether prostate cancer is present, or another cause may be to blame.
Your doctor will evaluate your test results and any symptoms you may be experiencing and recommend the next tests you may need. The most common diagnostic tests for the prostate include:
Ultrasound: A transrectal ultrasound involves inserting a small ultrasound probe into the rectum. The ultrasound machine sends out sound waves and then measures the echoes that bounce back off body structures to create an image of the landscape of the structure. It can provide images that show the extent of prostate enlargement or abnormalities.
MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging is sometimes used to create a more detailed set of images than an ultrasound can provide. Results will be reported as a PI-RADS score.
- PI-RADS 1: very lowclinically significant cancer is highly unlikely to be present
- PI-RADS 2: lowclinically significant cancer is unlikely to be present
- PI-RADS 3: intermediatethe chance of clinically significant cancer is neutral
- PI-RADS 4: highclinically significant cancer is likely to be present
- PI-RADS 5: very highclinically significant cancer is highly likely to be present
Regardless of which procedure is used to take a sample, the prostate tissue is then examined under a microscope by a pathologist, to confirm the presence or absence of cancerous cells.
You May Like: Urinozinc Prostate
How Common Is Prostate Cancer
About one in nine men will receive a prostate cancer diagnosis during his lifetime. Prostate cancer is second only to skin cancer as the most common cancer affecting males. Close to 200,000 American men receive a diagnosis of prostate cancer every year. There are many successful treatments and some men dont need treatment at all. Still, approximately 33,000 men die from the disease every year.
How To Check For Prostate Cancer At Home
Medically Reviewed by: Dr. BautistaUpdated on: November 18, 2019
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men, but the good news is its also one of the most successfully treated through both conventional and holistic prostate cancer treatment. Prostate cancer develops in the walnut-shaped gland that is responsible for producing semen and transporting sperm. Many men, and some women, question, can prostate cancer spread?. Although its not always the case, this type of cancer is typically slow-growing. It lingers in the prostate gland without spreading or causing major damage.
However, if prostate cancer is left untreated, it will eventually destroy the prostate and spread to local and distant organs. The best thing you can do is be proactive, take control of your health, and be familiar with any changes going on in your body. With that said, regular checkups are important, but you can also do this yourself. If youre wondering how to check for prostate cancer at home, the best thing you can do is know what symptoms to look for, and stay knowledgeable about what the four stages of prostate cancer are.
Don’t Miss: Zinc And Prostate
Biopsy During Surgery To Treat Prostate Cancer
If there is more than a very small chance that the cancer might have spread , the surgeon may remove lymph nodes in the pelvis during the same operation as the removal of the prostate, which is known as a radical prostatectomy .
The lymph nodes and the prostate are then sent to the lab to be looked at. The lab results are usually available several days after surgery.
Can A Blood Test Determine If You Have Prostate Cancer
When it comes to prostate cancer, screenings play a key role in saving lives. Earlier detection when there are no symptoms leads to earlier treatment and better outcomes. And the good news is that many prostate cancer screenings can be done with a simple blood test. But thats just the start.
Learn more about how the PSA is the first step in the prostate cancer journey.
Understanding the PSA
For more than 20 years, there has been a blood test to monitor men for high levels of a protein called a prostate-specific antigen, or PSA, that is often associated with prostate cancer. Unfortunately, this test is not perfect many harmless conditions can cause heightened levels of this protein, leading to unnecessary tests and procedures that carry their own risk.
The uncertainty over the value of the PSA test led the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in 2012 to recommend it only be given to people at high risk of prostate cancer. Other groups, including the American Urological Association, opposed this decision at the time.
But that recommendation has been softened. Instead of advising against this test for most men, the task force now suggests that men aged 55 to 69 should talk to their doctor about its risks and potential benefits.
Dr. Vipul Patel, a urologist and robotic surgeon at the AdventHealth, calls that a step in the positive direction.
If youre over 50 years old, get PSA screening and get a rectal prostate exam, he says.
What the PSA Can Reveal
Read Also: Characteristics Of Prostate Cancer
What Causes Prostate Cancer
Experts arent sure why some cells in the prostate gland become cancerous . Genetics appear to play a role. For example:
- Youre two to three times more likely to get prostate cancer if your father, brother or son has the disease.
- Inherited mutated breast cancer genes and other gene mutations contribute to a small number of prostate cancers.
What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is often grouped into four stages.
- Stages I & II: The tumor has not spread beyond the prostate. This is often called early stage or localized prostate cancer.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread outside the prostate, but only to nearby tissues. This is often called locally advanced prostate cancer.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread outside the prostate to other parts such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver or lungs. This stage is often called advanced prostate cancer.
When an early stage prostate cancer is found, it may be treated or placed on surveillance . If prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer. Stage IV prostate cancer is not curable, but there are many ways to control it. Treatment can stop advanced prostate cancer from growing and causing symptoms.
There are several types of advanced prostate cancer, including:
Biochemical Recurrence
If your Prostate Specific Antigen level has risen after the first treatment but you have no other signs of cancer, you have “biochemical recurrence.”
Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Non-Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- Lymph nodes outside the pelvis
- Bones
- Other organs
Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer
Don’t Miss: Does An Enlarged Prostate Make It Hard To Poop
Prostate Cancer Stages And Gradesthis Is What They Tell Us
Cancer grade refers to how quickly the cancer cells will grow and spread prostate cancer is graded using the Gleason score. Cancer stage refers to the size of the tumor and whether or not it has spread to other parts of the body prostate cancer is staged using the TNM system. T= the size of the tumor. N= whether there is any lymph node spread. M=whether there is any metastasis.
How Does Tumor Grade Affect A Patients Treatment Options
Doctors use tumor grade and other factors, such as cancer stage and a patients age and general health, to develop a treatment plan and to determine a patients prognosis . Generally, a lower grade indicates a better prognosis. A higher-grade cancer may grow and spread more quickly and may require immediate or more aggressive treatment.
The importance of tumor grade in planning treatment and determining a patients prognosis is greater for certain types of cancer, such as soft tissue sarcoma, primary brain tumors, and breast and prostate cancer.
Patients should talk with their doctor for more information about tumor grade and how it relates to their treatment and prognosis.
Selected Reference
American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed. New York, NY: Springer 2010.
Related Resources
Also Check: Prostate Gland Definition And Function
What The Stages Mean
The higher the stage, the more advanced the cancer.
Stage I cancer. The cancer is found only in only one part of the prostate. Stage I is called localized prostate cancer. It cannot be felt during a digital rectal exam or seen with imaging tests. If the PSA is less than 10 and the Gleason score is 6 or less, Stage I cancer is likely to grow slowly.
Stage II cancer. The cancer is more advanced than stage I. It has not spread beyond the prostate and is still called localized. The cells are less normal than cells in stage I, and may grow more rapidly. There are two types of stage II prostate cancer:
- Stage IIA is most likely found in only one side of the prostate.
- Stage IIB may be found in both sides of the prostate.
Stage III cancer. The cancer has spread outside the prostate into local tissue. It may have spread into the seminal vesicles. These are the glands that make semen. Stage III is called locally advanced prostate cancer.
Stage IV cancer. The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body. It could be in nearby lymph nodes or bones, most often of the pelvis or spine. Other organs such as bladder, liver, or lungs can be involved.
Staging along with the PSA value and Gleason score help you and your doctor decide on the best treatment, taking into account:
- Your age
- Your symptoms
- Your feelings about side effects of treatment
- The chance that treatment can cure your cancer or help you in other ways
Metastases: Whether The Cancer Has Spread
The spread of cancer is measured in two ways: by lymph node involvement, and by its appearance in other organs or parts of the body, or metastasis.
Lymph node staging, or N-staging, determines whether the cancer is present in nearby lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are tiny organs that are part of the immune system.NX: The regional lymph nodes cannot be evaluated.N0: The cancer has not spread to lymph nodes in the immediate area.N1: The cancer has spread to lymph nodes in the pelvic region.
The M in the TNM system indicates whether the prostate cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs or the bones. This is called distant metastasis.
MX: Metastasis cannot be evaluated.M0: The cancer has not metastasized beyond the immediate prostate region.M1: The cancer has metastasized deeper into the body.
- M1a: The cancer has spread to lymph nodes away from the groin area.
- M1b: The cancer has spread to the bones.
- M1c: The cancer has spread to another part of the body, with or without spread to the bones.
The combination of your full staging results, including your grade and your T, N, and M stages, paints a more complete picture of how the cancer is progressing. This enables your doctors to determine which treatments have the best chance or controlling or eradicating your cancer.
Also Check: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Stages Of Prostate Cancer
|
Any T, any N, M1 Any Grade Group Any PSA |
The cancer might or might not be growing into tissues near the prostate and might or might not have spread to nearby lymph nodes . It has spread to other parts of the body, such as distant lymph nodes, bones, or other organs . The Grade Group can be any value, and the PSA can be any value. |
Prostate cancer staging can be complex. If you have any questions about your stage, please ask someone on your cancer care team to explain it to you in a way you understand.
While the stage of a prostate cancer can help give an idea of how serious the cancer is likely to be, doctors are now looking for other ways to tell how likely a prostate cancer is to grow and spread, which might also help determine a mans best treatment options.
What Can Be Done
If your prostate cancer has recurred, your doctor will likely order some imaging tests to better determine where in your body the cancer has returned. Bone scans, CT scans, and MRIs are the most common tests ordered to find where in the body prostate cancer has recurred.
Many treatment options are available for prostate cancer that has returned. The one that you and your physician choose depends on individual factors such as what treatment you have already received, where in the body your prostate cancer has returned, how your cancer has spread, your general health, and your age.
If your prostate cancer is thought to have recurred in only a small area and has not spread to other areas of the body, then radiation therapy to that area may be an option.
If your prostate cancer has most likely spread to multiple areas of the body, then hormonal therapy would likely be an option. Chemotherapy can also be used when the cancer has spread to multiple sites.
-
Geller J. Basis for Hormonal Management of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cancer. 1993 Feb 1 71:1039-45.
-
Kupelian PA, Buchsbaum JC, Elshaikh M, et al. Factors Affecting Recurrence Rates After Prostatectomy or Radiotherapy in Localized Prostate Carcinoma Patients With Biopsy Gleason Score 8 or Above. Cancer. 2002 Dec 1 95:2302-7.
-
Vickers AJ, Bianco FJ Jr, Boorjian S, et al. Does a Delay Between Diagnosis and Radical Prostatectomy Increase the Risk of Disease Recurrence? Cancer. 2006 Feb 1 106:576-80.
You May Like: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
How Is The Gleason Score Derived
The pathologist looking at the biopsy sample will assign one Gleason grade to the most predominant pattern in your biopsy and a second Gleason grade to the second most predominant pattern. For example: 3 + 4. The two grades will then be added together to determine your Gleason score. Theoretically, Gleason scores range from 2-10. However, since Dr. Gleasons original classification, pathologists almost never assign scores 2-5, and Gleason scores assigned will range from 6 to 10, with 6 being the lowest grade cancer.
What Is Prostate Cancer Staging And Why Is It Used
Prostate cancer staging is a system used during the diagnosis process to determine the extent of a patients cancer. The stages of prostate cancer are used to describe the growth and spread of the cancer cells.
The four prostate cancer stages are used by healthcare professionals to:
- Classify the severity of the prostate cancer
- Provide a prognosis
- Determine the best course of treatment
- Enable researchers and healthcare providers to share patient information
Determining the stage of cancer may also necessary at other times. Cancer staging might also be done after drug therapy is used to shrink a tumor before surgery, for example. This is called post-neoadjuvant therapy staging. In addition to this, staging might also be done after treatment or if prostate cancer comes back.
Don’t Miss: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
Whats The Difference Between Cancer Grading And Staging
If your healthcare provider suspects prostate cancer, he or she will refer you for a prostate biopsy. During this procedure, a small sample of prostate cells from the tumor is removed and evaluated under the microscope. This microscopic examination is what gives a cancer its grade. Cancer grade refers to how quickly it may grow or spread . For the most part, the lower the grade, the slower the growth of the tumor.
In addition to finding out the grade of your prostate cancer, it is important to determine its stage. Cancer stage refers to the size of the tumor and whether or not it has spread to other parts of the body. Stages mean different things for different types of cancer, but usually the higher the number, the more advanced the cancer.
How Is Prostate Cancer Staged
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer that develops in men and is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in American men, behind lung cancer and just ahead of colorectal cancer. The prognosis for prostate cancer, as with any cancer, depends on how advanced the cancer has become, according to established stage designations.
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized gland present only in men, found in the pelvis below the bladder. The prostate gland wraps around the urethra and lies in front of the rectum. The prostate gland secretes part of the liquid portion of the semen, or seminal fluid, which carries sperm made by the testes. The fluid is essential to reproduction.
The term to stage a cancer means to describe the evident extent of the cancer in the body at the time that the cancer is first diagnosed.
- Clinical staging of prostate cancer is based on the pathology results, physical examination, PSA, and if appropriate, radiologic studies.
- The stage of a cancer helps doctors understand the extent of the cancer and plan cancer treatment.
- Knowing the overall results of the different treatments of similarly staged prostate cancers can help the doctor and patient make important decisions about choices of treatment to recommend or to accept.
You May Like: What Is The Va Disability Rating For Prostate Cancer
