Can Prostate Cancer Be Found Early
Screening tests are available to find prostate cancer early, but government guidelines don’t call for routine testing in men at any age. The tests may find cancers that are so slow-growing that medical treatments would offer no benefit. And the treatments themselves can have serious side effects. The American Cancer Society advises men to talk with a doctor about screening tests, beginning at:
- Age 50 for average-risk men who expect to live at least 10 more years
- Age 45 for men at high risk this includes African-Americans and those with a father, brother, or son diagnosed before age 65
- Age 40 for men with more than one first-degree relative diagnosed at an early age
The U.S.Preventive Services Task Force says that testing may be appropriate for some men age 55 â 69. They recommend that men talk to their doctor to discuss the potential risks and benefits of being tested.
8
What Are Grade Groups
Grade Groups are a new way to grade prostate cancer to address some of the issues with the Gleason grading system.
As noted above, currently in practice the lowest Gleason score that is given is a 6, despite the Gleason grades ranging in theory from 2 to 10. This understandably leads some patients to think that their cancer on biopsy is in the middle of the grade scale. This can compound their worry about their diagnosis and make them more likely to feel that they need to be treated right away.
Another problem with the Gleason grading system is that the Gleason scores are often divided into only 3 groups . This is not accurate, since Gleason score 7 is made up of two grades , with the latter having a much worse prognosis. Similarly, Gleason scores of 9 or 10 have a worse prognosis than Gleason score 8.
To account for these differences, the Grade Groups range from 1 to 5 :
- Grade Group 1 = Gleason 6
- Grade Group 2 = Gleason 3+4=7
- Grade Group 3 = Gleason 4+3=7
- Grade Group 4 = Gleason 8
- Grade Group 5 = Gleason 9-10
Although eventually the Grade Group system may replace the Gleason system, the two systems are currently reported side-by-side.
Anatomic structures and major veins of the male pelvis.
FIGURE 1.
Anatomic structures and major veins of the male pelvis.
FIGURE 2.
FIGURE 2.
How Prostate Cancer Is Diagnosed And Staged
Cancer staging helps you and your doctor understand how advanced your cancer is and how much it has spread at the time of diagnosis. Knowing your cancer stage also helps your doctor determine the best treatment options for you and estimate your chance of survival.
The most widely used staging system for cancer is the TNM system that classifies cancer from stage 1 to stage 4.
TNM stands for:
- Tumor: the size and extent of the tumor
- Nodes: the number or extent of nearby lymph node involvement
- Metastasis: whether cancer has spread to distant sites in the body
The TNM scale is used for many types of cancer. When a doctor uses it to determine your prostate cancer stage, theyll consider several other factors as well, including:
- grade groups
Recommended Reading: Prostatic Neoplasms
What Does It Mean When There Are Different Core Samples With Different Gleason Scores
Cores may be samples from different areas of the same tumor or different tumors in the prostate. Because the grade may vary within the same tumor or between different tumors, different samples taken from your prostate may have different Gleason scores. Typically, the highest Gleason score will be the one used by your doctor for predicting your prognosis and deciding on treatment options.
What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
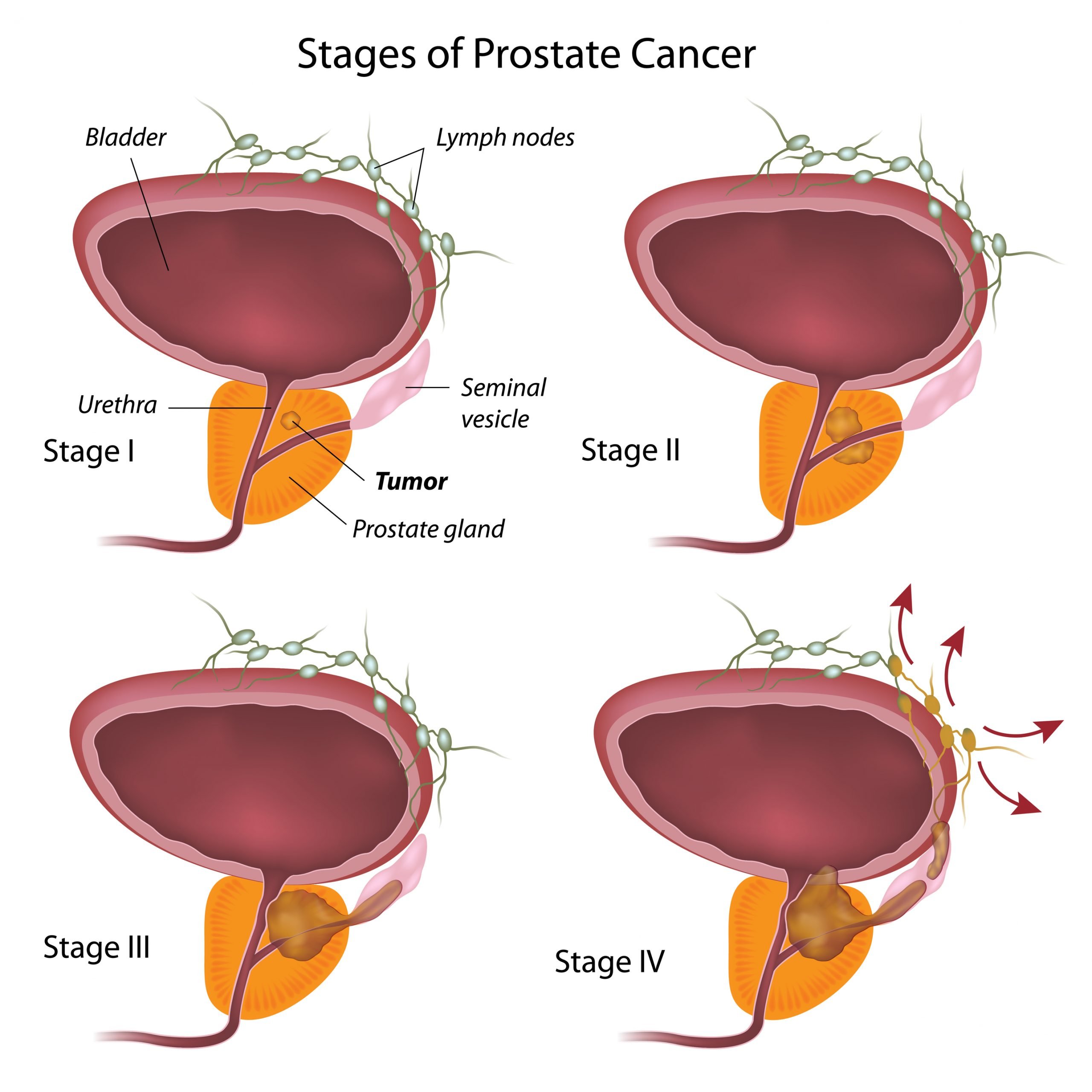
Your healthcare provider uses the Gleason score and Grade Groups to stage prostate cancer based on its projected aggressiveness. To get this information, the pathologist:
- Assigns a grade to each type of cell in your sample. Cells are graded on a scale of three to five . Samples that test in the one to two range are considered normal tissue.
- Adds together the two most common grades to get your Gleason score .
- Uses the Gleason score to place you into a Grade Group ranging from one to five. A Gleason score of six puts you in Grade Group 1 . A score of nine or higher puts you in Grade Group five . Samples with a higher portion of more aggressive cells receive a higher Grade Group.
Read Also: How Long Can You Take Lupron For Prostate Cancer
How Common Is Prostate Cancer
About one in nine men will receive a prostate cancer diagnosis during his lifetime. Prostate cancer is second only to skin cancer as the most common cancer affecting males. Close to 200,000 American men receive a diagnosis of prostate cancer every year. There are many successful treatments and some men dont need treatment at all. Still, approximately 33,000 men die from the disease every year.
Features Of Pin Cells
Basal cellspecific monoclonal antibodies directed against highmolecular weight keratin are used to identify HGPIN cells. Normal prostatic epithelial cells are consistently stained with these antibodies, showing a continuous, intact, circumferential basal cell layer. Cancer cells have lost their receptors for these antibodies.
Basal cell disruption affects 56% of patients with HGPIN and is usually found in glands adjacent to invasive cancer. The degree of disruption correlates with HGPIN. More than one third of the basal cell layer is lost in 52% of foci that contain HGPIN.
In persons with HGPIN and in many with low-grade cancer, the basement membrane that surrounds the prostatic glands remains intact. The expression of collagenase type 4 in PIN and associated cancer cells is abnormally high. The presence of collagenase type 4 and other enzymes is associated with a degradation of the basement membrane, allowing cell invasion into the stroma. Concurrently, the basal cell layer is diminished. This seems to occur primarily at sites of glandular outpouching.
Increased angiogenesis with an increased number of microvessels is associated with the progression of HGPIN to cancer. The microvessels in HGPIN are shorter than those in benign epithelium and have irregular contours and open lumens, an increased number of endothelial cells, and a greater distance from the basement membrane.
Also Check: Can An Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
Also Check: Tamsulosin Ejaculation
How Important Is The Gleason Score
The Gleason score is very important in predicting the behavior of a prostate cancer and determining the best treatment options. Still, other factors are also important, such as:
- The blood PSA level
- How much of each core is made up of cancer
- The number of cores that contain cancer
- Whether cancer was found in both sides of the prostate
- Whether the cancer has spread outside the prostate
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have prostate cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get prostate cancer?
- What is my Gleason score? What is my Grade Group? What do these numbers mean for me?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the prostate gland?
- What is the best treatment for the stage of prostate cancer I have?
- If I choose active surveillance, what can I expect? What signs of cancer should I look out for?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Is my family at risk for developing prostate cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Prostate cancer is a common cancer that affects males. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and remain in the prostate gland. For a small number, the disease can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. Men with slow-growing prostate cancers may choose active surveillance. With this approach, you can postpone, and sometimes completely forego, treatments. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for you based on your Gleason score and Group Grade.
You May Like: Fiducials Prostate Cancer
If Diagnosed Keep Records
If you are diagnosed with prostate cancer, the Prostate Cancer Free Foundation offers help. View or print our Patient Form. Or get a notebook and keep records. You will need to share personal health information, medications, tests and diagnostic information with your Urologist, Radiologist, Oncologist and health insurance.
Cancer Lethality Set Early
The study looked for changes in cancer aggressiveness in men diagnosed with prostate cancer from 1982 to 2004. All of the men had their prostates removed after diagnosis, and biopsy samples were taken from the glands. The Harvard team reexamined the samples and graded them using a tool called the Gleason score, which assigns a number from 2 to 10 based on how abnormal the cells look under a microscope. High-scoring or high-grade cancers tend to be the most lethal.
Over the study period, fewer and fewer men were diagnosed with advanced, late-stage prostate cancers that had spread beyond the prostate gland. This reflected the growing use of prostate-specific antigen testing to diagnose prostate cancers earlier and earlier. In contrast, the proportion of high-grade cancers, as measured by the Gleason score, remained relatively stable rather than gradually becoming more aggressive. Previous studies have seen a similar pattern.
Its a very interesting study that confirms what previous studies have found, says Dr. Marc B. Garnick, a prostate cancer specialist at Harvard-affiliated Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center who was not involved in the study. There may be rare exceptions, but in the vast majority the cancer is born with a particular Gleason score.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Definition Of Prostate
Build A Plan For Treatment
Get a copy of the the Study to share with your Doctor as you develop your treatment plan. The Study follows almost 130,000 men for 15 years after treatment, displaying their trends for recurrence of cancer. See which men had their cancer return, versus those who were treated once requiring no additional treatment. Ask your Doctor about your odds of remaining in remission.
How Fast Does Prostate Cancer Spread To The Bones
Early detection can catch prostate cancer even before there are any symptoms. Some types of prostate cancer grow very slowly.
There are four main stages of prostate cancer. Within each stage, the cancer is graded based on factors like the size of tumor, prostate-specific antigen level, and other clinical signs.
If the cancer has spread to the bones, its considered to be the most advanced, or stage 4.
Newer lab tests look at the genes inside cancer cells. This can provide more information on how quickly the prostate cancer may progress.
Theres also a grading system known as the Gleason system, which assigns the cancer into a grade group based on how closely it resembles normal tissue.
During the biopsy to diagnose prostate cancer, the cells are closely examined. The more abnormal cells that are in the biopsy sample, the higher the Gleason score and grade group.
When more abnormal cells are present, the cancer is more likely to spread quickly.
You May Like: Describe The Effect Of An Enlarged Prostate Gland On The Urinary Function Of A Male
Morphologic Similarities Of Hgpin And Cancer
Many studies have demonstrated a remarkable similarity between the nuclear characteristics of prostate cancer cells and HGPIN compared with those of normal and hyperplastic epithelium. These include nuclear area, deoxyribonucleic acid content, chromatin content, chromatin distribution, nuclear perimeter, nuclear diameter, and nuclear roundness.
Cancer cells and PIN also share nucleolar abnormalities. The results of these studies further support the concept that a morphologic continuum from normal to PIN to cancer exists.
Are Older Men Undertreated
Schwartz and colleagues reviewed the treatment decisions and factors influencing them in a cohort of men with localized prostate cancer. Age, comorbidity, and Gleason score were found to be independent predictors of suboptimal treatment. It was concluded that most men older than 70 years with moderately or poorly differentiated tumors and no to mild comorbidity were given suboptimal treatment. Most of these men were undertreated, receiving watchful waiting therapy when potentially curative therapy could have been applied. With optimal treatment, clinical outcomes could have been improved.
Thompson and colleagues investigated otherwise healthy octogenarians diagnosed with prostate cancer who underwent radical prostatectomy. At the last follow-up visit, 10 patients had survived more than a decade after surgery, and 3 patients had died within 10 years of surgery. The remaining 6 patients were alive at less than 10 years of follow-up. Seventy-four percent of patients were continent. No patient had died of prostate cancer, and the 10-year, all-cause survival rate was similar to that observed in healthy patients 60 to 79 years old undergoing radical prostatectomy. These findings indicate that careful selection of patients even older than 80 years can achieve satisfactory oncologic and functional outcomes after surgery. It is important to note, however, that the rate of urinary incontinence after surgery exceeds that of younger counterparts.
Don’t Miss: Tamsulosin Side Effects Ejaculation Problems
Putting People At The Centre Of Research
PCR intend to set up the first-of-its-kind prostate cancer registry in the UK.
This registry would revolutionise prostate cancer diagnosis, treatment and care by putting real people at the centre of it all. But joining would not only benefit others. You would also be able to access more relevant information about your treatment and care, be kept informed about the most relevant clinical trials you are eligible for, and provide critical evidence to speed up and shape vital research. We are in the planning stage for this registry, but we need your support to make it a reality!
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Having An Mri Scan Before A Biopsy
Advantages
- It can give your doctor information about whether there is cancer inside your prostate, and how quickly any cancer is likely to grow.
- Its less likely than a biopsy to pick up a slow-growing cancer that probably wouldnt cause any problems in your lifetime.
- It can help your doctor decide if you need a biopsy if theres nothing unusual on the scans, this means youre unlikely to have prostate cancer that needs to be treated. You may be able to avoid having a biopsy, and its possible side effects.
- If you do need a biopsy, your doctor can use the scan images to decide which parts of the prostate to take samples from.
- If your biopsy finds cancer, you probably wont need another scan to check if it has spread, as the doctor can get this information from your first MRI scan. This means you can start talking about suitable treatments as soon as you get your biopsy results.
Disadvantages
- Being in the MRI machine can be unpleasant if you dont like closed or small spaces.
- Some men are given an injection of dye during the scan this can sometimes cause mild side effects.
Read Also: Chemo Drug For Prostate Cancer
Prognoses Associated With Hgpin And Asap
Prostate cancer develops within 1-2 years in an estimated 30% of men with multiple cores containing HGPIN and in perhaps even more men with ASAP. Indeed, the presence of HGPIN or ASAP cells in multiple areas has such a high predictive value for prostate adenocarcinoma that the existence of these cells alerts the pathologist to search for any areas in the biopsy sample that might harbor carcinoma.
However, the presence of HGPIN or ASAP does not necessarily imply that prostate cancer is inevitable although these conditions may progress to invasive cancer, HGPIN and ASAP remain stable for years in many patients and regress in some individuals.
When biopsy reveals prostate cancer, the prognosis is determined by the grade and stage of the cancer. The presence of HGPIN or ASAP in such cases does not alter the prognosis. The mean volume of HGPIN or ASAP in prostates with cancer is 1.2-1.32 mL. The volume of HGPIN correlates directly with increasing pathologic stage, Gleason grade, positive surgical margins, and perineural invasion.
Patients with HGPIN or ASAP not associated with existing prostate cancer should be informed about the need for surveillance. Patients should also be told that neither HGPIN nor ASAP seems to affect PSA levels.
No data demonstrate a correlation between the amount of PIN and the timing of tumor progression or length of survival.
What Are The Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Early-stage prostate cancer rarely causes symptoms. These problems may occur as the disease progresses:
- Frequent, sometimes urgent, need to urinate, especially at night.
- Weak urine flow or flow that starts and stops.
- Painful urination .
- Painful ejaculation and erectile dysfunction .
- Blood in semen or urine.
- Lower back pain, hip pain and chest pain.
- Leg or feet numbness.
You May Like: Fiducial Marker Placement Prostate
Diagnosis Of Pin And Asap
Only prostate biopsy can be used to identify HGPIN or ASAP. Neither type of lesion alone causes symptoms, and therefore, no physical examination findings reveal the presence of PIN or ASAP. The PSA and other tumor markers such as Exosome and Decipher do not assist when HGPIN or ASAP is present.
The prostate may be enlarged secondary to BPH, but this is unrelated to HGPIN. Areas in the prostate may have palpable nodules, or other areas may indicate cancer. None of these physical findings suggests the presence of HGPIN or ASAP.
Some pathologists may note that a small focus of atypical glands has been identified in a biopsy specimen but that, although the finding is suspicious for cancer, not enough cytologic or architectural atypia are present to diagnose cancer. In this scenario, the pathologist usually suggests that another biopsy be performed.
Neither HGPIN nor ASAP seems to affect PSA production, meaning that PSA evaluation cannot be used to detect or to monitor the progression of these entities. In addition, neither HGPIN nor ASAP are readily detectable with any imaging technology.
What Does It Mean If My Biopsy Report Mentions The Word Core
The most common type of prostate biopsy is a core needle biopsy. For this procedure, the doctor inserts a thin, hollow needle into the prostate gland. When the needle is pulled out it removes a small cylinder of prostate tissue called a core. This is often repeated several times to sample different areas of the prostate.
Your pathology report will list each core separately by a number assigned to it by the pathologist, with each core having its own diagnosis. If cancer or some other problem is found, it is often not in every core, so you need to look at the diagnoses for all of the cores to know what is going on with you.
Recommended Reading: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
