Sex And The Prostate: Overcoming Erectile Dysfunction When You Have Prostate Disease
If you are concerned about erectile function, its important to understand what erectile dysfunction really is. Failing to have an erection one night after youve had several drinks or even for a week or more during a time of intense emotional stress is not erectile dysfunction. Nor is the inability to have another erection soon after an orgasm. Nearly every man occasionally has trouble getting an erection, and most partners understand that.
Erectile dysfunction is the inability to attain and maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse at least 25% of the time. The penis doesnt get hard enough, or it gets hard but softens too soon. The problem often develops gradually. One night it may take longer or require more stimulation to get an erection. On another occasion, the erection may not be as firm as usual, or it may end before orgasm. When such difficulties occur regularly, its time to talk to your doctor.
Erectile dysfunction can have many causes, including some forms of prostate disease and medications and surgery for prostate cancer. Fortunately, in many cases, this problem can often be effectively addressed. Some men find relief by taking medications to treat erectile dysfunction. If these arent effective for you, a number of other options, including injections and vacuum devices, are available. The possibility of finding the right solution is now greater than ever.
Can You Live Without A Prostate
You can live without a prostate, though there are some side-effects.
The prostate is removed to prevent the spread of prostate cancer, while it might also be removed because it has enlarged through normal ageing and is putting pressure on the uretha .
A prostatectomy;is the removal of all or part of a prostate, with the most common procedure being the;transurethral resection of the prostate .
Laser;prostatectomies are also performed which is the least invasive type of removal.
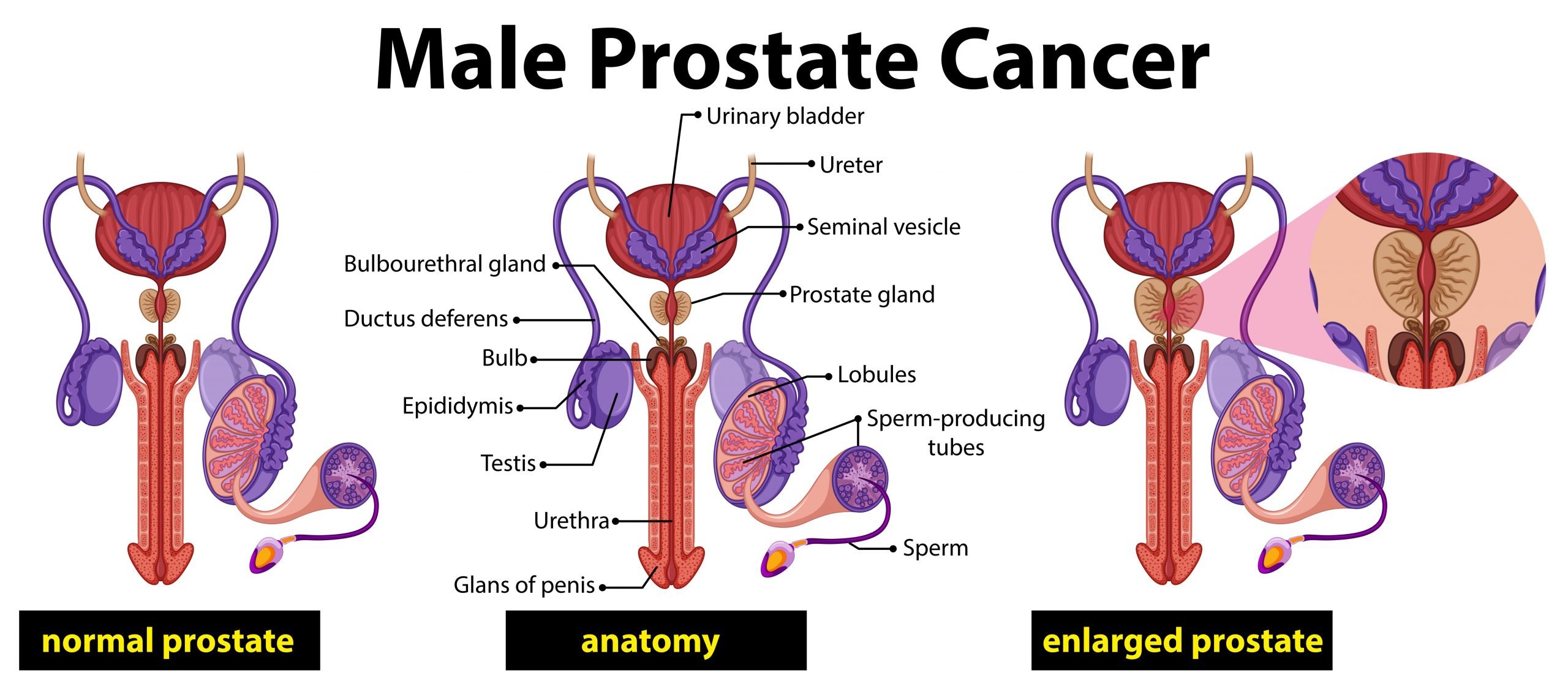
What Is An Enlarged Prostate
The prostate is an essential gland in the male reproductive system. It contributes to the semen volume and synthesizes a substance that supports sperm cells.
This gland is below the urinary bladder, surrounding the urethra. In the bladder neck. Thus, as it grows, it can put pressure over the urethra or the urinary bladder. However, what is an enlarged prostate? Is it the same as prostate cancer?
An enlarged prostate is simply a gland that increased in size. It is not caused by cancer. Another medical term is benign prostatic enlargement, where benign means theres no cancer. Another name is benign prostatic hyperplasia .
When we talk about hyperplasia, we refer to an increase in number and not size. Thus, in prostatic hyperplasia, there are more prostate cells . However, they remain the same size as normal prostate tissue. Such an increase in the number of cells causes an enlarged prostate. It usually starts in men after the age of 40. But they typically find out when they are near their 50s .
In some cases, an enlarged prostate grows evenly. In other instances, prostate growth is more irregular. When the overgrowth is near the center, it presses the urethra on the outside.
As a result, the urethra becomes narrow, compromising the urine flow. As a result, 1 out of 3 men over 50 years old report urinary symptoms. In the majority of cases, they are caused by an enlarged prostate gland .
Don’t Miss: Will Blood Test Show Prostate Cancer
Is It Common To Have Prostate In Women
You might have heard few people talking about female prostate issues. But the real fact is that female body does not include prostate gland. The glands that women often talk about are actually small glands that can be observed at front portion of vagina whereas corresponding ducts to these glands are well recognised as Skenes Glands/Ducts.
The researchers have defined few specific terminologies related to this condition. It is observed that Phosphatase and Prostate Specific Antigen use to stay present in both Skenes glands as well as in male prostate.
But the fact is that it is still not clear during researches that whether female prostate glands turns into small ducts on every side of urethra or it is urethra itself. You must be aware about function of urethra, it use to carry urine out of body so it is definitely a functional part for genital of females and for the urinary system.
Female urinary system
Here is an important thing to know for all worried people that as prostate gland in females share same functionality as that of male prostate gland so we cannot say that it will always lead to a prostate cancer.
What Is The Actual Purpose Of Prostate In Female Body
Many experts believe that prostate in female body use to release some kind of fluid. This fluid appears thick, scanty and has whitish color while containing PSA. Note that, female ejaculation is actually not a part of orgasm and frequency of this has be estimated somewhere around 10 to 54 percent.
During few recent years, medical professionals have taken help from MRIs to detect the presence as well as functionality of female prostate. However, the research should be continued ahead to make ideas more clear but the basic understanding have obtained a boost with this initiative. You might be aware of the fact that prostate gland in males use to store infections inside body. Several studies around the world reveal that Skenes glands also serve the similar kind of function.
Now, it is already clear that skenes glands use to release some fluid during sexual activity and it use to be of watery in appearance. As per one detailed study published in 2007, this fluid that is excreted into the tract from Skene;s Duct use to be consistent with the prostate fluid but it is not observed to have consistency with urine.
You May Like: Does Prostate Cancer Cause Ed
How Is The Prostate Involved In Reproduction
The prostatic fluid accounts for 20 to 30 percent of the volume of seminal fluid .
As mentioned before, this fluid contains enzymes, proteins, and minerals that protect and nourish sperm ;and are necessary for the proper functioning of sperm cells.
What’s more, research, such as one paper published in July 2015 in the journal;PloS;One, has suggested the alkalinity of the fluid helps ensure the viability of sperm in reproduction.
What Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasiaalso called BPHis a condition in men in which the prostate gland is enlarged and not cancerous. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is also called benign prostatic hypertrophy or benign prostatic obstruction.
The prostate goes through two main growth periods as a man ages. The first occurs early in puberty, when the prostate doubles in size. The second phase of growth begins around age 25 and continues during most of a mans life. Benign prostatic hyperplasia often occurs with the second growth phase.
As the prostate enlarges, the gland presses against and pinches the urethra. The bladder wall becomes thicker. Eventually, the bladder may weaken and lose the ability to empty completely, leaving some urine in the bladder. The narrowing of the urethra and urinary retentionthe inability to empty the bladder completelycause many of the problems associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Read Also: How To Cum From Prostate
How Common Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is the most common prostate problem for men older than age 50. In 2010, as many as 14 million men in the United States had lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia.1 Although benign prostatic hyperplasia rarely causes symptoms before age 40, the occurrence and symptoms increase with age. Benign prostatic hyperplasia affects about 50 percent of men between the ages of 51 and 60 and up to 90 percent of men older than 80.2
Diagnosis Of Prostate Disease
Prostate disease is diagnosed using a variety of tests, including:
- physical examination, including digital rectal examination , where the doctor inserts a gloved finger into your rectum to check the size of your prostate
- blood test for prostate specific antigen
- mid-stream urine tests to look for infection or blood in the urine
- ultrasound scans and urinary flow studies
- biopsies of the prostate.
Also Check: Can Prostate Issues Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
Some risk factors have been linked to prostate cancer. A risk factor is something that can raise your chance of developing a disease. Having one or more risk factors doesn’t mean that you will get prostate cancer. It just means that your risk of the disease is greater.
- Age. Men who are 50 or older have a higher risk of prostate cancer.
- Race. African-American men have the highest risk of prostate cancerâthe disease tends to start at younger ages and grows faster than in men of other races. After African-American men, prostate cancer is most common among white men, followed by Hispanic and Native American men. Asian-American men have the lowest rates of prostate cancer.
- Family history. Men whose fathers or brothers have had prostate cancer have a 2 to 3 times higher risk of prostate cancer than men who do not have a family history of the disease. A man who has 3 immediate family members with prostate cancer has about 10 times the risk of a man who does not have a family history of prostate cancer. The younger a man’s relatives are when they have prostate cancer, the greater his risk for developing the disease. Prostate cancer risk also appears to be slightly higher for men from families with a history of breast cancer.
- Diet. The risk of prostate cancer may be higher for men who eat high-fat diets.
Another Common Issue: Enlarged Prostate Or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Noncancerous prostate enlargement is the most common prostate problem for men over 50 years old, according to the NIDDK.
It’s not well understood what causes prostate enlargement, also known as;benign prostatic hyperplasia , but research suggests age-related hormonal changes may be to blame. Men younger than 40 rarely experience symptoms of BPH.
In men with BPH, the prostate presses into and pinches the urethra as it enlarges.
This pressure can negatively affect the urine-holding bladder, which is connected to the urethra, by weakening it and preventing it from emptying completely.
Prostate enlargement can cause a number of related urination symptoms, such as:
- Increased urinary frequency and urgency
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Urine with an unusual color or smell
- Nocturia, or frequent urination during periods of sleep
- Pain after urination
Over time, BPH may cause complications, including urinary tract infections, damage to the bladder or kidneys, and bladder stones, among other things.
Treatment of BPH includes lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery, which may be minimally invasive.
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce Prostate Size
Possible Cancer Protection From Prostate Drugs
Early research suggested that 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors , a class of drugs used to treat prostate enlargement, might increase the risk of developing more aggressive prostate cancer. However, newer studies have found that not only do the drugs appear to pose no extra risk, they may even protect against prostate cancer.
For instance, research from the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial study in 2013 showed that taking the 5-ARI finasteride for seven years could lower the chance of getting low-grade prostate cancer by 25% among men ages 55 and older. A follow-up study of almost 9,500 men, published in the Nov. 1, 2018, issue of the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, also showed that finasteride lowered the risk by a similar amount , and found the protective effect lasted for at least 16 years.
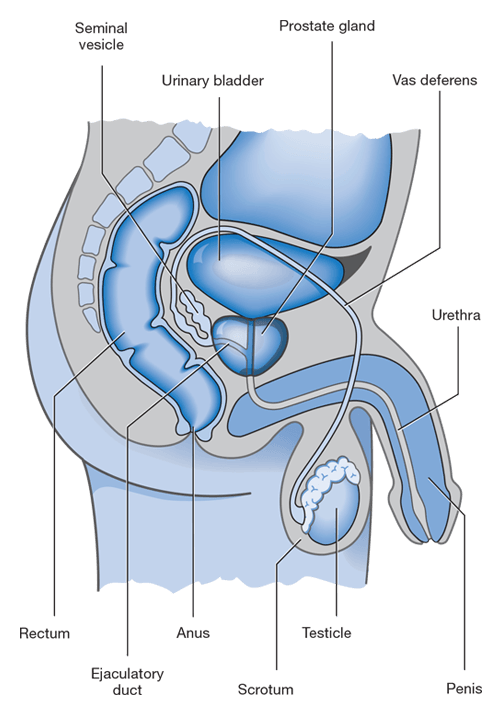
Side View Of The Prostate
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is just in front of the rectum. The urethra runs through the center of the prostate, from the bladder to the penis, letting urine flow out of the body.
The prostate secretes fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. During ejaculation, the prostate squeezes this fluid into the urethra, and itâs expelled with sperm as semen.
The vasa deferentia bring sperm from the testes to the seminal vesicles. The seminal vesicles contribute fluid to semen during ejaculation.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have A Prostate Infection
What Are The Symptoms Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia may include
- urinary frequencyurination eight or more times a day
- urinary urgencythe inability to delay urination
- trouble starting a urine stream
- a weak or an interrupted urine stream
- dribbling at the end of urination
- nocturiafrequent urination during periods of sleep
- urinary incontinencethe accidental loss of urine
- pain after ejaculation or during urination
- urine that has an unusual color or smell
Symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia most often come from
- a blocked urethra
- a bladder that is overworked from trying to pass urine through the blockage
The size of the prostate does not always determine the severity of the blockage or symptoms. Some men with greatly enlarged prostates have little blockage and few symptoms, while other men who have minimally enlarged prostates have greater blockage and more symptoms. Less than half of all men with benign prostatic hyperplasia have lower urinary tract symptoms.3
Prostate Disease And Ageing
Around 25 per cent of men aged 55 years and over have a prostate condition. This increases to 50 per cent by the age of 70 years. Early stages of prostate disease may have no symptoms.
If you are a man and you are in your 50s or 60s, talk to your doctor about whether you need to have your prostate gland checked and, if so, how often. If you have a family history of prostate disease , talk to your doctor earlier about when prostate checks might be suitable for you.
Also Check: How Do People Get Prostate Cancer
Understanding The Anatomy Of The Prostate
Despite its importance, the prostate gland in an adult man is only about the size and shape of a walnut and weighs less than 1 ounce .
It is located below the bladder, above the pelvic floor muscles, and in front of the rectum.
The prostate reaches its mature size during puberty and will keep its walnut size until the man is in his late forties or early fifties. After this age, it slowly begins to enlarge.
The prostate, which surrounds the urethra, is made up of glandular, stromal tissue, and smooth muscles fused within a capsule.
Though the prostate gland is often referenced as a singular entity, it is actually made up of a number of tubular or saclike glands that secrete fluids into the urethra through the ejaculatory ducts.
The prostate is divided into three histologically and anatomically separate glandular areas: The transition zone, the central zone, and the peripheral zone.
Transition Zone This surrounds the part of the urethra that passes through the prostate . This zone only represents about 5 percent of the gland, but is the primary origination of benign prostatic hyperplasia, or enlarged prostate. That is, the transition zone is the region of the prostate that grows as men age.
Central Zone Making up quarter of the prostate, this area surrounds the transition zone, as well as the ejaculatory ducts that stretch from the seminal vesicles which produces the majority of the fluid of semen ;to the prostatic region of the urethra.
Urinary Tract Infections In Men: Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment
Nonbacteria microbes may cause a different type of chronic prostatitis, known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome, which may also develop as a result of chemicals in the urine, a;urinary tract infection, or pelvic nerve damage.
Affecting 10 to 15 percent of the U.S. male population, chronic pelvic pain syndrome is the most common type of prostatitis,;but also the least understood.
Symptoms vary depending on the type of prostatitis, but can include urination problems, pain , fever, and body aches, among other things.
Some people develop asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis, in which the prostate is inflamed but doesnt produce any symptoms or require treatment.
Bacterial prostatitis is most often treated with antibiotics. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome may require drugs, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
Over time, prostatitis may cause sexual dysfunction, abscesses in the prostate, inflammation of nearby reproductive organs, and infection of the bloodstream.
Read Also: How Long Does A Prostate Biopsy Take
What Is The Normal Prostate Size
A small prostate has a volume of 30 ml to 40 ml and a weight of 20 g to 70 g. A medium prostate has a volume of 40 ml to 80 ml and a weight of 20 g to 125g . A large prostate has a volume of 40ml to 100 ml and a weight of 40 g to 125 g.
Around age 40, prostate gland begins to grow. With a benign prostatic hyperplasia , glands size can increase by 4 to 5 times compared to its initial size.
Détection précoce du;cancer;de la prostate, Actualisation du référentiel de pratiques de lexamen périodique de santé , document PDF , HAS, mai 2013
Prostate Massage Therapy And Why It May Be Helpful
Prostate massage therapy , in which the prostate is stimulated through the rectum, was once a popular treatment for prostatitis.
The procedure is similar to a digital rectal exam, except rather than briefly looking for abnormalities on the prostate, the person performing the prostatic message rubs the prostate with light to moderate pressure until it secretes fluid through the urethra .
It was once thought that people could relieve symptoms related to prostatic congestion by expelling inflammatory cells and fluid from the obstructed glands. But this therapy largely fell out of favor in the 1960s, once antibiotics became available.
A study published in the journal Neurology tested whether prostate massage could be used as an adjunct treatment for people with chronic prostatitis, but the researchers found that the treatment did not significantly help patients.
In some cases, doctors have used prostate massage therapy to obtain sperm from men with spinal cord injuries, leading to successful pregnancies. But electroejaculation ;stimulating the prostate using an electric current delivered through a probe inserted into the rectum typically yields more sperm, noted an article published in the journal Nature Reviews Urology.
Using prostate massage to achieve ejaculation is sometimes called prostate milking. Both prostate massage and prostate milking can also be sexual techniques to stimulate pleasure.
Don’t Miss: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
