After Prostate Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Prostate Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within theprostate or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The results of the tests used to diagnoseprostate cancer are often also used to stage the disease. In prostate cancer, staging tests may not be done unless the patient has symptoms or signs that the cancer has spread, such as bone pain, a high PSA level, or a high Gleason score.
The following tests and procedures also may be used in the staging process:
What Are The Tests To Diagnose And Stage Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancers 6 are found through blood tests or digital rectal exams , as most early prostate cancers do not show symptoms .
During the digital rectal exam , the doctor will insert a lubricated finger into the rectum to feel for bumps or hard areas. The PSA blood test refers to a prostate-specific antigen or a protein made by both normal and cancer cells in the prostate. PSA is found primarily in the semen with small amounts found in the blood.
When prostate cancer is thought to be probable based on these tests or symptoms, patients are sometimes referred to a urologist, who treats cancers of the urinary tract and genitals. A prostate cancer diagnosis is then made with a prostate biopsy.
During this biopsy, small samples of the prostate are removed and analyzed with a microscope. Often, a core needle biopsy is the method and is performed by a urologist.
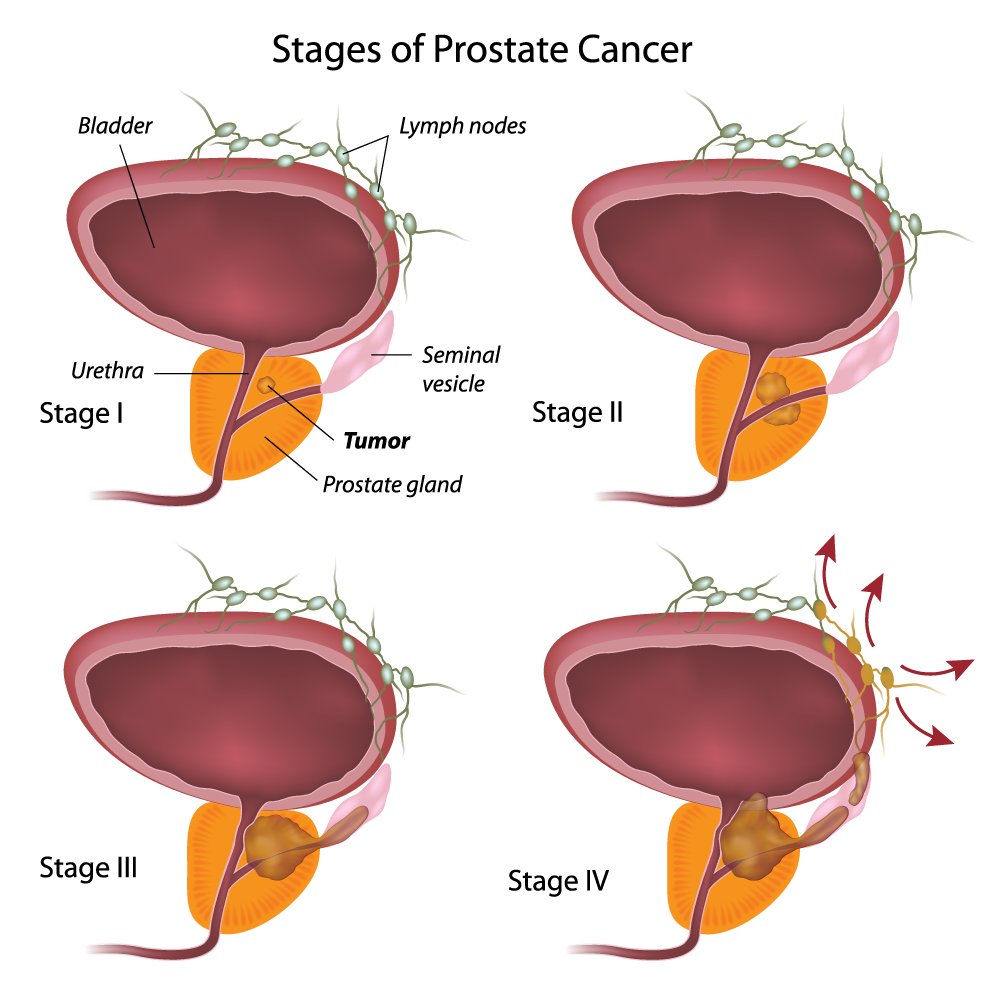
Staging Of Prostate Cancer
The stage of a cancer describes its size and how far it has spread. The results of your tests help your doctors decide on the stage and plan your treatment.
We understand that waiting to know the stage and grade of your cancer can be a worrying time. We’re here if you need someone to talk to. You can:
Macmillan is also here to support you. If you would like to talk, you can:
Read Also: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Prostate Infection
Prostate Cancer: Signs And Symptoms
So, the good news is that when you detect prostate cancer in its very early stages, youve got a much better chance of survival. The bad news is that in its absolute earliest stages, prostate cancer causes very few symptoms. However, as it develops and even before it spreads to other organs in the body there are some signs you should be aware of.
One of the most easily recognizable signs of a prostate problem is difficulty urinating. That includes having a weak stream of urine, dribbling urine, and having frequent urges to urinate, even during sleep and even if you dont have a lot of urine in your bladder. Urinary symptoms occur as the tumor enlarges and begins pressing on your bladder or against your urethra .
Urinary troubles may be the symptom most commonly associated with prostate cancer, but its not the only symptom you need to be aware of. Other symptoms include:
- Blood in your urine or semen
- Problems getting or maintaining an erection
- Pain during ejaculation
- Pain or pressure in the pelvic area
- Pain or pressure in the rectum area, the hips, or the lower back
End Stage Prostate Cancer Symptoms
These are some of the common symptoms of end stage prostate cancer:
- frequent urination and even more at night
- pain in lower back, hips or upper legs from metastasis
- occasional blood in your urine
- painful urination
- aches and pains and tiredness
- erectile difficulties
The pain in the pelvis and hips can be the result of prostate bone cancer that has spread outside the prostate due to metastasis.
You May Like: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
What Are The Types Of Prostate Cancer
Before we dive into answering what the 4 stages of prostate cancer are, lets take a look at the different types of prostate cancer.
Nearly all prostate cancers 3 are referred to as adenocarcinomas. Adenocarcinomas are cancers that develop in the glandular cells of your body. Lots of our organs have these glands, and common types of adenocarcinomas 4 and include breast cancer, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and prostate cancer.
In the prostate, the glandular cells are what create the prostate fluid that is added to the semen. Most often, when individuals are diagnosed with prostate cancer, it is an adenocarcinoma.
Other types of cancer can start in the prostate, though these types are rare. They include:
- Small cell carcinomas
- Neuroendocrine tumors
- Transitional cell carcinomas
- Sarcomas
Some prostate cancers grow and spread fast, though most grow slowly. Interestingly enough, many autopsies of men who passed away from other causes were shown to have prostate cancer 5 , though it did not affect them throughout their lives and often went unnoticed by both the patient and the doctor.
Are Prostate Problems Always A Sign Of Prostate Cancer
Not all growths in the prostate are cancerous, and not all prostate problems indicate cancer. Other conditions that cause similar prostate cancer symptoms include:
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia : At some point, almost every man will develop benign prostatic hyperplasia . This condition enlarges the prostate gland but doesnt increase cancer risk. The swollen gland squeezes the urethra and blocks the flow of semen and urine. Medications, and sometimes surgery, can help.
- Prostatitis: Men younger than 50 are more prone to prostatitis, inflammation and swelling of the prostate gland. Bacterial infections are often the cause. Treatments include antibiotics or other medications.
Read Also: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Metastatic Signs And Symptoms
Metastatic symptoms include weight loss and loss of appetite bone pain, with or without pathologic fracture and lower extremity pain and edema due to obstruction of venous and lymphatic tributaries by nodal metastasis. Uremic symptoms can occur from ureteral obstruction caused by local prostate growth or retroperitoneal adenopathy secondary to nodal metastasis.
Stages Types And Grades
The tests and scans you have to diagnose your cancer will give some information about:
- the type of cell the cancer started in and where it began
- how abnormal the cells look under the microscope
- the size of the cancer and whether it has spread
In the UK, doctors use the Gleason system to grade prostate cancer. They might also talk about your Grade Group. This is a new grading system.
You might also be told about the TNM stage, or you may see this on your pathology report. Another way doctors may describe your cancer is as localised, locally advanced or advanced.
Recommended Reading: How To Reduce Prostate Swelling Naturally
Prostate Health Index Testing
The Prostate Health Index test is a diagnostic blood test that combines free and total PSA and the pro-PSA isoform . The PHI test is intended to reduce the number of unnecessary prostate biopsies in PSA-tested men. In prospective multicenter studies, the PHI test has outperformed free and total PSA for detection of prostate cancer and has improved prediction of clinically significant prostate cancer in men with a PSA of 2 or 4 ng/mL to 10 ng/mL.
Stage : Prostate Cancer Is Limited To A Small Part Of The Prostate
- Often, the cancer is found as a result of needle examination of tissue for another reason, such as benign prostatic hypertrophy , also known as an enlarged prostate, or because of an elevated result on a prostate specific antigen test, which uses PSA levels as an indicator of potential cancerous growth.
- Cancer cells are only found in a small part of the prostate. The cells look like normal cells and the prostate feels normal with a digital rectal exam .
- PSA is less than 10.
- Gleason score, which assigns a grade to what the cancer cells looks like under a microscope, is less than 6, the Prostate Cancer Foundation notes.
You May Like: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have prostate cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get prostate cancer?
- What is my Gleason score? What is my Grade Group? What do these numbers mean for me?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the prostate gland?
- What is the best treatment for the stage of prostate cancer I have?
- If I choose active surveillance, what can I expect? What signs of cancer should I look out for?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Is my family at risk for developing prostate cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Prostate cancer is a common cancer that affects males. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and remain in the prostate gland. For a small number, the disease can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. Men with slow-growing prostate cancers may choose active surveillance. With this approach, you can postpone, and sometimes completely forego, treatments. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for you based on your Gleason score and Group Grade.
What Are The Causes Of Polyps
While the specific cause of certain polyps is unknown, according to Mayo Clinic, the cause of bowel and/or rectum polyps may be a result of a simple gene mutation. While healthy cells grow and divide by the book, a mutation in a gene will cause cells to continue dividing – even when new cells arent needed. This continued growth can potentially cause polyps to form.
See also:What Causes a Change in Bowel Movement?
Read Also: Perineural Invasion Prostate Cancer Prognosis
What Are The Possible Treatment Options For Prostate Cancer
Staging is not the only information that doctors need. Symptoms and the patients age, life expectancy, co-existing health conditions and personal preferences may also be considered when deciding on treatment. Doctors use a general guideline for treatment based on stage groups.
Stage I prostate cancer:
The Ajcc Tnm Staging System
A staging system is a standard way for the cancer care team to describe how far a cancer has spread. The most widely used staging system for prostate cancer is the AJCC TNM system, which was most recently updated in 2018.
The TNM system for prostate cancer is based on 5 key pieces of information:
- The extent of the main tumor *
- Whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- Whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
- The PSA level at the time of diagnosis
- The Grade Group , which is a measure of how likely the cancer is to grow and spread quickly. This is determined by the results of the prostate biopsy .
*There are 2 types of T categories for prostate cancer:
- The clinical T category is your doctors best estimate of the extent of your disease, based on the results of the physical exam and prostate biopsy, and any imaging tests you have had.
- If you have surgery to remove your prostate, your doctors can also determine the pathologic T category . The pathologic T is likely to be more accurate than the clinical T, as it is done after all of your prostate has been examined in the lab.
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M provide more details about each of these factors. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Once the T, N, and M categories have been determined, this information is combined in a process called stage grouping to get the overall stage of the cancer.
Don’t Miss: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if prostate cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually prostate cancer cells. The disease is metastatic prostate cancer, not bone cancer.
Denosumab, a monoclonal antibody, may be used to preventbone metastases.
Don’t Miss: Masturbation And Prostatitis
Sudden Or Unexplained Weight Loss
If youve cleaned up your diet and have been exercising regularly, its very clear why you might be shedding a few pounds. But if youre suddenly losing weight out of nowhere without trying to, it could be a signal of a health problemâprostate cancer included. According to Prostate Cancer U.K., weight loss often occurs with prostate cancer because of a change in the way your body uses energy, and that can eventually make you feel tired and weak.
You May Like: Does Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
Can Women Get Prostate Cancer
Women do not have a prostate gland, therefore, they cannot develop the prostate cancer that affects men. However, some people refer to a womans Skenes glands as the female prostate.
Maslow emphasizes, Women do not have a prostate. They do not need to worry about prostate cancer. We do appropriate screenings for female patients.
The Skenes glands are the two small ducts located in front of the vaginal wall and along both sides of the urethra. These glands are not the same as prostate glands in men, though they function similarly in how they drain fluids into the urethra.
Cancer in the Skenes glands is extremely rare and accounts for an estimated 0.003% of female cancers that originate in the urinary tract and genitals. The primary symptom of this cancer is bleeding out of the urethra. Make an appointment with your doctor as soon as possible if you are female and experience abnormal bleeding from your vagina or urethra.
Read Also: How To Massage A Mans Prostate
Read Also: Prostaglandins Erectile Dysfunction
Pain In Your Hips And Upper Thighs
In addition swelling in your lower body, pain in your hips or upper thighs can also be potential symptoms of prostate cancer, according to Robert J. Cornell, MD, a urologist in Houston, Texas. And for other discomforts you should address with your doctor, check out 25 Common Pains You Should Never Ignore.
Pain In The Lower Pelvic Area
Cornell also says that as prostate cancer becomes more advanced, you may also experience a dull pain in your lower pelvic area. Its described as being very similar to the pain you feel when you have a toothacheânot the type of pain or soreness you would feel after a hard workout. And for misconceptions about your well-being, check out 20 Worst Mens Health Myths That Just Wont Die.
Don’t Miss: No Ejaculate Flomax
How Is Advanced Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
If youve previously been diagnosed with prostate cancer, be sure to tell your doctor if you have any new symptoms, even if youve completed treatment.
To determine if prostate cancer has returned or has spread, your doctor will likely order some imaging tests, which may include:
- X-rays
- PET scans
- bone scans
You probably wont need all of these tests. Your doctor will choose the tests based on your symptoms and physical exam.
If any of the images reveal abnormalities, it doesnt necessarily mean that you have cancer. Additional testing may be necessary. If they find a mass, your doctor will probably order a biopsy.
For a biopsy, your doctor will use a needle to remove samples from the suspicious area. A pathologist will then analyze the removed cells under a microscope to see if theyre cancerous. The pathologist can also determine if you have an aggressive form of prostate cancer.
Prostate Cancer Treatments How Many Stages Of Prostate Cancer
The treatments for cancer will be determined after a diagnosis and placing is complete. There will be a lot of information to think about before discussing management options with medical doctors. If an individual has been lately diagnosed, then many prostate cancer treatments are available.
ManagementBasic prostate cancer treatments involve the active surveillance of the cancer and wary waiting. Active surveillance is a medication option that involves monitoring the cancer expending specific blood tests and numerous ultrasounds.This is normally done at standard intervals to determine if the cancer is stretching. Attentive waiting will be less intensive with evaluation and basing the decisions on the evidences of individual patients. The option to use any form of managing the proficiency is often done in early stages.
SurgeryA common therapy that is meant to medication cancer is surgery. This is often a therapy alternative when the cancer is at the T1 or T2 stage and has not spread outside the gland. The most common type of surgery for cancer is called revolutionary prostatectomy.In this activity, the surgeon is removing the prostate gland along with some of the smothering material. There are many practices this running can be done discussing options with medical doctors will be a good thing.
Any prostate cancer treatments that are considered will take into account the current age of individual patients, lifespan apprehensions, and the tier or stage of the cancer.
Read Also: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
