Ejaculation: What To Expect As You Age
There is little written on ejaculatory issues aside from timing problems and hematospermia . However, not a day goes by in my urology practice where I do not see at least several patients who complain about declining ejaculation function.
What does the word ejaculation mean?
Ejaculation derives from ex, meaning out;+;jaculari, meaning to throw, shoot, hurl, cast.
Trivia: You do not need an erection to ejaculate and achieve an orgasm. A limp penis cannot penetrate, but is very capable of ejaculation and orgasm.;
What happens to ejaculations as we age?
Ejaculation and orgasm often become less intense, with diminished force, trajectory and volume. What was once an intense climax with a substantial volume of semen that could be forcefully ejaculated gives way to a lackluster experience with a small volume of semen weakly dribbled out the penis.;
So whats the big deal?
Men dont like meager, lackadaisical-quality ejaculations and orgasms. Sex is important to many of us and getting a good quality rigid erection is foremost, but the culminationejaculation and orgasmis equally vital. We may be 40 or 50 years old, but we still want to point and shoot like we did when we were 20. As the word origin indicates, we want to be able to shoot out, hurl or cast like an Olympian and we want that intensely pleasurable feeling of yesteryear.
The science of ejaculation
Big head versus little head
What makes up the love juices?
Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
Some risk factors have been linked to prostate cancer. A risk factor is something that can raise your chance of developing a disease. Having one or more risk factors doesn’t mean that you will get prostate cancer. It just means that your risk of the disease is greater.
- Age. Men who are 50 or older have a higher risk of prostate cancer.
- Race. African-American men have the highest risk of prostate cancerâthe disease tends to start at younger ages and grows faster than in men of other races. After African-American men, prostate cancer is most common among white men, followed by Hispanic and Native American men. Asian-American men have the lowest rates of prostate cancer.
- Family history. Men whose fathers or brothers have had prostate cancer have a 2 to 3 times higher risk of prostate cancer than men who do not have a family history of the disease. A man who has 3 immediate family members with prostate cancer has about 10 times the risk of a man who does not have a family history of prostate cancer. The younger a man’s relatives are when they have prostate cancer, the greater his risk for developing the disease. Prostate cancer risk also appears to be slightly higher for men from families with a history of breast cancer.
- Diet. The risk of prostate cancer may be higher for men who eat high-fat diets.
Questions You May Want To Consider Asking Your Doctor Include:
- What type of prostate problem do I have?
- Is more testing needed and what will it tell me?
- If I decide on watchful waiting, what changes in my symptoms should I look for and how often should I be tested?
- What type of treatment do you recommend for my prostate problem?
- For men like me, has this treatment worked?
- How soon would I need to start treatment and how long would it last?
- Do I need medicine and how long would I need to take it before seeing improvement in my symptoms?
- What are the side effects of the medicine?
- Are there other medicines that could interfere with this medication?
- If I need surgery, what are the benefits and risks?
- Would I have any side effects from surgery that could affect my quality of life?
- Are these side effects temporary or permanent?
- How long is recovery time after surgery?
- Will I be able to fully return to normal?
- How will this affect my sex life?
- How often should I visit the doctor to monitor my condition?
Related Resources
Also Check: Is Turmeric Good For Prostate
How Is It Treated
If you have BPH but no symptoms, or your symptoms are mild, you may not need any treatment. You should have regular exams to be sure that you are not developing more serious problems.
If your symptoms get bothersome or there is a risk that your kidneys will be affected, your provider may recommend treatment. BPH may be treated with medicines. If medicines do not work, several different procedures may be done to treat BPH. They may use energy, like radio waves or a laser, to remove or destroy excess prostate tissue, or they may make cuts in prostate tissue to reduce pressure on the urethra. In some cases, surgery may be done to remove the center of the prostate. Your healthcare provider will discuss the risks and benefits of the procedures available to you.
Tests Used To Check The Prostate
This first step lets your doctor hear and understand the “story” of your prostate concerns. You’ll be asked whether you have symptoms, how long you’ve had them, and how much they affect your lifestyle. Your personal medical history also includes any risk factors, pain, fever, or trouble passing urine. You may be asked to give a urine sample for testing.
Also Check: Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
How Does Your Penis Change As You Age
Like everything in nature, your penis goes through a series of changes over your lifetime. Each phase is controlled mostly by your testosterone levels.
Somewhere between the ages of 9 and 15, your pituitary gland releases hormones that tell your body to start making testosterone. Puberty begins and brings changes. Your testes , scrotum, penis, and pubic hair all begin to grow. Testosterone levels peak in your late teens to early 20s.
The amount of testosterone in your body may drop slightly in your late 20s through your 40s, but the change is minimal.
After 40, your total levels may drop only a small amount. But your body slowly begins to make more of a protein called sex hormone binding globulin . This sticks to the testosterone in your blood and lowers the amount your body has available to use.
As testosterone levels fall, youâll notice other changes to your:
Pubic hair: Like the hair on the rest of your body, it will thin and may turn gray.
Penis size: You may notice that it doesnât seem as large as it used to. The actual size probably hasnât changed at all. But if you have more fat on the pubic bone just above your penis, that area can sag and make it look smaller.
Testicles: The small organs inside your scrotum mostly exist to make sperm. As your testosterone levels fall, sperm production slows and they shrink.
If you get hormone replacement therapy, your pituitary gland will stop sending signals to your testes to make testosterone, and they will shrink more.
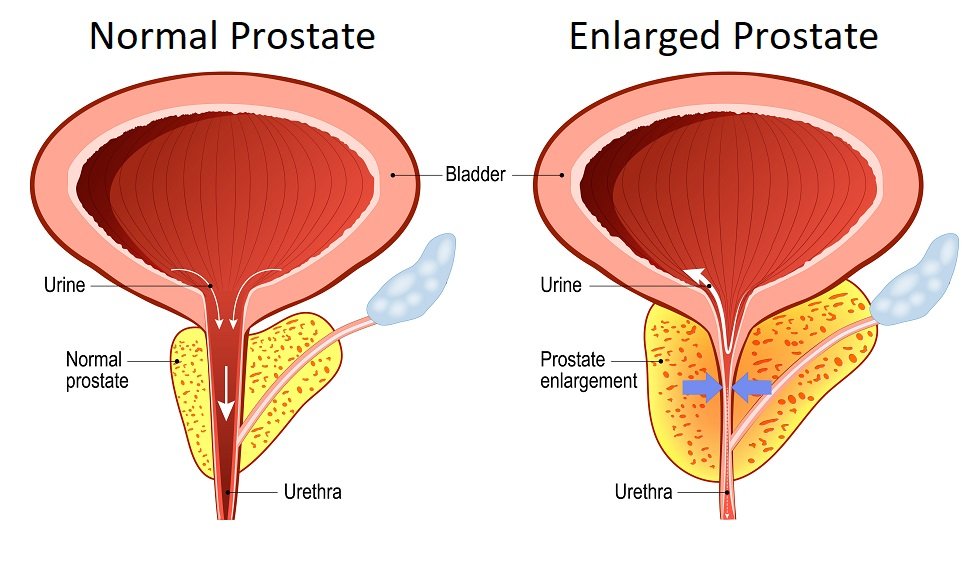
What Causes An Enlarged Prostate
We still dont really know all the things that cause the prostate to grow. But we do know about two risk factors that can increase your risk of having an enlarged prostate.
Age
Your risk of having an enlarged prostate increases as you get older. Many men aged 50 or over have an enlarged prostate, but they dont all get symptoms. And some men have symptoms that don’t bother them.
Hormone levels
The balance of hormones in your body changes as you get older. This may cause your prostate to grow.
Other factors
Some studies show that obese men and men who have diabetes may be more likely to develop an enlarged prostate. Regular exercise may help to reduce your risk of urinary symptoms. But we still need more studies into the causes of enlarged prostate to know for certain if, and how, we can prevent it.
There is also some research that suggests you may be more at risk of developing an enlarged prostate if your father or brother has one. Again, further studies are needed to confirm this.
Also Check: What Is The Va Disability Rating For Prostate Cancer
What Causes Prostate Enlargement
The causes of prostate enlargement are not yet fully understood but are thought to be related to the male sex hormone which controls the growth of the prostate. The prostate is initially quite small, but as men age, testosterone feeds the prostate and it starts to get bigger. From birth to around the early teenage years, the prostate increases in size by around 8 times. It doubles again in size from around the early 20s through to 50 years of age, and then doubles again by around the age of 80. With such large increases in size, its easy to see why the prostate can begin to squeeze the urethra and make it difficult to urinate.
There may also be a genetic link to prostate enlargement, because the sons of men with an enlarged prostate are more likely to develop prostate disease.
When To Contact A Medical Professional
- Less urine than usual
- Back, side, or abdominal pain
- Blood or pus in your urine
Also call if:
- Your bladder does not feel completely empty after you urinate.
- You take medicines that may cause urinary problems, such as diuretics, antihistamines, antidepressants, or sedatives. DO NOT stop or change your medicines without talking to your provider.
- You have tried self-care steps for 2 months and symptoms have not improved.
You May Like: Perineural Invasion Prostate Cancer
Treatment For Urinary Problems
If your urinary problems are caused by infection or enlargement of the prostate gland, treatment may include:
- a long course of antibacterial medication because infection is difficult to get rid of, the antibacterial medication will need to be taken for many weeks
- medication to improve urine flow and other symptoms
- surgical procedures the type of surgery required depends on the size of the prostate and the condition of the urethra. Types of procedures include:
- transurethral resection of the prostate
- transurethral incision of the prostate
- laser resection of the prostate
- open surgery prostatectomy ;
- removal of prostate tissue using water jets or steam
Personal And Family Medical History
Taking a personal and family medical history is one of the first things a health care provider may do to help diagnose benign prostatic hyperplasia. A health care provider may ask a man
- what symptoms are present
- when the symptoms began and how often they occur
- whether he has a history of recurrent UTIs
- what medications he takes, both prescription and over the counter
- how much liquid he typically drinks each day
- whether he consumes caffeine and alcohol
- about his general medical history, including any significant illnesses or surgeries
Also Check: What Is The Definition Of Prostate Gland
Is Treatment Always Necessary
No. In most cases, an enlarged prostate does not do any damage or cause complications. Whether treatment is needed usually depends on how much bother the symptoms cause. For example, you may be glad for some treatment if you are woken six times a night, every night, with an urgent need to go to the toilet. On the other hand, slight hesitancy when you go to the toilet and getting up once a night to pass urine may cause little problem and not need treatment.
How Is Prostate Enlargement Diagnosed
Your GP will take steps to diagnose the cause of your urinary symptoms. Your doctor may:
- Ask about your personal, medical and family history;
- Ask you to describe your symptoms and how much they interfere with your life;
- Do a physical examination this will usually include the doctor checking the size, shape and feel of the prostate by placing a lubricated gloved finger into the rectum ;
- Request urine or blood tests a blood test can check levels of a particular protein. Levels of this protein can become high due to prostate problems such as an enlarged prostate or prostate cancer; or
- Request an ultrasound scan of your prostate, bladder and kidneys. This may include a scan before and after emptying your bladder to see if significant urine remains after voiding.
Also Check: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Complications Of Prostate Enlargement
Left untreated, an enlarged prostate may lead to a number of complications, including:
- Pain in the lower abdomen due to the urethra becoming too narrow. Urine cannot flow through the urethra normally, which leads to a painful build-up of urine in the bladder;
- Bladder infections due to stale urine sitting in the bladder which becomes infected with bacteria;
- Bladder stones small, hard, gritty lumps that form in the bladder, due to the build-up of stale urine in the bladder. The stones dont usually cause any problems when they are in the bladder, but if they pass into the urethra, they may become stuck and cause sudden severe pain;
- Interrupted sleep because of the need to get up several times during the night to urinate;
- A lower quality of life because of the inconvenience and embarrassment of problems with urination; or
- Serious kidney problems if the flow of urine out of the bladder becomes blocked and causes a build-up of pressure all the way back to the kidneys.
Wednesday 4 October 2017
Hey guys, we know that talking about your prostate can be a little uncomfortable. You might not know where or what it is, or you might have only heard about it in stories about older men having difficulty peeing or the doctor sticking their finger up you know where to check on it.
Below, weve got all the details about what your prostate is, where it is and what it does. Well also discuss how it might change as you age, and any changes or symptoms you should keep an eye on and tell your doctor about.
Also Check: What Is The Va Disability Rating For Prostate Cancer
Why Choose Bens Natural Health Supplements
At Bens Natural Health, our motto is to combine holistic healing with modern science.
Bens Natural Health is the worlds first high-quality, all-natural, scientifically proven clinical supplement company. Our supplements are effective, natural and 100% side effect free.
Moreover, at Bens Natural Health, we have four rules for all our supplements:
- We only use the highest quality ingredients
- We only use them if they have been proven to work in independent, peer-reviewed double-blind studies
- With all our supplements, we find a way to get every ingredient into a single bottle
- We always formulate them in clinically significant doses of the most bioavailable form
And, all our supplements come with a 90-day money-back guarantee. So if you arent happy with the results, we will provide you with credit or a full refund.
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
- Frequent urge to pass urine, especially at night
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Pain or burning when passing urine
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Painful ejaculation
- Nagging pain in the back, hips, or pelvis
Prostate cancer can spread to the lymph nodes of the pelvis. Or it may spread throughout the body. It tends to spread to the bones. So bone pain, especially in the back, can be a symptom of advanced prostate cancer.
Read Also: Enlarged Prostate Sexuality
When Is Bph Treatment Necessary
The course of BPH in any individual is not predictable. Symptoms, as well as objective measurements of urethral obstruction, can remain stable for many years and may even improve over time for as many as one-third of men, according to some studies. In a study from the Mayo Clinic, urinary symptoms did not worsen over a 3.5-year period in 73% of men with mild BPH. A progressive decrease in the size and force of the urinary stream and the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying are the symptoms most correlated with the eventual need for treatment. Although nocturia is one of the most annoying BPH symptoms, it does not predict the need for future intervention.
If worsening urethral obstruction is left untreated, possible complications are a thickened, irritable bladder with reduced capacity for urine; infected residual urine or bladder stones; and a backup of pressure that damages the kidneys.
- Inadequate bladder emptying resulting in damage to the kidneys
- Complete inability to urinate after acute urinary retention
- Incontinence due to overfilling or increased sensitivity of the bladder
- Bladder stones
- Recurrent severe hematuria
- Symptoms that trouble the patient enough to diminish his quality of life
Find a Location
Currently, the main options to address BPH are:
- Watchful waiting
- Medication
- Surgery
What Makes My Prostate Grow
The male sex hormone testosterone makes the prostate grow in size. As you get older, the prostate grows larger. At puberty, your testosterone levels start to increase, and the prostate grows to about eight times its size. It continues to grow, doubling in size between the ages of 21 and 50, and almost doubles again between the ages of 50 and 80. We still dont fully understand the reasons for this ongoing growth.
Read Also: What Happens To The Prostate Later In Life
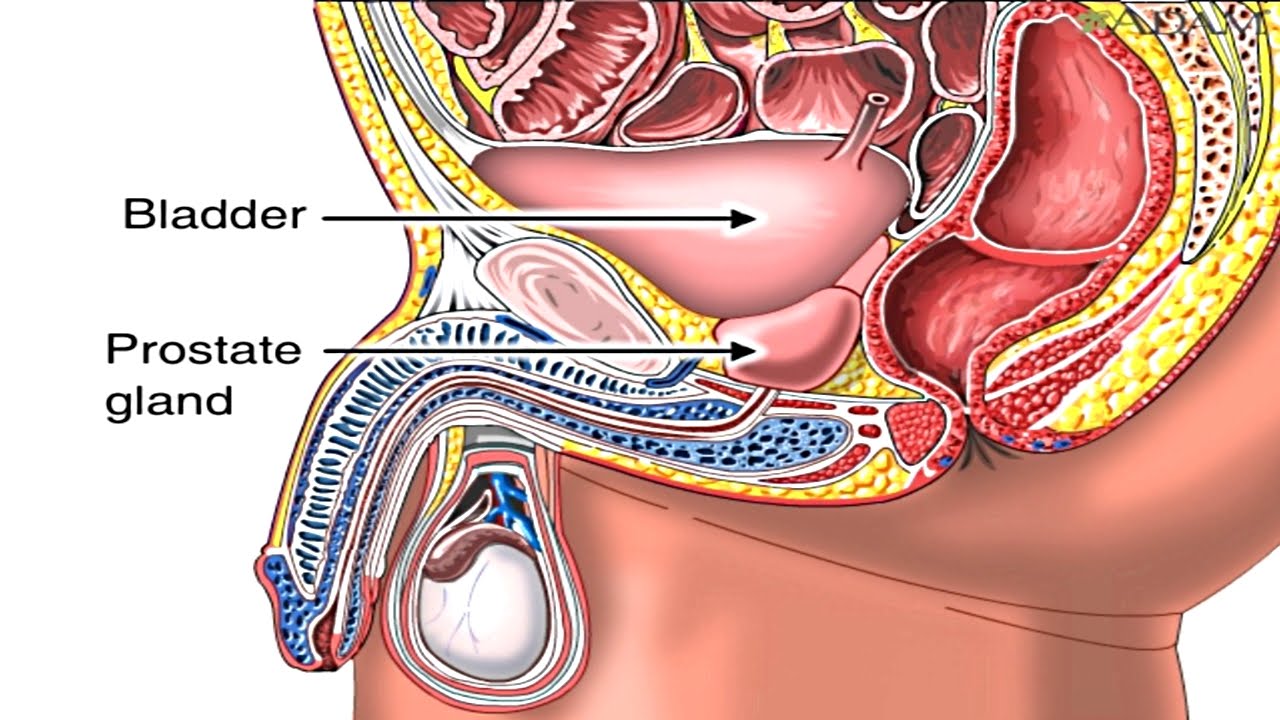
What Is Your Prostate And What Does It Do
Your prostate is a small gland that lives inside your body, just below your bladder. It sits around the urethra, which is the tube that carries pee from your bladder through your penis. Only men have a prostate.
Your prostate produces some of the fluids contained in your semen, the liquid that transports sperm. This liquid contains special enzymes and hormones that help your sperm cells function properly, which means the prostate plays a key part in your fertility. The muscles in your prostate also help push semen through your urethra when you ejaculate.
