How Fast Does Prostate Cancer Spread To The Bones
Early detection can catch prostate cancer even before there are any symptoms. Some types of prostate cancer grow very slowly.
There are four main stages of prostate cancer. Within each stage, the cancer is graded based on factors like the size of tumor, prostate-specific antigen level, and other clinical signs.
If the cancer has spread to the bones, its considered to be the most advanced, or stage 4.
Newer lab tests look at the genes inside cancer cells. This can provide more information on how quickly the prostate cancer may progress.
Theres also a grading system known as the Gleason system, which assigns the cancer into a grade group based on how closely it resembles normal tissue.
During the biopsy to diagnose prostate cancer, the cells are closely examined. The more abnormal cells that are in the biopsy sample, the higher the Gleason score and grade group.
When more abnormal cells are present, the cancer is more likely to spread quickly.
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
- Frequent urge to pass urine, especially at night
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Pain or burning when passing urine
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Painful ejaculation
- Nagging pain in the back, hips, or pelvis
Prostate cancer can spread to the lymph nodes of the pelvis. Or it may spread throughout the body. It tends to spread to the bones. So bone pain, especially in the back, can be a symptom of advanced prostate cancer.
Early Detection Is Key
When detected early, prostate cancer is usually confined to the prostate gland itself. Treatment can then be targeted on the prostate without the need to explore other organs. However, when prostate cancer is not detected in time, it can invade other organs, which can complicate treatment. Thus highlights the importance of early screenings so that prostate cancer can be detected early before it spreads .
Don’t Miss: Chemo Treatment For Prostate Cancer
Getting More Information About What To Expect
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Palliative care for adults: strong opioids for pain relief. Clinical guideline 140. 2012.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Prostate cancer: Diagnosis and treatment. NICE clinical guideline 175. 2014.
- Salvati M, Frati A, Russo N, Brogna C, Piccirilli M, DAndrea G, et al. Brain metastasis from prostate cancer. Report of 13 cases and critical analysis of the literature. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR. 2005 Jun 24:2037.
- Thompson JC, Wood J, Feuer D. Prostate cancer: palliative care and pain relief. Br Med Bull. 2007 83:34154.
- Vinjamoori AH, Jagannathan JP, Shinagare AB, Taplin M-E, Oh WK, Van den Abbeele AD, et al. Atypical Metastases From Prostate Cancer: 10-Year Experience at a Single Institution. Am J Roentgenol. 2012 Aug 199:36772.
- Kate Bullen, Head of School for Applied Social Science, University of Brighton, Brighton
- Jackie Dawson, Community Palliative Care Clinical Nurse Specialist, Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust
- Hazel Parsons, Palliative Care Nurse Specialists, Dorothy House Hospice, Winsley, Bradford on Avon
- Elizabeth Rees, Lead Nurse for end of life care, Leeds Teaching Hospitals
- Our Specialist Nurses
Prognosis And Predictive Factors
As in other locations, prognosis in prostatic involvement by leukemia/lymphoma is dependent on the subtype.
The majority of cases are low grade, predominantly chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma . As such, the prognosis in these cases is generally favorable. In a large consecutive series with follow-up data, which showed predominantly low-grade leukemia/lymphoma, only one patient had died from disease at follow-up.
In contrast, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma , which is often primary, carries a considerably less favorable prognosis. In a large series of primary prostatic lymphomas to date, which notably included numerous high-grade secondary prostatic lymphomas in survival analysis, 5-year lymphoma-specific survival was only 33%.
References
Terris MK, Hausdorff J, Freiha FS. Hematolymphoid malignancies diagnosed at the time of radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 1997 Oct. 158:1457-9. .
Chu PG, Huang Q, Weiss LM. Incidental and concurrent malignant lymphomas discovered at the time of prostatectomy and prostate biopsy: a study of 29 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005 May. 29:693-9. .
Warrick JI, Owens SR, Tomlins SA. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the prostate. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014 Oct. 138 :1286-9. . .
Gajendra S, Sharma R, Sahoo MK. Triple cancer: chronic lymphocytic leukemia with bladder and prostate carcinoma. Malays J Pathol. 2015 Aug. 37 :159-63. . .
Don’t Miss: What Happens To The Prostate Later In Life
Elisa And Ig Quantitation
ELISAs for Ig screening and quantitation were performed as described , using pooled human IgM as a standard. Briefly, plates were coated for 24 h at 4°C with rabbit IgG against human IgG, IgA, and IgM , and hybridoma supernatants were incubated in the wells. Alkaline phosphatase-conjugated rabbit Ig against human , , , , or chains was added and incubated . Extinction was read at 410 nm and compared with positive and negative controls.
Dont Miss: How Effective Is Chemotherapy For Prostate Cancer
Chances Of Developing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
About 50% of men diagnosed with local prostate cancer will get metastatic cancer during their lifetime. Finding cancer early and treating it can lower that rate.
A small percentage of men aren’t diagnosed with prostate cancer until it has become metastatic. Doctors can find out if it’s metastatic cancer when they take a small sample of the tissue and study the cells.
Read Also: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Surgery To Remove The Prostate Gland
In this type of surgery, the surgeon removes the prostate gland and seminal vesicles . The prostate gland surrounds the upper part of the urethra . So, that part of the urethra must be removed as well. The remaining urethra is reattached to the bladder. The surgeon may also remove lymph nodes or other tissues around the prostate gland to check if the cancer has spread.
Before surgery to remove the prostate gland
After surgery to remove the prostate gland
Staging: The Tnm System
Staging is done as part of the diagnosis process to determine how extensive your cancer is within your prostate and whether it has spread to lymph nodes or other organs.
Prostate cancer is typically staged using the TNM system, which is based on:
- The extent of the primary tumor
- Whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- The presence or absence of distant metastasis
- Your PSA level at the time of diagnosis
- Your Gleason score and the amount of cancer
Using this information, prostate cancer is then grouped into stages I through IV, with stage I being the least advanced and stage IV being the most advanced.
- Stage I: Cancer is confined to your prostate. Gleason score is 6 or below. PSA level is less than 10.
- Stage II: The tumor is more advanced but does not extend beyond your prostate.
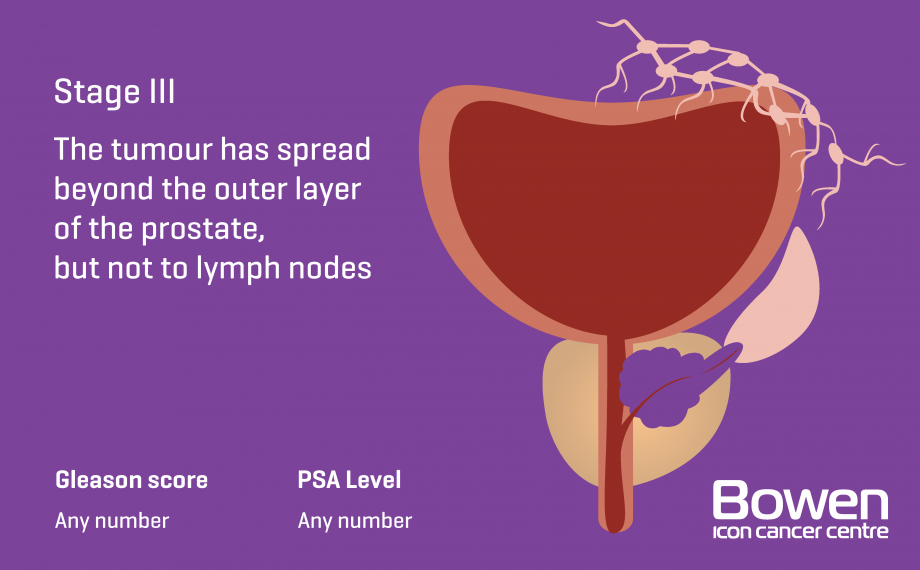
- Stage III: The tumor extends beyond your prostate and may be in a seminal vesicle. Cancer has not spread to lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: The tumor has spread to another part of your body, such as your bladder, rectum, lymph nodes or bones.
You May Like: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Testing For Prostate Cancer Metastasis
After your biopsy, additional tests or imaging may be performed to check for cancer spread, though these are not required in all men with newly diagnosed prostate cancer.
You may need additional tests if you have:
- High PSA levels
- Extensive prostate involvement on biopsy
- High Gleason scores
- Computed tomography scans of your abdomen and pelvis
- Bone scans
- Magnetic resonance imaging of your pelvis
Many centers, including SCCA, are testing other means of finding cancer spread using new types of positron emission tomography scans. Sometimes lymph nodes around the prostate may be checked for metastasis in order to design treatment appropriately.
At SCCA and University of Washington Medical Center, a long-term effort has identified cells in the bone marrow that originated from prostate cancer, even in the absence of other evidence of spread. With these and other studies being offered to men with advanced prostate cancer, we hope to find ways to identify men at the highest risk of relapse so this knowledge can inform our treatment recommendations.
Should I Have A Psa Test
- The Prostate Cancer Risk Management Programme gives you information on risks and benefits of the PSA test to help you decide whether or not to have it. Go to the website
- Also, an online decision aid called Prosdex provides information, including real-life stories, to help you make a decision on whether or not to have the PSA test.
Also Check: Tamsulosin Ejaculation
Signs And Symptoms Of Testicular Cancer
Many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than testicular cancer. A number of non-cancerous conditions, such as testicle injury or inflammation, can cause symptoms a lot like those of testicular cancer. Inflammation of the testicle and inflammation of the epididymis can cause swelling and pain of the testicle. Both of these also can be caused by viral or bacterial infections.
Some men with testicular cancer have no symptoms at all, and their cancer is found during medical testing for other conditions. For instance, sometimes imaging tests done to find the cause of infertility can uncover a small testicular cancer.
But if you have any of these signs or symptoms, see your doctor right away.
If the cancer is small and localized, a doctor may recommend:
Watchful waiting or monitoring
The doctor may check PSA blood levels regularly but take no immediate action.
Prostate cancer grows slowly, and the risk of side effects may outweigh the need for immediate treatment.
Surgery
A surgeon may carry out a prostatectomy. They can remove the prostate gland using either laparoscopic or open surgery.
Radiation therapy
Options include:
Brachytherapy: A doctor will implant radioactive seeds into the prostate to deliver targeted radiation treatment.
Conformal radiation therapy: This targets a specific area, minimizing the risk to healthy tissue. Another type, called intensity modulated radiation therapy, uses beams with variable intensity.
Screening For Prostate Cancer
There are no tests available with sufficient accuracy to screen populations of men for early signs of prostate cancer. However, early detection and treatment can significantly improve prostate cancer survival.
The test most commonly used to aid early detection of prostate cancer is the prostate specific antigen blood test. This is not a diagnostic test as it can only indicate changes in the prostate. If you are concerned about prostate cancer you should talk to your doctor and make an informed choice about whether to have one of the tests designed to find early signs of prostate cancer, in view of the potential risks and benefits.
There are no proven measures to prevent prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
How Doctors Find Metastatic Prostate Cancer
When you are diagnosed with prostate cancer, your doctor will order tests such as:
- X-rays
- MRI scans
- PET scans
These tests may focus on your skeleton and in your belly and pelvic areas. That way doctors can check for signs that the cancer has spread.
If you have symptoms such as bone pain and broken bones for no reason, your doctor may order a bone scan. It can show if you have signs of cancer spread in your bones.
Your doctor will also ask for blood tests, including a check of PSA levels, to look for other signs that the cancer is spreading.
PSA is a protein made by the prostate gland. A rise in PSA is one of the first signs your cancer may be growing. But PSA levels can also be high without there being cancer, such as if you have an enlarged prostate a prostate infection, trauma to the perineum, or sexual activity can also cause PSA level to be high.
If you’ve been treated, especially if a surgeon removed your prostate, your PSA levels should start to go down. Doctors usually wait seve,ral weeks after surgery before checking PSA levels. A rise in PSA after treatment may suggest the possibility cancer is back or spreading. In that case, your doctor may order the same tests used to diagnose the original cancer, including a CT scan, MRI, or bone scan. The radiotracer Axumin could be used along with a PET scan to help detect and localize any recurrent cancer.
Though very rare, it’s possible to have metastatic prostate cancer without a higher-than-normal PSA level.
What Are The Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
In most cases, prostate cancer causes no symptoms.
In rare cases, men may experience certain symptoms when they have advanced prostate cancer. However, these symptoms are also present in many men who do not have cancer, so it is best to discuss them with a doctor before jumping to any conclusions. Some of these symptoms can include difficulty emptying the bladder, blood in the urine, and bone pains.
You May Like: What Happens To The Prostate Later In Life
Management Of Weakness Or Numbness By Prostate Cancer Patients
When patients experience weakness or numbness in the limbs, it is likely that the disease has spread to the spinal cord and patients are already in stage IV of the disease. Stage IV cancers have already spread to nearby areas such as the bladder or rectum , to nearby lymph nodes, or to distant organs such as the bones. A small portion of T4 cancers may be curable using some of the same treatments for stage III cancers above. But most stage IV cancers cant be cured with standard treatment, state the American Cancer Society.
Treatment options for patients with stage IV prostate cancer include hormone therapy, external beam radiation combined with hormone therapy, TURP surgery to relieve the symptoms, drug treatments aimed at bone metastases like denosumab , a bisphosphonate like zoledronic acid , external radiation aimed at bones, or a radiopharmaceutical such as strontium-89, samarium-153 or radium-223, active surveillance for those patients with other severe disease, or taking part in a clinical trial of newer treatments. Specific for patients whose cancer is pressing the spinal cord, steroids, lying flat to reduce movement, pain control medication, radiotherapy, surgery, and bisphosphonates may be recommended.
What Are The Symptoms Of Advanced Prostate Cancer And Bone Metastases
When cancer cells spread to the bones, the condition weakens the very frame on which the body rests. The cells interfere with the strength and hardness of the bones structure, interrupting its normal cycle of building up and dissolving.
Theres no cure for advanced prostate cancer, but theres a lot that doctors can do to help with the symptoms that might develop. This includes managing pain. A common misconception is that if theres cancer in the bone, there must be pain, Tagawa says. Thats not true. Cancer can be in the bone without pain. However, if there is pain, he says, it can be controlled with anticancer therapies and pain medication, and good quality of life can be maintained.
In addition to pain, some men with bone metastases develop a condition called hypercalcemia, in which, because of the damage to bones from the cancer cells, too much calcium builds up in the blood. Hypercalcemia can make you feel constipated, thirsty, sleepy, or sluggish, and it can increase the urge to urinate, according to the ACS. Over time, hypercalcemia can cause muscle and joint achiness, as well as weakness in the muscles. In advanced stages, it can cause the kidneys to shut down.
There are treatments for hypercalcemia as well as for other complications from advanced prostate cancer, such as bones that become weak and break or fracture, and for growths in the spine that can press on the spinal cord and damage nerves.
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
Some risk factors have been linked to prostate cancer. A risk factor is something that can raise your chance of developing a disease. Having one or more risk factors doesn’t mean that you will get prostate cancer. It just means that your risk of the disease is greater.
- Age. Men who are 50 or older have a higher risk of prostate cancer.
- Race. African-American men have the highest risk of prostate cancerâthe disease tends to start at younger ages and grows faster than in men of other races. After African-American men, prostate cancer is most common among white men, followed by Hispanic and Native American men. Asian-American men have the lowest rates of prostate cancer.
- Family history. Men whose fathers or brothers have had prostate cancer have a 2 to 3 times higher risk of prostate cancer than men who do not have a family history of the disease. A man who has 3 immediate family members with prostate cancer has about 10 times the risk of a man who does not have a family history of prostate cancer. The younger a man’s relatives are when they have prostate cancer, the greater his risk for developing the disease. Prostate cancer risk also appears to be slightly higher for men from families with a history of breast cancer.
- Diet. The risk of prostate cancer may be higher for men who eat high-fat diets.
Pearls And Other Issues
PSA Testing: The Pros and the Cons
Prostate Specific Antigen is a protein produced by the prostate and is abundant in semen. Its natural function is to divide seminogelin in the semen, which helps in liquefaction. The expression of PSA is androgen-regulated.
It was originally used as a prostatic tissue stain to help determine the etiology of tumors of unknown origin. Later, serum levels of PSA were used as a prostate cancer screening tool because serum PSA levels start to increase significantly about seven to nine years before the clinical diagnosis of malignancy. While a good indicator of prostatic disorders, PSA elevation is not specific for cancer as it is also elevated in benign prostatic hyperplasia, infection, infarction, inflammation and after prostatic manipulation. It also cannot reliably distinguish between low risk/low grade disease and high risk/high grade cancers.
About 80% of the patients currently diagnosed with prostate cancer are initially investigated due to an elevated serum PSA.
While it unquestionably increases prostate cancer detection rates, the value of PSA testing is less clear in avoiding overtreatment, improving quality of life and lengthening overall survival which is why routine PSA screening for prostate cancer remains quite controversial.
PSA testing became widely available in the United States in 1992, and since then, prostate cancer detection rates have increased substantially.
The Current USPSTF Recommendation
Against PSA Screenings
Read Also: Female Equivalent Of Prostate
