Questions To Ask Your Doctor
To help understand the progression of prostate cancer, discuss these questions with your doctors:
- What is my Gleason score?
- Has the cancer spread outside my prostate?
- Whats my prostate cancer stage?
- Are other tests needed to determine my cancer stage?
- What are the treatment options for my stage of cancer?
- Can I avoid treatment right now and go on active surveillance?
Gleason Prostate Cancer Score
1960s as a way to measure how aggressive your prostate cancer may be.
A pathologist determines your Gleason score by looking at a biopsy of your prostate tissue under a microscope. They grade the cells in the biopsy on a scale of 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are healthy prostate, whereas grade 5 cells are highly mutated and dont resemble healthy cells at all.
The pathologist will calculate your Gleason score by adding together the number of the most prevalent type of cell in the sample and the second most prevalent type of cell.
For example, if the most common cell grade in your sample is 4 and the second most common is 4, you would have a score of 8.
A Gleason score of 6 is considered low-grade cancer, 7 is intermediate, and 8 to 10 is high-grade cancer.
Prostate Cancer Risk Factors
Throughout this article, the prostate biopsy was highlighted as an essential step in diagnosing prostate cancer. But the prostate biopsy is only performed after the screening of a suspicious case, and screening is only performed in patients with a high risk.
The most important risk factors include :
- Age: As we age, the risk of prostatic carcinoma increases. It is one of the most common types of cancer in aging males. 80% of cases are diagnosed in men after 65 years of age.
- Family history: Prostate cancer has a genetic link. If you have close male relatives with prostate cancer, you have a higher chance of having the same problem.
- Race: Males of African American descendancy have a higher rate of prostate cancer. They may also have a higher rate of aggressiveness.
Read Also: Does Cialis Shrink An Enlarged Prostate
Stage 1 Prostate Cancer Treatment
Prostate cancer is found in the prostate gland only and is non-detectable by an imaging test or DRE physical examination. Older men, men who suffer other serious health issues or younger men may consider active surveillance due to the slow growth rate, possibility of never experiencing any symptoms or preference to delay treatment. However, radiation or proton therapy for stage 1 prostate cancer is often recommended to reduce the risk of cancer spreading, especially for those with higher Gleason scores and PSA levels. Almost 80% of the time, prostate cancer is discovered at this stage and the 5-year survival rate is nearly 100%.
Initial Treatment Of Prostate Cancer By Stage
The stage of your cancer is one of the most important factors in choosing the best way to treat it. Prostate cancer is staged based on the extent of the cancer and the PSA level and Gleason score when it is first diagnosed.
For prostate cancers that haven’t spread , doctors also use risk groups to help determine treatment options. Risk groups range from very low risk to very high risk, with lower risk group cancers having a smaller chance of growing and spreading compared to those in higher risk groups.
Other factors, such as your age, overall health, life expectancy, and personal preferences are also taken into account when looking at treatment options. In fact, many doctors determine a mans possible treatment options based not just on the stage, but on the risk of cancer coming back after the initial treatment and on the mans life expectancy.
You might want to ask your doctor what factors he or she is considering when discussing your treatment options. Some doctors might recommend options that are different from those listed here.
Read Also: Can Bph Cause Constipation
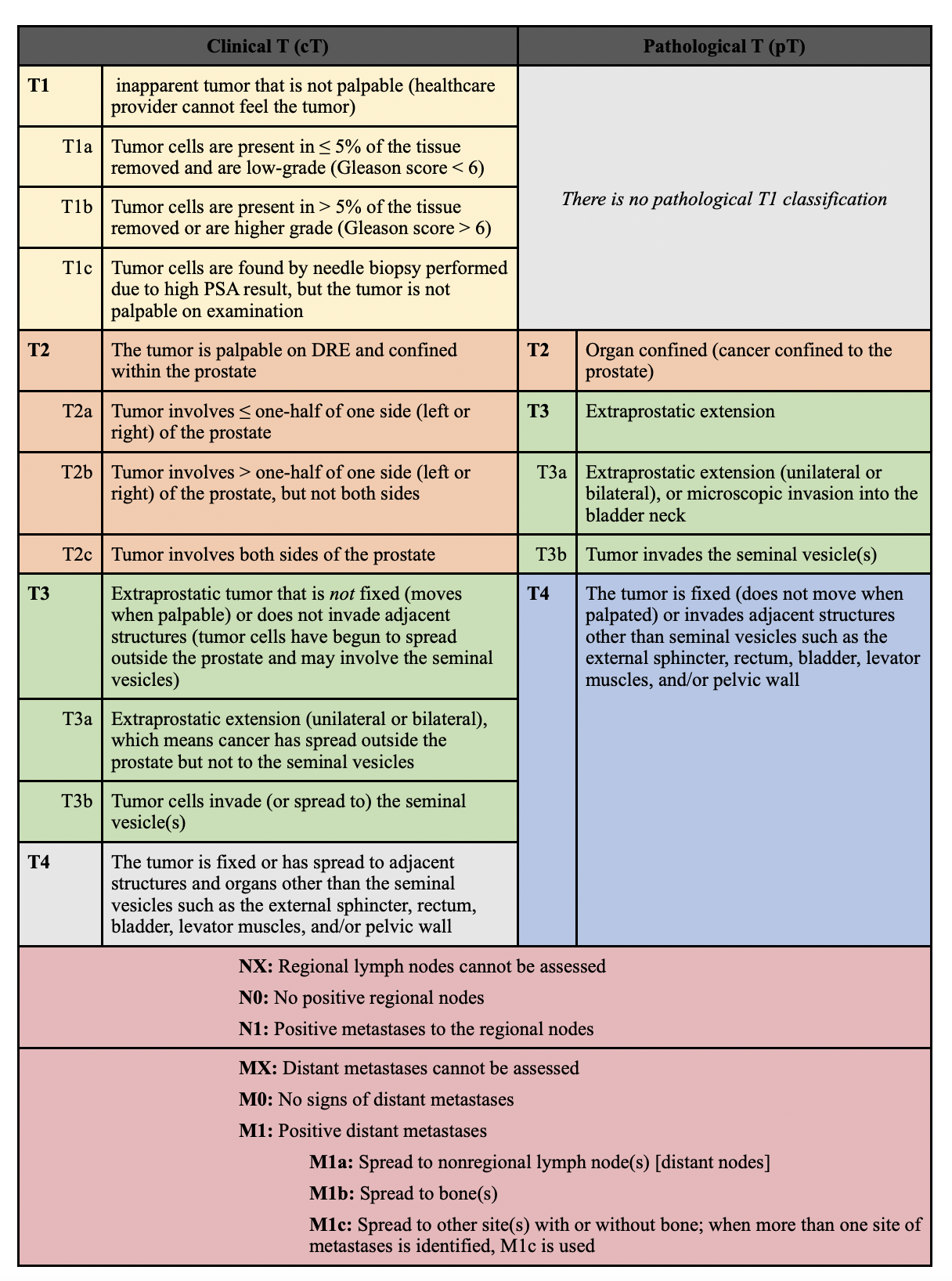
Evaluation Of The Tumor
Clinical T stage
- cTX: cannot evaluate the primary tumor
- cT0: no evidence of tumor
- cT1: tumor present, but not detectable clinically or with imaging
- cT1a: tumor was incidentally found in 5% or less of prostate tissue resected
- cT1b: tumor was incidentally found in greater than 5% of prostate tissue resected
- cT1c: tumor was found in a needle biopsy performed due to an elevated serum PSA
It should be stressed that the designation “T2c” implies a tumor which is palpable in both lobes of the prostate. Tumors which are found to be bilateral on biopsy only but which are not palpable bilaterally should not be staged as T2c.
Pathological T stage
- pT2: organ confined
What Does It Mean To Have A Gleason Score Of 6 Or 7 Or 8
The lowest Gleason Score of a cancer found on a prostate biopsy is 6. These cancers may be called well-differentiated or low-grade and are likely to be less aggressive – they tend to grow and spread slowly.;
Cancers with Gleason Scores of 8 to 10 may be called poorly differentiated or high grade. ;These cancers tend to be aggressive, meaning they are likely to grow and spread more quickly.
Cancers with a Gleason Score of 7 may be called moderately differentiated or intermediate grade. ;The rate at which they grow and spread tends to be in between the other 2.
Don’t Miss: Prostatitis Symptoms Mayo
Grade And Risk Category
The biopsy results will show the grade of the cancer. This is a score that describes how quickly the cancer may grow or spread.
For many years, the Gleason scoring system has been used to grade the tissue taken during a biopsy. If you have prostate cancer, youll have a Gleason score between 6 and 10. A new system has been introduced to replace the Gleason system. Known as the International Society of Urological Pathologists Grade Group system, this grades prostate cancer from 1 to 5 .
Risk of progression
Based on the stage, grade and your PSA level before the biopsy, localised prostate cancer will be classified as having a low, intermediate or high risk of growing and spreading. This is known as the risk of progression. The risk category helps guide management and treatment.
Grading prostate cancer
| High risk. The cancer is likely to grow aggressive. |
Evaluation Of The Histologic Grade
Usually, the grade of the cancer is evaluated separately from the stage. For prostate cancer, cell morphology is graded based on the Gleason grading system.
Of note, this system of describing tumors as “well-“, “moderately-“, and “poorly-” differentiated based on Gleason score of 2-4, 5-6, and 7-10, respectively, persists in SEER and other databases but is generally outdated. In recent years pathologists rarely assign a tumor a grade less than 3, particularly in biopsy tissue.
You May Like: Prostate Cancer Ruined My Marriage
Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial Risk Calculator
The Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial Risk Calculator was developed to help clinicians decide whether a biopsy is needed. It takes into account many clinical factors, including:
- PSA level
- Family history
- Biopsy history
The results of the calculator may not apply to all individuals. Clinicians should only use it for those who:
- Are 55 or older
- Havent been diagnosed with prostate cancer in the past
- Have results from a PSA or DRE that are less than 1 year old
What Are Prostate Cancer Survival Rates By Stage
Staging evaluation is essential for the planning of treatment for prostate cancer.
- A basic staging evaluation includes the patient examination, blood tests, and the prostate biopsy including ultrasound images of the prostate.
- Further testing and calculations may be performed to best estimate a patient’s prognosis and help the doctor and patient decide upon treatment options.
Prognosis refers to the likelihood that the cancer can be cured by treatment, and what the patient’s life expectancy is likely to be as a consequence of having had a prostate cancer diagnosis.
If a cancer is cured, your life expectancy is what it would have been had you never been diagnosed with prostate cancer. If the cancer cannot be cured due to it recurring in distant locations as metastases, or recurs either locally or in an area no longer able to be treated in a curative manner, then estimates can be made of what is likely to be your survival based again on group statistics for people who have been in the same situation.
Nomograms are charts or computer-based tools that use complex math from analysis of many patients’ treatment results.
The prognosis for prostate cancer varies widely, and depends on many factors, including the age and health of the patient, the stage of the tumor when it was diagnosed, the aggressiveness of the tumor, and the cancer’s responsiveness to treatment, among other factors.
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Pathological Stage: A Look At The Actual Cancer Cells And Their Distribution Within The Pelvic Area
This system assesses how pervasive the cancer cells are within and around the prostate. These stages begin at T2.
T2: The tumor is located in the prostate only.T3: The tumor has breached the prostate border on 1 or more sides.T3b: The tumor has begun to grow in the seminal vesicles.T4: The tumor has grown into other neighboring structures, like the bladder, the rectum, or the pelvic wall.
What Are The Different Stages Of Prostate Cancer
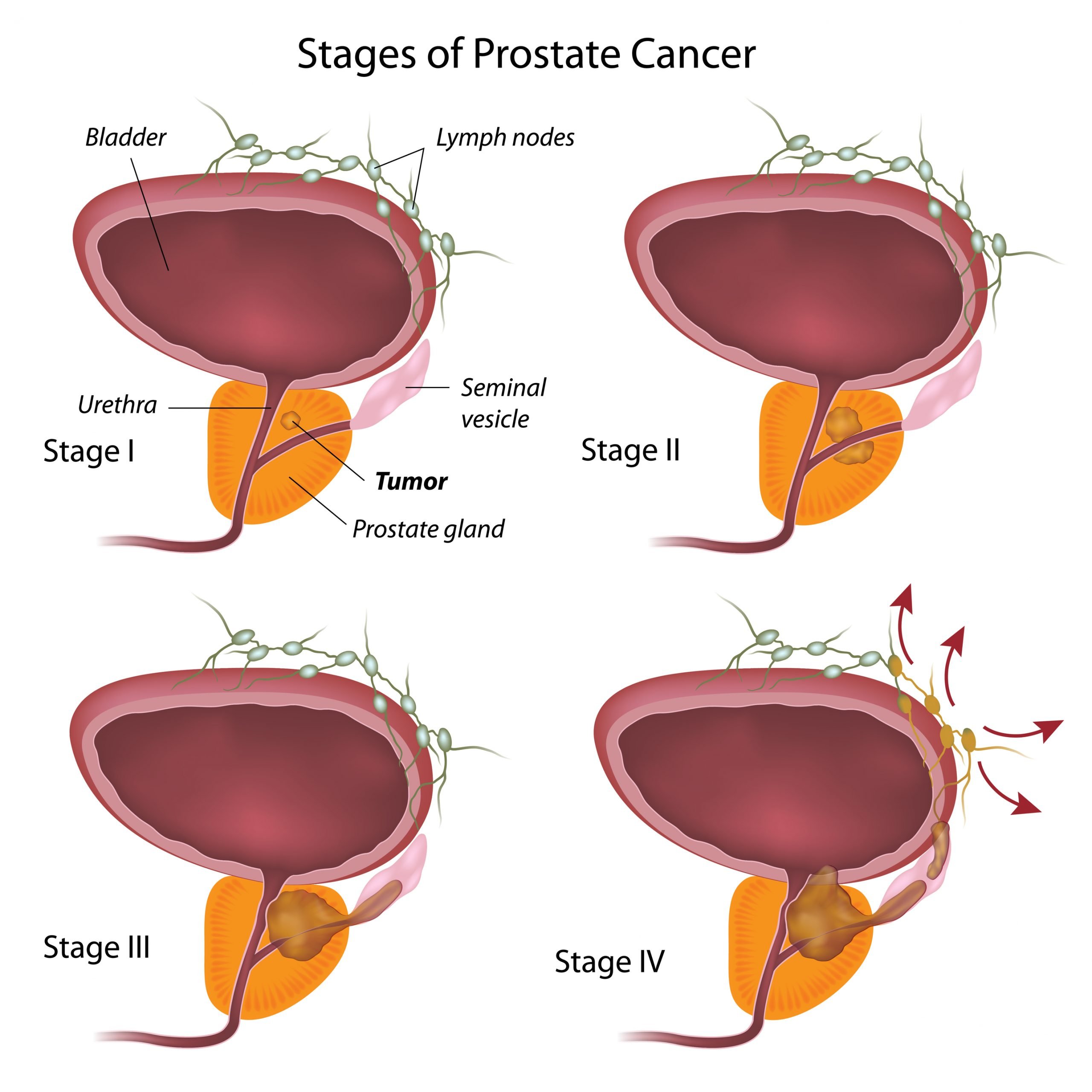
The most common way doctors describe the stage of prostate cancer is with the TNM system. In this system, the stage is based on the size and extent of your tumor, whether the lymph nodes are involved, and how far the cancer has spread, as well as the Gleason score and PSA level. Your doctor gets this information from your digital rectal exam , lab tests, biopsies, and scans.
Don’t Miss: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
What Are The Damico Risk Categories
The DAmico system provides an estimate of the risk of recurrence at five years after treatment. This system is one of the most widely used for risk assessment. It combines the PSA, Gleason score, and the clinical stage to create low, intermediate, and high risk categories. The higher the risk category, the higher the chance of recurrence is five years after treatment.
The DAmico risk categories are below. If one factor is putting you in a lower category but another is putting you in a higher category, then the higher category takes precedent.
How Important Is The Gleason Score
The Gleason Score is very useful for predicting the behavior of a prostate cancer.; However, other factors also contribute to determining the stage of prostate cancer, including:
- The PSA level
- Findings from a rectal exam
- The number of biopsy core samples that contain cancer
- The percentage of cancer making up each biopsy core sample
- If cancer is found in one or both sides of the prostate
- If the cancer has spread outside the prostate
Recommended Reading: Can An Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
Has Your Cancer Spread Beyond The Prostate
Prostate Cancer Stage is the rating system consisting of four stages used to describe the spread of cancer. The different stages of cancer describe cancer confined within the prostate, growth that extends to tissue outside the prostate, to local organs or metastasized to distant parts of the body. Several different tests can be used either alone or in combination to determine the extent of spread of the cancer. Not all of these tests are needed in all men. Staging tests include the DRE, PSA Blood Test, Ultrasound, Biopsy, Bone Scan, Cat Scan, MRI and PET Scan.
Prostate Cancer Stage is the rating system consisting of four stages used to describe the spread of cancer. The different stages of cancer describe cancer confined within the prostate, growth that extends to tissue outside the prostate, to local organs or metastasized to distant parts of the body. Several different tests can be used either alone or in combination to determine the extent of spread of the cancer. Not all of these tests are needed in all men. Staging tests include the DRE, PSA Blood Test, Ultrasound, Biopsy, Bone Scan, Cat Scan, MRI and PET Scan.
Stage : Prostate Cancer Is Limited To A Small Part Of The Prostate
- Often, the cancer is found as a result of needle examination of tissue for another reason, such as benign prostatic hypertrophy , also known as an enlarged prostate, or because of an elevated result on a prostate specific antigen ;test, which uses PSA levels as an indicator of potential cancerous growth.
- Cancer cells are only found in a small part of the prostate. The cells look like normal cells and the prostate feels normal with a digital rectal exam .
- PSA is less than 10.
- Gleason score, which assigns a grade to what the cancer cells looks like under a microscope, is less than 6, the Prostate Cancer Foundation notes.
Read Also: Is Viagra Good For Enlarged Prostate
Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
In stage 2, the tumor is still confined to your prostate and hasnt spread to lymph nodes or other parts of your body. A doctor may or may not be able to feel the tumor during a prostate exam, and it may appear on ultrasound imaging. The survival rate is still near 100 percent.
The PSA score for stage 2 is less than 20 ng/mL.
Stage 2 cancer is further divided into three phases depending on the grade group and Gleason scores:
- Grade group: 1
- Gleason score: 6 or less
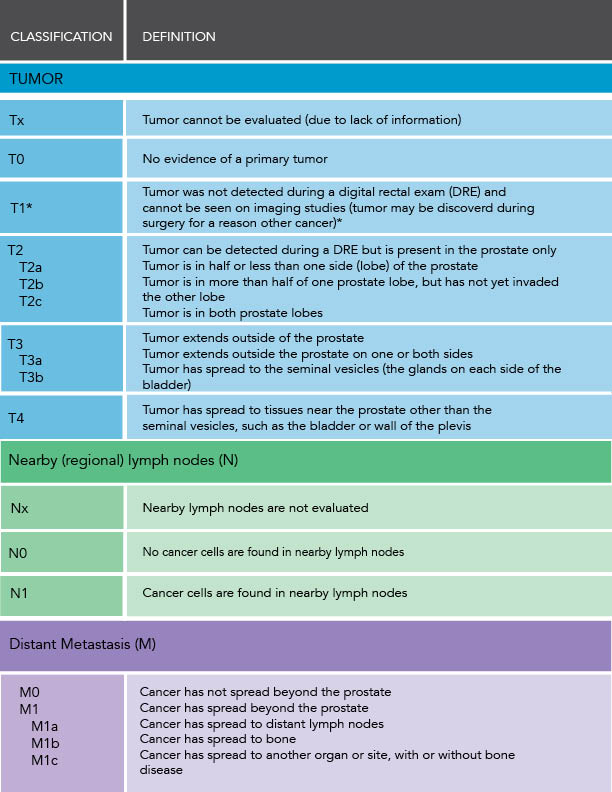
Tnm Staging System The Most Widely Used Staging System For Prostate Cancer Isthe Ajcc Tnm System For Prostate Cancerthere Are 4 Stages Often The Stages 1 To 4 Are Written As The Roman Numeralsi Ii Iii And Iv Generally The Higher The Stage Number The More The Cancerhas Spread The Stages Can Be Further Divided Into A B Or C An Earlier Lettermeans A Lower Stage Talk To Your Doctor If You Have Questions About Staging Tnm Staging Is Based On The Following: T Describes Thetumour And Whether Doctors Can Feel It Or See It On Imaging Tests It Alsodescribes Whether The Tumour Has Grown Outside Of The Prostate To Thesurrounding Tissues T Is Usually Given As A Number From 1 To 4 A Highernumber Means That The Tumour Takes Up More Of The Prostate Or That The Tumourhas Grown Outside Of The Prostate Into Nearby Tissues Some Stages Are Alsodivided Further Into A B Or C An Earlier Letter Means A Lower Stage The Clinical T Is Your Doctor’s Best Estimate Of Theextent Of The Cancer Based On A Physical Exam A Digital Rectal Exam A Prostatebiopsy And Imaging Tests If You Have Surgery To Remove Your Prostate Apathological T Will Be Given Pt Is More Accurate Than Ct T The Tumour Has Grown Outside The Prostate And Into The Seminal Vesicles T4 The Tumour Has Grown Outside The Prostate And Into Nearby Structures Suchas The Bladder Rectum Pelvic Muscles And Pelvic Wall
N describeswhether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the prostate. N0 means that thecancer hasn’t spread to any nearby lymph nodes. N1 means that it has spread tonearby lymph nodes.
M describeswhether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. M0 means that the cancerhas not spread to other parts of the body. M1 means that it has spread to otherparts of the body.
PSA level describes the amount of the prostate-specificantigen in the blood.
Grade Group is a measureof how likely the cancer is to grow and spread.
Read Also: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
Gleason Score Vs Grade Groups
The International Society of Urological Pathology released a revised prostate cancer grading system in 2014. The grade group system seeks to simplify Gleason scores and give a more accurate diagnosis.
One of the major problems with the Gleason score is that some scores can be made up in different ways. For example, a score of 7 can mean:
- 3 + 4. The 3 pattern is the most common in the biopsy and 4 is the second most common. This pattern is considered favorable intermediate risk.
- 4 + 3. The 4 pattern is the most common in the biopsy and 3 is the second most common. This pattern is considered unfavorable and may mean local or metastatic spread.
So, although both situations give a Gleason score of 7, they actually have very different prognoses.
Heres an overview of how the two grading systems compare:
| Cancer grade | |
|---|---|
| grade group 5 | 910 |
Not all hospitals have switched to the grade group system. Many hospitals give both grade group and Gleason scores to avoid confusion until grade groups become more widely used.
What Does It Mean If In Addition To Cancer My Biopsy Report Also Says Acute Inflammation Or Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation of the prostate is called prostatitis. ;Most cases of prostatitis reported on a biopsy are not caused by infection and do not need to be treated. ;In some cases, inflammation may increase you PSA level, but it is not linked to prostate cancer. ;The finding of prostatitis on a biopsy of someone with cancer does not affect their prognosis or the way the cancer is treated.
Read Also: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
