Why Choose Bens Natural Health Supplements
At Bens Natural Health, our motto is to combine holistic healing with modern science.
Bens Natural Health is the worlds first high-quality, all-natural, scientifically proven clinical supplement company. Our supplements are effective, natural and 100% side effect free.
Moreover, at Bens Natural Health, we have four rules for all our supplements:
- We only use the highest quality ingredients
- We only use them if they have been proven to work in independent, peer-reviewed double-blind studies
- With all our supplements, we find a way to get every ingredient into a single bottle
- We always formulate them in clinically significant doses of the most bioavailable form
And, all our supplements come with a 90-day money-back guarantee. So if you arent happy with the results, we will provide you with credit or a full refund.
Also Check: Can Prostate Issues Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
What Is The Normal Size Of The Prostate Gland
Additionally, this gland is responsible for protecting men from urinary tract infections and maintains a healthy bladder, so it is paramount that it is in perfect condition. The size of this gland varies with age, however in an adult male the normal prostate size is between 4cm X 3 cm, similar in shape to a chestnut.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Definition Of Prostate
Questions You May Want To Consider Asking Your Doctor Include:
- What type of prostate problem do I have?
- Is more testing needed and what will it tell me?
- If I decide on watchful waiting, what changes in my symptoms should I look for and how often should I be tested?
- What type of treatment do you recommend for my prostate problem?
- For men like me, has this treatment worked?
- How soon would I need to start treatment and how long would it last?
- Do I need medicine and how long would I need to take it before seeing improvement in my symptoms?
- What are the side effects of the medicine?
- Are there other medicines that could interfere with this medication?
- If I need surgery, what are the benefits and risks?
- Would I have any side effects from surgery that could affect my quality of life?
- Are these side effects temporary or permanent?
- How long is recovery time after surgery?
- Will I be able to fully return to normal?
- How will this affect my sex life?
- How often should I visit the doctor to monitor my condition?
Related Resources
Read Also: External Prostate Massage For Prostatitis
What Is The Function Of The Prostate
The prostate plays a fundamental role in the formation of seminal fluid, making sure it produces the correct volume. Their secretions also benefit the mobility of sperm, ensuring that they arrive safely to the egg to fertilize it.
Additionally, this gland is responsible for protecting men from urinary tract infections and maintains a healthy bladder, so it is paramount that it is in perfect condition.
Don’t Miss: How Are Fiducial Markers Placed In The Prostate
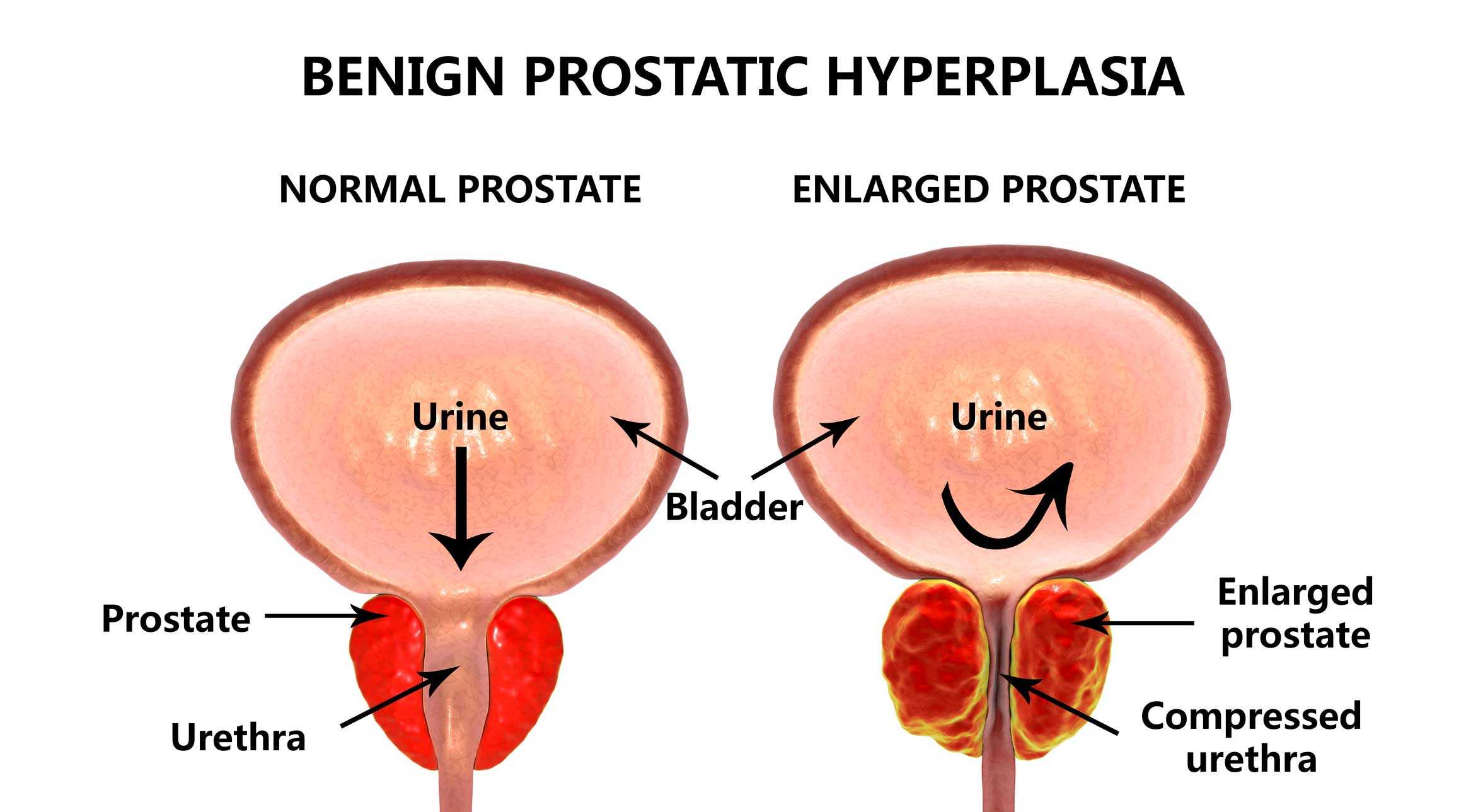
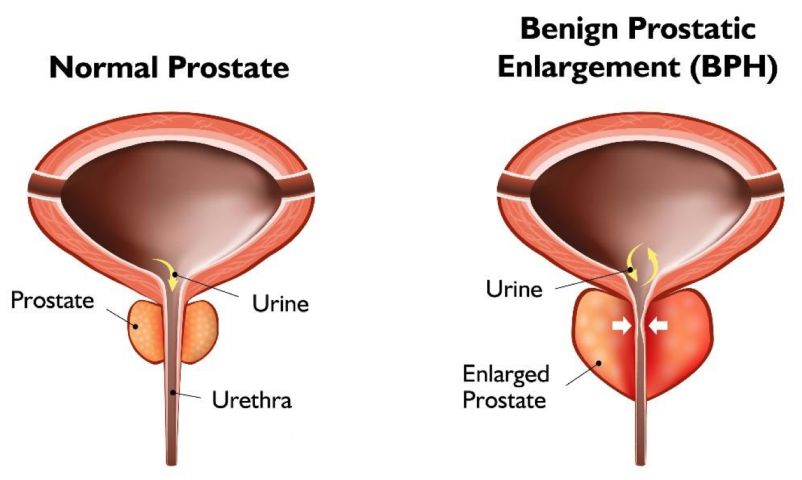
What Is Enlarged Prostate
Enlarged prostate refers to the state in which the prostate is enlarged but not cancerous.
Hormonal changes and cell growth resulting from the aging process may cause the prostate to swell, often impinging upon and compressing the urethra. This causes the bladder walls to become thicker and can prevent the bladder from emptying completely.
Risks Factors Of An Enlarged Prostate
Risk factors for benign prostatic hyperplasia include:
- AgeAs men age, they are more likely to develop BPH. More than half of men over 80 have symptoms from the condition.
- Family history If your father or brother have prostate conditions including BPH, you are more likely to develop the prostate conditions.
- Chronic conditions Chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease can increase your risk of developing BPH.
- Obesity Being overweight makes you more likely to develop BPH as you age.
Don’t Miss: Chemo Drug For Prostate Cancer
How Does The Size Of The Prostate Change With Age
The size of the prostate varies with age. In normal adults, the prostate is about the size of a walnut, but it can become significantly larger in older men. Around the age of 40, the prostate gland tends to enlarge as the result of a condition called benign prostatic hypertrophy . SPECIAL TIP: The One Thing Your Prostate Needs Every Morning
Managing The Enlarged Prostate Gland In Elderly Men
Megan Janeway and Neil Baum, MD
Case Presentation
A 67-year-old male is seen in the Emergency Department for urinary retention. He has a history of moderate lower urinary tract obstructive and irritative symptoms consisting of frequency, urgency, poor force and caliber of his urinary stream, and nocturia. In the last few days prior to his admission to the hospital, he had dribbling of urination and lower abdominal pain. A physical exam revealed a bladder palpable above the pubic symphysis, the rectal exam revealed a markedly enlarged prostate gland, and a urinalysis revealed 5-7 white blood cells/high power field. The patients prostate-specific antigen was 6.5 ng/mL. The blood urea nitrogen was 40 mg/dL, and serum creatinine was 2.6 mg/dL. An abdominal ultrasound revealed hydroureteronephrosis with a markedly distended bladder. A Foley catheter was inserted, and he had approximately 900 cc of residual urine. He experienced a post-obstructive diuresis with normalization of his BUN and creatinine levels. A cystoscopy revealed coaptation of the lateral lobes of the prostate and grade 3 trabeculation of the bladder. The patient had GreenLight laser treatment of his outlet obstruction and used a catheter for 3 days after the procedure. He was able to void with a good stream and had less than 75 cc of post-void residual. Follow-up BUN and creatinine levels 3 weeks after the GreenLight laser procedure were 15 mg/dL and 1.7 mg/dL.
Discussion
Summary
References
Read Also: Expressed Prostatic Secretion
How Is Bph Diagnosed And Evaluated
Early diagnosis of BPH is important because if left untreated it can lead to urinary tract infections, bladder or kidney damage, bladder stones and incontinence. Distinguishing BPH from more serious diseases like prostate cancer is important.
Tests vary from patient to patient, but the following are the most common:
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer: What Are The Symptoms For Prostate Cancer
Usually, prostate cancer does not produce symptoms by itself until it is fairly advanced. Prostate cancer arises silently and usually passes through a curable stage into an incurable stage silently. Therefore, the only means of detecting it when it is curable is to actively look for it with screening. Symptoms could include urinary difficulties however, these symptoms are usually caused by benign enlargement of the prostate. However, these symptoms are usually caused by urinary obstruction from benign prostatic enlargement,scar tissue or from inflammation. Bone pain occurs in very advanced prostate cancer, but the aches and pains that most people experience are usually caused by arthritis.
Read Also: Chemo Pills For Prostate Cancer
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of An Enlarged Prostate
An enlarged prostate is the most common cause of urinary problems in men as they get older. Possible symptoms include:
- a weak flow when you urinate
- a feeling that your bladder hasnt emptied properly
- difficulty starting to urinate
- dribbling urine after you finish urinating
- needing to urinate more often, especially at night
- a sudden urge to urinate you may sometimes leak before you get to the toilet.
You may not get all of these symptoms, and some men with an enlarged prostate dont get any symptoms at all. These symptoms can also be caused by other things, such as cold weather, anxiety, other health problems, lifestyle factors, and some medicines. Blood in your urine may be a symptom of an enlarged prostate. But this is rare and is usually caused by something else.
If you have any of the symptoms above, you should visit your GP to find out what may be causing them.
Tips For Relieving Bph Symptoms
Four simple steps can help relieve some of the symptoms of BPH:
For more on advances in the diagnosis and treatment of prostate diseases, read the Annual Report on Prostate Diseases from Harvard Medical School.
Recommended Reading: Finding The Prostate Externally
Diagnosis And Management Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
JONATHAN L. EDWARDS, MD, Barberton Citizens’ Hospital, Barberton, Ohio
Am Fam Physician. 2008 May 15 77:1403-1410.
Patient information: See related handout on benign prostatic hyperplasia, written by the author of this article.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a common condition in older men. Histologically, it is characterized by the presence of discrete nodules in the periurethral zone of the prostate gland.1 Clinical manifestations of BPH are caused by extrinsic compression of the prostatic urethra leading to impaired voiding. Chronic inability to completely empty the bladder may cause bladder distension with hypertrophy and instability of the detrusor muscle. Some patients with BPH present with hematuria. Because the severity of symptoms does not correlate with the degree of hyperplasia, and other conditions can cause similar symptoms, the clinical syndrome that often accompanies BPH has been described as lower urinary tract symptoms.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Men with suspected BPH can be evaluated with a validated questionnaire to quantify symptom severity.
BPH = benign prostatic hyperplasia.
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence B = inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, see page 1360 or .
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Medications For Enlarged Prostate
There are two main classes of pharmaceuticals that work to alleviate enlarged prostate symptoms: alpha blockers and alpha reductase inhibitors
-
Alpha Blockers. Alpha blockers relax the smooth muscle around the bladder neck and within the urethra.
-
Inhibitors. Inhibitors stop the conversion of the male hormone testosterone to DHT to reduce the prostate’s size, eliminating blockage.
Dont be surprised if your physician prescribes a combination of the two medications, as they have been shown to work more effectively together than alone. The downside is that combination therapy may increase the likelihood of experiencing side effects from the medications. Be sure to work with your doctor to assess the benefits and costs before starting on combination therapy.
Also Check: Ejaculation Problems With Tamsulosin
What Causes An Enlarged Prostate
We still dont really know all the things that cause the prostate to grow. But we do know about two risk factors that can increase your risk of having an enlarged prostate.
Age
Your risk of having an enlarged prostate increases as you get older. Many men aged 50 or over have an enlarged prostate, but they dont all get symptoms. And some men have symptoms that donât bother them.
Hormone levels
The balance of hormones in your body changes as you get older. This may cause your prostate to grow.
Other factors
Some studies show that obese men and men who have diabetes may be more likely to develop an enlarged prostate. Regular exercise may help to reduce your risk of urinary symptoms. But we still need more studies into the causes of enlarged prostate to know for certain if, and how, we can prevent it.
There is also some research that suggests you may be more at risk of developing an enlarged prostate if your father or brother has one. Again, further studies are needed to confirm this.
Symptoms Of An Enlarged Prostate
As mentioned above, the most common symptoms of an enlarged prostate are urination problems. Its because the prostate portion surrounding the urethra narrows the normal passage of urine. These problems become worse as the patient gets older.
The progression prolongs which some patients may not even realize. They learn to live with the symptoms and sometimes wont even report them. However, it is crucial to recognize the symptoms of an enlarged prostate and consult your doctor.
Heres a list of the most important symptoms .
You May Like: Can Zytiga Cure Prostate Cancer
What Causes Prostate Enlargement
The causes of prostate enlargement are not yet fully understood but are thought to be related to the male sex hormone which controls the growth of the prostate. The prostate is initially quite small, but as men age, testosterone feeds the prostate and it starts to get bigger. From birth to around the early teenage years, the prostate increases in size by around 8 times. It doubles again in size from around the early 20s through to 50 years of age, and then doubles again by around the age of 80. With such large increases in size, its easy to see why the prostate can begin to squeeze the urethra and make it difficult to urinate.
There may also be a genetic link to prostate enlargement, because the sons of men with an enlarged prostate are more likely to develop prostate disease.
What Other Problems Might An Enlarged Prostate Cause
A small number of men may find it difficult to empty their bladder properly this is called urine retention. If youve been diagnosed with an enlarged prostate, your doctor will look at your test results to see if youre at risk of urine retention. You may be more likely to get urine retention if:
- youre aged 70 or over
- your prostate is very large
- you have a raised prostate specific antigen level
- you have severe urinary symptoms and a very slow flow.
Chronic urine retention
This is where you cant empty your bladder fully, but can still urinate a little. It usually develops slowly over time. Chronic means long-lasting. The first signs often include a weak flow when you urinate, or leaking urine at night. You may feel that your abdomen is swollen, or that youre not emptying your bladder fully.
Chronic urine retention is usually painless. But the pressure of the urine can slowly stretch your bladder muscle and make it weaker. This can cause urine to be left behind in the bladder when you urinate. If you dont empty your bladder fully, you might get a urine infection, need to urinate more often, leak urine at night, or get painful bladder stones. You might also see some blood in your urine. Chronic urine retention can damage your bladder and kidneys if it isnt treated.
There are treatments for chronic urine retention, including:
- passing a thin, flexible tube called a catheter to drain urine from your bladder
- surgery to widen the urethra.
Acute urine retention
Also Check: Define Prostate
Medications For Prostate Enlargement
Typical medications used to treat prostate issues are Finasteride , dutasteride , and tamsulosin . Finasteride and dutasteride are 5-alpha reductase inhibitors that reduce the amount of the 5-alpha reductase enzyme in the blood. This enzyme converts testosterone in the blood into estrogen. High levels of estrogen exacerbate prostate growth and can result in BPH.
Men with high estrogen levels also tend to develop breast enlargement . Any man who spends a lot of time at the gym has probably noticed older men with enlarged breasts due to a high estrogen level. Enlarged male breasts are an outward indicator, but BPH is most likely also present inwardly.
Tamsulosin is an alpha-blocker that works by relaxing the prostate and bladder muscles so that urine flows easier.
Each of these drugs has a profile of severe sexual side effects. Alpha-blockers can lead to difficulty ejaculating, and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can destroy libido as well as alter the sensation of orgasm or interfere with erections. For example, in several studies, Finasteride has been shown to increase the risk for men with BPH to develop erectile dysfunction.
Also Check: Can Exercise Reduce Prostate Size
Diagnosing Benign Prostate Enlargement
You might have several different tests to find out if you have an enlarged prostate.
A GP may do some of these tests, such as a urine test, but others might need to be done at a hospital.
Some tests may be needed to rule out other conditions that cause similar symptoms to BPE, such as prostate cancer.
Read Also: How Long Can You Take Lupron For Prostate Cancer
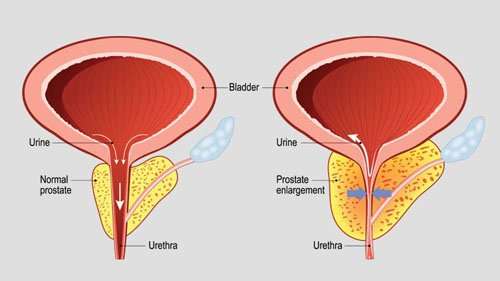
When Does An Enlarged Prostate Block Urine Flow
When the prostate becomes more enlarged over time, it might press against the urethra and block urine flow . This condition is called benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH. Enlarged prostates differ in size.
Additionally, this gland is responsible for protecting men from urinary tract infections and maintains a healthy bladder, so it is paramount that it is in perfect condition. The size of this gland varies with age, however in an adult male the normal prostate size is between 4cm X 3 cm, similar in shape to a chestnut.
If You Have Any Problems
If you have any discomfort when urinating, any pain in the area around the prostate or any indication of a problem, the recommendation is to visit a urologist who can examine you to determine the source of discomfort or the problem.
It is important to visit a urologist whenever you feel the smallest discomfort, as the problem could get worse with time.
This article is merely informative, oneHOWTO does not have the authority to prescribe any medical treatments or create a diagnosis. We invite you to visit your doctor if you have any type of condition or pain.
If you want to read similar articles to What is the Normal Size of the Prostate, we recommend you visit our Family health category.
Recommended Reading: Super Beta Prostate Advanced Side Effects
