Screening For Prostate Cancer
There are no tests available with sufficient accuracy to screen populations of men for early signs of prostate cancer. However, early detection and treatment can significantly improve prostate cancer survival.
The test most commonly used to aid early detection of prostate cancer is the prostate specific antigen blood test. This is not a diagnostic test as it can only indicate changes in the prostate. If you are concerned about prostate cancer you should talk to your doctor and make an informed choice about whether to have one of the tests designed to find early signs of prostate cancer, in view of the potential risks and benefits.
There are no proven measures to prevent prostate cancer.
What Is Localized Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the prostate gland. Localized prostate cancer has not spread outside the gland. Early prostate cancer usually doesnât cause symptoms.
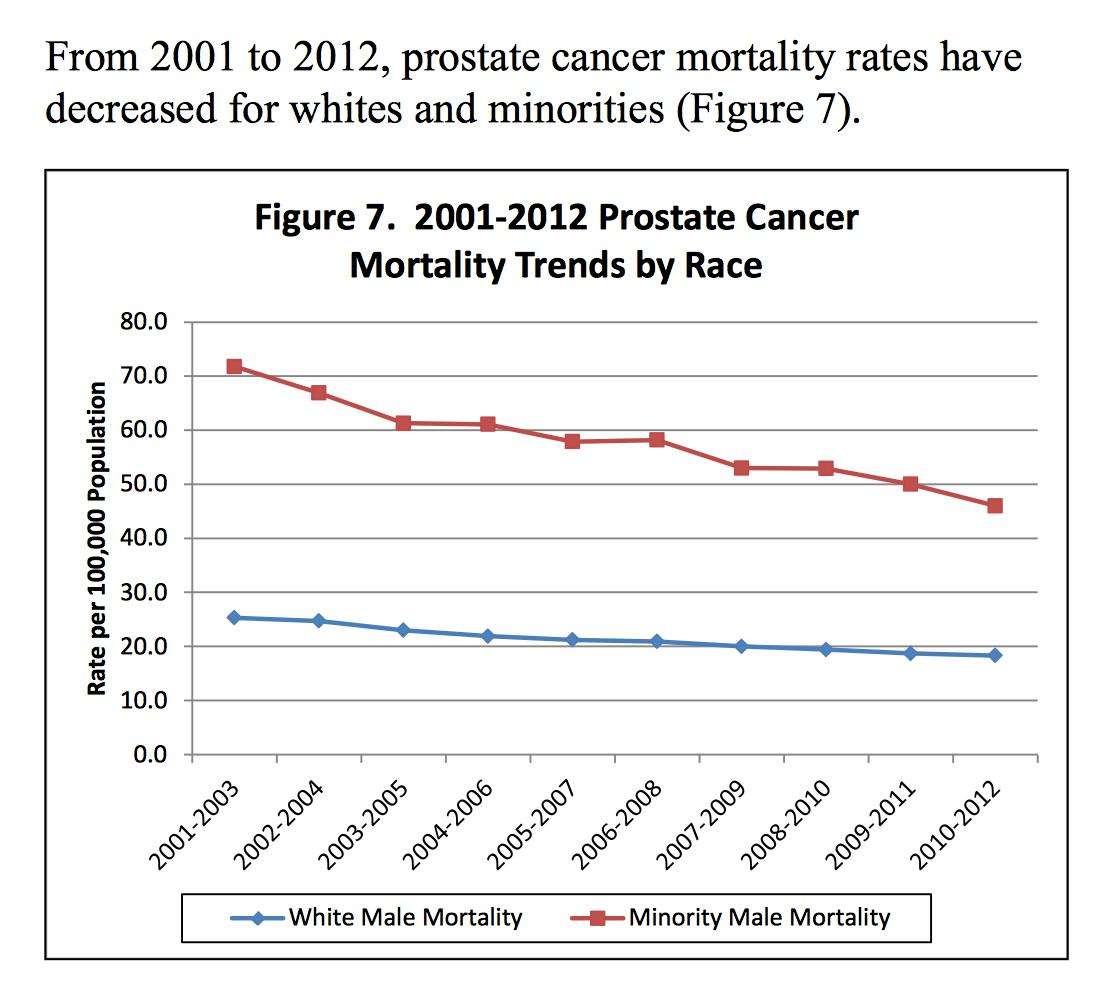
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men. Most men who get it are older than 65. If your father, brother, or son has had prostate cancer, your risk is higher than average.
Men of African descent have the highest rates of both prostate cancer and deaths from it.
About 21,000 men are diagnosed with prostate cancer in Canada every year.footnote 1 In the United States, about 12 out of 100 men in the U.S. will be diagnosed with prostate cancer sometime in their lifetime.footnote 2 But most men who are diagnosed with prostate cancer donât die from prostate cancer.
Unlike many other cancers, prostate cancer is usually slow-growing. When prostate cancer is found earlybefore it has spread outside the glandit may be cured with radiation or surgery.
Prostate cancer that has grown beyond the prostate is called advanced prostate cancer. Treatment choices are different for that stage of cancer.
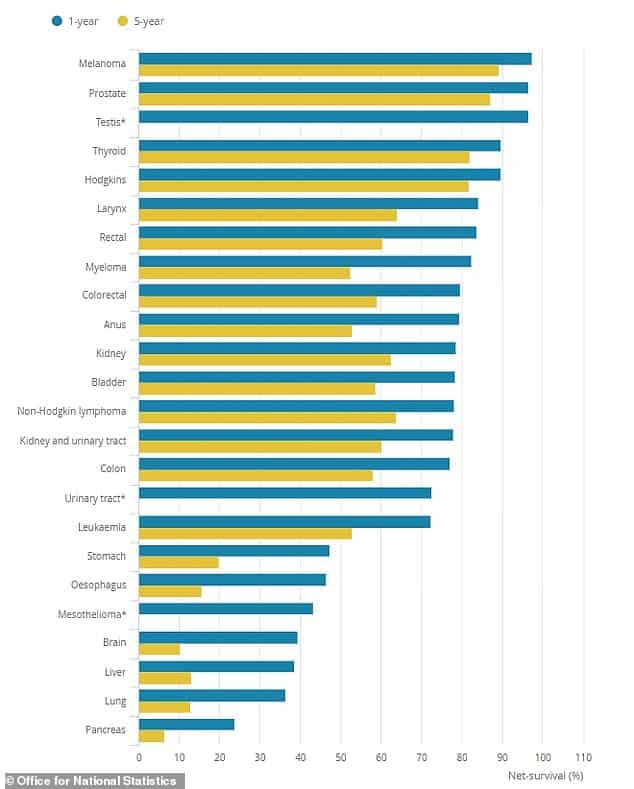
Survivability For Prostate Cancer According To Stage
Relative survival looks at a persons chances of surviving after diagnosis compared to a healthy person from the general population who shares similar characteristics, such as age, sex, and race.
For prostate cancer, relative survival depends on the stage of the disease . It is important to note that this prognostic grouping, also established by the UICC, is more accurate than stage grouping in assessing a survival prognostic.
Recommended Reading: Is Coffee Bad For Your Prostate
Prognosis And Survival For Prostate Cancer
If you have prostate cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctor’s best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type and stage and other features of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
The following are prognostic and predictive factors for prostate cancer.
Experimental Treatments For Advanced Prostate Cancer
Researchers are currently testing many new approaches and treatments for prostate cancer, including new medications. These include the following:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
The immune system uses âcheckpointsâ to stop it from attacking the bodyâs healthy cells. These checkpoints are proteins on immune cells.
Cancer cells often use these checkpoints to keep the immune system from attacking them.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are drugs that can these checkpoints on cancer cells. Inhibiting these checkpoints can allow a personâs immune system to attack the cancer cells.
Chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy
This treatment involves taking immune cells from the personâs blood. A scientist then alters these cells in a lab to have receptors called chimeric antigen receptors on their surface.
These receptors help the cells attach to proteins on the surface of prostate cells. A scientist then multiplies these altered T cells in a lab before putting them back into the personâs blood.
Scientists hope these T cells can then find prostate cancer cells and launch a targeted immune attack.
However, this treatment is complicated and may have some serious side effects. This means it is currently only available as part of clinical trials.
Targeted drug therapies
Targeted drug therapies can act on specific parts of cancer cells and the environments surrounding them.
These drugs
Two possible targeted therapy treatments are:
Treating prostate cancer that has spread to the bones
Also Check: What Do Doctors Look For In A Prostate Exam
The Stages Of Prostate Cancer: What You Need To Know
After a prostate cancer diagnosis, your oncologist will refer to the stage of your cancer. All cancers are categorized into four distinct stages, each of which identifies the progress of the growth of cancerous cells within clinically defined standards. These stages help doctors determine the most appropriate care for each patient based on his or her condition, and can also provide easy-to-understand context for your diagnosis. Learn more about the stages of prostate cancer, how each stage will affect your treatment plan and the survival rates for each stage, then contact Regional Cancer Care Associates to schedule a consultation.
Detecting Prostate Cancer Early
Thanks to advances in screening options for prostate cancer, it is very possible to detect this cancer early to improve a patients outlook. Prostate cancer screening is recommended for men ages 50 to 70, as well as younger men with risk factors, such as obesity or a family history of prostate cancer. The screening process typically involves a digital rectal examination , in which a physician inserts a gloved finger into the rectum, and a blood test called the prostate-specific antigen .
PSA is a protein produced by prostate tissue cancerous cells emit more PSA than noncancerous cells. Therefore, an elevated PSA level in a blood test may indicate prostate cancer. However, this screening test is not infallible, as there are other, less-serious reasons for an elevated PSA level, such as prostate inflammation, a urinary tract infection, benign prostatic hyperplasia or even the natural aging process. A physician will take other factors into account when evaluating a patients PSA levels and will recommend a biopsy if they suspect prostate cancer may be the cause.
You May Like: Can Enlarged Prostate Cause Back Pain
What Factors Determine Life Expectancy For Metastatic Prostate Cancer
The life expectancy of someone with cancer depends on the extent of metastasis and which organs are involved. Metastatic prostate cancer is designated as stage IV:
- Stage IVA: Cancer has progressed to surrounding lymph nodes but not to distant locations.
- Stage IVB: Cancer has progressed to distant tissues and organs, such as the bones or smooth muscles.
Generally, prostate cancers do not spread rapidly to other areas of the body. Most prostate tumors grow slowly and may not cause symptoms or complications for years, if at all.
Even when prostate cancer has spread to other regions of the body, it is usually treatable for an extended period. As a result, even men with advanced prostate cancer can enjoy good health for many years. However, if not properly treated, prostate cancer can cause serious symptoms and even turn fatal.
There Are 2 Types Of Staging For Prostate Cancer:
The Clinical Stage The clinical stage is based on the results of tests that can be done prior to the surgery. They include the DRE, biopsy, X-rays, CT and/or MRI scans and bone scans. X-rays, bone scans, CT scans and MRI scans may not always be needed. They are recommended based on the PSA level, the size of the cancer, which is determined by its grade and volume and the clinical stage of the cancer.
The Pathologic Stage The pathologic stage is based on information found during surgery, plus the laboratory results referred to as pathology, of the prostate tissue removed during surgery. The surgery often includes the removal of the entire prostate and some lymph nodes.One important part of the staging process is determining the grade of the cancer. The grading system is based on the microanalysis of the prostatic tissue. While the stage of the cancer is determined based on the macro appearance of the tumor, in connection with the nearby organs and tissues, the grade of cancer is usually determined after a biopsy, when the cells are analyzed under a microscope.
Recommended Reading: Could An Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
Fast Facts On Prostate Cancer
- Prostate cancer rarely reaches an advanced stage.
- People with the condition normally have a very good outlook when they receive an early diagnosis and treatment.
- Hormone therapy is a treatment option for advanced prostate cancer, as are chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
- Prostate cancer can spread to the bones, brain, and lungs.
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland mutate and start to develop abnormally, multiplying at an uncontrolled rate. In some instances, the cancerous cells can spread to other body parts through tissue, the blood, or the lymphatic system.
After a doctor diagnoses prostate cancer, they will test to see if the cancer has spread to other areas of the body, or how much of the body is affected.
The doctor will assign a stage of prostate cancer from 1 to 4. Stage 4 is the most advanced form.
Stage 4 prostate cancer has spread to pelvic lymph nodes or is blocking the ureters. The ureters are the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. Stage 4 prostate cancer may also have spread to the bladder, the rectum, the bones, or distant lymph nodes.
Doctors will test any cancerous cells in the body to determine if the additional cells came from the prostate. Even if they detect cancer in the bones, doctors still consider this prostate cancer if that is where the cancer originated.
There are two types of stage 4 prostate cancer:
Flagler Beach Shark Attacks 2022
Prostatecancer is cancer of the prostate gland. No one knows why or how prostatecancer starts. Autopsy studies show 1 in 3 men over the age of 50 have some cancer cells in the prostate. What Are The SurvivalRates For ProstateCancer?. Conversely, patients with unfavorable intermediate-risk prostatecancer have prostatecancer-specific mortality and all-cause mortality rates Dose escalation for prostatecancer radiotherapy: predictors of long-term biochemical tumor control and distant metastases-free survival outcomes.
Investigators found the highest prostatecancer death rates among patients with a primary Gleason 5 pattern. Prostatecancer survival differs by specific “Prostatecancer characteristics were increasingly unfavorable with increasingly aggressive Gleason pattern from 4+5 to 5+4 to 5+5,” Dr.
Improved survival in patients with locally advanced prostatecancer treated with radiotherapy and goserelin. Morphologic changes induced by neoadjuvant androgen ablation may result in underdetection of positive surgical margins and capsular involvement by prostatic adenocarcinoma.
Recommended Reading: What Age To Check Prostate Cancer
Understanding Prostate Cancers Progression
To determine the appropriate treatment, doctors need to know how far the cancer has progressed, or its stage. A pathologist, the doctor trained in analyzing cells taken during a prostate biopsy, will provide two starting pointsthe cancers grade and Gleason score.
- Cancer grade: When the pathologist looks at prostate cancer cells, the most common type of cells will get a grade of 3 to 5. The area of cancer cells in the prostate will also be graded. The higher the grade, the more abnormal the cells.
- Gleason score: The two grades will be added together to get a Gleason score. This score tells doctors how likely the cancer is to grow and spread.
After a biopsy confirms prostate cancer, the patient may undergo additional tests to see whether it has spread through the blood or lymph nodes to other parts of the body. These tests are usually imaging studies and may include a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or computed tomography scan.
Prostate cancer treatment: The care you need is one call away
Your multidisciplinary team will work with you to develop a personalized plan to treat your prostate cancer in a way that fits your individual needs and goals.
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
Stage 4 prostate cancer is the final stage in the development of prostate tumors. By this stage, cancer cells have spread to parts of the body that are distant from the prostate gland. Once again, stage 4 prostate cancer branches into 2 subcategories.
- Stage IVA: Any PSA value, any Gleason score. There are cancer cells around lymph nodes.
- Stage IVB: Any PSA value, any Gleason score. There are cancer cells around lymph nodes and other parts of the body, including organs far away from the prostate gland.
The metastatic prostate cancer survival rate drops to a 30% chance to survive in the first 5 years of their diagnosis. Treatment plans can include anything at this point, be it hormone therapy, chemotherapy, prostatectomy, external beam radiation, or a mixture of several of these options.
You May Like: What Does Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Mean
Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
In stage 2, the tumor is still confined to your prostate and hasnt spread to lymph nodes or other parts of your body. A doctor may or may not be able to feel the tumor during a prostate exam, and it may appear on ultrasound imaging. The survival rate is still .
The PSA score for stage 2 is less than 20 ng/mL.
Stage 2 cancer is further divided into three phases depending on the grade group and Gleason scores:
- Gleason score: 6 or less
Eight Types Of Standard Treatment Are Used:
Watchful waiting or active surveillance
Watchful waiting and active surveillance are treatments used for older men who do not have signs or symptoms or have other medical conditions and for men whose prostate cancer is found during a screening test.
Watchful waiting is closely monitoring a patients condition without giving any treatment until signs or symptoms appear or change. Treatment is given to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Active surveillance is closely following a patients condition without giving any treatment unless there are changes in test results. It is used to find early signs that the condition is getting worse. In active surveillance, patients are given certain exams and tests, including digital rectal exam, PSA test, transrectal ultrasound, and transrectal needle biopsy, to check if the cancer is growing. When the cancer begins to grow, treatment is given to cure the cancer.
Other terms that are used to describe not giving treatment to cure prostate cancer right after diagnosis are observation, watch and wait, and expectant management.
Surgery
Patients in good health whose tumor is in the prostategland only may be treated with surgery to remove the tumor. The following types of surgery are used:
Read Also: Advanced Prostate Cancer With Bone Metastases
Stage 3 Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
When doctors deem a prostate tumor as a stage 3 prostate cancer case, then cancer cells may have left the confinements of the prostate gland. Stage 3 is also broken down into 3 subgroups.
- Stage IIIA: PSA reading is slightly over 20ng/mL, the Gleason score is 8 or less. The location of cancer cells is on both sides of the prostate gland or even outside of it
- Stage IIIB: PSA reading is any level, the Gleason score is 8 or less. The location of cancer cells is inside or outside the prostate gland, but they havent reached lymph nodes yet
- Stage IIIC: PSA reading is at any level, the Gleason score is 9 or 10. The location of cancer cells is inside or outside the prostate gland, and they may have even reached lymph nodes or other parts of the body near the prostate gland.
With the right treatment, 95% of patients diagnosed with prostate cancer are likely to survive for at least 5 years. While active surveillance is outside the question at this point, other treatments are likely to lead to satisfactory results. External beam radiation coupled with hormone therapy, radiation coupled with hormone therapy, and radical prostatectomy are viable plans of action at this point.
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer: Survival Rates Treatment And Support
Prostate cancer is in stage 4 when the cancer spreads beyond the lymph nodes and into other areas of the body. While the vast majority of prostate cancer cases are caught before this happens, when the cancer is treatable, stage 4 is far more difficult to treat. Therefore, the survival rate among men with stage 4 prostate cancer is much lower.
There are two types of stage 4 prostate cancer: 4A and 4B, according to the American Cancer Society. The type assigned to a persons diagnosis is based on whether the cancer has spread and to what degree, and the value assigned to two additional factors called the Grade Group and the prostate-specific antigen . The Grade Group is a measure of how likely the cancer is to spread quickly, and the PSA is a measure of a protein in the blood produced by cells in the prostate.
With stage 4A, the tumor has already spread into the lymph nodes and may be spreading into tissues adjacent to the prostate, but has not spread to other areas of the body. The Grade Group can be of any value, as can the PSA.
With stage 4B, the tumor may have spread into the lymph nodes, may be spreading into nearby tissues and has spread to other areas of the body like the bones, certain organs and distant lymph nodes. The Grade Group and PSA can be of any value.
Also Check: What To Expect From Radiation Therapy For Prostate Cancer
