Repeating The Psa Test
A mans blood PSA level can vary over time , so some doctors recommend repeating the test after a month or so if the initial PSA result is abnormal. This is most likely to be a reasonable option if the PSA level is on the lower end of the borderline range . For higher PSA levels, doctors are more likely to recommend getting other tests, or going straight to a prostate biopsy.
Getting The Results Of The Biopsy
Your biopsy samples will be sent to a lab, where they will be looked at with a microscope to see if they contain cancer cells. Getting the results usually takes at least 1 to 3 days, but it can sometimes take longer. The results might be reported as:
- Positive for cancer: Cancer cells were seen in the biopsy samples.
- Negative for cancer: No cancer cells were seen in the biopsy samples.
- Suspicious: Something abnormal was seen, but it might not be cancer.
If the biopsy is negative
If the prostate biopsy results are negative , and the chance that you have prostate cancer isnt very high based on your PSA level and other tests, you might not need any more tests, other than repeat PSA tests sometime later.
But even if many samples are taken, biopsies can still sometimes miss a cancer if none of the biopsy needles pass through it. This is known as a false-negative result. If your doctor still strongly suspects you have prostate cancer , your doctor might suggest:
- Getting other lab tests to help get a better idea of whether or not you might have prostate cancer. Examples of such tests include the Prostate Health Index , 4Kscore test, PCA3 tests , and ConfirmMDx. These tests are discussed in Whats New in Prostate Cancer Research?
- Getting a repeat prostate biopsy. This might include getting additional samples of parts of the prostate not biopsied the first time, or using imaging tests such as MRI to look more closely for abnormal areas to target.
Prostate cancer grade
Gleason score
How Is Prostatitis Treated
Treatment depends on the type of prostatitis.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Treatment for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome aims to decrease pain, discomfort, and inflammation. A wide range of symptoms exists and no single treatment works for every man. Although antibiotics will not help treat nonbacterial prostatitis, a urologist may prescribe them, at least initially, until the urologist can rule out a bacterial infection. A urologist may prescribe other medications:
- silodo
- cans such as chondroitin sulfate
- muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine and clonazepam
- neuromodulators such as amitriptyline, nortriptyline , and pregabalin
Alternative treatments may include
- warm baths, called sitz baths
- local heat therapy with hot water bottles or heating pads
- physical therapy, such as
- Kegel exercisestightening and relaxing the muscles that hold urine in the bladder and hold the bladder in its proper position. Also called pelvic muscle exercises.
- myofascial releasepressing and stretching, sometimes with cooling and warming, of the muscles and soft tissues in the lower back, pelvic region, and upper legs. Also known as myofascial trigger point release.
Don’t Miss: Viagra Bph
Tests To Diagnose And Stage Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancers are first found as a result of screening. Early prostate cancers usually dont cause symptoms, but more advanced cancers are sometimes first found because of symptoms they cause.
If prostate cancer is suspected based on results of screening tests or symptoms, tests will be needed to be sure. If youre seeing your primary care doctor, you might be referred to a urologist, a doctor who treats cancers of the genital and urinary tract, including the prostate.
The actual diagnosis of prostate cancer can only be made with a prostate biopsy .
On this page
When You Should Screen For Prostate Cancer
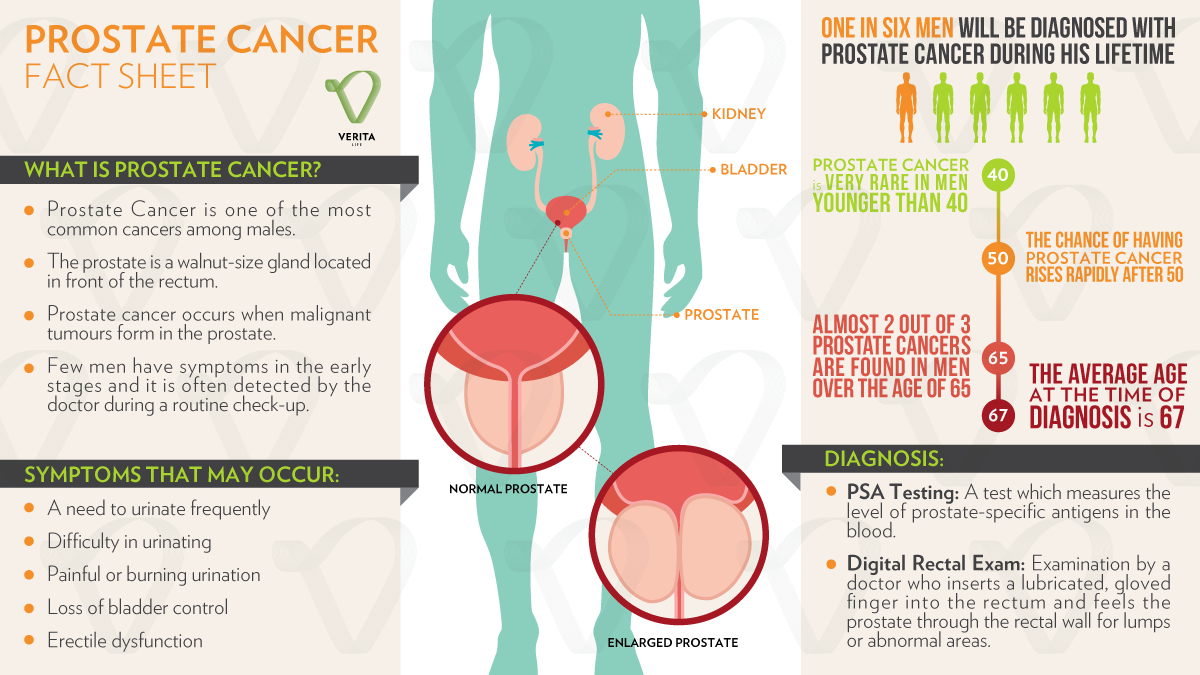
Staying on top of health screenings is important to try to catch conditions early. That is the case with prostate cancer, the most common cancer in men in the United States.
Most men with prostate cancer have no symptoms and prostate cancer is detected with routine screening, said Dr. Bharat K. Shah, an internist at Advocate Medical Group at Irving and Western in Chicago.
Dr. Shah said early symptoms of prostate cancer may include:
- Frequency of urination
- Frequent nighttime urination
- Dribbling or blood in the urine
However, these symptoms are not specific to prostate cancer. The same symptoms can occur with other urologic conditions like an enlarged prostate or infection, Dr. Shah said.
Screening for prostate cancer is done using a blood test called a prostate specific antigen, or PSA, and digital rectal exam, according to Dr. Shah.
There is some controversy about screening for prostate cancer because some believe that screening has the potential of overtreatment of early-stage cancer. However, since widespread use of screening, mortality from prostate cancer has gone down 70%. Therefore, screening is done after discussion with your primary care physician about your risk factors, Dr. Shah said.
Screening is not recommended after age 70 or if a persons life expectancy is less than ten years, Dr. Shah said. Generally, screenings are done every two years.
The actual diagnosis of prostate cancer is made by ultrasound or MRI guided prostate biopsy.
You May Like: Tamsulosin Ejaculation
How Do You Screen For Prostate Cancer
One way of screening for prostate cancer is with a PSA test. This measures the level of PSA in your blood. There are other types of tests that can help us diagnose prostate cancer, including new imaging technologies. MRI scans and other types of next gen imaging can help us find prostate cancer early in the game while the treatment options are most effective.
How Are Researchers Trying To Improve The Psa Test
Scientists are investigating ways to improve the PSA test to give doctors the ability to better distinguish cancerous from benign conditions and slow-growing cancers from fast-growing, potentially lethal cancers. None has been proven to decrease the risk of death from prostate cancer. Some of the methods being studied include:
You May Like: Household Items For Prostate Massage
Downsides Of Psa Screening
- Most prostate cancers are slow growing and never spread beyondthe prostate gland.
- Not all prostate cancers need treatment. Treatment for prostatecancer may have risks and side effects, including urinaryincontinence, erectile dysfunction, or bowel dysfunction.
- PSA tests arent foolproof. Most men flagged for prostate biopsyfrom an elevated PSA will likely test negative for cancer.
- A diagnosis of prostate cancer can provoke anxiety and confusion.Concern that the cancer may not be life-threatening can makedecision-making complicated.
- PSA testing has lowered deaths, but the number may not besubstantial enough to justify the cost and possibility of harmto the person undergoing the testing.
The results of these trials in addition to some of the downsides of the screening test led the US Preventive Services Task Force – a governmental agency that advises physicians on a wide range of health-related topics, including cancer screening – to recommend against annual PSA screening. As a result of this decision, early detection rates and prostate cancer screenings are declining. At the same time, the number of men with incurable disease is on the rise.
Our genetic test encourages men to be actively involved in the development of their personalized prostate cancer screening approach at an early stage. With a simple cheek swab, Prompt PGS compares your specific genetic profile to tens of thousands of others and can help you and your healthcare practitioner determine what is best for you.
Tests Are Used To Screen For Different Types Of Cancer When A Person Does Not Have Symptoms
Scientists study screening tests to find those with the fewest harms and most benefits. Cancer screening trials also are meant to show whether early detection helps a person live longer or decreases a person’s chance of dying from the disease. For some types of cancer, the chance of recovery is better if the disease is found and treated at an early stage.
Also Check: External Prostate Massage Prostatitis
Prostate Cancer Is The Most Common Nonskin Cancer Among Men In The United States
Prostate cancer is found mainly in older men. Although the number of men with prostate cancer is large, most men diagnosed with this disease do not die from it. Prostate cancer causes more deaths in men than any other cancer except lung cancer. Prostate cancer occurs more often in African American men than in White men. African American men with prostate cancer are more likely to die from the disease than White men with prostate cancer.
What Is A Psa Test And How Does It Work
PSA is an enzyme which is only made by the prostate and is measured by a blood test.
In addition to prostate cancer, many benign conditions can increase a mans PSA levels. The most commoncauses of PSA elevation are inflammation of the prostate and benign prostatic hyperplasia , or enlargement of the prostate1, so having a high PSA score does not automatically indicate prostate cancer.
Men may elect to get a prostate-specific antigen test as it can be an early sign that cancer may be present. Unfortunately, as PSA is not specific to cancer, many men suffer from needless anxiety and undergo painful and expensive diagnostic procedures to follow up on a PSA rise which is not cancer related.
You May Like: Female Prostate Equivalent
There Is No Standard Or Routine Screening Test For Prostate Cancer
Although there are no standard or routine screening tests for prostate cancer, the following tests are being used or studied to screen for it:
Digital rectal exam
Digital rectal exam is an exam of the rectum. The doctor or nurse inserts a lubricated, gloved finger into the lower part of the rectum to feel the prostate for lumps or anything else that seems unusual.
Prostate-specific antigen test
A prostate-specific antigen test is a test that measures the level of PSA in the blood. PSA is a substance made mostly by the prostate that may be found in an increased amount in the blood of men who have prostate cancer. The level of PSA may also be high in men who have an infection or inflammation of the prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia .
A PSA test or a DRE may be able to detect prostate cancer at an early stage, but it is not clear whether early detection and treatment decrease the risk of dying from prostate cancer.
Studies are being done to find ways to make PSA testing more accurate for early cancer detection.
When Is A Psa Test Needed

If you are age 50 to 74, you should discuss the PSA test with your doctor. Ask about the possible risks and benefits.
Men under 50 or over 75 rarely need a PSA test, unless they have a high risk for prostate cancer.
- You are more likely to get prostate cancer if you have a family history of prostate cancer, especially in a close relative such as a parent or sibling.
- Your risks are higher if your relative got prostate cancer before age 60 or died from it before age 75. These early cancers are more likely to grow faster.
- If you have these risks, you may want to ask your doctor about getting the PSA test before age 50.
This report is for you to use when talking with your healthcare provider. It is not a substitute for medical advice and treatment. Use of this report is at your own risk.
04/2014
Read Also: Fiducials Prostate Cancer
Risks And Benefits Of Psa Test
There are benefits of having a PSA test which include early detection of prostate cancer. The earlier cancer is detected, the better the chance of a cure.
There are also risks involved. These include:
- Worry about false-positive results caused by elevated PSA levels from something other than prostate cancer. A raised PSA result could be from something benign
- Invasive, stressful, expensive or time-consuming follow-up tests
- Stress or anxiety caused by knowing you have a slow-growing prostate cancer that doesnt need treatment
- Deciding to have surgery, radiation or other treatments that cause side effects that are more harmful than untreated cancer
Referrals From Your Gp
The symptoms of prostate cancer can be very similar to some other prostate problems, so it can be very difficult for GPs to decide who may have a suspected cancer and who may have something much more minor that will go away on its own.
There are particular prostate symptoms that mean your GP should refer you to a specialist straight away. The National Cancer Control Programme has produced guidelines for GPs in Ireland. The guidelines help GPs decide which patients need to be seen urgently by a specialist called a urologist. A urologist is a doctor who specialises in treating disorders of the urinary tract, including the kidney,, bladder and prostate.
Don’t Miss: Pseudoephedrine And Prostate
Screening Tests Have Risks
Decisions about screening tests can be difficult. Not all screening tests are helpful and most have risks. Before having any screening test, you may want to discuss the test with your doctor. It is important to know the risks of the test and whether it has been proven to reduce the risk of dying fromcancer.
Screening For Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer patients almost always have an excellent prognosis if their cancer is caught early. Consequently, experts recommend that men speak with their doctors to develop a regular screening plan for prostate cancer.
Screening guidelines will differ according to a mans individual risk factors.
Don’t Miss: Define Prostate
Prostate Cancer: Symptoms Signs And Screenings
-
Prostate cancer is the second leading cancer among American men. To learn more about prostate cancer, read this section.
-
Some warning signs of prostate cancer include a variety of sometimes very subtle symptoms. To learn more about early signs of prostate cancer, read this section.
-
Most cases of prostate cancer have no symptoms, so early detection is dependent on testing. To learn more about how screening is done for prostate cancer, read this section.
-
Although there are benefits to detecting prostate cancer early, there can also be some problems. To learn more about the benefits and possible drawbacks of prostate cancer screening, read this section.
Cancer has become a word feared by many people, perhaps because of its association with being untreatable and often fatal. Many people view cancer as something that cant be cured or controlled. But this is far from the truth. There are many different types of cancer, most of which can be treated. New treatments for cancer, including prostate cancer, are being developed every day. Most men who have prostate cancer show no symptoms at first, so early screening plays an important role in its detection, especially for those who are at increased risk of developing it. Even after a diagnosis of prostate cancer, most men survive for 5 years or longer.
Factors That Might Affect Psa Levels
One reason its hard to use a set cutoff point with the PSA test when looking for prostate cancer is that a number of factors other than cancer can also affect PSA levels.
Factors that might raise PSA levels include:
- An enlarged prostate: Conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia, a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate that affects many men as they grow older, can raise PSA levels.
- Older age: PSA levels normally go up slowly as you get older, even if you have no prostate abnormality.
- Prostatitis: This is an infection or inflammation of the prostate gland, which can raise PSA levels.
- Ejaculation: Thiscan make the PSA go up for a short time. This is why some doctors suggest that men abstain from ejaculation for a day or two before testing.
- Riding a bicycle: Some studies have suggested that cycling may raise PSA levels for a short time , although not all studies have found this.
- Certain urologic procedures: Some procedures done in a doctors office that affect the prostate, such as a prostate biopsy or cystoscopy, can raise PSA levels for a short time. Some studies have suggested that a digital rectal exam might raise PSA levels slightly, although other studies have not found this. Still, if both a PSA test and a DRE are being done during a doctor visit, some doctors advise having the blood drawn for the PSA before having the DRE, just in case.
- Certain medicines: Taking male hormones like testosterone may cause a rise in PSA.
Some things might lower PSA levels :
Also Check: How To Shrink Prostate Mayo Clinic
What Are The Screening Guidelines For Prostate Cancer
The general recommendation for prostate cancer is to start being examined by your doctor and have a PSA test at the age of 50 if youre a man at average risk for prostate cancer. PSA, or prostate specific antigen, is a protein produced by cancerous and non-cancerous tissue in the prostate.
If you have a family history of prostate cancer, or if youre an African American man, you are at higher-than-average risk for prostate cancer. For these men, the recommendation is to start getting tested at age 40. This is so crucial for prostate cancer, because its all about early detection. If we can find it early, we can cure it.
Not enough men are being screened for prostate cancer. We need to get the word out and we need to rectify this.
How Is Prostate Cancer Detected
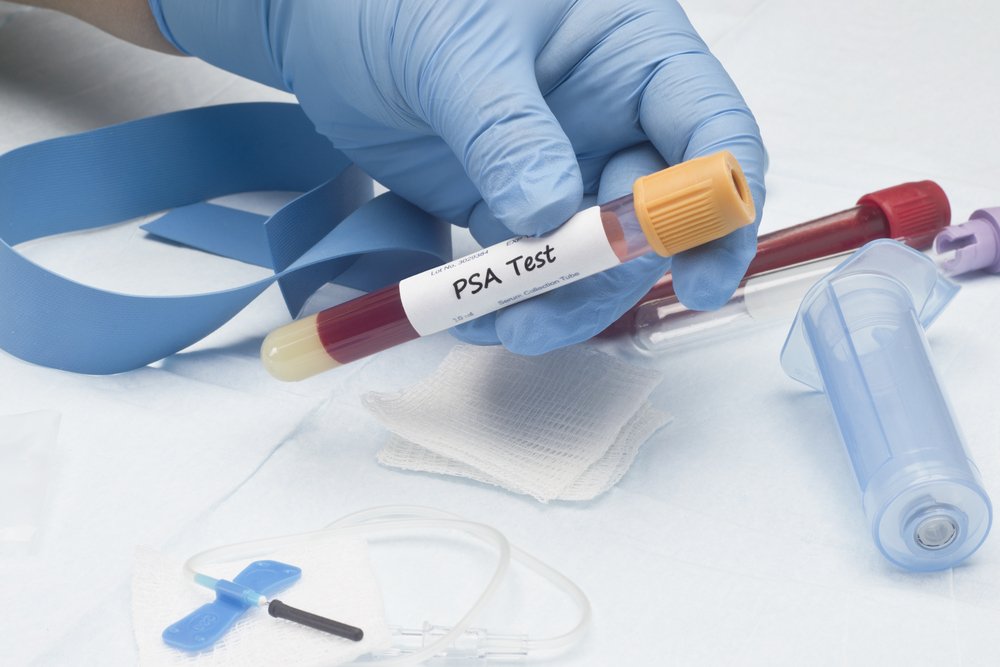
There is no single test to detect prostate cancer. The two most common tests are the prostate specific antigen blood test and the digital rectal examination .
The PSA test measures the level of PSA in your blood. It does not specifically test for cancer. Virtually all PSA is produced by the prostate gland. The normal range depends on your age. A PSA above the typical range may indicate the possibility of prostate cancer. However, two-thirds of cases of elevated PSA are due to noncancerous conditions such as prostatitis and BPH.
A DRE is generally conducted by a urologist to feel the prostate. While DRE is no longer recommended as a routine test for men who do not have symptoms of prostate cancer, it may be used to check for any changes in the prostate before doing a biopsy.
If either of these tests suggest an abnormality, other tests are necessary to confirm a diagnosis of prostate cancer, usually a magnetic resonance imaging scan and transrectal ultrasound biopsy.
Also Check: Prostatic Neoplasms
