Can Prostatitis Affect Your Sex Life
Problems affecting this small gland can affect your sex life. For example, BPH and even prostate cancer treatment such as radiation therapy can contribute to sexual problems. So, what about this disease then?
Prostatitis has a significant impact on a mans health and quality of life. The disease can affect the urinary tract, but also your sexual performance.
A growing body of evidence confirms that prostatitis can cause erectile dysfunction , a common sexual problem where a man cannot achieve or maintain an erection for pleasurable intercourse.
Below you can learn more about prostatitis erectile dysfunction.
Medical Procedures Can Cause Psa To Rise
“Anything that traumatically interferes with the architecture around the prostate gland can make PSA go up,” says Dr. Milner. “One of the most common causes of significantly high PSA from this type of trauma is the placing of a catheter into the bladder.”
Another cause is a prostate or bladder exam that involves passing a scope or taking a biopsy.
“Since it takes about two to three days for PSA to go down by half, you should wait two to three weeks after this type of trauma to do a PSA test,” Milner says.
In Men Over : Bph May Be The Cause Of High Psa
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is an enlargement of the prostate gland, but its not prostate cancer. “BPH means more cells, so that means more cells making PSA,” explains Dr. Castle.
BPH is the most common prostate problem in men over age 50. It may not need to be treated unless its causing frequent or difficult urination.
Your primary care doctor may be able to tell the difference between BPH and prostate cancer by doing a digital rectal exam, but commonly this will require evaluation by a urologist and further testing, such as a biopsy or imaging studies.
Don’t Miss: Flomax Side Effects Ejaculation
What Are The Most Common Prostate Problems
For such a little gland, the prostate seems to cause a lot of concern. Like a troubled, war-torn country, it’s in the news all the time and something always seems to be going wrong there, but you don’t really know where it is or why it’s important.
All men are at risk for prostate problems. That’s because all men have a prostate. Take a look at this overview of prostate problems to assess your risk for trouble with your prostate.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia .BPH, also known as an enlarged prostate, is growth of the prostate gland to an unhealthy size. A man’s chances of having BPH go up with age:
- Age 31-40: one in 12
- Age 51-60: about one in two
- Over age 80: more than eight in 10
However, only about half of men ever have BPH symptoms that need treatment. BPH does not lead to prostate cancer, although both are common in older men.
Prostate Cancer. Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men . About one man in six will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime. Let’s keep these numbers in perspective, though. Because prostate cancer is usually slow growing, only about one in 35 men will die of prostate cancer.
Like BPH, the risk for prostate cancer increases with age. About two out of every three men with prostate cancer are over age 65. No one knows exactly what causes prostate cancer, but risk factors associated with it include:
Diagnosis Of Prostate Disease
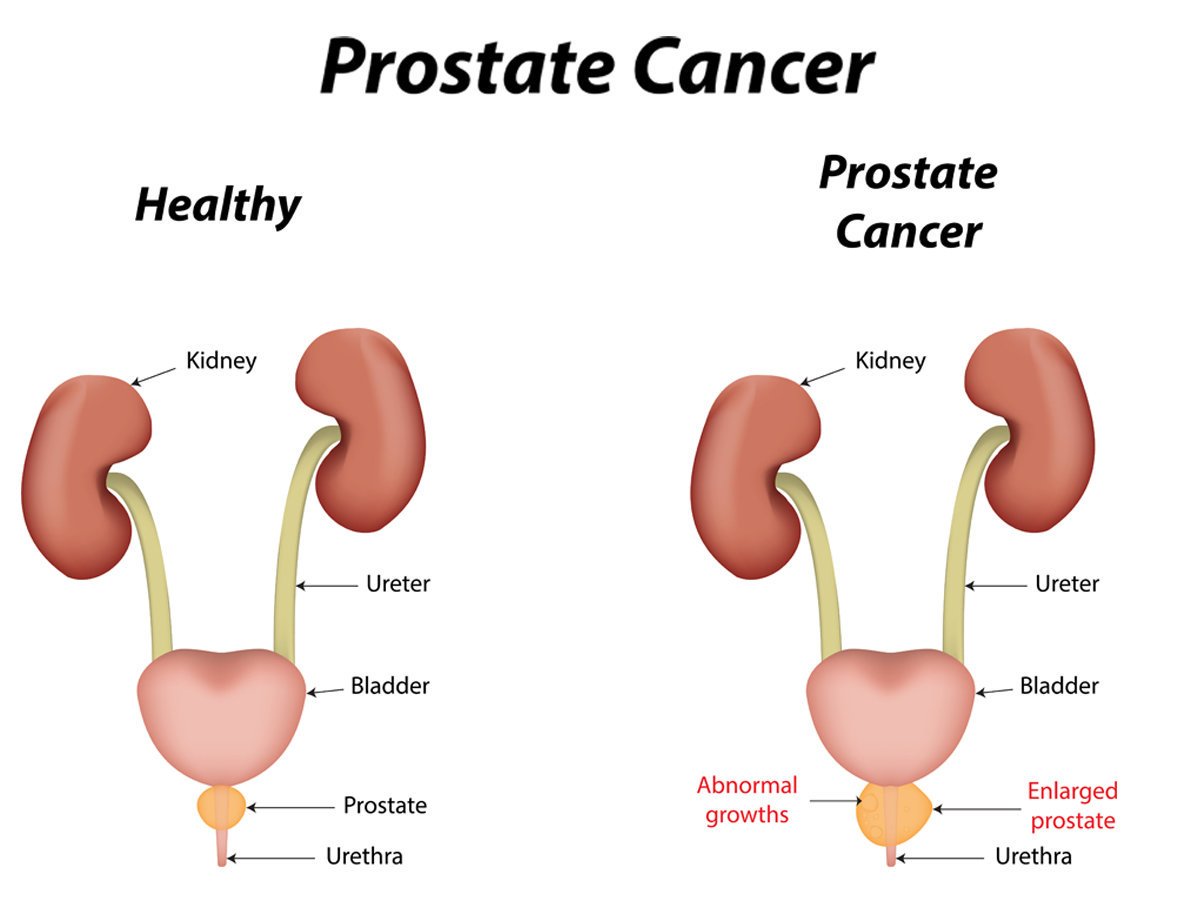
Prostate disease is diagnosed using a variety of tests, including:
- physical examination, including digital rectal examination , where the doctor inserts a gloved finger into your rectum to check the size of your prostate
- blood test for prostate specific antigen
- mid-stream urine tests to look for infection or blood in the urine
- ultrasound scans and urinary flow studies
- biopsies of the prostate.
Read Also: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
Causes Of Prostatitis Past Bacterial Infections
If you have experienced bacterial infections before, whether they are urinary tract infections or other bacterial infections, this can affect whether or not you have prostatitis in the future. This type of prostatitis is more difficult to treat as it is harder to tell the exact cause of your infection. If you have experienced a past bacterial infection, especially when your reoccurring urinary tract infection never seems to disappear, go to sit your doctor immediately. It is very important for you to follow the doctors instructions and complete the treatments in order to ensure that all of the symptoms are gone away.
In fact, they are also common causes of prostatitis, so you should try to treat these infections completely as soon as possible to reduce the risks of developing prostatitis.
What Is An Enlarged Prostate
The prostate is an essential gland in the male reproductive system. It contributes to the semen volume and synthesizes a substance that supports sperm cells.
This gland is below the urinary bladder, surrounding the urethra. In the bladder neck. Thus, as it grows, it can put pressure over the urethra or the urinary bladder. However, what is an enlarged prostate? Is it the same as prostate cancer?
An enlarged prostate is simply a gland that increased in size. It is not caused by cancer. Another medical term is benign prostatic enlargement, where benign means theres no cancer. Another name is benign prostatic hyperplasia .
When we talk about hyperplasia, we refer to an increase in number and not size. Thus, in prostatic hyperplasia, there are more prostate cells . However, they remain the same size as normal prostate tissue. Such an increase in the number of cells causes an enlarged prostate. It usually starts in men after the age of 40. But they typically find out when they are near their 50s .
In some cases, an enlarged prostate grows evenly. In other instances, prostate growth is more irregular. When the overgrowth is near the center, it presses the urethra on the outside.
As a result, the urethra becomes narrow, compromising the urine flow. As a result, 1 out of 3 men over 50 years old report urinary symptoms. In the majority of cases, they are caused by an enlarged prostate gland .
You May Like: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
Inflammation Of The Prostate
While prostatitis can affect men of any age, it is more common in younger men, aged between 30 and 50 years. The main types of prostatitis are:
- bacterial prostatitis acute or chronic bacterial infection
- non-bacterial prostatitis inflamed prostate, also known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome .
In most cases, the cause of prostatitis is unknown. Bacterial prostatitis responds well to antibiotic drugs that can get into the prostate.
Non-bacterial prostatitis, or CPPS, is the most common form of prostatitis and is more difficult to manage. Symptoms vary from one man to another. There is no single test to diagnose CPPS, so your doctor will need to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms before making a diagnosis.Possible causes of CPPS include:
- a past bacterial prostatitis infection
- irritation from some chemicals
- chronic anxiety problems.
Prostatitis: A Common Problem In Men Under 50
“The PSA test is a good screening tool for prostate cancer, but it is not very specific,” says Erik P. Castle, MD, a urologist and researcher at the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, Arizona. “Common causes of inflammation in the gland, called prostatitis, can cause high PSA levels.”
Prostatitis is the most common prostate problem for men younger than 50.
Prostatitis caused by bacteria can be treated with antibiotics. Another, more common type of prostatitis, called nonbacterial prostatitis, can be harder to treat and may last a long time.
You May Like: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
What Is The Prostate
The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland that is part of the male reproductive system. The main function of the prostate is to make a fluid that goes into semen. Prostate fluid is essential for a mans fertility. The gland surrounds the urethra at the neck of the bladder. The bladder neck is the area where the urethra joins the bladder. The bladder and urethra are parts of the lower urinary tract. The prostate has two or more lobes, or sections, enclosed by an outer layer of tissue, and it is in front of the rectum, just below the bladder. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. In men, the urethra also carries semen out through the penis.
How Old Do You Have To Be To Have An Enlarged Prostate
When there is an Enlarged Prostate the swelling that caused starts to put pressure on the urethra and this limits the flow of urine. Enlarged prostate or prostate enlargement is normally seen in people above the age of 50 years of age and it is very rare in individual in the age range of 20-40 years.
Recommended Reading: Neurovascular Bundle Invasion Prostate Cancer
How Is Prostatitis Treated
Treatment depends on the type of prostatitis.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Treatment for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome aims to decrease pain, discomfort, and inflammation. A wide range of symptoms exists and no single treatment works for every man. Although antibiotics will not help treat nonbacterial prostatitis, a urologist may prescribe them, at least initially, until the urologist can rule out a bacterial infection. A urologist may prescribe other medications:
- silodo
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors such as finasteride and dutasteride
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugsalso called NSAIDssuch as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen sodium
- glycosaminogly
- cans such as chondroitin sulfate
- muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine and clonazepam
- neuromodulators such as amitriptyline, nortriptyline , and pregabalin
Alternative treatments may include
- warm baths, called sitz baths
- local heat therapy with hot water bottles or heating pads
- physical therapy, such as
- Kegel exercisestightening and relaxing the muscles that hold urine in the bladder and hold the bladder in its proper position. Also called pelvic muscle exercises.
- myofascial releasepressing and stretching, sometimes with cooling and warming, of the muscles and soft tissues in the lower back, pelvic region, and upper legs. Also known as myofascial trigger point release.
What Are The Symptoms Of Prostatitis

Symptoms of Prostatitis vary greatly. Patients can suffer from systemic symptoms of infection including fever, chills and rigors. This is especially when the infection of the prostate is quite severe and caused by an Infection.
More localized symptoms include pain when passing urine, erectile dysfunction, discharge from the penis, a heaviness or dragging sensation in the scrotum and pain at the tip of the penis.
Other symptoms include a constant need to go to the toilet to pass urine, low back pain, muscles aches, poor flow when passing urine or pain during ejaculation.
Don’t Miss: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
What Are Clinical Trials And Are They Right For You
Clinical trials are part of clinical research and at the heart of all medical advances. Clinical trials look at new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease. Researchers also use clinical trials to look at other aspects of care, such as improving the quality of life for people with chronic illnesses. Find out if clinical trials are right for you.
How Can I Prevent Prostate Problems
In some ways, prostate problems, particularly BPH, are a natural part of growing older. Still, there are specific steps you can take to keep your prostate healthy.
- A diet low in saturated fat and high in fruits and vegetables may lower your risk of developing BPH. Research is ongoing to identify who might benefit from early treatment to prevent BPH.
- According to the American Cancer Society, most cases of prostate cancer can’t be prevented. This is because prostate cancer’s causes are still unknown. As with BPH, however, experts recommend eating a healthy diet with lots of fruits and vegetables.
- No herbal supplements have been proven to prevent prostate cancer. Studies of selenium, a mineral, have had mixed results, but the majority of the evidence shows no real benefit. Trials for drugs to prevent prostate cancer are also ongoing.
- No activity or drug is known to prevent prostatitis. Experts recommend good hygiene, including keeping the penis clean. Most men will never develop prostatitis.
You May Like: How Effective Is Chemotherapy For Prostate Cancer
What Causes Prostatitis In Young Men
The causes of prostatitis are not always apparently clear in young adults. When traceable prostatitis causes are found, it is usually due to bacterial infection.
However, prostatitis is broken down into infectious and non-infectious types.
An aberrant immune response triggers nonbacterial prostatitis, and the exact cause is difficult to trace.
The microbes that infect the prostate are usually the same found in urinary tract infections.
They include Escherichia coli, Enterobacter species, Klebsiella species, Proteus mirabilis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
It is usually one of them that triggers the inflammatory process, more commonly E. coli .
How do these microbes reach the prostate?
Different mechanisms have been proposed as prostatitis causes, including:
How To Treat Prostate Cysts In Male Dogs
They are cysts that form outside the prostate and can be viewed on ultrasound or an x-ray. Paraprostatic cysts are best treated by being surgically corrected and when the dog is neutered. Neutering will cure BPH and prostatitis. However, it is very difficult to breed neutered male dogs, unless they have had semen frozen.
Recent Posts
Don’t Miss: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
Prostatitis: Diagnosis And Treatment
VICTORIA J. SHARP, MD, and ELIZABETH B. TAKACS, MD, University of Iowa Health Care, Iowa City, Iowa
CHARLES R. POWELL, MD, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Aug 15 82:397-406.
Patient information: See related handout on prostatitis.
The prevalence of prostatitis is approximately 8.2 percent .1 It accounts for 8 percent of visits to urologists, and up to 1 percent of visits to primary care physicians.2 In 2000, the estimated cost to diagnose and treat prostatitis was $84 million, not including pharmaceutical spending.3 Men with chronic prostatitis experience impairment in mental and physical domains of health-related quality of life as measured through validated questionnaires.4 In 2002, approximately 14 percent of men with a medical claim for prostatitis missed work.3 These statistics clearly underscore the broad and far-reaching effect of prostatitis on patient quality of life and the economic impact of the condition.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
The 2-glass pre- and post-prostatic massage test is a reasonable alternative to the preferred Meares-Stamey 4-glass test for diagnosing prostatitis.
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence B = inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, go to .
More Information About Prostatitis
The following is an English-language resource that may be useful. Please note that THE MANUAL is not responsible for the content of this resource.
-
Prostatitis Foundation: This organization provides access to relevant publications , patient testimonials, a list of providers who treat prostatitis in the United States and the United Kingdom, and access to third-party prostatitis-based web sites in French, Swedish, and Italian.
Also Check: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
What Is The Prognosis For Prostatitis Does It Increase The Risk Of Developing Prostate Cancer
Prostatitis caused by bacterial illness often can be treated with antibiotics, or the condition can be chronic that recurs and requires long-term medical attention.
- Acute bacterial prostatitis can often be treated very successfully and has a very good prognosis.
- Chronic prostatitis, and especially chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, can often lead to long-term symptoms and discomfort if treatment is unsuccessful. It is important to have close follow-up and continued care by either your primary care doctor or a urologist.
- Prostatitis does not increase your risk of developing prostate cancer.
Prostate Problems In Young Men

Prostate problems in young men are considered to be serious problems, as the prostate glands form a vital part of the male reproductive system. This article will give you an insight into some important aspects associated with prostate problems in young men.
Prostate problems in young men are considered to be serious problems, as the prostate glands form a vital part of the male reproductive system. This article will give you an insight into some important aspects associated with prostate problems in young men.
Prostate problems are often encountered in the form of infections in the prostate glands. In some cases, these problems are also found to be in the form of prostate cancer. Prostate infections, also known as Prostatitis, are characterized by pain and inflammation in the prostate glands due to the infections caused by certain bacteria present in the large intestine, while prostate cancer signifies the growth of cancerous cells in the prostate glands. Prostate problems are more widely observed in men who are around 70 to 80 years old. However, prostate problems in young men have become a common observation nowadays, as many people around the age of 30 are experiencing this problem too. Let us focus our discussion on the causes, symptoms, and the relevant treatment of prostate problems in young males.
Also Check: When To Start Chemotherapy For Prostate Cancer
How Is Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Managed Or Treated
Prostatitis treatments vary depending on the cause and type. Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis doesnt require treatment.
For chronic pelvic pain syndrome , your healthcare provider may use a system called UPOINT to classify symptoms into six categories. Your provider uses multiple treatments at the same time to treat only the symptoms youre experiencing.
Approximately 80% of men with CPPS improve with the UPOINT system. The system focuses on these symptoms and treatments:
- Urinary: Medications, such as tamsulosin and alfuzosin , relax muscles around the prostate and bladder to improve urine flow.
- Psychosocial: Stress management can help. Some men benefit from counseling or medications for anxiety, depression and catastrophizing .
- Organ: Quercetin and bee pollen supplements may relieve a swollen, inflamed prostate gland.
- Infection:Antibiotics kill infection-causing bacteria.
- Neurologic: Prescription pain medicines, such as amitriptyline and gabapentin , relieve neurogenic pain. This pain can include fibromyalgia or pain that extends into the legs, arms or back.
- Tenderness: Pelvic floor physical therapy may include myofascial release . This therapy can reduce or eliminate muscle spasms.
