Prostate Cancer Risk Factors
A risk factor is anything that raises your risk of getting a disease such as cancer. Different cancers have different risk factors. Some risk factors, like smoking, can be changed. Others, like a persons age or family history, cant be changed.
But having a risk factor, or even several, does not mean that you will get the disease. Many people with one or more risk factors never get cancer, while others who get cancer may have had few or no known risk factors.
Researchers have found several factors that might affect a mans risk of getting prostate cancer.
Being Overweight Or Obese
Obese means being very overweight with a body mass index of 30 or higher. And being overweight means having a BMI of between 25 and 30.
Try to keep a healthy weight by being physically active and eating a healthy, balanced diet.
There is some evidence that being active might help to lower your risk of developing prostate cancer.
Being overweight or obese increases your risk of advanced prostate cancer. Researchers have found a link between being obese or overweight and cancers being higher grade .
What Causes Prostate Cancer
Researchers do not know exactly what causes prostate cancer. But they have found some risk factors and are trying to learn just how these factors might cause prostate cells to become cancer cells.
On a basic level, prostate cancer is caused by changes in the DNA of a normal prostate cell. DNA is the chemical in our cells that makes up our genes, which control how our cells function. We usually look like our parents because they are the source of our DNA. But DNA affects more than just how we look.
Some genes control when our cells grow, divide into new cells, and die:
- Certain genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes.
- Genes that normally keep cell growth under control, repair mistakes in DNA, or cause cells to die at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
Cancer can be caused by DNA mutations that keep oncogenes turned on, or that turn off tumor suppressor genes. These types of gene changes can lead to cells growing out of control.
DNA changes can either be inherited from a parent or can be acquired during a persons lifetime.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Prostate To Enlarge Mayo Clinic
Can Ejaculating Help To Prevent Prostate Cancer
There has been an interesting study that shows that the more a man ejaculates, the less likely he is to develop advanced prostate cancer. This was a single study and is not being confirmed. However, it is important for a man to ejaculate at least two or three times a week if he is in his younger, very virile age period. The older a man gets, the less he is able to orgasm.
Screening For Prostate Cancer
There are no tests available with sufficient accuracy to screen populations of men for early signs of prostate cancer. However, early detection and treatment can significantly improve prostate cancer survival.
The test most commonly used to aid early detection of prostate cancer is the prostate specific antigen blood test. This is not a diagnostic test as it can only indicate changes in the prostate. If you are concerned about prostate cancer you should talk to your doctor and make an informed choice about whether to have one of the tests designed to find early signs of prostate cancer, in view of the potential risks and benefits.
There are no proven measures to prevent prostate cancer.
You May Like: Can Your Prostate Cause Testicle Pain
Prognosis For Prostate Cancer
It is not possible for a doctor to predict the exact course of a disease, as it will depend on each person’s individual circumstances. However, your doctor may give you a prognosis, the likely outcome of the disease, based on the type of prostate cancer you have, the test results, the rate of tumour growth, as well as your age, fitness and medical history.
Prostate cancer often grows slowly and even more aggressive types tend to grow more slowly than other types of cancer. If diagnosed early, prostate cancer has one of the highest five year survival rates.
What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Prostate Cancer
Because prostate cancer tends to grow slowly, most men die from something other than the disease. Early detection is key to better outcomes. Almost all men 97% to 98% diagnosed with localized cancer that hasnt spread outside of the prostate live at least five years after diagnosis. When metastatic cancer has spread outside of the gland, one-third of men continue to survive after five years.
You May Like: What Does The Prostate Produce
Can Drinking Cause Prostate Cancer
No. Alcohol use can increase the risk for many types of cancer, but prostate cancer is not on this list.
Prostate cancer treatment: The care you need is one call away
Your multidisciplinary team will work with you to develop a personalized plan to treat your prostate cancer in a way that fits your individual needs and goals.
What About Trans People
People born with a prostate can develop prostate cancer. Individuals born without a prostate cannot develop prostate cancer.
Trans women who use hormone therapy such as estrogen may have a lower risk, but the risk is still present.
Anyone born with a prostate should speak to their doctor about screening for prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Can You Do For An Enlarged Prostate
What Increases Your Risk Of Prostate Cancer
Factors that can elevate risk prostate cancer include:
- A family history of prostate cancer
- Inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA1/BRCA2 genes and Lynch syndrome
- Conditions such as prostatitis, inflammation of the prostate, and benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH, a noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland
- A diet high in red meats and high-fat dairy and low in fruits and vegetables
- Obesity
- Age: approximately 60 percent of cases are diagnosed in men older than 65
- Race and ethnicity: African-American men and Caribbean men of African ancestry are more likely to be diagnosed with prostate cancer
Research has also shown that a healthy lifestyle, including a well-balanced diet and maintaining a healthy weight, may reduce prostate cancer risk.
Rectal Exams And Blood Test
Prostate specific antigen, or PSA, is a blood test that looks for a protein made by the prostate and prostate cancer cells. When this test is used to screen healthy men between the ages of 5569 years old, it can decrease prostate cancer death by about 20%. Your doctor will draw blood and pair it with a digital rectal exam for initial screening.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can You Live With Prostate Cancer Without Treatment
Facteurs De Risques Professionnels Et Environnementaux
Aucun facteur de risque dorigine environnementale ou professionnelle nest avéré cancérogène pour le cancer de la prostate .
Plusieurs facteurs sont cependant débattus : lexposition à larsenic, au cadmium et aux pesticides.
Des études complémentaires sont nécessaires pour pouvoir conclure à lexistence dune association entre ces facteurs et le risque de cancer de la prostate.
Arsenic
Larsenic est présent en France dans certains anciens sites miniers fermés, qui contaminent encore lenvironnement . De nombreuses industries utilisent encore couramment larsenic . Lexposition à larsenic peut donc être environnementale ou professionnelle.
Elle peut se faire par inhalation de poussières venues des sols contaminés, ou par ingestion . Larsenic est également un composant du tabac. Selon lInVS , leau distribuée constituerait la principale source dexposition à larsenic . Ce risque est toutefois local et en régression .
Larsenic et ses composés inorganiques sont classés cancérogènes avérés, groupe 1 du CIRC , mais cet effet na pas été spécifiquement démontré pour le cancer de la prostate car les données disponibles étaient insuffisantes. Bien que plusieurs études montrent une association positive entre exposition à larsenic et cancer de la prostate, des études supplémentaires sont nécessaires pour déterminer le rôle de cet élément dans la survenue de la maladie .
Cadmium
Pesticides et perturbateurs endocriniens
Infection Inflammation And Chemokines
Chronic inflammation is often a result of numerous exogenous stimuli like infections, radiation, hormones, chemicals, and other noxious stimuli. Following on from this, cancers can often be a subsequent chain of events related chronic inflammation. The key feature of cancer-related inflammation is the recruitment of leukocytes, production of cytokines and chemokines, and subsequent progression, angiogenesis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition , migration, and metastasis . Prostate cancer is no different and numerous studies have investigated the role of chemokines produced by cancer cells and prostate cancer-related chronic inflammation pathway. Chemokines are chemotactic cytokines that influence immune responses and inflammation . These inflammatory milieus will then interact with the tumor microenvironment and can lead to development and progression of the tumor. Examples of such important chemokines in prostate cancer are CXCRupregulated in prostate cancer , and DARCabsence of which will lead to increased incidence and mortality of prostate cancer . Better understanding of chemokines and its receptor axis in the tumor microenvironment will pave way for future chemokine targeted therapies in prostate cancer.
Recommended Reading: How To Give Yourself A Prostate Massage
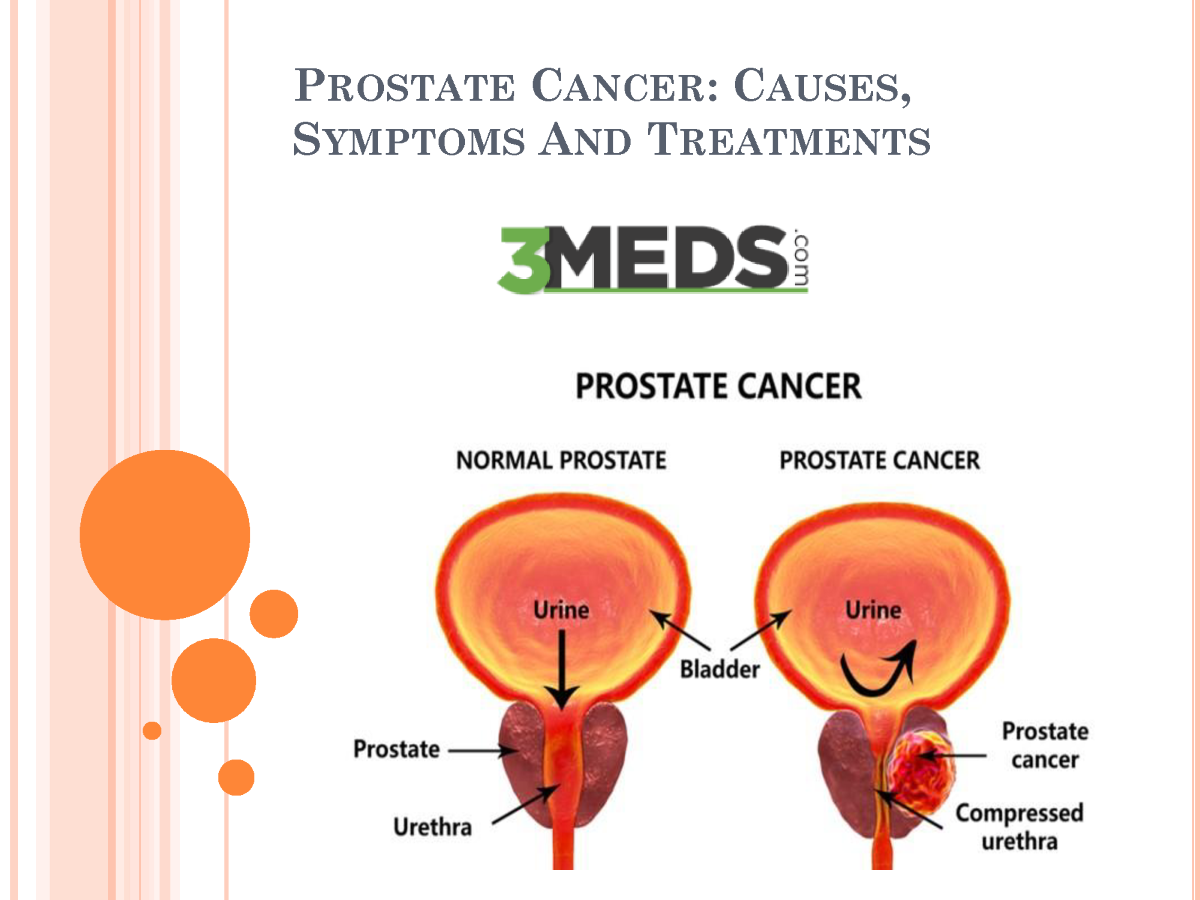
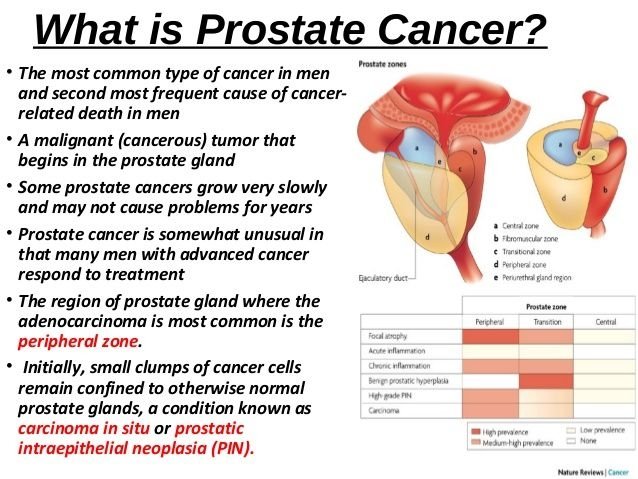
What Is Prostate Cancer
Check out this factsheet for a summary of the video.
Prostate cancer starts in the cells of the prostate. A cancerous tumour consists of cancer cells that can grow into nearby tissue and destroy it. The tumour can also spread to other parts of the body.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in Canadian men. It is most common in older men. It is more common in Black men than in white men, and it is less common in Asian men. Trans women and non-binary people who were assigned male at birth can also get prostate cancer.
The prostate is part of the male reproductive and urinary systems. It makes some of the fluid that is part of semen. It is located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The urethra goes through the prostate.
The prostate is usually about the size of a walnut in younger men but can change as you age and grow larger in older men.
Prostate cancer usually grows slowly and can often be completely removed or successfully managed when it is diagnosed before it has spread outside of the prostate. Older men with prostate cancer often die of other causes. Adenocarcinoma of the prostate is the most common type of prostate cancer. It accounts for 95% of all prostate cancers.
Who Is At Risk For Prostate Cancer
Certain men are at higher risk than others for prostate cancer, which may affect when they should start being screened. The risk increases with age, particularly after age 50. Some risk factors include:
- African American men are twice as likely as white men to develop the disease.
- Having a family history a father or a brother diagnosed with prostate cancer, particularly if it is at a relatively early age increases the risk.
- Having a family history of breast and ovarian cancer may also be associated with an inherited risk of developing prostate cancer
- High-fat diet and/or obesity
Also Check: How To Find The Prostate Gland Externally
Can Lack Of Sex Cause Prostate Cancer
Lack of sex is not known to cause prostate cancer. But, as noted, there is some evidence that frequent ejaculation, whether through masturbation or sex, may confer some protection against this cancer. Researchers are still trying to understand the exact biologic mechanisms that give rise to prostate cancer.
Facteurs De Risques Comportementaux
Surpoids, obesite
Lactualisation en 2018 menee par le WCRF/AICR a conclu a lassociation du statut ponderal avec laugmentation de risque de cancer de la prostate au stade avancé .
Les donnees montrent par ailleurs que ladiposite abdominale est egalement predictif du risque de cancer de la prostate
Don’t Miss: What Are The Different Treatments For Prostate Cancer
What Age Should You Check For Prostate Cancer
Different organizations or healthcare organizations have varying answers, but, on average, screening should begin at age 50. If a man has increased risk factors such as strong family history, is Afro-American, or consumes a lot of red meat, he should be screened in his mid-40s. There is evidence that if the PSA is very low in the mid-40s, it does not have to be checked again for a number of years. If, however, the PSA is elevated, it should result in more careful screening in the subsequent years.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment can be complex and is often controversial. an interprofessional team of specialty-trained nurses, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, primary care providers, oncologists, radiation therapists, genetic counselors, and urologists must work together to manage:
These and many more issues continue to challenge clinicians who deal with prostate cancer patients and men at risk for this common, potentially lethal male malignancy.
The interprofessional team can optimize the treatment of these patients through communication and coordination of care. Primary care providers, urologists, oncologists, radiation oncologists, and nurse practitioners provide diagnoses and care plans. Specialty care urologic nurses should work with the team to coordinate care and be involved in patient education and monitoring compliance. The interprofessional team can thus improve outcomes for patients with prostate cancer.
You May Like: Is Ejaculation Healthy For The Prostate
Prostate Cancer Caregiver Podcast Series
We are proud to announce a new podcast series geared toward helping give support, hope and guidance to prostate cancer caregivers. The goal of this Prostate Cancer Caregiver Podcast Series is to help others connect with a diverse group of people who have felt the impact of prostate cancer in their lives and empower them on their journey.
Expert Review And References
- American Cancer Society. Prostate Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging. 2019: .
- Garnick MB . Harvard Medical School 2015 Annual Report on Prostate Diseases. 2015.
- Hermanns T, Kuk C, Zlotta AR. Clinical presentation, diagnosis and staging. Nargund VH, Raghavan D, Sandler HM . Urological Oncology. Springer 2015: 40: 697-718.
- Logothetis CJ, Kim J, Davis J, Kuban D, Mathew P, Aparicio A. Neoplasms of the prostate. Hong WK, Bast RC Jr, Hait WN, et al . Holland Frei Cancer Medicine. 8th ed. People’s Medical Publishing House 2010: 94: 1228-1254.
- PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. Prostate Cancer Treatment Patient Version. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute 2020: .
- PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. Prostate Cancer Treatment Health Professional Version. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute 2020: .
Don’t Miss: When Do Men Get Prostate Exams
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have prostate cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get prostate cancer?
- What is my Gleason score? What is my Grade Group? What do these numbers mean for me?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the prostate gland?
- What is the best treatment for the stage of prostate cancer I have?
- If I choose active surveillance, what can I expect? What signs of cancer should I look out for?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Is my family at risk for developing prostate cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Prostate cancer is a common cancer that affects males. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and remain in the prostate gland. For a small number, the disease can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. Men with slow-growing prostate cancers may choose active surveillance. With this approach, you can postpone, and sometimes completely forego, treatments. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for you based on your Gleason score and Group Grade.
Does Undergoing A Vasectomy Cause Prostate Cancer
The link between prostate cancer and vasectomy is controversial. A 2020 study in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute suggests that undergoing a vasectomy may result in a small increased risk of prostate cancer that persists for at least three decades, regardless of the age at vasectomy. However, other studies have not found this to be true and more research is needed, according to the American Cancer Society.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Massage The Prostate
How Common Is Prostate Cancer
About one in nine men will receive a prostate cancer diagnosis during his lifetime. Prostate cancer is second only to skin cancer as the most common cancer affecting males. Close to 200,000 American men receive a diagnosis of prostate cancer every year. There are many successful treatments and some men dont need treatment at all. Still, approximately 33,000 men die from the disease every year.
Genetic Testing For Prostate Cancer
You may hear a lot about genetics or genomics. Both terms are related to genes and cell DNA, but they are different. These tests are being used to learn more about the DNA of cancer cells, and link DNA mutations with treatments. In the future, genetic testing may be the first step doctors take when diagnosing prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: Does Fish Oil Tablets Cause Prostate Cancer
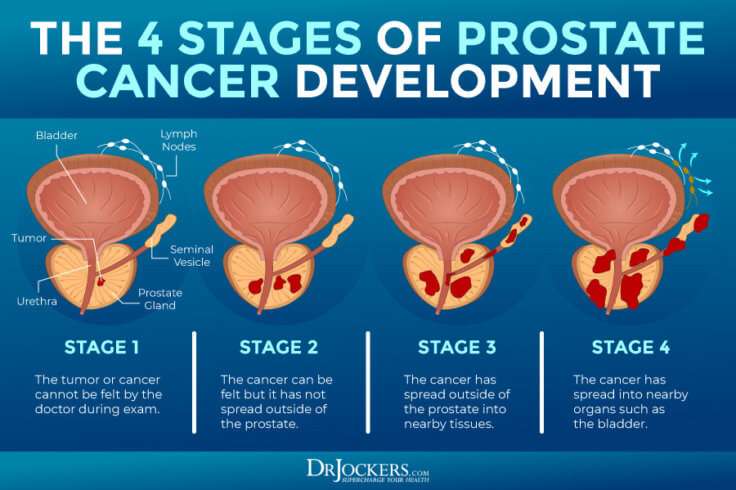
What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Your healthcare provider uses the Gleason score and Grade Groups to stage prostate cancer based on its projected aggressiveness. To get this information, the pathologist:
- Assigns a grade to each type of cell in your sample. Cells are graded on a scale of three to five . Samples that test in the one to two range are considered normal tissue.
- Adds together the two most common grades to get your Gleason score .
- Uses the Gleason score to place you into a Grade Group ranging from one to five. A Gleason score of six puts you in Grade Group 1 . A score of nine or higher puts you in Grade Group five . Samples with a higher portion of more aggressive cells receive a higher Grade Group.
