What Is A Transperineal Prostate Biopsy
Transperineal biopsy is a type of prostate biopsy and a method of evaluating for prostate cancer. With this ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy, your doctor will place a biopsy needle through the skin and into the prostate between the scrotum and rectum. The sampled tissue will be sent to the lab and evaluated by a pathologist to look for prostate cancer cells. This type of prostate biopsy is an outpatient procedure that takes 30-45 minutes to complete. This targeted biopsy approach is much more accurate than the traditional transrectal method.
Transperineal Prostate Biopsy: A Review Of Technique
Alice Thomson1, Mo Li1,2, Jeremy Grummet3,4, Shomik Sengupta1,2,5
1Urology Department, Eastern Health, 3Urology Department, Alfred Hospital, Prahran, Victoria 4Central Clinical School, Monash University, Prahran, Victoria , Australia
Contributions: Conception and design: S Sengupta Administrative support: S Sengupta Provision of study material or patients: None Collection and assembly of data: A Thomson, M Li Data analysis and interpretation: A Thomson, M Li Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Keywords: Prostate cancer transperineal prostate biopsy transrectal prostate biopsy
Submitted Oct 02, 2019. Accepted for publication Dec 24, 2019.
doi: 10.21037/tau.2019.12.40
Preparing For Your Transperineal Biopsy
You usually have this test in the outpatient department under local anaesthetic. Sometimes, you may have it in the operating theatre under a general anaesthetic. This is when you are asleep and dont feel anything.
Your doctor will ask you to sign a consent form once you have all the information about the test.
You take antibiotics to stop an infection from developing after the biopsy. You take them before the biopsy and for a few days afterwards. Your doctor will explain when you need to take the antibiotics and for how long. This is usually for a couple of days afterwards.
You usually have a tube into your bladder to drain urine if you have a general anaesthetic. Your nurse removes the catheter on the day of surgery or the morning after.
Also Check: Best Treatment For Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
What Does The Equipment Look Like
Ultrasound equipment:
Ultrasound scanners consist of an electronic console containing a computer, video monitor, and a handheld transducer . The transducer sends out inaudible high frequency sound waves into the body and listens for the returning echoes. The principle is similar to the sonar used by boats and submarines.
The computer displays the ultrasound image on a video monitor. This image is based on the amplitude and frequency of the signal. It is also based on signal travel time, tissue composition, and the type of body structure through which the sound travels.
The ultrasound probe for a prostate biopsy is about the size of a finger. Once the doctor inserts the probe into the rectum, they take tissue samples using a spring-driven needle core biopsy device . The handheld device includes a long but very thin needle. The needle opens inside the prostate, takes the sample, and then closes.
MRI equipment:
The traditional MRI unit is a large cylinder-shaped tube surrounded by a circular magnet. You will lie on a table that slides into a tunnel towards the center of the magnet.
What To Expect During The Procedure
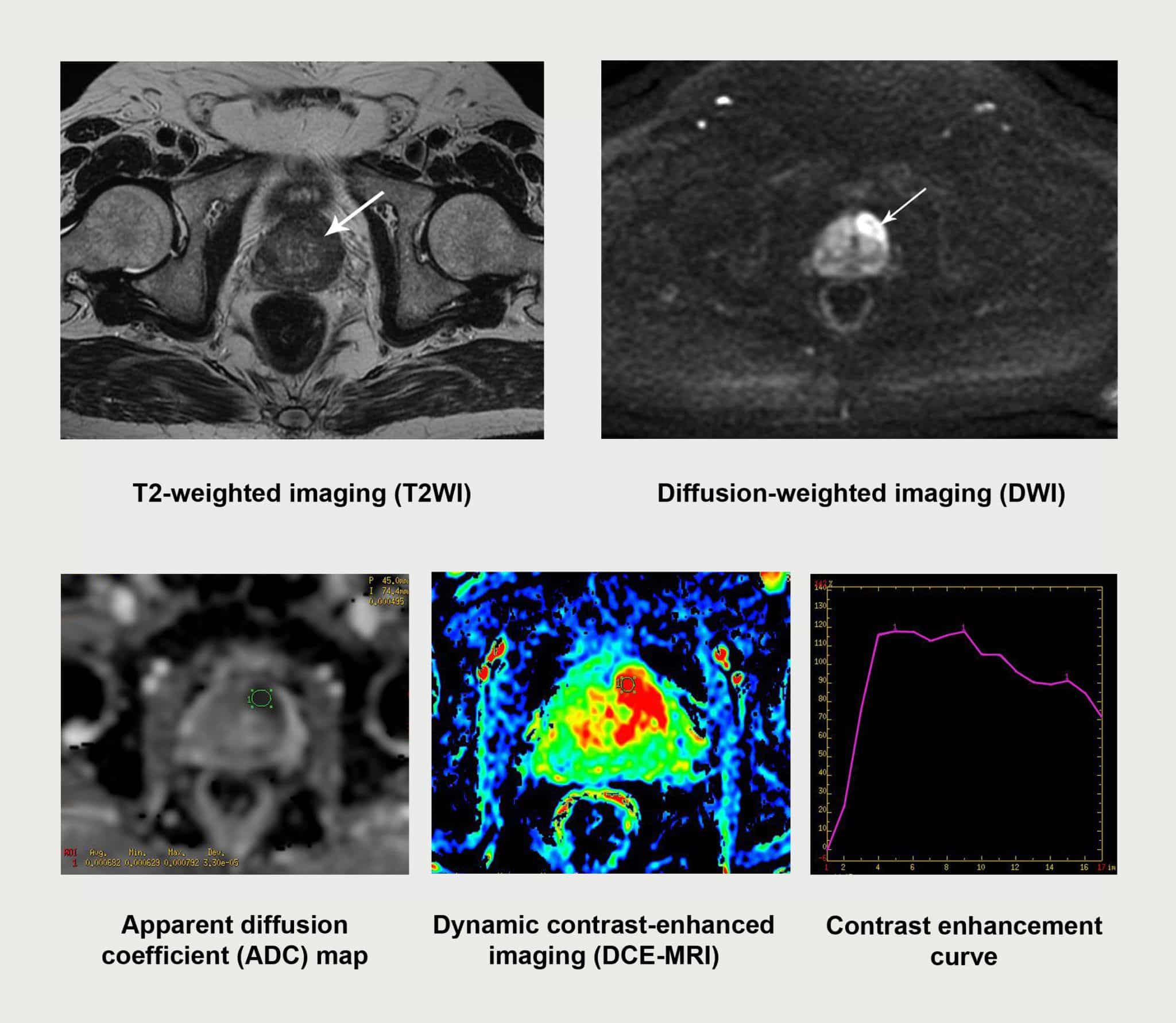
During a transperineal biopsy performed under local anesthetic, the doctor will inject the anesthetic into the perineum to numb the area. He or she will then insert an ultrasound probe into the back passage to show the prostate gland and guide the insertion of the biopsy needle through the perineum and into the prostate.
The MRI scan will help the doctor identify the best location to insert a biopsy needle. During the procedure, the doctor may need to take 30 to 50 samples.
Also Check: How To Lower Prostate Specific Antigen
Sexual Activity After A Prostate Biopsy
You may also want to wear condoms for a week or two to help prevent bacteria or other substances from irritating the areas around your rectum, perineum, or urethra.
Here are some ways you can help reduce your recovery time before and after your prostate biopsy:
- Stop taking blood thinners like aspirin or warfarin to help promote blood clotting during healing.
- Take any antibiotics a doctor instructs you to take before and after the biopsy.
- Use any enemas that a doctor instructs you to take to clean out your rectum and reduce your risk of infection.
- Consider giving a urine sample before the biopsy so that the doctor can ensure you dont have a urinary tract infection.
- Rest for a few days after the biopsy and try to stay off your feet to prevent irritation at the biopsy site.
- Consider taking a few days off work or other activities to reduce stress and movement.
- Reduce stress or anxiety to keep your body calm and promote your immune system function.
- Drink about 64 ounces of water a day to hydrate and promote healing.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol, which can thin your blood, interfere with antibiotics, and make you pee more frequently.
Transperineal Biopsy For Prostate Cancer
A transperineal biopsy is a needle biopsy to look for cancer cells in the prostate. This helps to diagnose prostate cancer.
Your doctor puts a needle into the prostate through the skin behind the testicles . They take a number of samples, which are sent to the laboratory. In the laboratory, a specialist doctor looks at the samples under the microscope.
Recommended Reading: Most Effective Supplement For Enlarged Prostate
What Is The Test
Your doctor is likely to recommend this test if you’ve had a rectal exam or blood tests that suggest that you might have prostate cancer. For this test, a urologist takes tissue samples from several places in your prostate, to be examined for cancer. A transrectal ultrasound helps the urologist see the prostate during the procedure.
Are There Alternatives To A Prostate Biopsy
A prostate biopsy is the most accurate tool a doctor can use to confirm a diagnosis of prostate cancer.
But you may not always need a prostate biopsy. Here are a few other tests that a doctor might recommend during a regular prostate cancer screening to rule out cancer without doing a biopsy:
- Digital rectal exam : During a DRE, a doctor will insert a gloved finger into your rectum to feel your prostate.
- Prostate-specific antigen test: A PSA test analyzes your blood for levels of the PSA protein. High levels could indicate prostate cancer.
- Transrectal ultrasound : A doctor may use TRUS to look at the prostate gland through your rectum, using an ultrasound machine to check for tumors or other abnormalities.
- Urine test: A urine test can detect other signs of prostate cancer in your pee, such as genetic markers that may indicate your risk.
Recommended Reading: Can Chronic Prostatitis Be Sexually Transmitted
Transperineal Biopsy Preparation For The Test
You do not need any antibiotic before or after the biopsy. You will be given a general anaesthetic for the procedure so you will need to fast for 6 hours before the test. So if the test is in the morning you should have nothing by mouth from midnight the night before. If your test is in the afternoon, then you can have a light breakfast at around 6 AM and then nothing after that. Please let Dr Gianduzzo and the staff know if you are on any blood thinners as you may need to stop these before the test. You will be advised of this at your appointment when the test is scheduled.
What Is A Transperineal Biopsy
The transperineal biopsy of the prostate is a type of guided prostate biopsy where the urologist passes the biopsy needle through the perineal skin and into the almond-shaped gland. The perineum is the skin between the testicles and rectum.
The whole purpose of this approach is to improve the cancer detection rate.
An ultrasound was placed in the rectum guides biopsy needle. In fact, several approaches for transperineal prostate biopsy exist. The choice of the technique depends on whether a fusion or a systematic biopsy is necessary. It also depends on whether the patient is in the clinic under sedation.
The first approach uses a stepper, a device that cradles the ultrasound probe and provides a guidance grid for the biopsy needle. The disadvantage of this approach is that each biopsy requires a skin puncture. As a result, this techniques utility is limited in clinics where transperineal prostate is performed under local anesthesia only.
The freehand approach is yet another technique. The approach uses a needle access guide. Only one or two skin punctures are necessary for each side of the prostate.
Since the needle access guide is positioned through the perineums anesthetized skin, the urologist can reintroduce the biopsy needle for multiple biopsies. That way, new skin puncture for each biopsy is unnecessary. The ultrasound probe in the rectum guides the biopsy needle. The freehand technique improves patient comfort.
You May Like: Psma Pet Scan For Prostate Cancer
What Is A Prostate Biopsy
A biopsy is a procedure used to remove a small piece of tissue or cellsfrom the body so it can be examined under a microscope.
In a prostate biopsy, prostate gland tissue is taken out with a biopsyneedle or during surgery. The tissue is checked to see if there are canceror other abnormal cells in the prostate gland.
A prostate biopsy may be done in several different ways:
-
Transrectal method. This is done through the rectum and is the most common.
-
Perineal method. This is done through the skin between the scrotum and the rectum.
-
Transurethral method. This is done through the urethra using a cystoscope .
Ultrasound is usually used to look at the prostate gland and guide thebiopsy needle.
How To Prepare For The Procedure
Patients may continue taking most of their medications as usual but should consult with their doctor to find out which ones should be paused.
Five days before the biopsy, patients should stop taking anticoagulants. Low doses of aspirin are allowed, but patients should stop taking clopidogrel and other antiplatelet medicines seven days before the biopsy. In addition, patients will need to have an INR check one day before the procedure.
On the day of the procedure, patients will be asked to give a urine sample to screen for a urine infection. A nurse will then review the patients medications and administer antibiotics to help prevent infection.
Patients may choose to be under local or general anesthesia during a transperineal prostate biopsy. If the biopsy is performed under local anesthesia, patients may eat and drink as usual before the exam. If the biopsy is performed under general anesthesia, the patient will need to start fasting six hours before the biopsy and stop drinking at least four hours beforehand.
Read Also: Does Flomax Cause Prostate Cancer
Potential Side Effects And Risks
Though the procedure is relatively safe, some patients may experience temporary side effects such as bleeding, infection, and pain. Patients should visit an emergency room if they experience one or more of the following signs of infection:
- High temperature or fever
- Blood in the urine or stool
- Need to urinate frequently
Assistant Professor of Clinical Urology
HS Assistant Clinical Professor
Residency Program Director, HS Clinical Professor
Professor of Clinical Urology
Professor
UCI Urology seeks to provide all patients with the best in innovative urological diagnosis and treatment. We focus on treating the whole patient and not just the symptoms, with an ultimate goal of effective and personally tailored healthcare.
UCI Urology Orange101 The City Drive SouthPavilion III, Building 29,
Transrectal Prostate Ultrasound And Biopsy
Prostate ultrasound and biopsy are tests that check the abnormal results of a digital rectal exam or an elevated prostate-specific antigen blood test.
Prostate ultrasound uses a probe about the size of a finger thatâs inserted a short distance into your rectum. This probe creates harmless sound waves. You canât hear them, but they bounce off the surface of your prostate. A machine records the sound waves and turns them into videos or photos of your prostate gland.
The probe can provide images at different angles to help your doctor estimate the size of your prostate and spot abnormal growths.
A prostate biopsy uses transrectal ultrasound imaging to guide several small needles through the rectum wall into areas of the prostate where the doctor sees something unusual. The needles remove a tiny amount of tissue. This is called a biopsy. Most doctors take six or more biopsies to test various areas of the prostate. The tissue samples are checked in a lab to see if theyâre cancerous. The results will help your doctor diagnose disorders and diseases in your prostate. If the doctor finds cancer, theyâll be able to grade it and figure out how aggressive, or likely to spread, it is. This helps them decide how to treat the cancer.
Some doctors do the biopsy through the perineum, the small area of skin between your scrotum and rectum. Researchers are looking into new biopsy procedures to get more accurate results.
Read Also: Prostate Cancer 3+4 Active Surveillance
How Does The Procedure Work
Ultrasound procedure:
Ultrasound imaging uses the same principles as the sonar that bats, ships, and fishermen use. When a sound wave strikes an object, it bounces back or echoes. By measuring these echo waves, it is possible to determine how far away the object is as well as its size, shape, and consistency. This includes whether the object is solid or filled with fluid.
Doctors use ultrasound to detect changes in the appearance of organs, tissues, and vessels and to detect abnormal masses, such as tumors.
In an ultrasound exam, a transducer both sends the sound waves and records the echoing waves. When the transducer is pressed against the skin, it sends small pulses of inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body. As the sound waves bounce off internal organs, fluids and tissues, the sensitive receiver in the transducer records tiny changes in the sound’s pitch and direction. A computer instantly measures these signature waves and displays them as real-time pictures on a monitor. The technologist typically captures one or more frames of the moving pictures as still images. They may also save short video loops of the images.
MRI procedure:
A computer processes the signals and creates a series of images, each of which shows a thin slice of the body. The radiologist can study these images from different angles.
MRI is often able to tell the difference between diseased tissue and normal tissue better than x-ray, CT, and ultrasound.
Why Transperineal Prostate Biopsy
- Transperineal Prostate Biopsy offers a theoretically lower false-negative rate, similar to improved diagnostic accuracy, and the possibility of more accurate staging than transrectal biopsy. In addition, TPB is the superior choice for many men with benefits including:
- Reduction in infection rates
- Can be completed in-office with the comfort of local anesthetic
- Improved sampling of anterior prostate area
Also Check: White Button Mushroom Prostate Cancer
What Are The Limitations Of Ultrasound
A biopsy can only show if there is cancer in the tissue samples. It is possible to miss cancer in unsampled areas of the prostate.
For MRI-guided biopsies, you must remain perfectly still to ensure the technologist captures high-quality images. If you are anxious, confused, or in severe pain, it may be hard to lie still. If so, the images may not be of high enough quality to be useful.
Likewise, the presence of an implant or other metallic object sometimes makes it difficult to obtain clear MR images. A person who is very large may not fit inside certain types of MRI machines.
Bleeding may sometimes occur in the prostate after a biopsy. MR imaging cannot always tell the difference between cancer, inflammation, or the presence of blood. To avoid confusing them, your doctor may perform a repeat MRI six to eight weeks after the biopsy to allow residual bleeding to resolve.
An MRI exam typically costs more and may take more time than other imaging exams. Talk to your insurance provider if you have concerns about the cost of MRI.
Preparing For Your Biopsy
Your urologist will inform you about the targeted biopsy and the course of the procedure. Make sure to ask questions and express your concerns.
Before the biopsy, you should let the doctor know if youre taking some medications. This can help the doctor determine the best form of anesthesia but also to avoid potential complications.
When you arrive at the doctors office, hospital, or clinic, you will get a specimen pot for a urine sample. Before the biopsy can even start, the healthcare professional will check urine for the signs of infection. Should they find the presence of infection, they will need to postpone biopsy.
To prevent infection, you will get antibiotics 40 to 60 minutes before the surgery. This practice is called antibiotic prophylaxis. Then, you will need to change into a hospital gown so the biopsy can start.
You May Like: Treatment For Prostate Cancer With Seminal Vesicle Invasion
Are There Any Problems To Expect After A Prostate Ultrasound And Biopsy
In some cases, men can develop a urinary tract infection or an infection in the prostate. These infections are rare and easy to treat with prescribed antibiotics.
Some men may also have trouble urinating after the procedure. Most problems are minor and go away on their own after a few days. If you arent able to urinate at all, call your healthcare provider or go to the emergency room. Make sure that you tell them that you just had the ultrasound and biopsy.
- A fever of 100 degrees F or higher.
- Shaking or chills.
Who Is A Candidate
Patients may need a transperineal biopsy if they:
- Have had a transrectal prostate biopsy that did not show signs of prostate cancer, but have a high PSA level and/or an MRI scan that showed suspicious areas
- Have an unusually large prostate
- Have a suspicious area observed on an MRI scan requiring further evaluation
- Have been previously diagnosed with prostate cancer that has not been treated but may have changed to require treatment
Don’t Miss: Why Does The Prostate Get Bigger With Age
