Acute Prostatitis: Causes Symptoms And Diagnosis
What is acute prostatitis?
Acute prostatitis happens when your prostate gland becomes suddenly inflamed. The prostate gland is a small, walnut-shaped organ located at the base of the bladder in men. It secretes fluid that nourishes your sperm. When you ejaculate, your prostate gland squeezes this fluid into your urethra. It makes up a large portion of your semen.
Acute prostatitis is usually caused by the same bacteria that cause urinary tract infections or sexually transmitted diseases . Bacteria can travel to your prostate from your blood. It can enter your prostate during or after a medical procedure, such as a biopsy. It can also be caused by infections in other parts of your genitourinary tract.
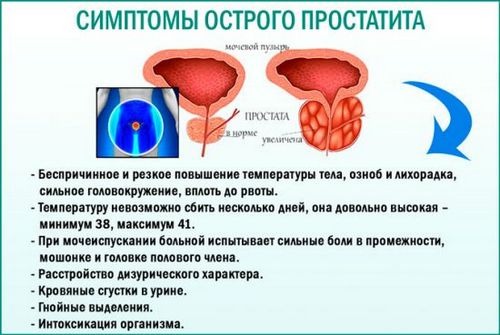
If you have acute prostatitis, you may develop:
- chills
- pain above your pubic bone
- pain in your genitals, testicles, or rectum
Any bacteria that causes UTIs can cause prostatitis. Bacteria that commonly cause UTIs and prostatitis include:
- Proteus species
- Klebsiella species
- Escherichia coli
Some bacteria that cause STDs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can also cause acute bacterial prostatitis. Other conditions that can lead to acute bacterial prostatitis include:
Factors that increase your risk of UTIs, STDs, and urethritis also increase your risk of acute prostatitis. For example, these risk factors include:
- not drinking enough fluids
- having unprotected vaginal or anal intercourse
Other risk factors include:
What Is The Prostate Gland What Does It Look Like
The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system, and it is a walnut-sized gland found in men that is located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine and semen exit the body. Its main function is to produce seminal fluid in order to transport sperm through the urethra.
Prostatitis Frequently Asked Questions Part 1 Dr David Samadi Explains The Condition
Prostatitis is a condition that involves inflammation of the prostate and sometimes the area surrounding it. There are several types of prostatitis, each with their own unique range of symptoms. Some men with the disease will experience severe pain while others arent affected and the rest fall somewhere in between the two. However, the symptoms of the disease can have a significant impact on a mans quality of life. The following are some of the most frequently asked questions regarding prostatitis.
Don’t Miss: Is Sex Healthy For Your Prostate
Should I Avoid Having Sex If I Have Prostatitis
Prostatitis is an extremely common condition affecting men. While it is more common in older men, it can occur at any age.
Essentially, it is an inflammation of the male prostate gland that may be the result of a bacterial or fungal infection. It can also occur without any infection simply from the result of mechanical irritation.;
According to some experts, prostatitis is the symptom-producing condition of the genitourinary tract for which men most often seek medical help. Roughly 40 percent of visits by men to urologists are for prostatitis.;
In a healthy man, prostatitis can be brought about by irritation to the gland from external stimuli, such as; bike or motorcycle riding, excessive exercise, sexual activity, or even lack of sufficient sexual activity. The term prostatitis is used by many medical professionals for almost all cases of prostate inflammation, even when there is no readily apparent cause.;
The purpose of the male prostate gland is to generate fluids for lubrication and transporting sperm containing semen outside the male body during sexual intercourse. This seminal fluid contains enzymes, some minerals, and, most importantly, sperm cells for propagating the species.;
What Is Prostatitis And What Causes It
4.4/5Prostatitiscaused byprostatefull detail here
Acute bacterial prostatitis is often caused by common strains of bacteria. The infection can start when bacteria in urine leak into your prostate. Antibiotics are used to treat the infection. In many cases of prostatitis, the cause isnt identified.
One may also ask, what is prostatitis and how is it treated? Antibiotics. Taking antibiotics is the most commonly prescribed treatment for prostatitis. If you have severe symptoms, you might need intravenous antibiotics. Youll likely need to take oral antibiotics for four to six weeks but might need longer treatment for chronic or recurring prostatitis.
Additionally, is prostatitis serious?
Prostatitis. Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland. acute prostatitis where the symptoms are severe and develop suddenly; its rare, but can be serious and requires immediate treatment, and is always caused by an infection.
Can prostatitis be transmitted to a woman?
Prostatitis is frequently caused by bacterial infections, but its usually not caused by something that can be passed on to your partner during sex. In rare cases, prostatitis is caused by a sexually transmitted infection .
Also Check: How To Reduce Prostate Swelling Naturally
Don’t Miss: How Many Men Will Get Prostate Cancer
The Scheme Of Treatment For Chronic Infectious And Latent Infectious Prostatitis
It is important – at the primary reception, an examination algorithm should be maintained. Initially, a 3-glass urine sample with its bacteriological study, then – a digital rectal examination, obtaining a prostate secret for its microscopy and sowing. The sowing is intended to reveal the nonspecific microflora and mycobacterium tuberculosis; on the evidence – sexually transmitted infections. If a secretion of less than 25 white blood cells is found in the field of vision, tamsulosin should be tested for 5-7 days with repeated prostate massage and repeated examination of its secretion. If the number of leukocytes does not increase, and the crops are negative, the disease should be attributed to non-infectious prostatitis and to conduct appropriate pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy. If more than 25 white blood cells are visualized in the initial analysis or their number increases after the test therapy, the disease should be considered as infectious or latent infection. In this case, the basis of treatment is antibiotic therapy – empirical at the beginning, and corrected after receiving the results of bacteriological research.
What Is The Prognosis For Prostatitis Does It Increase The Risk Of Developing Prostate Cancer
Prostatitis caused by bacterial illness often can be treated with antibiotics, or the condition can be chronic that recurs and requires long-term medical attention.
- Acute bacterial prostatitis can often be treated very successfully and has a very good prognosis.
- Chronic prostatitis, and especially chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, can often lead to long-term symptoms and discomfort if treatment is unsuccessful. It is important to have close follow-up and continued care by either your primary care doctor or a urologist.
- Prostatitis does not increase your risk of developing prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Function Of The Prostate Gland
How Can You Differentiate Between Prostatitis And A Std
Prostatitis is a painful condition with inflammations in prostate gland. Acute prostatitis is usually a result of infection in the urinary tract or infection carried by the blood. Symptoms include fever, low back pain, and difficulty or pain in urination; the gland is tender and swollen. In many cases, the infection spreads from the urethra and is contracted through sexual transmission.;
STDDiuretic and anti-inflammatory pill
- Shop 1-3, Nan Hu Xin Cheng, Wenchang Road, Hongshan District, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China
Q&A
Treatments For Symptom Relief
The preferred treatment regimen for chronic bacterial prostatitis is a combination of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs .
Although NSAIDs can provide relief from the pain of prostatitis, theyre primarily used to reduce inflammation.
Other medications you may receive are:
- stool softeners to avoid constipation
- alpha-blocker medications, such as tamsulosin , to help treat urinary retention
Certain home remedies may be able to ease your symptoms too. Home remedies include:
- warm baths
Read Also: Does Cialis Shrink An Enlarged Prostate
Treatments That A Specialist May Suggest
Various treatments have been tried for chronic prostatitis. They may benefit some people but so far there are few research studies to confirm whether they help in most cases. They are not ‘standard’ or routine treatments but a specialist may advise that you try one.
For chronic bacterial prostatitis, possible treatments may include the following:
- A longer course of antibiotics. If the specialist suspects that you have chronic bacterial prostatitis and your symptoms have not cleared after a four-week course of antibiotics, they may suggest a longer course. Sometimes a course of up to three months is used.
- Removal of the prostate may be considered if you have small stones in the prostate. It is not clear how much this may help but it has been suggested that these small stones may be a reason why some people have recurrent infections in chronic bacterial prostatitis. However, this is not commonly carried out and is not suitable in everyone. Your specialist will advise.
For chronic prostatitis/CPPS, possible treatments may include the following:
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of prostatitis, such as pelvic pain, difficulty or pain when peeing, or painful ejaculation.
They’ll ask about the problems you’re having and examine your tummy.
You may also have;a rectal examination. This is where a doctor inserts a gloved finger into your bottom to feel for anything unusual. You may have some discomfort during this examination if your prostate is swollen or tender.
Your urine will usually be tested for signs of infection, and you may be referred to a specialist for further tests to rule out other conditions.
See a GP straight away if you get sudden and severe symptoms of prostatitis.
You may have acute prostatitis, which needs to be assessed and treated quickly because it can cause serious problems, such as suddenly being unable to pee.
If you have persistent symptoms , you may be referred to a doctor who specialises in urinary problems .
Recommended Reading: What Is A Transrectal Ultrasound Of The Prostate
What If My Prostatitis Is Not Caused By Infection
Because we do not understand what causes prostatitis without infection, it can be hard to treat. Your doctor might try an antibiotic to treat a hidden infection. Other treatments are aimed at making you feel better. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, and hot soaking baths may help you feel better. Some men get better by taking medicines that help the way the bladder or prostate gland work. These medicines include oxybutynin, doxazosin, prazosin, tamsulosin and terazosin.
Symptoms Of Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
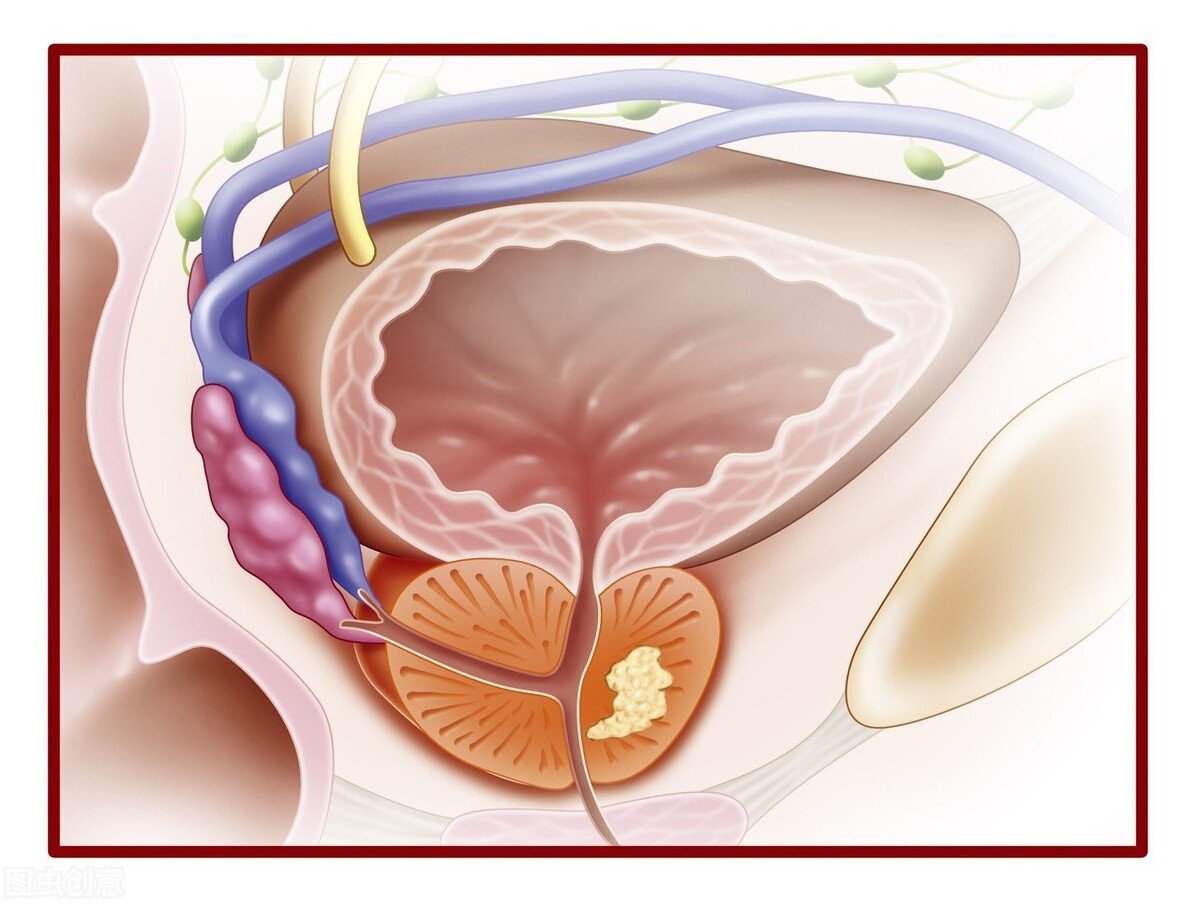
Bacterial infections in the prostate can be very painful.
The symptoms begin slowly and last 3 months or longer. Seek medical attention if you have any of the following symptoms:
Serious complications can arise if an infection isnt properly treated. Complications include:
- urinary retention, which is an inability to urinate
- , which occurs when bacteria spread into the bloodstream
- a prostate abscess, which is a collection of pus that causes inflammation
A bacterial infection causes chronic bacterial prostatitis. Even when the primary symptoms of infection have been treated, bacteria may continue to thrive in the prostate.
Causes of infection include:
- sexually transmitted infections , such as chlamydia and gonorrhea
- E. coli after having an infection of the testicles, urethritis , or a UTI
Certain factors put people at risk for developing this condition, such as:
Also Check: What Can Be Done For An Enlarged Prostate
Read Also: How To Massage Your Own Prostate Gland
Causes And Symptoms Of Prostatitis
Once a diagnosis is made, it will be categorized as either acute or chronic. Both acute and chronic prostatitis are likely caused by bacteria that have entered the prostatic ducts from the rectum due to a backward flow of infected urine. Prostatitis is not contagious or considered a type of sexually transmitted disease. However, it can result from several different sexually transmitted diseases.
Even though acute and chronic prostatitis can occur at any age, there are certain conditions that put men at a greater risk of developing it:
- Any man with recent bladder, urinary tract, or other infection elsewhere in the body
- Injury or trauma to the perineum
- Abnormal urinary tract anatomy
- Rectal intercourse
- A recent procedure involving the insertion of a urinary catheter or cystoscope
The symptoms of both acute and chronic prostatitis are generally the same even though each man may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
- Urinary frequency and/or urgency
- Burning or stinging sensation during urination
- Painful urination
- Reduced stream volume during urination
- Rectal pain and/or pressure
- Fever and chills
- Lower back pain and/or pelvic pain
- Discharge through the urethra during bowel movements
- Sexual dysfunction and/or loss of sex drive
- Throbbing sensation in the rectal and/or genital area
Who Is At Risk For Prostatitis
Although any man can develop prostatitis at any age, there are some conditions that put a man at greater risk for developing this condition, including the following:
-
Recent bladder, urinary tract, or other infection elsewhere in the body
-
Injury or trauma to the perineum
-
Abnormal urinary tract anatomy
-
Recent procedure involving the insertion of a urinary catheter or cystoscope
Also Check: Can A Prostate Biopsy Spread Cancer
What Is A Prostate Infection
A prostate infection occurs when your prostate and the surrounding area become inflamed. The prostate is about the size of a walnut. Its located between the bladder and the base of the penis. The tube that moves urine from the bladder to the penis runs through the center of your prostate. The urethra also moves semen from the sex glands to the penis.
Several types of infections can affect the prostate. Some men with prostatitis experience no symptoms at all, while others report many, including intense pain.
What Tests Diagnose Prostatitis What Are Prostate
Prostatitis is usually diagnosed by analyzing a urine sample and undergoing an examination of your prostate gland by your health care practitioner. This examination involves a digital rectal examination to palpate the prostate gland and feel for abnormalities of the gland. Occasionally, the physician may also collect and test a sample of the prostatic fluid.
Sometimes a prostate massage is performed to compare samples of the prostatic fluid both before and after this intervention has been performed. To perform this procedure, the doctor will stroke/massage the prostate gland during the digital rectal examination. Because there is the concern that this procedure can release bacteria into the bloodstream, this test is contraindicated in cases of acute bacterial prostatitis.
Additional tests that may be obtained include a complete blood count , an electrolyte panel, blood cultures, a swab of urethral discharge if present, and sometimes a prostate-specific antigen level. The PSA test, which is used as a screening test for prostate cancer, may also be elevated with prostatitis.
Other tests that may also be obtained include urodynamic tests , ultrasound imaging, computed tomography imaging, cystoscopy, and a prostate biopsy.
If recurring episodes of urinary tract infections and prostatitis occur, see your doctor for a more detailed evaluation of your genitourinary system for anatomic abnormalities, which may make you more prone to infections.
Don’t Miss: Is Fish Oil Bad For Men’s Prostate
Is Prostatitis Contagious
If you have an active infection in your prostate, it can also be present in a seminal fluid. If you engage in sexual intercourse with someone without a condom. the infection can be passed to another person. It would not necessarily cause any symptoms in your partner. Nevertheless, your partner may become a chronic carrier of infection and pass it back to you during consecutive sexual encounters without a condom.
What Is Prostatitis
Prostatitis is common and affects many men at some time. Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland. When part of your body is inflamed, it is red, hot and sore. Prostatitis can cause many symptoms. It can make it difficult or painful to urinate. It can make you have to urinate more often. It can also give you a fever, low-back pain or pain in your groin . It may make you less interested in having sex or unable to get an erection or keep it. Prostatitis is easy to confuse with other infections in the urinary tract.
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
How Is It Treated
Prostatitis caused by bacteria is treated with antibiotics and self-care.
Home treatment includes drinking plenty of fluids and getting lots of rest. Taking over-the-counter pain relievers can also help.
Your doctor may prescribe medicine to control pain and reduce swelling. He or she may also prescribe medicine to soften your stool and relax your bladder muscles.
Surgery is rarely used to treat prostatitis.
What Are The Complications Of Prostatitis
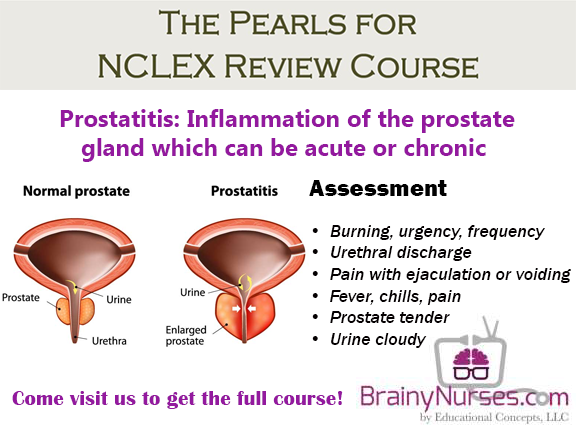
- abscess of the prostate gland,
- spreading of the infection to the blood stream , and rarely
- death.
Prostatitis can elevate the PSA level. There is no evidence that prostatitis leads to prostate cancer. If the acute inflammation/episode of prostatitis has resolved, the PSA level will usually return to baseline levels.
Also Check: How To Stop Leaking After Prostate Surgery
Case And Control Definitions
Several case definitions were used: 1) surgery for an enlarged prostate, defined as a report of surgery for prostatic enlargement between the date of return of the 1992 questionnaire and January 31, 2000; 2) prevalent LUTS, defined as an American Urological Association symptom index score of 15 or more points on any of the follow-up questionnaires or use of medications to treat LUTS among participants who never reported surgery for an enlarged prostate; and 3) total prevalent LUTS, consisting of surgery for an enlarged prostate and prevalent LUTS. Prevalent LUTS cases were further classified as having high-moderate to severe LUTS , severe LUTS , severe irritative LUTS , and severe obstructive LUTS . Parallel incident case definitions were used for men who reported a low American Urological Association symptom index score on the 1992 questionnaire and on the 1994 questionnaire, if completed, and LUTS on subsequent questionnaires.
Controls were defined as participants who never reported surgery for an enlarged prostate, who scored 07 points on the American Urological Association symptom index on all completed questionnaires, and who did not report use of medications to treat LUTS.
