Prostatitis: A Common Problem In Men Under 50
“The;PSA;test is a good screening tool for prostate cancer, but it is not very specific,” says Erik P. Castle, MD,;a urologist and researcher at the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, Arizona. “Common causes of inflammation in the gland, called;prostatitis, can cause high;PSA;levels.”
Prostatitis;is the most common prostate problem for men younger than 50.
Prostatitis;caused by bacteria can be treated with antibiotics. Another, more common type of;prostatitis, called;nonbacterial;prostatitis, can be harder to treat and may last a long time.
Natural Methods To Lower Elevated Psa
Higher PSA levels are not a cancer diagnosis in and of themselves. ;Further evaluation is warranted to determine the underlying cause contributing to abnormal PSA results. While further testing is important, there are natural measures that can help lower PSA levels.
Diet changes: A healthy diet that includes more fruits and vegetables with fewer amounts of meats may result in lower PSA levels. ; Excessive dairy products may contribute to poor prostate health. ;Eating antioxidant rich fruits and vegetables such as berries, tomatoes and leafy greens, helps protect the body from the damaging effect of oxidation on tissues. Although meats need not be eliminated, switch to; leaner options such as omega-rich fish and chicken. Protecting your prostate health and lowering PSA levels can be as simple as making healthier meal choices.
Exercise:;Obesity contributes to many health problems including those of the prostate.; With exercise and weight loss, PSA levels can benefit.
Manage stress:;As with many health conditions, stress can negatively affect prostate health and PSA levels. A lifestyle that is balanced and relaxed helps maintain good prostate health.
Aspirin regimens: Some studies have suggested a positive link between aspirin use and prostate health. Talk to your doctor before taking aspirin.
Related links
How Is The Psa Count Measured
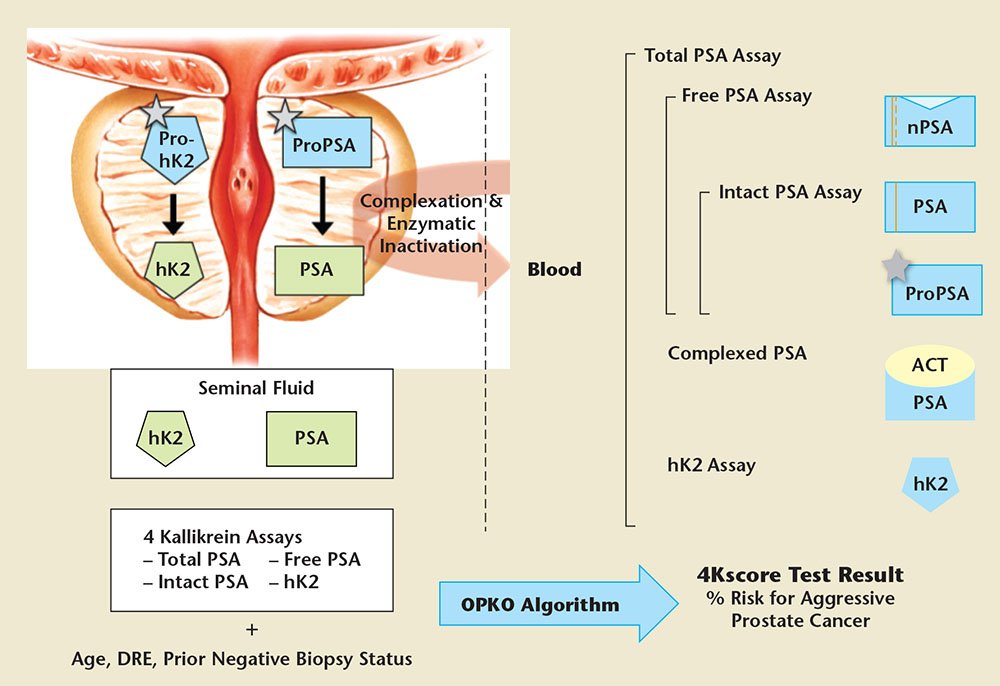
PSA is measured by a simple blood test that does not require fasting or special preparation. Since the amount of PSA in the blood is very low, detection of it requires a very sensitive type of technology . The PSA protein can exist in the blood by itself or be bound with other substances . PSA is mostly bound to three substances: alpha-2-macroglobulin, alpha 1-antichymotrypsin , and albumin. Total PSA is the sum of the free and the bound forms. The total PSA is what is measured with the standard PSA test. More recently, a precursor of PSA, proenzyme PSA , has been identified, which may be helpful in determining prostate cancer risk in men with a PSA under 10 and a normal digital rectal examination. The prostate health index is a new approved test that measures the total PSA, free PSA, and proenzyme PSA. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines include use of PHI as a secondary test option for men making decisions about an initial or repeat biopsy. The 4K score test is another test that incorporates PSA. The 4K score uses a prediction model based on clinical variables and laboratory measurements of total PSA, free PSA, intact PSA, and a related protein known as hK2 .
You May Like: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Prostate Infection
How Is Psa Testing Used For Pretreatment Staging Of Prostate Cancer
Once prostate cancer is diagnosed by the presence of cancer cells on prostate biopsy and assigned a cancer grade , PSA is used in combination with the grade of the prostate cancer to determine further medical studies needed for cancer staging. Staging determines if the cancer is localized or metastatic . Staging therefore drives the best management and appropriate treatment for the cancer. As mentioned earlier, serum PSA levels correlate with the risk of prostate cancer extension outside of the prostate including seminal vesicle invasion as well as metastasis to the pelvic lymph nodes.
If Screening Test Results Arent Normal
If you are screened for prostate cancer and your initial blood PSA level is higher than normal, it doesnt always mean that you have prostate cancer. Many men with higher than normal PSA levels do not have cancer. Still, further testing will be needed to help find out what is going on. Your doctor may advise one of these options:
- Waiting a while and having a second PSA test
- Getting another type of test to get a better idea of if you might have cancer
- Getting a prostate biopsy to find out if you have cancer
Its important to discuss your options, including their possible pros and cons, with your doctor to help you choose one you are comfortable with. Factors that might affect which option is best for you include:;
- Your age and overall health
- The likelihood that you have prostate cancer
- Your own comfort level with waiting or getting further tests
If your initial PSA test was ordered by your primary care provider, you may be referred to a urologist for this discussion or for further testing.
Read Also: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Excessive Intake Of Calcium Supplements And Dairy Products May Increase The Risk Of Prostate Cancer
- In a 24 year follow-up study called the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study done by the researchers of the Harvard School of Public Health in Boston, based on dietary information from 47,885 men, it was found that high consumption of phosphorus was independently associated with an increased risk of advanced stage and high-grade prostate cancer, approximately 0-8 years after consumption. The researchers also found that excessive Calcium intake of >2000 mg/day was associated with an increased risk of advanced-stage and high-grade prostate cancer, about 12 to 16 years after consumption.
- In another study, as part of the WCRF/AICR Continuous Update Project, the researchers from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology in Norway, Imperial College in London and University of Leeds in UK evaluated the association between the intake of calcium and dairy products and prostate cancer risk. The analysis used data from 32 studies which were obtained through literature search in Pubmed till April 2013. The researchers found that the consumption of total dairy products, total milk, low-fat milk, cheese, and dietary calcium were associated with an increased risk of total prostate cancer. They also found that supplemental calcium intake was associated with an increased risk of fatal prostate cancer.
Who Needs A Psa Test
Some experts recommend a PSA test for men ages 50 to 70. They also recommend testing men with a high risk for prostate cancer at age 40 or 45. Risk factors may include being African American or having a brother or father with prostate cancer. Other experts may not recommend PSA testing. Your healthcare provider can help you decide if you need a PSA test.
Don’t Miss: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Noncancerous Prostatic Disease And Urologic Manipulation
The serum PSA level can also be altered by noncancerous prostatic disease and urologic manipulations. Elevation of PSA levels has been demonstrated in acute prostatitis, subclinical or chronic prostatitis, and urinary retention. Nadler et al reported that serum PSA levels higher than 4.0 ng/mL in 148 men with subclinical prostatitis could be attributed to their disease because all these men had negative findings from biopsies repeated on multiple occasions.
No significant change occurs in the PSA level after a digital rectal examination , but a vigorous prostate massage can produce a short-term 2-fold increase. Cystoscopy, urethral catheterization, and transrectal ultrasonography of the prostate do not tend to elevate the PSA level. Needle biopsy of the prostate raises the PSA level by a median of 7.9 ng/mL within 5 minutes after the biopsy, and this level persists for 24 hours.
The time it takes for PSA to return to baseline levels depends on the precipitating event and the half-life . After a biopsy, 2 to 4 weeks may elapse before the PSA returns to its original level. If an infection occurs as a result of the biopsy, the return to baseline levels may take longer. After ejaculation, PSA levels have been reported to return to their original levels within 48 hours, whereas fPSA returns to baseline at 6 hours because of its shorter half-life .
When Should I Have My Psa Levels Tested
The first thing to do is talk to your doctor about the pros and cons of prostate cancer screening before you decide whether to be tested. Donât get tested until you have that talk. Opinions differ about when you should do that.
The American Cancer Society says to get tested at age:
- 40 or 45 if youâre at high risk
- 50 if youâre at average risk
The American Urological Association suggests:
- Under 40: No screening
- 40 to 54: No screening if youâre at average risk. If youâre at a high risk, you and your doctor can decide.
- 55 to 69: Screening if your doctor suggests
- Over 70 or less than a 10-15 year life expectancy: No screening
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force says:
- 55 to 69: Men with prostate cancer risks may need testing.
If your doctor thinks you might have prostate cancer based on either a PSA level or a rectal exam, a biopsy is the next step. This is a test where the doctor takes a small amount of tissue from your prostate and sends it to a lab for tests. Itâs the only way to be sure you have cancer.
Recommended Reading: Is Turmeric Good For Prostate
Who Should Have Regular Screening Tests For High Psa
The PSA test was first developed to observe prostate changes in men who had a history of prostate cancer. Then it became more widely used in the general population as a way to detect and prevent prostate cancer before symptoms developed. But routine screening can find prostate cancers that grow slowly and do not need treatment. Talk to your healthcare provider to see if you should have regular PSA tests.
If I Have Elevated Psa Levels What Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have any symptoms of prostate cancer, or if it runs in your family, ask your provider:
- Should I have regular tests to check my PSA level?
- What can I do to lower my risk for prostate cancer?
- What other tests or monitoring do I need?
- What are my treatment options if I get prostate cancer?
- What other signs or symptoms should I look out for?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
An elevated PSA level can be a sign of prostate cancer, but it doesnt always mean you have cancer. Your healthcare provider will watch you and do more tests to arrive at a diagnosis. Prostate cancer is often slow-growing and may never become life-threatening. If you have symptoms of prostate problems, such as difficulty urinating, don’t hesitate to let your provider know.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 04/06/2021.
References
Recommended Reading: Prostate Meds Side Effects
How Much Does The Test Cost
The price of a PSA test will vary based on where the test is conducted and whether you have health insurance. If you have health care coverage, you can reach out to your insurance provider directly to find out what a PSA test will cost under your plan. Depending on your plan, you may be responsible for out-of-pocket costs, such as copays and deductibles.
The cost of at-home PSA testing ranges from about $30 to $70.
Add Some Pomegranate To Your Diet
Whether you enjoy pomegranate juice, the tasty pulp and seeds, or prefer the supplement, be sure to include this fruit in your diet more often. Research at Johns Hopkins has shown that this phytonutrient-rich fruit can reduce the rate of PSA doubling in men who have prostate cancer. Overall, the doubling time increased from 11.9 months at baseline to 18.5 months after treatment with pomegranate extract. Since pomegranate is rich in sugar, taking a;supplement;may be better than having the fruit on a regular basis.
Recommended Reading: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
What Abnormal Results Mean
A high PSA level has been linked to an increased chance of having prostate cancer.
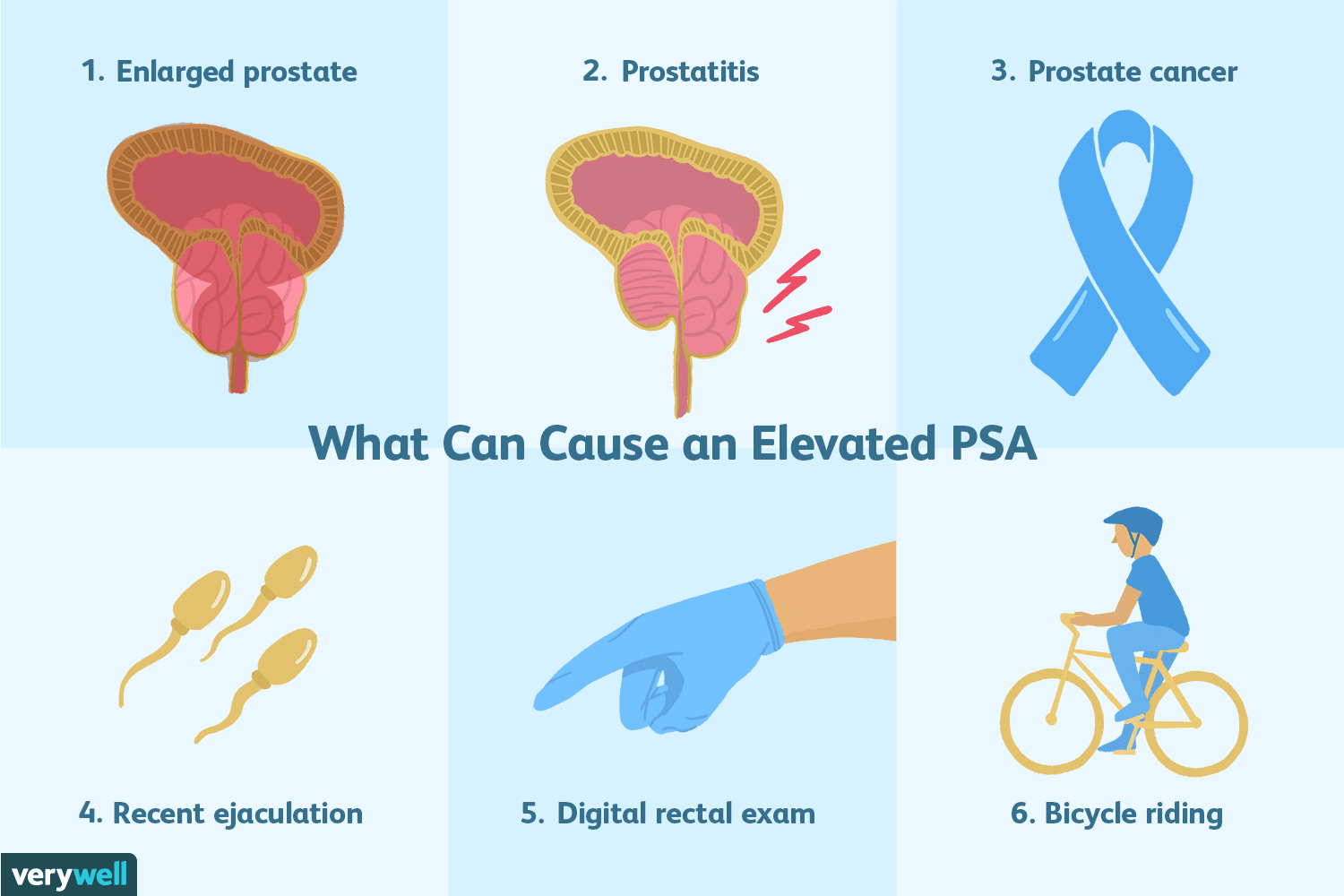
PSA testing is an important tool for detecting prostate cancer, but it is not foolproof. Other conditions can cause a rise in PSA, including:
- A larger prostate
- Recent tests on your bladder or prostate
- Catheter tube recently placed into your bladder to drain urine
- Recent intercourse or ejaculation
Your provider will consider the following things when deciding on the next step:
- Your age
- If you had a PSA test in the past and how much and how fast your PSA level has changed
- If a prostate lump was found during your exam
- Other symptoms you may have
- Other risk factors for prostate cancer, such as ethnicity and family history
Men at high risk may need to have more tests. These may include:
- Repeating your PSA test, most often sometime within 3 months. You may receive treatment for a prostate infection first.
- A prostate biopsy will be done if the first PSA level is high, or if the level keeps rising when the PSA is measured again.
- A follow-up test called a free PSA . This measures the percentage of PSA in your blood that is not bound to other proteins. The lower the level of this test, the more likely it is that prostate cancer is present.
Other tests may also be done. The exact role of these tests in deciding on treatment is unclear.
- A urine test called PCA-3.
- An MRI of the prostate may help identify cancer in an area of the prostate that is hard to reach during a biopsy.
How Is Psa Testing Used In The Management Of Prostate Cancer After Treatment
A periodic PSA determination is used to detect disease recurrence after treatment. Serum PSA should decrease and remain at undetectable levels after a radical prostatectomy . An increase in the PSA over time after radical prostatectomy is suggestive of recurrent prostate cancer. Similarly, failure of the PSA to decrease to an undetectable level after radical prostatectomy may indicate residual prostate cancer. Similarly, serum PSA should fall to a low level following radiation therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, and cryotherapy and remain at or near this level over time.
You May Like: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
What If A Screening Test Shows An Elevated Psa Level
If a man who has no symptoms of prostate cancer chooses to undergo prostate cancer screening and is found to have an elevated PSA level, the doctor may recommend another PSA test to confirm the original finding. If the PSA level is still high, the doctor may recommend that the man continue with PSA tests and DREs at regular intervals to watch for any changes over time.
If a mans PSA level continues to rise or if a suspicious lump is detected during a DRE, the doctor may recommend additional tests to determine the nature of the problem. A urine test may be recommended to check for a urinary tract infection. The doctor may also recommend imaging tests, such as a transrectal ultrasound, x-rays, or cystoscopy.
If prostate cancer is suspected, the doctor will recommend a prostate biopsy. During this procedure, multiple samples of prostate tissue are collected by inserting hollow needles into the prostate and then withdrawing them. Most often, the needles are inserted through the wall of the rectum . A pathologist then examines the collected tissue under a microscope. The doctor may use ultrasound to view the prostate during the biopsy, but ultrasound cannot be used alone to diagnose prostate cancer.
Can I Take The Test At Home
Although testing for PSA at home is uncommon, several at-home PSA tests are available. At-home PSA tests typically involve collecting samples of blood at home through a fingerstick and sending the samples into a laboratory for testing. When considering at-home PSA testing, its important to understand the potential harms of this test.
At-home testing may be less accurate than testing a sample taken from a vein. PSA testing can also show a higher result when cancer isnt present and can lead to additional diagnostic procedures. Because the role of PSA testing is highly individualized, its important to seek testing only under the care and guidance of a doctor.
Recommended Reading: Enlarged Prostate Viagra
Recommendations For Psa Testing
According to a 2019 position statement from the European Association of Urology, a baseline PSA test in men aged 45 years at risk of prostate cancer should be used in combination with family history, ethnicity, and other factors to establish individualized screening frequency.
The American Urological Association and the American Cancer Society offer divergent recommendations on prostate-specific antigen screening. The AUA recommends baseline PSA testing, along with digital rectal examination , at age 40 for all men with a life expectancy of 10 years or more, with subsequent testing intervals determined on the basis of the PSA level and DRE results.
The ACS does not specify an age at which to pursue screening in asymptomatic men with a life expectancy of 10 years or more; rather, the ACS advises clinicians to provide men with information on the risks and benefits of screening so the patient can make an informed decision. In addition, the ACS recommends that men whose initial PSA level is below 2.5 ng/mL can be screened every 2 years, but men with higher PSA values should be tested annually.
From these findings, the investigators concluded that potentially curable prostate cancer is not compromised when measuring PSA every other year in men with PSA levels of 2 ng/mL or less, as long as the DRE findings are normal.
Clinical Information Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Prostate-specific antigen is a glycoprotein that is produced by the prostate gland, the lining of the urethra, and the bulbourethral gland. Normally, very little PSA is secreted in the blood. Increases in glandular size and tissue damage caused by benign prostatic hypertrophy, prostatitis, or prostate cancer may increase circulating PSA levels.
PSA exists in serum in multiple forms: complexed to alpha-1-anti-chymotrypsin , unbound , and enveloped by alpha-2-macroglobulin .
Higher total PSA levels and lower percentages of free PSA are associated with higher risks of prostate cancer.
Most prostate cancers are slow growing, so the utility of prostate cancer screening is marginal in most men with a life expectancy of less than 10 years.
Also Check: Can An Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
