Stages Of Prostate Cancer
In order to determine the stage of a patients prostate cancer, most doctors start by using the TNM staging system, which helps describe different aspects of the cancers growth.
- T the T category measures the size and extent of the Tumor
- N the N category measures whether and how far the cancer has spread to the Lymph Nodes
- M the M category whether the cancer has spread to other organs in the body (a process called Metastasis
The score for each of these categories is determined based on a pre-determined set of criteria. Your doctor cannot feel or see the tumor with a score of T1. A score of T3 means that the tumor has begun to grow outside of the prostate.
After calculating the TNM categories, doctors will combine the TNM score with the patients Gleason score and PSA levels assigning of a specific stage to the patients cancer.
Prostate cancer prognosis and survival rates can help give patients an idea of their chances of surviving the disease based on the stage and time of diagnosis. While some patients may find this information helpful, others may not want to know.
Prospective Randomized Trial Of Seminal Vesicle
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : April 5, 2013Last Update Posted : April 5, 2013 |
| Procedure: nerve-sparing radical prostatectomyProcedure: seminal vesicle-sparing radical prostatectomy | Phase 2Phase 3 |
What Are Some Common Treatments For Medical Conditions Related To The Seminal Vesicles
If you have issues involving your seminal vesicles, the treatment depends on the causes. Possible treatments include:
- Antibiotics. These drugs are used to treat infections.
- Paracentesis: This is a way of using a needle to remove fluid from your abdomen.
- Minimally invasive surgery to remove cysts, stones and tumors.
- Radical prostatectomy surgery for prostate cancer that also removes seminal vesicles.
Read Also: Can Prostate Exam Elevate Psa
Seminal Vesicle And Ejaculatory Duct
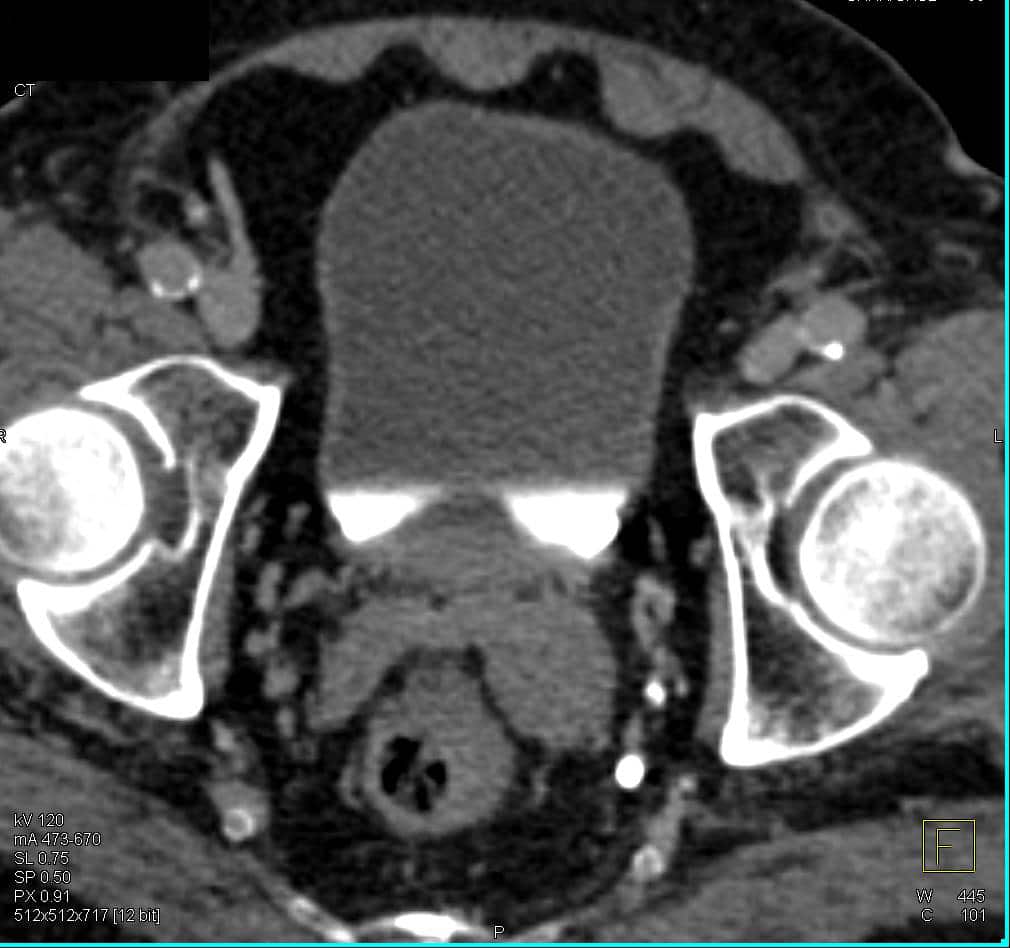
The seminal vesicle, is a thin-walled paired structure measuring about 5â10 cm in length and 3â5 cm diameter. Despite its oval macroscopic appearance, the seminal vesicle is actually a blind tube, about 10â15 cm long, and 1 cm in diameter. Rolled up on itself and surrounded by a connective tissue capsule, it takes on an appearance similar to a bag. Distally, the excretory duct of the seminal vesicle, the neck of the seminal vesicle, joins to the corresponding ductus deferens to form the ejaculatory duct . The seminal vesicle is located behind the urinary bladder, between the bottom of the bladder and the rectum. The upper ends of both seminal vesicles are covered by the peritoneum, which at this level forms the bottom of the rectovesical pouch, a recess that separates them from the anterior surface of the rectum. Their lower extremities are closely related to the ureter and the rectum, from which they are separated only by the rectovesical septum. The wall of the seminal vesicles has three layers: an internal layer of pseudostratified columnar epithelium, with goblet cells and a lamina propria an intermediate layer of smooth muscular tissue and an external layer composed of areolar tissue .
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Also Check: Treatment Options Of Prostate Cancer
Seminal Vesicle Invasion Predicts Decreased Survival In Bladder Cancer
1. Concomitant seminal vesicle invasion in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder and prostatic stromal infiltration was associated with decreased cancer-specific and overall survival rates.
2. Incorporation of cSVI into multivariate analysis increased accuracy in predicting mortality events.
Evidence Rating Level: 2
Metastasis And Contiguous Spread
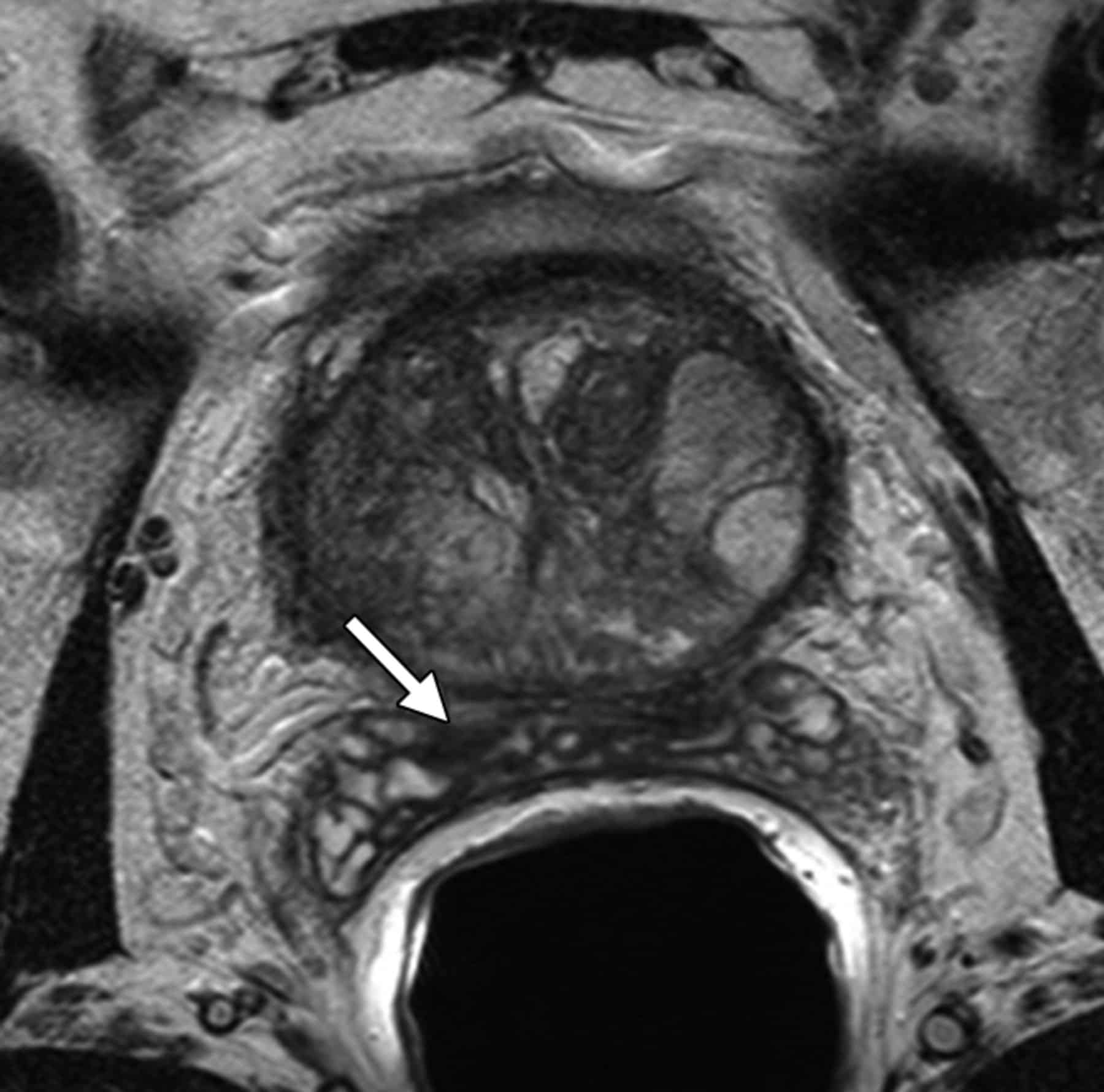
Seminal vesicle involvement by prostatic adenocarcinoma is common, observed in about 12% of contemporary radical prostatectomy specimens from patients with cancer clinically confined to the prostate . There are three patterns of seminal vesicle invasion: direct spread along the ejaculatory duct complex into the seminal vesicles prostatic capsular perforation followed by extension into the periprostatic soft tissues and spread into the seminal vesicles and isolated deposits of cancer in the seminal vesicles .171-175 Intraepithelial spread most likely results from direct invasion of carcinoma from the muscular wall of seminal vesicles rather than extension from the ejaculatory duct system in the invaginated extraprostatic space.176 Endorectal coil MRI is accurate in detecting seminal vesicle invasion according to radical prostatectomy correlation studies, with loss of architectural contour as a dominant feature.177 Bilateral invasion portends a worse prognosis than does unilateral invasion.178
Rectal adenocarcinoma occasionally invades the seminal vesicles and prostate, and may cause diagnostic difficulty.184 Metastases to the seminal vesicles and retrovesicular space from other organs are rare, including renal cell carcinoma, seminoma, malignant thymoma, and melanoma.185-189
David G. Bostwick, in, 2008
Read Also: Focused Ultrasound For Prostate Cancer
Prostatitis: A Common Prostate Problem In Younger Men
Prostatitis, or prostate inflammation, is the most common prostatic and urinary tract problem for men under age 50, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases . It accounts for 2 million doctor visits in the United States each year.
There are several types of prostatitis.
Prostatitis caused by bacteria is known as bacterial prostatitis, and it can cause an acute or chronic infection.
Prostate And Seminal Vesicles
| FIGURE 16.1. BPH. CT shows markedly enlarged prostate a portion of the bladder is seen anterior to the prostate. |
| FIGURE 16.2. BPH. The enlarged prostate indents and elevates the bladder floor. The ureterovesical junctions are displaced superiorly, producing a J shape of the distal ureter . |
| FIGURE 16.3. Bladder diverticula. The bladder is thick-walled due to chronic outlet obstruction and has an indwelling Foley catheter. There are two posterolateral diverticula, both with fluid-debris levels indicating stasis of urine. |
| FIGURE 16.4. Median lobe. This enlarged portion of the prostate produces a polypoid midline mass in the bladder lumen. |
| FIGURE 16.5. Bilateral symmetric hydronephrosis due to bladder outlet obstruction. Delayed film from an excretory urogram reveals bilateral symmetric dilation of the upper tracts to the level of the ureterovesical junctions . Even on this delayed film, no opacification of the bladder is seen. This pattern is consistent with large residual urine due to bladder outlet obstruction resulting in functional obstruction of the upper urinary tracts. |
| FIGURE 16.6. BPH. Transverse section of the prostate from a TRUS examination shows the central portion of the prostate to be enlarged. The mixed echogenicity is consistent with BPH. The centrally placed urethra is clearly seen. The peripheral zone can be seen posterior to the adenoma and extending laterally around its margins. The rectum is posterior. |
Read Also: Signs Of Aggressive Prostate Cancer
Prognostic Groups For Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer
Doctors divide locally advanced prostate cancer into groups depending on how likely it is that the cancer will grow quickly or spread. In the UK, doctors now divide prostate cancer into 5 groups. This is the Cambridge Prognostic Group . The 5 groups are from CPG 1 to CPG 5. This CPG system does not apply if you have cancer that has already spread to other parts of the body. This is metastatic or advanced prostate cancer.
Your group depends on:
- your Grade Group or Gleason score
- the prostate specific antigen level
- the size of your cancer. This is the T stage
Ask your doctor or specialist nurse if you have any questions about this.
Comparison Of Fiducials On The Anteriorposterior Image
The ANOVA on the shifts for the AP image showed there were highly significant differences between fiducials, both in the LR and SI directions . Overall, the prostate, bone and left seminal vesicle shifted to the right, and the right seminal vesicle shifted to the left compared to the initial setup. All fiducials shifted superiorly, with the LSV moving the most.
Figure 1
| 2.533 | 7.45 |
- Overall mean = mean of the mean shifts for 30 patients = group systematic error, SD mean = standard deviation of the mean shifts for 30 patients = systematic error, Root Mean Square SDs = square root of the mean of the squares of the standard deviations for 30 patients = random error, and PTV margin = 2.5Σ + 0.7Ï.
Don’t Miss: Is There Treatment For Prostate Cancer
Perineural Invasion And Seminal Vesicle Involvement Predict Pelvic Lymph Node Metastasis In Men With Localized Carcinoma Of The Prostate
Stone NN, Stock RG, Parikh D, et al.
J Urol. 1998 160:17221726 .
In an effort to evaluate the ability of the presence of biopsy PNI to predict a subsequent finding of lymphatic or seminal vesicle involvement by prostate cancer, Stone and associates evaluated 212 men who presented with clinically localized prostate cancer and underwent staging pelvic lymph node dissection. Using univariate and multivariate analyses, the presence of biopsy PNI was correlated with the likelihood of metastatic prostate cancer found on pelvic lymphadenectomy. Stone and colleagues found that biopsy PNI was a better predictor of lymph node metastasis than serum prostate-specific antigen , biopsy Gleason score, or clinical stage. The authors concluded that men with biopsy PNI seeking definitive therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer should be counseled for staging pelvic lymph node dissection before definitive therapy. The potential role of biopsy PNI in predicting an increased likelihood of seminal vesicle invasion or lymphatic metastasis warrants further research. Additional support of the predictive power of PNI for lymphatic metastasis could strengthen the argument for staging lymph node dissection in the large number men with this biopsy finding who choose to undergo brachytherapy or external beam radiotherapy for clinically localized prostate cancer.
You May Like: Prostate Cancer In Young Men
What Can I Do To Keep My Reproductive System Healthy
Things that you do to stay healthy overall can help you keep your sexual organs functioning well. These things may include:
- Stopping smoking, vaping or using other tobacco products.
- Eating a healthy diet, including drinking enough water.
- Reaching and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Practicing safe sex.
- Wearing protective equipment if you participate in contact sports.
Read Also: Incontinence After Prostate Removal Surgery
Stratification Of Svi By Prognostic Significance
Epstein and associates16 evaluated the surgical series of Walsh, identifying 60 men who underwent radical retropubic prostatectomy between January 1984 and December 1994 and who had isolated SVI on final pathologic analysis. The seminal vesicles in each case were serially sectioned and examined for evidence of invasion by prostate cancer. Diagnosis of SVI required involvement of the extraprostatic portion of the seminal vesicle and invasion of the muscular wall of the seminal vesicle. Multivariate analysis revealed that Gleason score, surgical margin status, and the presence of vascular invasion provided the best prediction of prognosis. This analysis stratified patients into 2 roughly equal-sized groups of good and poor prognosis using only routine pathologic variables. A small cohort of men in the series of Epstein and associates having tumors with isolated SVI and Gleason score 5 to 6 tumors and negative surgical margins had a much better prognosis than the remainder of the cohort. Interestingly, Epstein and colleagues did not find the route of SVI to be of prognostic significance. Their data did confirm that of other investigators in finding that discontinuous metastases to the seminal vesicle were very uncommon, accounting for only 6.7% of all tumors that demonstrated SVI.
Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer
Doctors may describe prostate cancer as localised, locally advanced and metastatic. Locally advanced prostate cancer means that the cancer has broken through the capsule of the prostate gland. It may have spread into the:
- tissue around the prostate
- body organs nearby such as the back passage or bladder
- lymph nodes close to the prostate gland
In the TNM staging system, locally advanced prostate cancer is the same as T3 or T4. Below is a simplified description of the T3 and T4 stage:
T3 means the cancer has broken through the capsule of the prostate gland.
T4 means the cancer has spread into other body organs nearby, such as the back passage, bladder, or the pelvic wall.
Read Also: Is Hemp Oil Good For Prostate Cancer
Seminal Vesicle Invasion: What Is The Best Adjuvant Treatment After Radical Prostatectomy
Cyrille Bastide
Level of Evidence2b
Whats known on the subject? and What does the study add?
Seminal vesicle invasion in prostate cancer has a poor prognosis. Nowadays, there is no consensus about the best adjuvant treatment after radical prostatectomy when seminal vesicle invasion is observed in the specimen.
To our knowledge, this is the first comparative study between different adjuvant treatments after radical prostatectomy when seminal vesicle invasion is observed in the specimen.
Perineural Invasion Associated With Increased Cancer
Beard. IJROBP 2006 66:403
The significance of PNI with respect to prognosis after surgery has been inconsistently demonstrated, with some investigators showing a clear risk of upstaging, upgrading, or adverse outcomes in their PNI+ patients, and others showing no effect whatsoever. There is less information on the association between outcomes after RT and PNI, but theavailable data suggest that PNI is associated with unfavorable outcomes after RT. Previously, an unfavorable outcome was defined as freedom from PSA failure. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report demonstrating a survival decrement in the PNI+ patient population. However, the results must be viewed as preliminary, given the small number of events, relatively short follow-up, and retrospective nature of the analysis.
Purpose: To identify an association between perineural invasion and cancer-specific survival in patients with prostate cancer after standard-dose external beam radiation therapy .
Results: At a median follow-up of 4.5 years, 84 patients have died, 15 of 84 from prostate cancer. PNI was the only significant predictor of prostate cancer-specific mortality after RT . The estimated prostate cancerspecific mortality was 14% at 8 years for PNI+ patients vs. 5% for PNI patients .
Dont Miss: Prostate Cancer How Long To Live
Read Also: What Are The 5 Warning Signs Of Prostate Cancer
Association Between Seminal Vesicle Invasion And Prostate Cancer Detection Location After Transrectal Systemic Biopsy Among Men Who Underwent Radical Prostatectomy
-
Affiliation Department of Urology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
-
Affiliation Department of Urology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
-
Affiliation Department of Urology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
-
Affiliation Department of Urology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
-
Affiliation Department of Urology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
-
Affiliation Department of Urology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
-
Affiliation Department of Urology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
Cysts In Other Organs
Seminal vesicles, pancreas, and arachnoid membrane cysts are present in 40% , 5%, and 8% of patients, respectively.68â73 Seminal vesicle cysts rarely result in infertility.74 Defective sperm motility is another cause of male infertility in ADPKD.75 Pancreatic cysts are almost always asymptomatic, with very rare occurrences of recurrent pancreatitis and possibly chance associations of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor or carcinoma reported in ADPKD.76â78 Arachnoid membrane cysts are asymptomatic, but may increase the risk for subdural hematomas.70,79 Spinal meningeal diverticula may occur with increased frequency and rarely present with intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leak.80 Ovarian cysts are not associated with ADPKD.81,82
Juan Andrés RamÃrez-González, Andrea Sansone, in, 2022
Also Check: Prostate Cancer Stage 2b Prognosis
Read Also: What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Prognostic Significance Of Svi
The finding of SVI at the time of radical prostatectomy is an adverse pathologic finding that confers a decrease in long-term freedom from biochemical recurrence exceeded in magnitude only by the finding of lymph node metastases.711 The natural history of prostate cancer with SVI was noted almost 30 years ago by Byar and Mostofi,12 who evaluated 208 radical prostatectomy specimens by step-sectioning and correlated their findings with long-term patient follow-up. They found that SVI conferred a 32% 7-year survival rate, while men without SVI had a 67% 7-year survival rate. In contemporary series utilizing elevated postoperative serum PSA levels to determine progression, 5-year progression-free rates range from 5% to 60% .
Urinary Tract Infections In Men: Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment

Nonbacteria microbes may cause a different type of chronic prostatitis, known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome, which may also develop as a result of chemicals in the urine, a urinary tract infection, or pelvic nerve damage.
Affecting 10 to 15 percent of the U.S. male population, chronic pelvic pain syndrome is the most common type of prostatitis, but also the least understood.
Symptoms vary depending on the type of prostatitis, but can include urination problems, pain , fever, and body aches, among other things.
Some people develop asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis, in which the prostate is inflamed but doesnât produce any symptoms or require treatment.
Bacterial prostatitis is most often treated with antibiotics. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome may require drugs, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
Over time, prostatitis may cause sexual dysfunction, abscesses in the prostate, inflammation of nearby reproductive organs, and infection of the bloodstream.
Learn More About Prostate Problems and Complications
Don’t Miss: Does Weed Irritate The Prostate
