What Happens Without Treatment
Healthcare providers will sometimes talk about a particular diseases natural history or typical progression if it is left untreated indefinitely.
With regard to prostate cancer, most cases of the disease are discovered while the cancer is still confined to the prostate itself. This is called local disease or localized disease.
The disease is easiest to treat while it is confined to the prostate. At this stage, surgery and radiation are most likely to be curative and completely kill or remove whatever cancer cells are present.
If left untreated, however, prostate cancer can proceed on a number of different paths.
What Causes Prostate Cancer
The exact cause of prostate cancer is not known. The tumor arises from cells with abnormal deoxyribonucleic acid changes in the prostate. These abnormal cells rapidly grow and divide, invading surrounding structures and can spread to other parts of the body .
Risk factors
There are certain factors that can increase the risk of prostate cancer. These include
- Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases with age and is most commonly seen after the age of 50.
- Race: African American men have a higher risk of prostate cancer than men of other ethnicities. Cancer in African Americans is also more likely to be aggressive.
- Family history: If a blood relative has prostate cancer, it increases the risk as well. Having a family history of genes that increase the risk of breast cancer or a very strong family history of breast cancer also increases the risk of developing prostate cancer.
- Obesity: Obese people have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer, which is also more likely to be aggressive and recurrent despite treatment.
About Dr Dan Sperling
Dan Sperling, MD, DABR, is a board certified radiologist who is globally recognized as a leader in multiparametric MRI for the detection and diagnosis of a range of disease conditions. As Medical Director of the Sperling Prostate Center, Sperling Medical Group and Sperling Neurosurgery Associates, he and his team are on the leading edge of significant change in medical practice. He is the co-author of the new patient book Redefining Prostate Cancer, and is a contributing author on over 25 published studies. For more information, contact the Sperling Prostate Center.
Search the spc blog
Don’t Miss: Finding Prostate Externally
What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is often grouped into four stages.
- Stages I & II: The tumor has not spread beyond the prostate. This is often called early stage or localized prostate cancer.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread outside the prostate, but only to nearby tissues. This is often called locally advanced prostate cancer.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread outside the prostate to other parts such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver or lungs. This stage is often called advanced prostate cancer.
When an early stage prostate cancer is found, it may be treated or placed on surveillance . If prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer. Stage IV prostate cancer is not curable, but there are many ways to control it. Treatment can stop advanced prostate cancer from growing and causing symptoms.
There are several types of advanced prostate cancer, including:
Biochemical Recurrence
If your Prostate Specific Antigen level has risen after the first treatment but you have no other signs of cancer, you have biochemical recurrence.
Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
- Lymph nodes outside the pelvis
- Bones
Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer
Do Biopsies Spread Cancer
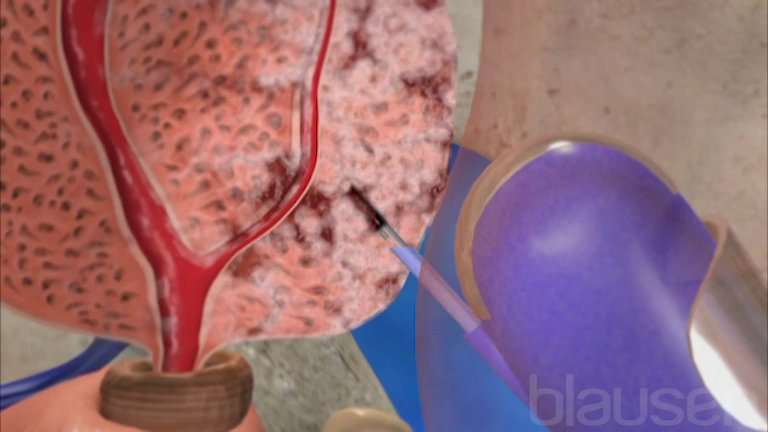
Cancer is almost always diagnosed by biopsy, a surgical procedure that removes tissue samples from tumors. The samples are viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to determine the presence and type of cancer. According to TMD Limited, a medical tourism company, it is the fear of biopsies spreading cancer that drives over half a million US citizens out of the country for medical treatment each year.
Doctors routinely recommend biopsies to diagnose cancer. PET and CT scans usually follow. All of these tests can harm the patient.
All cells are surrounded by interstitial fluid. This fluid drains into the lymph system through lymph channels, to the upper left chest, where the major lymphatic channel drains directly into a blood vessel. When a scalpel or needle invades tissue with cancer cells, there will be some bleeding, spilling cancer cells into the blood vessels or the lymph system via the interstitial fluid. Once a few of the billions of cancer cells break away and enter the bloodstream, they travel to distant organs and start to grow. This process is called seeding. The dangerously high amount of radiation in PET and CT scans damages normal cells, which produce abnormal cells when they divide, and those abnormal cells can become malignant.
Breast biopsy complications can include pain, swelling, bleeding, and drainage from the biopsy site, infection and false positive results, leading to unnecessary treatments.
Read Also: Expressed Prostatic Secretion
Evaluation Criteria For Circulating Epithelial Cellular Material
Cytokeratin positive, CD45 negative cellular material, was considered indicative of hematogenous epithelial cellular material. Those of 1020m size and with DAPI positive cell nuclei may be classified as representing circulating tumor cells , while those with a smaller size and lacking a DAPI detectable cell nucleus were classified as epithelial cellular material.
What Is Prostate Cancer
Cancer can start any place in the body. Prostate cancer starts in the prostate gland. It starts when cells in the prostate grow out of control.
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. Cancer cells in the prostate can sometimes travel to the bones or other organs and grow there. When cancer cells do this, its called metastasis. To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the prostate.
Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when prostate cancer spreads to the bones , its still called prostate cancer. Its not called bone cancer unless it starts from cells in the bone.
Ask your doctor to use this picture to show you where your cancer is.
The prostate
The prostate is a gland found only in men, so only men can get prostate cancer.
The prostate is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum . The tube that carries pee goes through the prostate. The prostate makes some of the fluid that helps keep the sperm alive and healthy.
There are a few types of prostate cancer. Some are very rare. Most prostate cancers are a type called adenocarcinoma. This cancer starts from gland cells. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
Read Also: Find Prostate Externally
What Does It Mean If In Addition To Cancer My Biopsy Report Also Mentions Acute Inflammation Or Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation of the prostate is called prostatitis. Most cases of prostatitis reported on biopsy are not caused by infection and do not need to be treated. In some cases, inflammation may increase your PSA level, but it is not linked to prostate cancer. The finding of prostatitis on a biopsy of someone with prostate cancer does not affect their prognosis or the way the cancer is treated.
Can Invasive Procedures Spread Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is seldom spread by invasive procedures such as biopsies, prostatectomy, TURP, LDR brachytherapy, HDR brachytherapy, or insertion of fiducials for image-guided radiotherapy. We know this because those procedures have high cure rates. Nevertheless, there have been isolated case reports of such inadvertent cancer dissemination occurring.
Don’t Miss: Zinc And Prostate Cancer
Precancerous Cells And Pin
Sometimes, the results will show that precancerous cells, or prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia , are present.
If these PIN are low grade, the doctor will not consider this a matter of concern. Many males have low grade PIN. However, if the PIN are high grade, there is a chance that cancer may develop. In these cases, a doctor may suggest further tests.
If a person already has prostate cancer, the grade of the PIN does not matter, as it does not affect the severity or the Gleason score of the cancer.
Carcinoma in situ refers to cells that have the potential to become cancerous. They can occur almost anywhere in the body.
How Fast And Where Does Prostate Cancer Spread
Like other cancers, prostate cancer can spread from the site of where it first started to other sites of the body. Once it spreads, the disease may still respond to the treatment, but typically it is now no longer to be cured. Bones, liver, and lungs are the most common sites for prostate cancer metastasis. How do you know that it has spread? And how fast this metastasis?
Since the early detection of the disease is very crucial for the prognosis and outlook of patients , its very important to diagnose the disease as early as possible.
In the U.S, the number of men diagnosed with the disease at later stages decreases drastically due to the implementation of PSA screening test .
Men with many risk factors of prostate cancer should start discussing the test with their doctor earlier. Visit this section for more information about this!
The PSA test is also recommended in other countries . However whether this test is necessary for all men is debatable.
For those who eventually dont have prostate cancer in their life, the choice to take the test may put them at high risk of getting over-diagnosis, making anxiety more likely.
Therefore, some experts agree that the screening prostate cancer test is more recommended for those who have some /many risk factors of the disease. For more advice, consult more with your GP!
How prostate cancer is diagnosed?
PSA screening test
Rectal examinations
Biopsy procedure
IVU or IVP Intravenous urogram
Read Also: Does Retrograde Ejaculation Go Away
What Is A Transperineal Biopsy
This is where the doctor inserts the biopsy needle into the prostate through the skin between the testicles and the back passage . In the past, hospitals would only offer a transperineal biopsy if other health problems meant you couldnt have a TRUS biopsy. But many hospitals have stopped doing TRUS biopsies and now only do transperineal biopsies.
A transperineal biopsy is normally done under general anaesthetic, so you will be asleep and wont feel anything. A general anaesthetic can cause side effects your doctor or nurse should explain these before you have your biopsy. Some hospitals now do transperineal biopsies using a local anaesthetic, which numbs the prostate and the area around it, or a spinal anaesthetic, where you cant feel anything in your lower body.
The doctor will put an ultrasound probe into your back passage, using a gel to make this easier. An image of the prostate will appear on a screen, which will help the doctor to guide the biopsy needle.
If youve had an MRI scan, the doctor may just take a few samples from the area of the prostate that looked unusual on the scan images. This is known as a targeted biopsy.
Incidence Of Track Seeding In Prostate Biopsies
An article published by Volanis, et al. in the prestigious British Journal of Urology reports a literature review conducted earlier that year. The authors systematically examined the huge PubMed literature database for research evidence with emphasis on the incidence of seeding, clinical presentation and on risk factors including type of needle used, transrectal vs. transperineal approach, as well as tumour grade and stage. They identified 26 articles reporting instances of needle tracking, for a total of 42 cases .
Considering a conservative figure of 220,000 cases of prostate cancer diagnosed per year, the fraction of needle tracking is astonishingly small. According to a review of the 2014 article, There were probably well in excess of 2 million prostate biopsies conducted in America last year. Even if as many as half of the 42 identified cases of seeding had occurred last year in America , this means that the individual risk for seeding at the time of a specific biopsy is certainly no higher than 21 × 100 ÷ 2,000,000 or 0.1 percent , and it may be a lot lower than that. Furthermore, even when such seeding does occur, there is no evidence to suggest that such seeding is associated with any increase in risk for clinically significant prostate cancer.
Recommended Reading: Is Sex Healthy For Your Prostate
Read Also: Define Prostate
What Is Localized Prostate Cancer
Localized prostate cancer is cancer that is only inside your prostate gland and has not spread to other parts of your body. The prostate is a gland in men about the size of a walnut. It makes and stores the liquid that carries sperm.
The prostate is near the bladder and rectum . It is just below the bladder and surrounds the upper part of the urethra .
Most men with localized prostate cancer have few or no symptoms. Possible symptoms can include:
- Problems when you urinate
- Pain in your lower back
- Pain when you ejaculate
- Blood in your urine
Note
What If My Biopsy Shows Cancer
If the biopsy shows prostate cancer, your doctor will determine how likely your cancer is to grow quickly and spread. Sometimes, prostate cancer grows slowly over many years. But other times, it grows quickly.
Your doctor can use your PSA level, Gleason score, and tumor score to determine your risk level. The following pages give more information about Gleason score, T-score, and prostate cancer risk levels.
Gleason Score
The Gleason score is a common scale used to determine how fast your prostate cancer is likely to grow. Gleason scores can range from 2 to 10, but most often range from 6 to 10. The higher the Gleason score, the more likely your cancer is to grow and spread.
Tumor Score
The T-score tells how far your prostate cancer has grown.
- T1: The cancer is too small to be felt during a digital rectal exam or seen in an imaging test . The cancer is found from a biopsy done after a man has a high PSA level or has surgery for problems urinating. The cancer is only in the prostate gland.
- T2: The cancer can be felt during a digital rectal exam and may be seen in an imaging test. The cancer is still only in the prostate gland.
- T2a: The cancer is in one-fourth of the prostate gland .
- T2b: The cancer is in more than one-fourth of the prostate gland , but has not grown into the other side of the prostate gland.
- T2c: The cancer has grown into both sides of the prostate gland.
Risk Level
| Risk Level* |
|---|
You May Like: Cranberry Juice Good For Prostate
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- Will I need other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- What can I do about side effects that I might have?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- How soon do I need to start treatment?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
J. Stephen Jones, MD
J. Stephen Jones, MD, is chairman of the department of regional urology at the Cleveland Clinic Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute, and is professor of surgery at Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine at Case Western Reserve University. He is author of The Complete Prostate Book and Overcoming Impotence.
Sign up to be a Bottom Line Insider today!
Get The Latest Health, Life & Money Trends
You May Like: Bph Drugs Comparison
What Is Prostate
PSA testing has been around since the 1990s and has decreased cancer metastases and the death rate from prostate cancer. However, this test has significant limitations. PSA testing has a false-positive rate as high as 70%. This means many men with elevated PSA levels will be referred for unnecessary biopsies. Youre probably thinking, there has to be a better way.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can You Take Lupron For Prostate Cancer
What Is A Mi
The MiPS score helps to evaluate your risk of prostate cancer and aggressive prostate cancer. Its usually performed after you have abnormal results from a PSA test and DRE.
This test involves a DRE, after which youll provide a urine sample. The Mi-prostate score combines three markers:
- serum PSA
- PCA3
- TMPRSS2:ERG
PCA3 and T2:ERG are genes found in the urine. Its rare for men without prostate cancer to have high amounts of these markers in their urine. The higher your levels, the more likely it is that you have prostate cancer.
A MiPS provides more information than a PSA test alone. Its a valuable risk assessment tool and may be helpful in deciding whether or not to go ahead with a biopsy. Like other tests, a MiPS test alone cannot confirm prostate cancer.
Screening For Prostate Cancer
There are no tests available with sufficient accuracy to screen populations of men for early signs of prostate cancer. However, early detection and treatment can significantly improve prostate cancer survival.
The test most commonly used to aid early detection of prostate cancer is the prostate specific antigen blood test. This is not a diagnostic test as it can only indicate changes in the prostate. If you are concerned about prostate cancer you should talk to your doctor and make an informed choice about whether to have one of the tests designed to find early signs of prostate cancer, in view of the potential risks and benefits.
There are no proven measures to prevent prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: Prostate Cancer Perineural Invasion
