What Are The Types Of Prostate Surgery For Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Several minimally invasive surgeries may be used for benign prostatic hyperplasia. These include:
GreenLight laser: Photoselective vaporization of the prostate is a treatment that vaporizes prostate tissue to create a channel in the urethra for free urination. This is surgical treatment performed in the operating room under general anesthesia.
Plasma button electrovaporization: Prostate tissue is removed using low temperature plasma energy. Tissue is vaporized. This is an operating room-based therapy and requires an anesthetic.
Water vapor therapy : Water vapor is directly delivered to the prostate tissue. Over a 3-month period the tissue is destroyed and reabsorbed by the body. This is an office-based therapy and is performed under a local nerve block.
UroLift®: A mechanical approach that places implants to pin the lateral prostate lobes out of the way to reduce obstruction. This is an office-based procedure performed under a local nerve block.
Prostatic artery embolization: This approach uses catheters to deliver agents that block blood flow to the prostatic artery to reduce symptoms of BPH by shrinking tissue. This prostate procedure uses local anesthesia and doesnt require a hospital stay.
When To Call Your Doctor Or Nurse
Its important to tell your doctor or nurse if:
- your bladder feels full or your catheter isnt draining urine
- your catheter leaks or falls out
- your urine contains blood clots, turns cloudy, dark or red, or has a strong smell
- your wound area or the tip of your penis becomes red, swollen or painful
- you have a fever
- you feel sick or vomit
- you get cramps in your stomach area that will not go away
- you get pain or swelling in the muscles in your lower legs.
Your doctor or nurse will let you know if you should go to the hospital.
What Are Prostate Stones
The prostate gland might be small in size, but it does play a critical part in reproductive health. Problems with the prostate can affect structures other than the prostate too.
Men with prostate problems often find that their urinary function is adversely affected, for example. Several conditions can affect the prostate gland. Some are more serious than others.
A particularly common issue in men is prostate stones. This is different from bladder stones. While not as serious as prostate cancer, the complications of prostate stones are often overlooked. The condition plays a role in the development of prostatitis too.
We take a closer look at what prostate stones are in this post. We also consider the symptoms and causes of the condition. The post also shares some useful details about the treatment options.
Don’t Miss: Bph Medications With Least Side Effects
Risks Of Prostate Surgery
The risks with any type of radical prostatectomy are much like those of any major surgery. Problems during or shortly after the operation can include:
- Reactions to anesthesia
- Blood clots in the legs or lungs
- Damage to nearby organs
- Infections at the surgery site.
Rarely, part of the intestine might be injured during surgery, which could lead to infections in the abdomen and might require more surgery to fix. Injuries to the intestines are more common with laparoscopic and robotic surgeries than with the open approach.
If lymph nodes are removed, a collection of lymph fluid can form and may need to be drained.
In extremely rare cases, a man can die because of complications of this operation. Your risk depends, in part, on your overall health, your age, and the skill of your surgical team.
Electroporation Of Lymph Nodes In Prostate Cancer
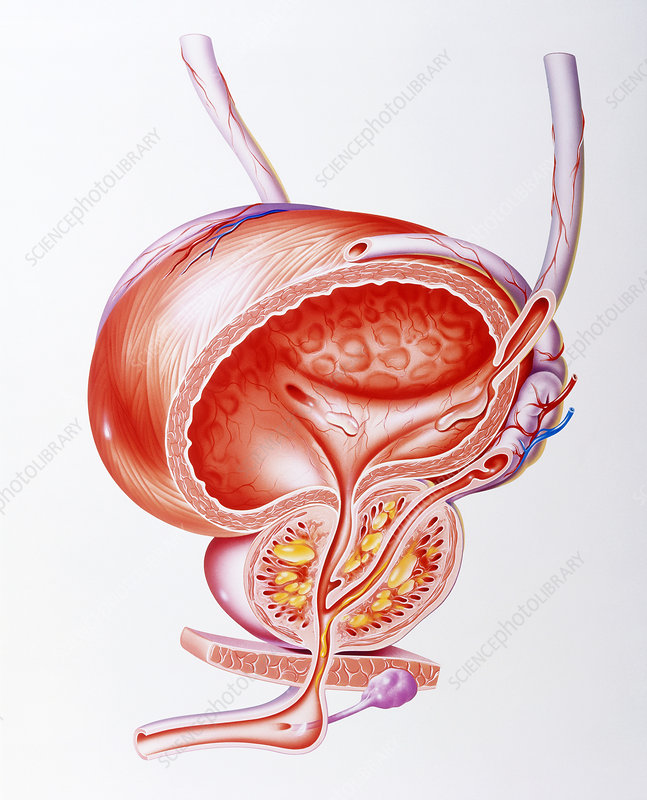
Targeted and gentle removal of affected lymph nodes without irradiation or surgery
Illustration 1: The lymphatic system.1
Prostate cancer often spreads into the surrounding lymph nodes. This is called lymph node metastases. The standard treatment is the surgical removal of all pelvic lymph nodes, which is a substantial intervention. Targeted radiation therapies can be an alternative, but these therapies severely restrict the options of follow-up treatments, which are unfortunately often necessary in case of scattered cancer. With NanoKnife, there now is the possibility for high-precision and minimally invasive treatment of lymph node metastases without radiation or surgery.
What are lymph nodes and lymph node metastases?
Lymph nodes are up to one centimeter large, bean-shaped organs, which are interlinked and connected to the so-called lymphatic system. They are also part of the immune system. In the lymph system, instead of blood, lymph fluid is transported. In this system the lymph nodes are the stations, where the lymph is filtered.
Lymph node metastases are the scattered cancer cells in lymph nodes . They usually cause no symptoms. Usually they are detected either by modern imaging techniques or by the histological analysis of the lymph nodes themselves, when removed prophylactically during a surgery.
Illustration 2: The remodulation of lymphatic vessels, which pre-drives the metastasis in cancer.2
The first important step: the precise diagnosis
Recommended Reading: Recurrent Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Enlarged Prostate Surgery: The Real Risks And Side Effects
Enlarged prostate surgery unfortunately has real risks and side effects that are often downplayed or minimized by urologists making you the guinea pig with very possible impotence and incontinence as a result.
Furthermore, you will often have to repeat the operation later on as your prostate continues to grow because the real causes of this prostate disease have not been addressed by radical surgeries.
Also known as a TURP surgery or BPH surgery, this is the gold standard of prostate surgeries for enlarged prostate symptoms.
TURP stands for Transurethral Resection of the Prostate. The surgery consists of passing a flexible instrument up your penis and into the prostate gland to shave off pieces of the prostate.
The bloody pieces are removed allowing more space for the urethra tube to pass urine from your bladder.
The operation is done under anesthesia… and you will usually spend a couple of days recovering. You will have to wear a catheter for some time while you heal, and then it can be removed.
It would be great if that was all there was to it. Yet, it’s not so simple…
How Is A Prostatectomy Performed
Your prostatectomy will be performed in a hospital, a surgeons private office, or an outpatient surgery clinic. It involves making incisions in the lower abdomen or behind the genitals, or inserting a small tube through the urethra.
The surgeon then cuts away part or all of the prostate from the tissues around it. The surgeon may also remove nearby lymph nodes if the surgery is for prostate cancer. The surgeon will tie off the remaining blood vessels and reattach the urethra to the bladder if the entire prostate is removed.
Surgical approaches to prostatectomy
Your doctor will perform a prostatectomy using one of the following approaches:
Your surgeon may decide after beginning a minimally invasive prostatectomy that you require an open prostatectomy to safely and most effectively complete your surgery. Your surgeon will advise you on which procedure is best for you and how long you need to stay in the hospital based on your diagnosis, age, medical history, general health, and possibly your personal preference. Learn about the different prostatectomy procedures and ask why your surgeon will use a particular type for you.
Types of anesthesia that may be used
Your doctor will perform a prostatectomy using either general anesthesia or regional anesthesia.
What to expect the day of your prostatectomy
The day of your surgery, you can generally expect to:
Also Check: What Is The Definition Of Prostate Gland
Advantages Of Simple Perineal Prostatectomy
Advantages of perineal prostatectomy include the following:
-
Ability to treat clinically significant prostatic abscess and prostatic cysts
-
Less postoperative pain
-
Ability to avoid the retropubic space
With regard to the last point, above, retropubic or suprapubic surgery is more difficult in patients who have had prior retropubic surgery.
What Causes Prostate Stones
Being educated about prostate stones is the first step for men to understand the condition better. At the moment, many theories have been suggested regarding the causes behind prostate stones. It is known that a calcification process is involved in the development of these stones.
Several suggestions have been made regarding the specific factors that may be involved in causing the calcification of these substances. Furthermore, there are also suggestions regarding the specific substances that may be calcified in the process of prostate stone development.
One suggestion link prostate stones to a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia. This is a condition where the prostate gland becomes enlarged. The gland is affected by inflammation. It is also known that the prostate gland causes problems with the urinary tract.
The inflammation that affects the prostate gland is thought to affect the secretion of fluids and substances from the prostate. This can cause the secretions to become thick. As the fluid becomes thick, it starts to bind with proteinaceous substances that are located in the prostate gland.
This can cause fluids to calcify and become hard. In turn, prostatic stones may develop. Prostate enlargement has also been previously linked to a higher risk of developing bladder calculi3.
A bacterial infection in the gland will cause pus to accumulate. The pus and debris that collects in the prostate gland may harden. As they harden, they start to form stones.
Read Also: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Surgery To Remove Your Prostate Gland
You might have surgery to remove your prostate gland if:
- your cancer hasn’t spread outside the prostate gland
- you are younger and have a fast growing tumour
- as part of treatment for locally advanced or high risk localised prostate cancer
The aim of a radical prostatectomy operation is to cure prostate cancer. It is major surgery with some possible side effects. If you’re an older man with a slow growing prostate cancer, this type of surgery may not be necessary for you. This is because your cancer might grow so slowly that you’re more likely to die of old age or other causes than from prostate cancer.
What Is The Prostate Gland
The prostate gland is about the size of a walnut and surrounds the neck ofa man’s bladder and urethrathe tube that carries urine from the bladder.It’s partly muscular and partly glandular, with ducts opening into theprostatic portion of the urethra. It’s made up of three lobes, a centerlobe with one lobe on each side.
As part of the male reproductive system, the prostate gland’s primaryfunction is to secrete a slightly alkaline fluid that forms part of theseminal fluid , a fluid that carries sperm. During male climax, the muscular glands of the prostate help to propel the prostatefluid, in addition to sperm that was produced in the testicles, into theurethra. The semen then travels through the tip of the penis duringejaculation.
Researchers don’t know all the functions of the prostate gland. However,the prostate gland plays an important role in both sexual and urinaryfunction. It’s common for the prostate gland to become enlarged as a manages, and it’s also likely for a man to encounter some type of prostateproblem in his lifetime.
Many common problems that don’t require a radical prostatectomy areassociated with the prostate gland. These problems may occur in men of allages and include:
Cancer of the prostate is a common and serious health concern. According tothe American Cancer Society, prostate cancer is the most common form ofcancer in men older than age 50, and the third leading cause of death fromcancer.
Find a Location
Don’t Miss: Flomax Abnormal Ejaculation
Caring For Your Incision
The incision runs from above the base of the pubic area to below the navel. It is important to keep it clean and dry. Showering once a day should be sufficient. If you notice extreme or increasing tenderness, progressive swelling, more than a small amount of drainage or any pus or redness, notify your doctor right away.
What Happens To A Man When He Has His Prostate Removed
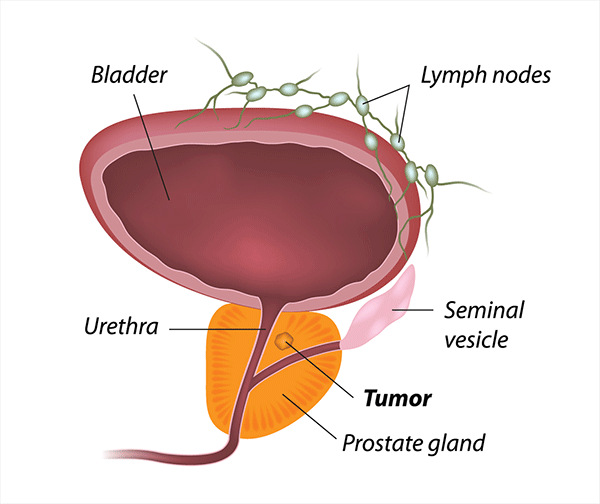
Prostate is a male reproductory gland located anterior to the rectum and inferior to the bladder surrounding the urethra. It is involved in the secretion of prostate fluid that forms an important constituent of semen. It also works in the propulsion of seminal fluid into the urethra and also blocks the connection between the urethra and the bladder by contracting at the time of ejaculation. The prostatic fluid constitutes about one third of the total seminal fluid containing various enzymes of which PSA is of specific importance, not only in thinning of the seminal fluid and helping proper motility of the sperm, but also in the testing procedure for prostate related diseases, such as BPH .
The location of prostate is such that, if the patient experiences BPH then it might lead to urethral compression causing difficulty in urination and leading to LUTS . Unfortunately, BPH is a common problem in adult men and the chances of BPH drastically increases after the age of 60 years. A growth in size of prostate is also a sign of prostatic cancer.
Also Check: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Open Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy
In this surgery, the doctor makes a cut just below your belly button down to your pubic bone. The surgeon moves aside muscles and organs to remove the prostate, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles. Lymph nodes are also removed. This type of surgery can also be done with a nerve-sparing approach. If so, your doctor tries to not cut any of the tiny nerves that are needed to maintain an erection. If the cancer has affected these nerves, this may not be possible.
Prostate Surgery: What To Expect On The Day Of Surgery
There are a few prostate surgery types and techniques, and what you can expect from your procedure depends on which one your surgeon uses. An incision may or may not be required all, some, or none of prostate gland may be removed and some surrounding tissue may or may not be excised as welljust to name a few differences.
The choice in prostate surgery largely comes down to whether you are having it to treat prostate cancer or the urinary symptoms or complications of an enlarged prostate, a.k.a. benign prostatic hyperplasia .
Also Check: Would You Expect A Male With Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia To Have Difficulty With Ejaculation
Risks Of Radical Prostatectomy
Radical prostatectomy has a low risk of serious complications. Death or serious disability caused by radical prostatectomy is extremely rare.
Important nerves travel through the prostate on the way to the penis. Skilled surgeons can usually protect most of these nerves during radical prostatectomy. Still, complications from inadvertent nerve damage do occur after radical prostatectomy. They include:
- Urinary incontinence: More than 95% of men younger than age 50 are continent after radical prostatectomy. Around 85% of men aged 70 or older maintain continence after the operation.
- Erectile dysfunction : Problems with erections are common after prostatectomy. Still, most men are able to have sex after prostatectomy while using medicines for ED , an external pump, or injectable medications. The younger the man, the higher the chance of maintaining potency after prostatectomy. A period of penile rehabilitation is often necessary.
Much of the skill involved in radical prostatectomy centers on sparing these nerves during the operation. A man undergoing radical prostatectomy by a surgeon at an advanced prostate cancer center has a better chance of maintaining sexual and urinary function.
Other complications of radical prostatectomy include:
- Bleeding after the operation
During Surgery For Bph
The vast majority of BPH surgeries are performed using a transurethral technique, of which there are several types. With each, a tube-like instrument called a cystoscope or resectoscope reaches the prostate gland via the urethra.
Some transurethral techniques include:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate : An electrified wire loop is used to remove prostate tissue. This is the most common surgery used to treat BPH.
- Transurethral electrovaporization of the prostate : Electrical energy applied through an electrode is used to heat and vaporize an area of enlarged prostate tissue.
- Transurethral incision of the prostate : No prostate tissue is removed, but two deep cuts are made starting in the bladder neck . The purpose of these cuts is to widen the urethra in order to improve urine flow.
- Laser energy is used to vaporize prostate tissue.
- Laser enucleation of the prostate: A holium or thulium laser is used to remove excess prostate tissue that is blocking urine flow.
- Transurethral microwave therapy : A specialized urinary catheter with a small microwave antenna is used to heat and destroy prostate tissue.
Read Also: How Effective Is Chemotherapy For Prostate Cancer
What Are The Side Effects
The most common side effects of surgery are leaking urine and problems with getting or keeping an erection .
Your risk of getting these side effects depends on your overall health and age, how far the cancer has spread in and around the prostate and how likely it is to grow, and your surgeons skill and experience.
What Is The Most Common Approach
A technique called transurethral resection of the prostate is considered to be the standard surgical approach. This procedure involves inserting a thin tube called a resectoscope into the urethra and guiding it through to the prostate. The resectoscope is equipped with a tiny camera and an electrical loop that is used to mechanically remove prostate tissue. The loop produces heat at the same time, which quickly seals off the blood vessels. The resectoscope also has valves that regulate the release of fluid to flush the removed tissue out. TURP takes about 90 minutes and is done under local or general anesthetic. Men who have had this procedure usually need to have a urinary for a few days after, and generally stay in the hospital for two to seven days. They then have to rest and take it easy for a few weeks.
Some variations of TURP are also considered to be standard treatments and have similar outcomes and consequences to conventional TURP. These include transurethral electrovaporization , transurethral vaporesection and plasmakinetic enucleation of the prostate .
You May Like: Enlarged Prostate Viagra
