When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of prostatitis, such as pelvic pain, difficulty or pain when peeing, or painful ejaculation.
They’ll ask about the problems you’re having and examine your tummy.
You may also have a rectal examination. This is where a doctor inserts a gloved finger into your bottom to feel for anything unusual. You may have some discomfort during this examination if your prostate is swollen or tender.
Your urine will usually be tested for signs of infection, and you may be referred to a specialist for further tests to rule out other conditions.
See a GP straight away if you get sudden and severe symptoms of prostatitis.
You may have acute prostatitis, which needs to be assessed and treated quickly because it can cause serious problems, such as suddenly being unable to pee.
If you have persistent symptoms , you may be referred to a doctor who specialises in urinary problems .
Natural Treatment Options For Prostate Pain
As prostate pain is associated with all three conditions like prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatitis so it is good to find some natural remedies for such prostate troubles. Although, medical science has developed several medications and treatment solutions for this condition but natural therapies are always the most trustworthy options. The major reason behind using home based remedies is that they do not lead to any side effect so person can stay safe.
Testing Options For Prostate Cancer
There is no one age for prostate cancer testing, but the American Cancer Society makes recommendations about prostate cancer screenings. According to the ACS, patients in any of these groups should consider asking their doctor about testing:
- Men age 50 or older who have an average risk of prostate cancer and a life expectancy of at least 10 more years
- Men age 45 or older with a high risk, including African-American men and those with a first-degree relative who had prostate cancer before age 65
- Men age 40 or older who have a higher risk, such as more than one first-degree relative diagnosed with prostate cancer at an early age
Expert
You May Like: Prostatic Neoplasms
Other Locations Of Pain From Prostate Cancer
Pain during urination
Painful ejaculation
Leg and foot pain from swelling/edema
Shooting, burning or stabbing pain can occur in the lower extremities if a metastasis is pressing against a nerve.
Lower abdominal pain or soreness can occur if a tumor is causing pressure on the organs that surround the prostate.
If youve been having any of the following symptoms, many benign conditions can explain them. But so can prostate cancer. Better safe than sorry.
Get yourself checked out if youve been experiencing any of the following:
Urination discomfort of any sort
Any difficulty with urination
Increased urges to urinate overnight
Loss of bladder control
Reduced flow of urine stream
Appearance of blood in the urine
Blood in semen
Numbness in the lower extremities
Unexplained fatigue or weight loss
WARNING: Many of the aforementioned symptoms are signs of advanced disease.
The time to get checked is at the first sign of symptoms, even if they seem trite such as reduced urine stream or having more urges to urinate overnight.
Furthermore, annual PSA tests are highly recommended beginning at age 50 for men at average risk of prostate cancer.
For more information on prostate cancer screening, call Cancer Center Treatments of America at 993-3381.
.
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
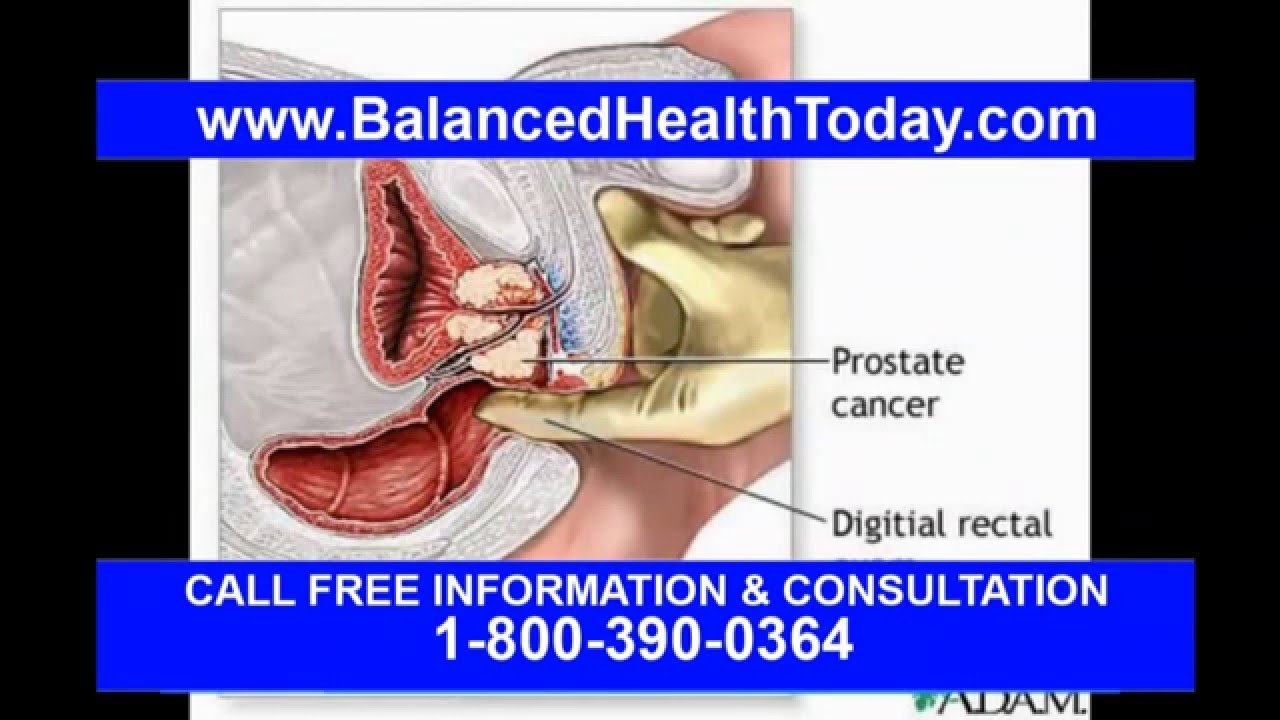
Once a tumor causes your prostate gland to swell, or once cancer spreads beyond your prostate, you may have symptoms including:
- The need to pee often, especially at night
- Trouble starting or stopping a stream of urine
- A weak stream or one that starts and stops
- Leaking pee when you laugh or cough
- Not being able to pee standing up
- Pain or burning when you pee
- Pain or burning when you ejaculate
- Less fluid when you ejaculate
- Blood in your pee or semen
- Pressure or pain in your rectum
- Pain or stiffness in your lower back, hips, pelvis, or thighs
- New trouble getting an erection
These arenât symptoms of the cancer itself. They happen because the cancer growth is blocking your prostate.
Read Also: Does Cialis Shrink An Enlarged Prostate
The Tension Headache Of The Groin
Prostatitis is a benign but painful condition that causes inflammation of the prostate or surrounding area. While half of all men will experience it, many dont know what it is.
When prostatitis happens to younger men, it can be alarming and a little scary.
We asked UNC Medical Center urologist Eric Wallen, MD, to explain prostatitis and what can be done to fix it.
Signs Of Prostate Cancer Your Doctor Can Assess
Your doctor can tell a lot about your prostate by the way that it feels.
The back wall of your prostate is very close to your rectum. If your doctor inserts a finger into your rectum, he can feel the back and sides of your prostate through the thin, soft wall of the rectum. This examination of the prostate is called a digital rectal examination .
The DRE is used to detect possible signs of prostate illness:
- A DRE that finds a smooth, soft prostate but that causes intense pain is commonly a sign of prostate infection, also known as prostatitis.
- A DRE that finds a smooth, rubbery, and enlarged prostate is commonly a sign of prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostate hyperplasia.
- A DRE that finds hard nodules, generalized firmness, or an unusual shape to the prostate is commonly a sign of prostate cancer.
DRE can be used to raise suspicion of prostate cancer. DRE can not be used to rule out prostate cancer.
Many prostate cancers produce no physical signs that can be felt by DRE. In other words, a normal DRE is not a sign that there is no prostate cancer.
It is also well known that if different doctors carry out a DRE on the same patient , they may come to different decisions about what they think they feel.
Figure 1: How the DRE is carried out.
Content on this page last reviewed and updated April 5, 2008.
Don’t Miss: Fiducials Prostate Cancer
Are There Other Non
Yes, aside from BPH, there are a number of prostate problems that also have nothing at all to do with prostate cancer. Among these benign disorders of the prostate are acute prostatitis and chronic prostatitis and, rarely, prostatic infarct .
Acute prostatitis is a bacterial infection of the prostate. It can occur in men at any age. Symptoms include fever, chills, and pain in the lower back and between the legs. This problem also can make it hard or painful to urinate. Doctors prescribe antibiotic medicines for acute prostatitis and recommend that the patient drink more liquids. Treatment is usually successful.
Chronic prostatitis is a prostate inflammation that tends to recur over time. It is usually not associated with true bacterial infection but causes similar symptoms of pain and discomfort, without fevers or chills. Chronic prostatitis is difficult to treat, and the exact cause is not well understood. Antibiotics may be used in some cases as well as anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen. In many cases, symptoms will resolve on their own.
Prostate infarct is a localized area of dead prostate tissue as a result of inadequate blood supply. Prostate infarct is uncommon and may cause sudden increases in the PSA test.
Symptoms For Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
If you have acute bacterial prostatitis the symptoms usually develop very quickly. They include:
- a high temperature , feeling feverish, sweating, chills and shivering
- pain in the area between your testicles and back passage , the skin around your testicles , your penis, lower back, muscles or joints in your pelvic area, inner thighs, and sometimes in your back passage
- needing to urinate more often, especially at night
- a sudden urge to urinate
- pain when urinating
- difficulty urinating.
About 1 in 10 men with this type of prostatitis find they suddenly and painfully cant urinate. This is called acute urine retention. It needs treating straight away, usually at a hospital. The doctor or nurse will pass a thin, flexible tube called a catheter up your penis into your bladder to drain the urine. Or they might pass the catheter through the wall of your stomach area . This will help drain urine from your bladder.
Dont wait
It is very important to seek medical advice immediately if you think you might have acute bacterial prostatitis and have a high temperature. It needs treating straight away.
Don’t Miss: How Are Fiducial Markers Placed In The Prostate
Where Do You Feel Prostate Pain When You Get Prostatitis
Prostatitis causes pain in the groin, pelvic area, or genitals. It also causes pain when you pee. Sometimes it can make you feel like you have a cold.
Prostatitis is when a man has an infection in his prostate. The condition can happen to men of any age, but it is more common in men that are 50 or younger. There are many causes for prostatitis, but sometimes the reason isnt known. For example, if bacteria caused someones prostatitis, antibiotics could usually cure the infection.
There are different types of prostatitis. It can come gradually or suddenly. Some classes last for months or keep coming back .
There are many signs and symptoms of prostatitis. They can include:
- When I go to the bathroom, it feels like pain or burning.
- Urinating can be hard. You can dribble or urinate too slowly.
- You might pee a lot at night if you have this condition.
- You need to go pee now!
- Cloudy urine. When the pee looks like milk.
- You might see blood in your pee.
- Some people have pain in their stomachs. The pain might be in the groin or low back.
- It can hurt when you go poop.
- Pain or discomfort in your penis.
- Pain when you ejaculate.
- People with bacterial prostatitis have signs and symptoms that are like the flu.
Wednesday 4 October 2017
Hey guys, we know that talking about your prostate can be a little uncomfortable. You might not know where or what it is, or you might have only heard about it in stories about older men having difficulty peeing or the doctor sticking their finger up you know where to check on it.
Below, weve got all the details about what your prostate is, where it is and what it does. Well also discuss how it might change as you age, and any changes or symptoms you should keep an eye on and tell your doctor about.
Recommended Reading: How To Shrink Prostate Mayo Clinic
Read Also: How Long Can You Take Lupron For Prostate Cancer
How Are Bacterial Forms Of Prostatitis Managed Or Treated
Antibiotics can kill bacteria that cause bacterial types of prostatitis. Men with acute bacterial prostatitis may need 14 to 30 days of antibiotics, starting with IV antibiotics in the hospital. Rarely, men need surgery to drain an abscess on the prostate.
Treating chronic bacterial prostatitis is challenging. You may need up to three months of antibiotics to sterilize the prostate. If the prostate cant be sterilized, low-dose antibiotics can be used long term to prevent recurrences. Some men need surgery to remove prostate stones or scar tissue in the urethra. Rarely, surgeons remove part or all of the prostate gland .
Prostatitis Vs Prostate Cancer Symptoms And Signs
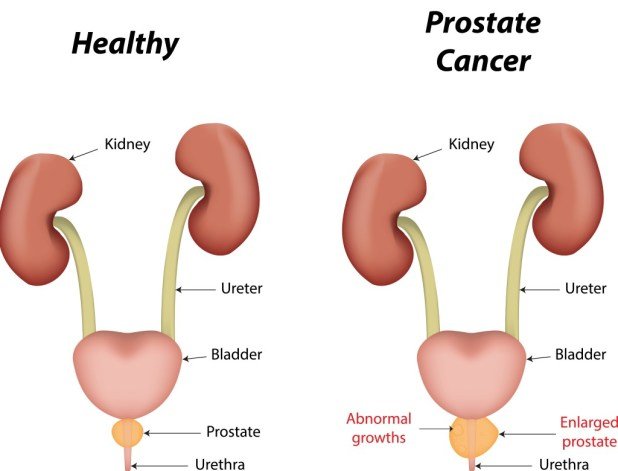
- Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland the four types are acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome, and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis.
- Prostate cancer develops when abnormal prostate gland cells multiply without control and may metastasize to other organs.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a noncancerous condition where normal prostate gland cells keep multiplying, thereby increasing the size of the prostate.
- Prostatitis usually does not lead to death, but prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in men, even though it is a slow-moving disease.
- Most men with early prostate cancer have no symptoms or signs symptoms and signs appear when the cancer becomes large enough to cause urinary blockage. Prostatitis, in contrast, usually appears with symptoms such as urinary frequency, urgency and/or pain with urination and possibly, some type of sexual dysfunction.
- Prostate cancer, when it produces signs and symptoms, may produce one or more of the following symptoms or signs that may also be seen in patients with prostatitis or BPH:
- Painful ejaculation
You May Like: Prostate Medical Definition
How We Diagnose Prostatitis:
Prostatitis may be a clinical diagnosis, meaning it is presumed to be the causative issue even when no definitive findings are found. Our urologists may order/perform the following to diagnose prostatitis:
- History & Physical Exam
- Digital Rectal Exam: Inserting a gloved, lubricated, finger into the rectum to feel the prostate. The prostate may feel boggy and is usually more tender than normal in men with prostatitis.
- Urinalysis & Culture: Urine will almost always be positive for infection in men with bacterial prostatitis. However, because not all prostatitis is caused by bacteria, the urine may be negative for infection.
- Blood cultures/labs
- Transrectal ultrasound: An ultrasound probe is inserted into the rectum to visualize the prostate.
- Cystoscopy: A look at the prostate and bladder with a small camera inserted through the urethra.
- Urodynamics: A study used to exam the function of the bladder and help determine if there is an outflow obstruction.
Eating Diet And Nutrition
Researchers have not found that eating, diet, and nutrition play a role in causing or preventing prostatitis. During treatment of bacterial prostatitis, urologists may recommend increasing intake of liquids and avoiding or reducing intake of substances that irritate the bladder. Men should talk with a health care provider or dietitian about what diet is right for them.
Read Also: What Is The Definition Of Prostate
Question 7question 7 Of : How Long Does Prostate Pain Last
Read Also: Household Items For Prostate Massage
Question 3 Of : What Medications Help With Prostate Pain
Dont Miss: Is Cialis Good For Bph
Also Check: Seminal Vesicle Massage
Soreness In The Groin
When prostate cancer spreads, its common for cancer cells to go to your lymph nodes and then move to more areas of your body. The lymph nodes are a network of glands that help your body filter fluids and fight infections.
There are several lymph nodes in your groin. These are the ones closest to your prostate, so its common for the cancer to spread to them first. Cancer cells prevent your lymph nodes from draining fluid and working properly. When this happens, your lymph nodes swell. As a result, you might experience pain or soreness in the area.
Symptoms Associated With Prostate Pain
Studies reveal that in many cases, prostate problem may be silent and that is why pain is not reported always by the patients.
Enlarged prostate and male sexual organs: prostatitis
Some of the most common issues that are reported usually with prostate pain include several urinary problems. Below are few details most common signs associated with indication of the prostate pathology:
- It may include blood in semen.
- One may also notice blood in urine.
- Some conditions report post micturition dribble.
- It can also cause painful ejaculation.
- Sometime patient may face urgency to urinate.
- Few cases report sensations leading to feeling of fullness in bladder or person may feel incomplete urination at times.
- It may also cause straining for urination.
- There are few conditions where people may face frequent urination they may even wake up several times at night.
- Sufferers may find difficulties in urination.
- It leads to pain during urination.
- Burning sensation at the time of urination.
In few severe prostate conditions, person may face troubles like huge weight loss, fever, erectile dysfunction, and swelling in legs or decay in urine. In these typical conditions, one must consult doctors as soon as possible.
You May Like: Fiducial Marker Placement Prostate
Latest Men’s Health News
At the start, prostate cancer does not cause symptoms. As the cancer grows, you may have trouble urinating. Some men need to urinate often, especially at night. Others have pain or burning during urination, blood in the urine or semen, pain in the back, hips, or pelvis, and painful ejaculation.
To find out if these symptoms are caused by prostate cancer, your doctor will ask about your past medical problems and your family’s medical history. He or she will perform a physical exam. During the exam, your doctor will put a gloved finger into your rectum to feel your prostate for hard or lumpy areas.
Your doctor may also do a blood test to check the prostate-specific antigen level. PSA levels can be high in men with an enlarged prostate gland or with prostate cancer. You may also need an ultrasound exam that takes computer pictures of the prostate.
If tests show that you might have cancer, your doctor will want to confirm this with a biopsy. He or she will take out tiny pieces of the prostate to look for cancer cells. Your doctor may want to do a biopsy again to re-check the results.
Treatment for prostate cancer depends on whether cancer is in part or all of the prostate or if it has spread to other parts of the body. It also depends on your age and overall health. Talk with your doctor about the best treatment choice for you. You may want to ask another doctor for a second opinion.
