How Does The Doctor Know I Have Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer tends to grow slowly over many years. Most men with early prostate cancer dont have changes that they notice. Signs of prostate cancer most often show up later, as the cancer grows.
Some signs of prostate cancer are trouble peeing, blood in the pee , trouble getting an erection, and pain in the back, hips, ribs, or other bones.
If signs are pointing to prostate cancer, tests will be done. Most men will not need all of them, but here are some of the tests you may need:
PSA blood test: PSA is a protein thats made by the prostate gland and can be found in the blood. Prostate cancer can make PSA levels go up. Blood tests will be done to see what your PSA level is and how it changes over time.
Transrectal ultrasound : For this test, a small wand is put into your rectum. It gives off sound waves and picks up the echoes as they bounce off the prostate gland. The echoes are made into a picture on a computer screen.
MRI: This test uses radio waves and strong magnets to make detailed pictures of the body. MRI scans can be used to look at the prostate and can show if the cancer has spread outside the prostate to nearby organs.
Prostate biopsy: For a prostate biopsy, the doctor uses a long, hollow needle to take out small pieces of the prostate where the cancer might be. This is often done while using TRUS or MRI to look at the prostate. The prostate pieces are then checked for cancer cells. Ask the doctor what kind of biopsy you need and how its done.
Gleason Score For Grading Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is also given a grade called a Gleason score. This score is based on how much the cancer looks like healthy tissue when viewed under a microscope. Less aggressive tumors generally look more like healthy tissue. Tumors that are more aggressive are likely to grow and spread to other parts of the body. They look less like healthy tissue.
The Gleason scoring system is the most common prostate cancer grading system used. The pathologist looks at how the cancer cells are arranged in the prostate and assigns a score on a scale of 3 to 5 from 2 different locations. Cancer cells that look similar to healthy cells receive a low score. Cancer cells that look less like healthy cells or look more aggressive receive a higher score. To assign the numbers, the pathologist determines the main pattern of cell growth, which is the area where the cancer is most obvious, and then looks for another area of growth. The doctor then gives each area a score from 3 to 5. The scores are added together to come up with an overall score between 6 and 10.
Gleason scores of 5 or lower are not used. The lowest Gleason score is 6, which is a low-grade cancer. A Gleason score of 7 is a medium-grade cancer, and a score of 8, 9, or 10 is a high-grade cancer. A lower-grade cancer grows more slowly and is less likely to spread than a high-grade cancer.
Slowest And Fastest Growing Cancer Cells
The cancer cells that comprise more genetic damage tend to grow faster. Whereas, the cancer cells that contain less genetic damage grows slowly. However, you can grade tumors in the following:
- G4: high-grade or undifferentiated
Don’t Miss: What Does It Mean To Remove Your Prostate
Events In Prostate Cancer Metastatic Process
The classic model of metastasis of solid tumors, including prostate cancer, is guided by the âseed and soilâ hypothesis first proposed by Stephen Paget in 1889.24 In Pagetâs model, the âseedsâ metastasize only to âsoilâ well suited for the tumorâs growth. Although this concept remains an excellent guiding principle, it does not entirely explain the molecular bases for organ-specific metastases. Metastasis of prostate cancer, like that of other solid tumors, involves multiple steps, including angiogenesis, local migration, invasion, intravasation, circulation, and extravasation of tumor cells and then angiogenesis and colonization in the new site. We will describe only the hallmarks of these events, which have been reviewed in extensive detail elsewhere.25–28 We will then discuss our emerging understanding of properties of metastatic prostate tumor cells that facilitate their growth in the bone.
Can Prostate Cancer Spread
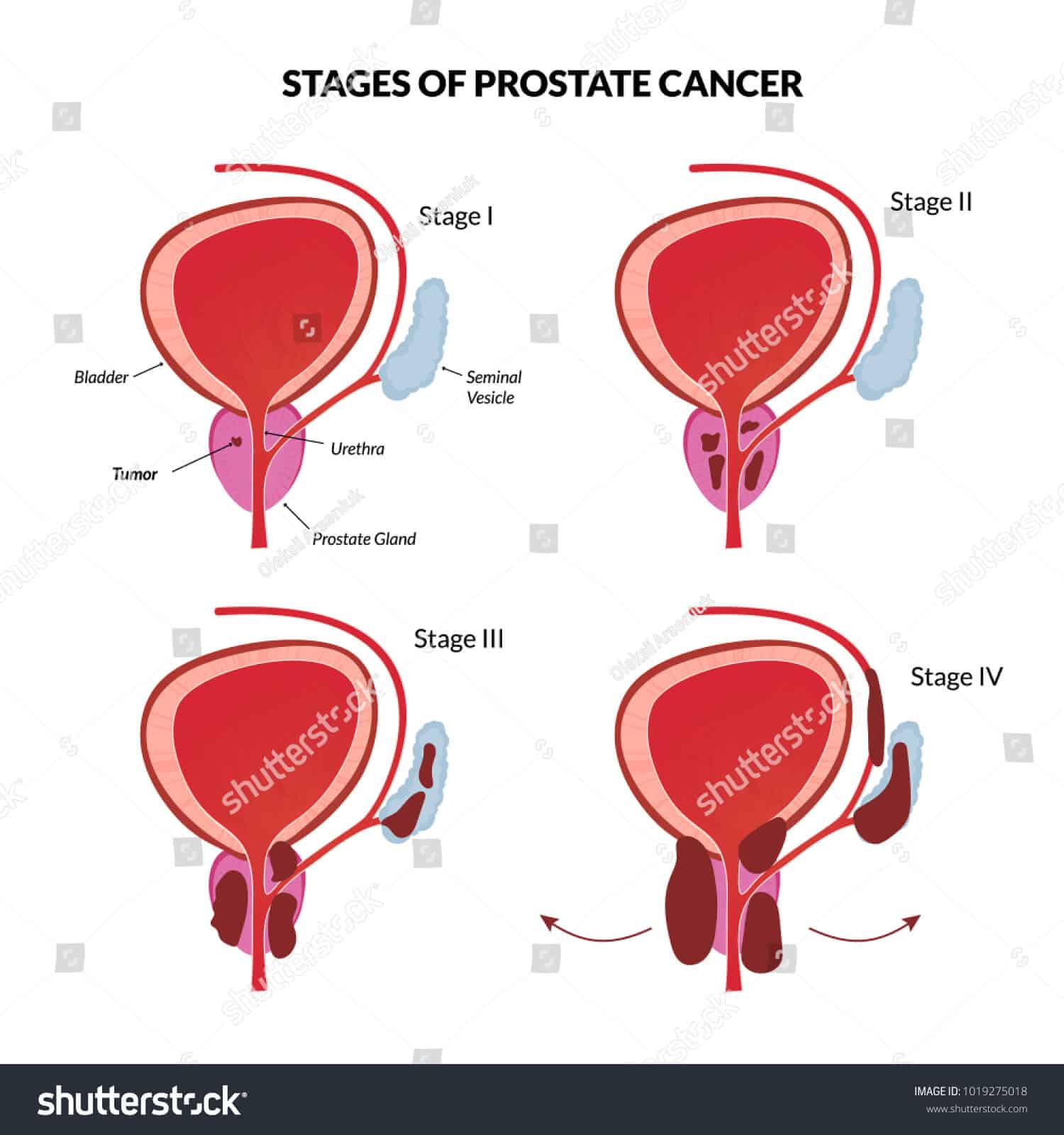
Simple cases of prostate cancer can develop into metastatic ones. This type of cancer appears when cancer cells are starting to spread outside their ground zero areas, the prostate gland.
Once they reach other parts of the body, cancer cells are beginning to grow there. Even though the new development reacts as bone cancer or lung cancer, doctors are always naming the type of cancer according to the organ from which it first originated.
Hypothetically, prostate cancer can spread anywhere in the body. However, prostate cancer metastasis is usually attacking lymph nodes first. Once they are connected to the lymphatic system, they can easily travel to other parts of the body:
Also Check: Does Prostate Swelling Go Down
How Quickly Does Prostate Cancer Spread
Prostate cancer is a cancer that develops in the prostate gland in men and it is one of the most common types of cancer. It is usually seen in men over the age of 50. The prostate is a small walnut-shaped gland in men, which produces seminal fluid required to nourish and transport the sperm. Prostate cancer is a slow-growing cancer and, more often, it is confined to the prostate gland, requiring minimal or no treatment.
In some cases, it can take up to eight years to spread from the prostate to other parts of the body , typically the bones. In many cases, prostate cancer does not affect the mans natural life span.
However, certain types of prostate cancer can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. If prostate cancer is detected early and is confined to the prostate gland, the prognosis is excellent.
What Are The Treatment Options For Aggressive Prostate Cancer
The majority of people with prostate cancer nearly 80% are diagnosed early and cured by their treatment, most often radiation or surgery.
But one in five of those diagnosed with prostate cancer has a more aggressive form of the disease. Even before the individual has received any treatment or experienced a recurrence, doctors can identify whether the cancer is likely to be more dangerous and aggressive.
Prostate cancer is determined to be high risk if it is distinguished by any of the following characteristics:
Physicians perform biopsies or take X-rays to determine a cancers grade and stage. The stage is based on the size of the primary tumor or the extent it has spread in the body. The grade describes the appearance of the cancer cells and tissue under a microscope: the more abnormal they are, the higher the grade.
What are the main treatment options for people with aggressive or high-risk prostate cancer and can the sequencing, or order in which different treatments are given, make a difference in overall effectiveness of these therapies?
Why Roswell Park for Prostate Cancer?
Find out what makes Roswell Park unique in treating prostate cancer.
Read Also: How To Stimulate Male Prostate
How Prostate Cancer Staging Is Done
Initial staging is based on the results of PSA blood tests, biopsies, and imaging tests. This is also called clinical staging.
PSA refers to a protein made by the prostate measured by a lab test.
- A higher level of PSA can indicate a more advanced cancer.
- The doctors will also look at how fast the PSA levels have been increasing from test to test. A faster increase could show a more aggressive tumor.
A prostate biopsy is done in your doctor’s office. The results can indicate:
- How much of the prostate is involved.
- The Gleason score. A number from 2 to 10 that shows how closely the cancer cells look like normal cells when viewed under a microscope. Scores 6 or less suggest the cancer is slow growing and not aggressive. Higher numbers indicate a faster growing cancer that is more likely to spread.
Receiving Treatment For Prostate Cancer That Has Spread
At Moffitt Cancer Center, the experts within our Urologic Oncology Program treat patients with all stages of prostate cancer, including advanced-stage cancers that have metastasized to other areas of the body. Our multispecialty team collaborates as a tumor board, ensuring each patient receives a treatment plan tailored to his unique needs. For individuals with metastatic prostate cancer, treatment plans aim to alleviate symptoms, slow the rate of cancer growth and shrink tumors to help improve quality of life.
Recommended Reading: How To Hit The Prostate Just Right
Transitional Cell Prostate Cancer
This is also known as urothelial carcinoma. This cancer starts in the cells that line the urethra .
Studies of men with transitional cell prostate cancer show that PSA levels can be low or high. More research is needed before we can know whether PSA tests can help to diagnose transitional cell prostate cancer.
Men with this cancer often have difficulty urinating and find blood in their urine. This is because the cancer grows around the urethra , causing it to narrow. So transitional cell carcinoma is often diagnosed when men have surgery called transurethral resection of the prostate to treat their urinary problems. Tissue removed during surgery is looked at under the microscope to confirm you have transitional cell prostate cancer. Youll also need scans to see if your cancer has spread.
If the cancer has not spread outside the prostate , then you may be offered surgery and radiotherapy.
If the cancer has spread to areas just outside the prostate or to more distant areas of the body such as the bones then chemotherapy and radiotherapy may be an option.
In the UK, docetaxel is the standard chemotherapy drug for men with advanced prostate cancer that is no longer responding to hormone therapy. But if you have transitional cell prostate cancer you may have other types of chemotherapy, called carboplatin or cisplatin chemotherapy. If you have cisplatin chemotherapy, you will probably have it alongside another chemotherapy drug called gemcitabine.
Diagnosing Rare Prostate Cancers
Rarer prostate cancers can be harder to diagnose. For example, some dont cause your prostate specific antigen level to rise. This means theyre not always picked up by a PSA test. Because of this, some rare cancers may not be diagnosed until they have already spread outside the prostate. Read more about the PSA test and other tests used to diagnose prostate cancer.
Some rare prostate cancers may only be picked up after having a biopsy to check for prostate cancer, or surgery called transurethral resection of the prostate to treat an enlarged prostate. The tissue removed during the biopsy or TURP is looked under a microscope to see if you have common prostate cancer or a rare type of prostate cancer. Rare cancers arent always given a Gleason score after a biopsy. This is because they can behave differently to common prostate cancer and cant be measured in the same way.
Because rare cancer can be aggressive and spread outside the prostate, you will probably have more tests to see if they have spread. These include:
You May Like: Types Of Surgery For Enlarged Prostate
Prognostic Groups For Localised Prostate Cancer
Doctors may divide localised prostate cancer into groups depending on how likely it is that the cancer will grow quickly or spread. In the UK, doctors now divide prostate cancer into 5 risk groups. This is the Cambridge Prognostic Group . The 5 risk groups are from CPG 1 to CPG 5.
Your group depends on:
- your Grade Group or Gleason score
- the prostate specific antigen level
- the size of your cancer. This is the T stage
Ask your doctor or specialist nurse if you have any questions about this.
Some doctors may use an older system that divides prostate cancer into 3 risk groups. These are:
- low risk prostate cancer. This is the same similar to CPG 1
- medium or intermediate risk prostate cancer. This is the similar to CPG 2 and CPG 3
- high risk prostate cancer. This is the same as CPG 4 and CPG 5
Treatment for localised prostate cancer depends on your risk group. It also depends on:
- your age and general health
- how you feel about the treatments and side effects
You might not have treatment straight away if its unlikely that your cancer will grow or develop for many years. Your doctor monitors your cancer closely and you have treatment if it starts to grow. This is active surveillance. Your doctor may recommend you have active surveillance if your cancer is in the CPG 1, 2 or 3.
If you decide to have treatment, it might include:
- surgery to remove your prostate or
- external radiotherapy
Tools To Help You Decide
The Predict Prostate tool can help you decide between monitoring and more radical treatment. It is for men whose prostate cancer hasn’t spread.
It can’t tell you exactly what is going to happen in the future, but it gives you an idea about the differences in survival between the different treatment options. The tool works less well for men with a very high PSA or those with a fast growing or large tumour.
To be able to use the tool you need to know the following about your cancer:
Also Check: Does Prostate Cancer Affect Sperm Production
> > > This Simple Morning Test Will Fix Your Prostate
Another type of prostate issue is chronic prostatitis, or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. This condition causes pain in the lower back and groin area, and may cause urinary retention. Symptoms include leaking and discomfort. In severe cases, a catheter may be required to relieve the symptoms. If the problem is unresponsive to other treatments, your doctor may suggest a surgical procedure. If these do not work, your symptoms could progress and become chronic.
An acute bacterial infection can cause a burning sensation. Inflammation of the prostate can affect the bladder and result in discomfort and other symptoms. This is the most common urinary tract problem in men under 50, and the third most common in men over 65. The symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are similar to those of CPPS. Patients may experience a fever or chills as a result of the infection.
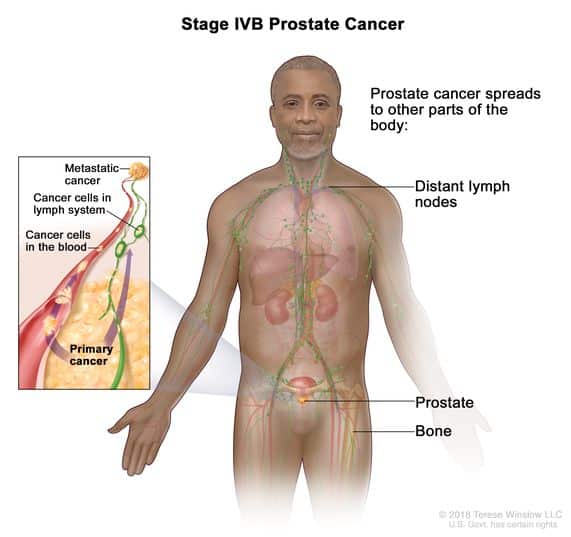
What Happens When Prostate Cancer Spreads To The Lymph Nodes
Prostate cancer cells can break away from their place of origin and spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body. This is called Stage 4 prostate cancer.
The lymphatic system plays an instrumental role in immunity maintenance. This organ system looks and behaves like a network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissue. Its main function is to gather the surplus liquid that cells and tissue are producing. This fluid is then reentering the bloodstream and starts recirculating throughout the body.
There is another component that filters this liquid, namely lymph nodes. They also hold white blood cells that attack any foreign organisms that travel via the lymph fluid. While this white army combats as many cancer cells as possible, some of them manage to survive. Then, they exploit the lymphatic system to reach far-away organs and grow there as well.
Don’t Miss: How Effective Is Chemotherapy For Prostate Cancer
What Treatments Are Available
If you have advanced prostate cancer, treatment wont cure your cancer. But it can help keep it under control and manage any symptoms.
If youve just been diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer, you may be offered the following treatments:
- chemotherapy with hormone therapy
- clinical trials.
Research has found that having radiotherapy together with one of the main treatments listed above can help some men with advanced prostate cancer to live longer. But radiotherapy isnt suitable for all men with advanced prostate cancer.
If you live in Scotland, you may also be offered a type of hormone therapy called abiraterone acetate together with standard hormone therapy. In the rest of the UK, abiraterone is currently only given to men with advanced prostate cancer that has stopped responding to other types of hormone therapy. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence is currently deciding whether to make it available for men who have just been diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer.
Before you start treatment
Before you start any treatment, make sure you have all the information you need. Its important to think about how you would cope with the possible side effects. Speak to your doctor or nurse about this.
It can help to write down any questions you want to ask at your next appointment. It may also help to take someone with you, such as your partner, a family member or friend.
If you have any questions, speak to our Specialist Nurses.
How To Spot Prostate Cancer Early
There are two types of screening that your doctor may recommend: the first requires blood collection to measure the level of the prostate-specific antigen PSA. Higher levels often indicate the presence of prostate cancer.
The second test is a physical examination in which a doctor puts on gloves, lubricates the finger and inserts it into the rectum to see if the prostate is enlarged. If any of the results indicate the possibility of prostate cancer, your doctor will recommend further tests.
“Early-stage prostate cancer typically does not have any physical signs or symptoms,” said Dr. Salim Cheriyan, a urologist with Baylor St. Luke’s Medical Group. “This is why discussing the risks and benefits of screening with your physician is an important part of detecting prostate cancer.”
Also Check: How Does Cialis Treat Enlarged Prostate
