What Is The Prostate Gland Definition
The prostate is a gland, like the thyroid gland or the adrenal gland. It is not an organ like the heart or the liver or the kidneys. It belongs to the male reproductive system and is present exclusively, therefore, in the male population.
The prostate lies located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum and surrounds the upper part of the urethra. The urethra is a tube that empties urine from the urinary bladder. The urethra runs through the center of the prostate, from the bladder to the penis.
Blood And Lymphatic Vessels
The prostate receives blood through the inferior vesical artery, internal pudendal artery, and middle rectal arteries. These vessels enter the prostate on its outer posterior surface where it meets the bladder, and travel forward to the apex of the prostate. Both the inferior vesical and the middle rectal arteries often arise together directly from the internal iliac arteries. On entering the bladder, the inferior vesical artery splits into a urethral branch, supplying the urethral prostate; and a capsular branch, which travels around the capsule and has smaller branches which perforate into the prostate.
The veins of the prostate form a network the prostatic venous plexus, primarily around its front and outer surface. This network also receives blood from the deep dorsal vein of the penis, and is connected via branches to the vesical plexus and internal pudendal veins. Veins drain into the vesical and then internal iliac veins.
The lymphatic drainage of the prostate depends on the positioning of the area. Vessels surrounding the vas deferens, some of the vessels in the seminal vesicle, and a vessel from the posterior surface of the prostate drain into the external iliac lymph nodes. Some of the seminal vesicle vessels, prostatic vessels, and vessels from the anterior prostate drain into internal iliac lymph nodes. Vessels of the prostate itself also drain into the obturator and sacral lymph nodes.
-
Microscopic glands of the prostate
What Is The Prostate
The prostate is a part of the male reproductive system, which includes the penis, prostate, seminal vesicles, and testicles. The prostate is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It is about the size of a walnut and surrounds the urethra . It produces fluid that makes up a part of semen.
As a man ages, the prostate tends to increase in size. This can cause the urethra to narrow and decrease urine flow. This is called benign prostatic hyperplasia, and it is not the same as prostate cancer. Men may also have other prostate changes that are not cancer.external icon
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Also Check: What Happens If Prostate Cancer Goes Untreated
Treatment For Prostate Disease
Treatment for prostatitis may include antibacterial drugs and supportive treatments, depending on the type of prostatitis.Treatment for BPH may include medications to relax the smooth muscle of the gland or to shrink the size of the prostate, and surgery to produce a permanently widened channel in the part of the urethra that passes through the prostate.Treatment for prostate cancer is tailored to suit individual circumstances. The nature of the cancer, other health problems the person may have, and their wishes will all be taken into account.Management approaches for prostate cancer include:
- active surveillance
- ablative treatments such as high-intensity focused ultrasound and NanoKnife®
- hormone treatment
- chemotherapy
Inflammation Of The Prostate
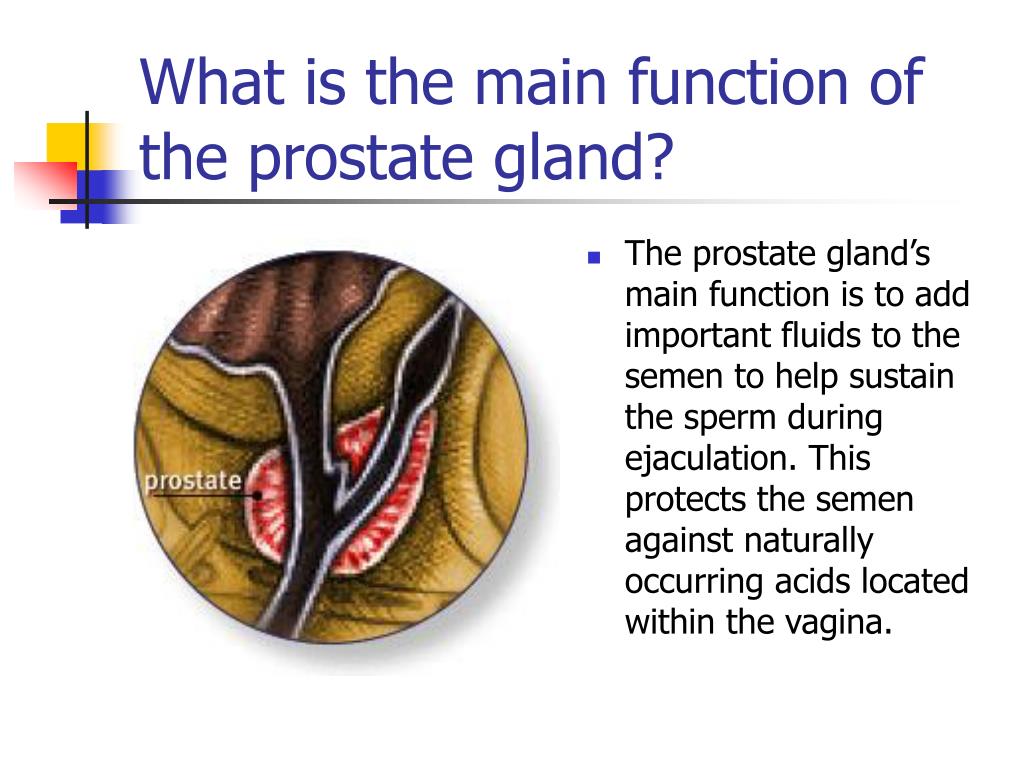
While prostatitis can affect men of any age, it is more common in younger men, aged between 30 and 50 years. The main types of prostatitis are:
- bacterial prostatitis acute or chronic bacterial infection
- non-bacterial prostatitis inflamed prostate, also known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome .
In most cases, the cause of prostatitis is unknown. Bacterial prostatitis responds well to antibiotic drugs that can get into the prostate.;
Non-bacterial prostatitis, or CPPS, is the most common form of prostatitis and is more difficult to manage. Symptoms vary from one man to another. There is no single test to diagnose CPPS, so your doctor will need to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms before making a diagnosis.Possible causes of CPPS include:
- a past bacterial prostatitis infection
- irritation from some chemicals
- chronic anxiety problems.
Read Also: Prostate Cancer Shortness Of Breath
What Is The Function Of The Prostate
The main function of the prostate gland is to secrete an alkaline fluid that forms around 70% of the semen. Apart from lubrication, these secretions act as a source of nutrients for the sperm. The alkaline fluid in the ejaculated semen also helps to neutralize the acidic vaginal environment during sexual intercourse.
Can Prostate Cancer Be Prevented
There are no clear prevention strategies for prostate cancer. There is some conflicting evidence that a healthy diet composed of low fat, high vegetables and fruits may help reduce your risk of prostate cancer. Routine screening, with PSA blood test and physical exam, is important to detect prostate cancer at an early stage. A healthy diet and regular exercise are also critical in maintaining good health and preventing disease in general.;
You May Like: How To Pleasure A Woman After Prostate Surgery
Recommended Reading: Prostate Cancer Ruined My Marriage
Can A Man Go Through Menopause
Menopause is a term used to describe the end of a woman’s normal menstrual function. In women, this is marked by changes in hormone production. One of the biggest changes for a woman after menopause is that she can no longer have children. The testes, unlike the ovaries, don’t lose the ability to make hormones. If a man is healthy, he may be able to make sperm well into his 80s or longer.
On the other hand, subtle changes in the function of the testes can happen as early as 45 to 50 years of age, and more dramatically after the age of 70. For many men, hormone production may remain normal into old age, while others may have declining hormone production earlier on. This can sometimes be a result of an illness, such as diabetes.
Its unclear whether decreasing testicular function contributes to symptoms like fatigue, weakness, depression or impotence.
If You Are A Trans Woman
If you are a trans woman and have had genital-gender affirming surgery as part of your transition, you still have a prostate. It is important to talk to your GP or nurse if you are worried about prostate cancer;or have symptoms.
Prostate cancer UK have detailed information about trans women and prostate cancer.
The LGBT Foundation can also give you confidential advice and support. You can also talk to one of our cancer support specialists.
Don’t Miss: Can Prostatitis Go Away On Its Own
Closing The Urethra During Ejaculation
During ejaculation, the prostate contracts and squirts prostatic fluid into the urethra. Here, it mixes with sperm cells and fluid from the seminal vesicles to create semen, which the body then expels.
When the prostate contracts during ejaculation, it closes off the opening between the bladder and urethra, pushing semen through at speed. This is why, in normal anatomic situations, it is impossible to urinate and ejaculate simultaneously.
What Is The Actual Purpose Of Prostate In Female Body
Many experts believe that prostate in female body use to release some kind of fluid. This fluid appears thick, scanty and has whitish color while containing PSA. Note that, female ejaculation is actually not a part of orgasm and frequency of this has be estimated somewhere around 10 to 54 percent.
During few recent years, medical professionals have taken help from MRIs to detect the presence as well as functionality of female prostate. However, the research should be continued ahead to make ideas more clear but the basic understanding have obtained a boost with this initiative. You might be aware of the fact that prostate gland in males use to store infections inside body. Several studies around the world reveal that Skenes glands also serve the similar kind of function.
Now, it is already clear that skenes glands use to release some fluid during sexual activity and it use to be of watery in appearance. As per one detailed study published in 2007, this fluid that is excreted into the tract from Skene;s Duct use to be consistent with the prostate fluid but it is not observed to have consistency with urine.
Read Also: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
Read Also: Prostatitis Symptoms Mayo
What Causes Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The cause of benign prostatic hyperplasia is not well understood; however, it occurs mainly in older men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia does not develop in men whose testicles were removed before puberty. For this reason, some researchers believe factors related to aging and the testicles may cause benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Throughout their lives, men produce testosterone, a male hormone, and small amounts of estrogen, a female hormone. As men age, the amount of active testosterone in their blood decreases, which leaves a higher proportion of estrogen. Scientific studies have suggested that benign prostatic hyperplasia may occur because the higher proportion of estrogen within the prostate increases the activity of substances that promote prostate cell growth.
Another theory focuses on dihydrotestosterone , a male hormone that plays a role in prostate development and growth. Some research has indicated that even with a drop in blood testosterone levels, older men continue to produce and accumulate high levels of DHT in the prostate. This accumulation of DHT may encourage prostate cells to continue to grow. Scientists have noted that men who do not produce DHT do not develop benign prostatic hyperplasia.
You May Like: What Are The Manifestations Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Problems With Enlarged Prostate Gland
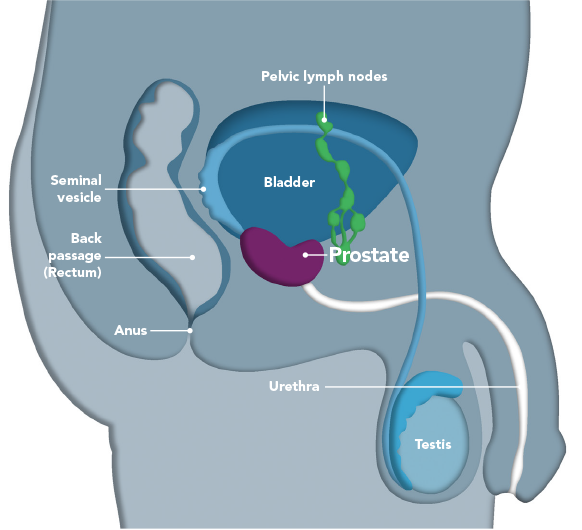
Benign enlargement of the prostate gland is more common as men get older. It can cause troublesome symptoms, although it doesnt always.
The urethra passes through the prostate gland, so men may have problems urinating if the enlarged gland restricts the flow of urine. If the flow stops completely, a catheter is required to empty the bladder. It is rare for this form of acute urinary retention to cause kidney damage.
An enlarged prostate doesnt always cause urinary problems. Studies indicate that the size of a mans prostate gland has little influence on the type or severity of his urination problems. BPH is just one possible cause of urinary symptoms.;
Another cause of urinary symptoms can be changes to the muscular wall of the bladder, which may cause spasms of the bladder or weaken the bladder, causing problems passing urine.
You May Like: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
Tests For Prostate Conditions
Digital rectal examination . The doctor inserts a lubricated gloved finger inside the rectum by which he can detect an enlarged prostate, lumps, or nodules caused by cancer, or tenderness caused by prostatitis.
Prostatespecific antigen . HIGH levels of the protein PSA mostly indicate prostate cancer. However, they may sometimes also increase in BHP
Transrectal ultrasound. ;An ultrasound probe is inserted into the rectum close to the prostate. It provides images at different angles to help gauge the size of the prostate and see any abnormal growths.
Prostate biopsy. ;A prostate biopsy is done if results from the initial tests mentioned above suggest that you may have cancer. ;The urologist inserts a needle into the prostate through the rectum to remove samples of suspicious tissue under ultrasound guidance. These samples are then examined under the microscope for cell abnormalities that indicate may prostate cancer.
What Is The Function Of The Prostate Gland
The prostate gland is a part of the male reproductive system whose main job it is to secrete the prostate fluid, which is one of the components of semen. The muscles of that gland also help this seminal fluid reach the urethra during ejaculation.
This organ is a muscular gland that weighs around ¾ of an ounce and is approximately the size of a small apricot. Its located just beneath the bladder and it surrounds the urethra as well.
When a man ejaculates, millions of sperm travel from the testes to the prostate, through some tubes known as the vas deferens. Here the prostate closes off the path between the urethra and the bladder by contracting and thus releasing fluid into the urethra and pushing the semen through.
The seminal fluid that is excreted by the prostate, composes about two-thirds of the total volume of semen, and it contains citric acid, zinc, and several enzymes. The prostate fluid has a lower pH level than other body fluids, making it acidic, but theres another fluid component that is produced in the seminal vesicles that raise that pH level, resulting in a slightly alkaline environment. This alkalinity protects the sperm and also gives it a longer lifespan after they reach the vagina that has an acidic environment.
The prostate fluid has an enzyme that is called Prostate Specific Antigen and its job is to help sperm by making semen that has thickened after ejaculation more fluid, therefore, the sperm will be able to swim with more ease.
Don’t Miss: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
How Does The Prostate Work
The prostate is a gland about the size of a chestnut and weighs about 30 grams . It is part of the male reproductive system and is located inside the body. The prostates most important function is the production of a fluid that, together with sperm cells from the testicles and fluids from other glands, makes up semen. The muscles of the prostate also ensure that the semen is forcefully pressed into the urethra and then expelled outwards during ejaculation.
The prostate is located directly below the bladder and above the muscles of the pelvic floor. The rectum is behind the prostate, making it possible to feel the gland from the rectum using the finger. The ducts in the prostate gland flow into the urethra, which passes through the prostate. The word prostate is taken from the Greek expression meaning one who stands before, which describes the position of the prostate gland. Viewed from below, where the urethra leaves the gland, the prostate stands before the bladder.
The tissue of the prostate gland can be divided into three different zones, listed here from innermost to outermost, which encircle the urethra like layers of an onion:
The prostate has various functions:
Production of fluid for semen:
Hormone metabolism: In the prostate the male sex hormone testosterone is transformed to a biologically active form, DHT .
Clinical Relevance Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is the increase in size of the prostate, without the presence of malignancy. It is much more common with advancing age, although initial histological evidence of hyperplasia may be evident from much earlier ages .
The enlarged prostate may compress the urethra, resulting in symptoms that refer to impaired storage of urine and symptoms that refer to impaired voiding .
BPH is usually caused by hyperplasia of the glands from the transitional zone of the prostate.
Don’t Miss: Does Cialis Shrink An Enlarged Prostate
Your Prostate Has Four Areas
The prostate gland contains four areas, or zones.
The peripheral zone is the largest segment, containing about 75% of the glands in the prostate. Most prostate cancer occurs in the peripheral zone and is the site where most needle biopsies are taken. The peripheral zone contains the majority of the prostatic tissue.
The central zone of the prostate gland is the area that surrounds the ejaculatory ducts. Less than 5% of prostate cancers originate here. However, if prostate cancer does originate here, it is more aggressive and can metastasize to the seminal vesicles.
The transition zone surrounds the urethra in the place where it enters the prostate. This part of the prostate grows in adult men and is responsible for BPH, or the enlarged prostate. Around 20% of cancers originate here.
The fourth zone is the anterior fibromuscular storma.
Its Another Muscle That Needs Work
The prostate gland contains muscles that help in expelling the semen out of the penis during sexual intercourse. The prostate is a muscle-driven mechanism between urination and ejaculation.
This gland works by expelling the seminal fluid through a contraction. The semen is then forced outside and the ejaculation takes place.
Recommended Reading: Does Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
Urinary Tract Infections In Men: Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment
Nonbacteria microbes may cause a different type of chronic prostatitis, known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome, which may also develop as a result of chemicals in the urine, a;urinary tract infection, or pelvic nerve damage.
Affecting 10 to 15 percent of the U.S. male population, chronic pelvic pain syndrome is the most common type of prostatitis,;but also the least understood.
Symptoms vary depending on the type of prostatitis, but can include urination problems, pain , fever, and body aches, among other things.
Some people develop asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis, in which the prostate is inflamed but doesnt produce any symptoms or require treatment.
Bacterial prostatitis is most often treated with antibiotics. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome may require drugs, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
Over time, prostatitis may cause sexual dysfunction, abscesses in the prostate, inflammation of nearby reproductive organs, and infection of the bloodstream.
Understanding The Anatomy Of The Prostate
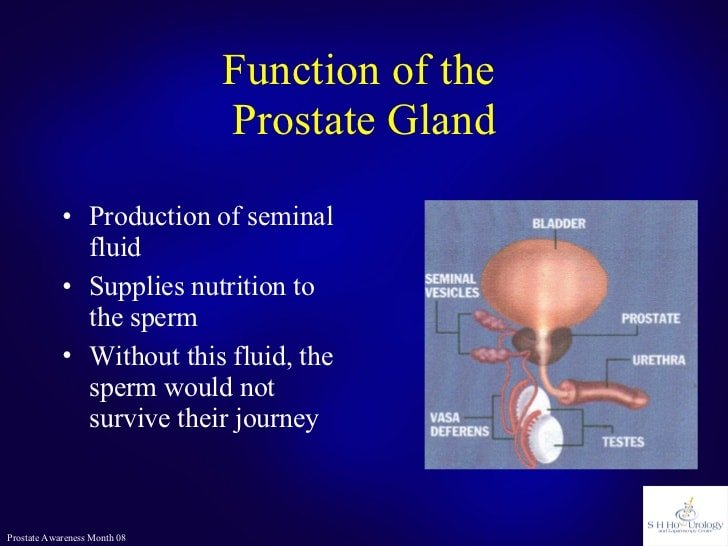
Despite its importance, the prostate gland in an adult man is only about the size and shape of a walnut and weighs less than 1 ounce .
It is located below the bladder, above the pelvic floor muscles, and in front of the rectum.
The prostate reaches its mature size during puberty and will keep its walnut size until the man is in his late forties or early fifties. After this age, it slowly begins to enlarge.
The prostate, which surrounds the urethra, is made up of glandular, stromal tissue, and smooth muscles fused within a capsule.
Though the prostate gland is often referenced as a singular entity, it is actually made up of a number of tubular or saclike glands that secrete fluids into the urethra through the ejaculatory ducts.
The prostate is divided into three histologically and anatomically separate glandular areas: The transition zone, the central zone, and the peripheral zone.
Transition Zone This surrounds the part of the urethra that passes through the prostate . This zone only represents about 5 percent of the gland, but is the primary origination of benign prostatic hyperplasia, or enlarged prostate. That is, the transition zone is the region of the prostate that grows as men age.
Central Zone Making up quarter of the prostate, this area surrounds the transition zone, as well as the ejaculatory ducts that stretch from the seminal vesicles which produces the majority of the fluid of semen ;to the prostatic region of the urethra.
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
