Reach Out To Us Today
Prostate screenings are crucial to have so that men can catch any signs of prostate cancer early on. Once a man reaches the ages of 40 and above, it is best that he begins to consult with a doctor about this test.
If you have questions about getting a prostate screening and the importance of them, then reach out to our office so that we can help you further. Give us a call or stop by our office today and wed be happy to assist you in any way that we can.
Request an appointment here: or call Center for Adult Medicine and Preventive Care at for an appointment in our Passaic office.
Check out what others are saying about our services on Yelp: Read our Yelp reviews.
When To Get Your Prostate Checked: Warning Signs And Advice
A healthy prostate plays a vital role in male fertility, producing fluid that helps keep sperm alive. But as you get older, particularly after the age of 40, you may find that your prostate starts to cause you problems. One reason for this is that the prostate continues to grow as you age. This is a normal process but for many men, an enlarged prostate can cause symptoms that affect their quality of life. This isnt the only problem that affects the prostate, there are several other prostate issues, which can produce similar symptoms to each other. A prostate exam can help you find out whats going on with your prostate so your doctor can then help you get relief from any symptoms you may be experiencing.
Also Check: Is Drinking Beer Bad For Prostate Cancer
When To Start Prostate Exams
The American Cancer Society recommends that men aged 50 start prostate cancer screenings. However, African American men and men with a family history of prostate cancer should start screening at age 45. In general, most experts recommend getting a prostate exam every three to five years.
Your doctor will check the prostate gland for any lumps or abnormalities during a prostate exam. It’s not painful, but some men may feel uncomfortable during the exam.
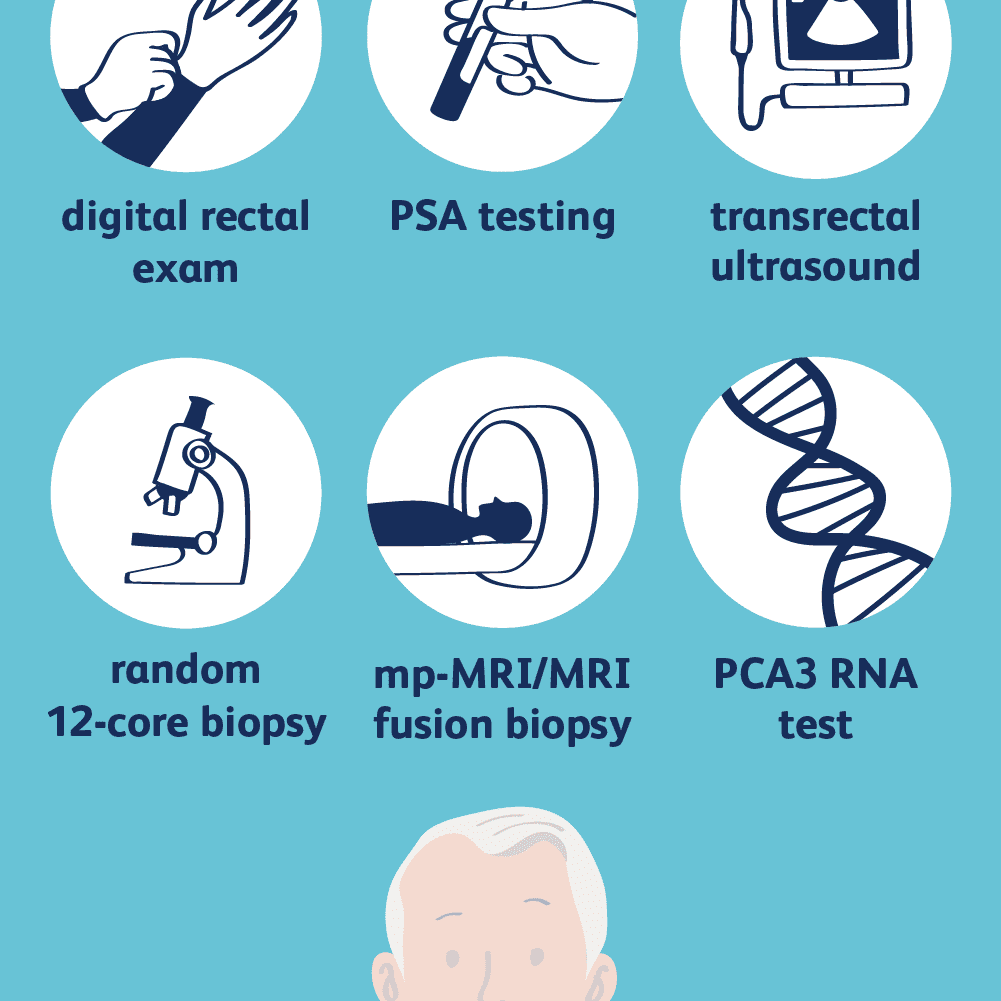
These are some types of prostate exams:
- Digital Rectal Exams : During a DRE, the doctor physically examines the rectum to feel for any abnormalities in the prostate. This exam can help detect prostate cancer in its early stages
- Prostate-Specific Antigen Tests : A PSA test measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate present in the blood. A high PSA level may be a sign of prostate cancer
If any of the above tests is abnormal, further testing may include:
- Biopsies: A needle is used to sample tissues for cancer cells. This is typically done as an MRI-guided biopsy.
- Screening Tests: Screening tests can sometimes have incorrect or unclear test results, making it essential to speak with your doctor about the risks and benefits of this test. Men should talk to their doctor about how often they should get a prostate exam, depending on their health status.
Read Also: Gleason Score 7 Prostate Cancer Treatment Options
Is The Psa Test Recommended For Prostate Cancer Screening
Beginning around 2008, as more was learned about both the benefits and harms of prostate cancer screening, a number of professional medical organizations began to caution against routine population screening with the PSA test. Most organizations recommend that individuals who are considering PSA screening first discuss the risks and benefits with their doctors.
Some organizations do recommend that men who are at higher risk of prostate cancer begin PSA screening at age 40 or 45. These include Black men, men with germline variants in BRCA2 , and men whose father or brother had prostate cancer.
In 2018, the United States Preventive Serves Task Force updated its recommendation statement for prostate cancer screening from a D to a C in men ages 55 to 69. The updated recommendation, which applies to the general population as well as those at increased risk due to race/ethnicity or family history, is as follows:
- For individuals ages 55 to 69 years, the decision to undergo periodic PSA-based screening for prostate cancer should be an individual one. Before making the decision, a person should discuss the potential benefits and harms of screening with their clinician and consider these in the context of their own values and preferences.
- PSA-based screening for prostate cancer is not recommended for individuals 70 years and older.
What Is Cancer Screening
Screening means testing people for early stages of a cancer, or for early changes that could develop into cancer if left untreated. For screening to be useful the tests:
- need to be reliable at picking up cancers that need treatment
- overall must do more good than harm to people taking part
- must be something that people are willing to do
Screening tests are not perfect and have some risks. The screening programme should also be good value for money for the NHS.
Recommended Reading: What Is C61 Prostate Cancer
Prostate Specific Antigen Test
A blood test called a prostate specific antigen test measures the level of PSA in the blood. PSA is a substance made by the prostate. The levels of PSA in the blood can be higher in men who have prostate cancer. The PSA level may also be elevated in other conditions that affect the prostate.
As a rule, the higher the PSA level in the blood, the more likely a prostate problem is present. But many factors, such as age and race, can affect PSA levels. Some prostate glands make more PSA than others.
PSA levels also can be affected by
- Certain medical procedures.
Screening Information For Prostate Cancer
Screening for prostate cancer is done to find evidence of cancer in otherwise healthy adults. Two tests are commonly used to screen for prostate cancer:
Digital rectal examination
A DRE is a test in which the doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum and feels the surface of the prostate through the bowel wall for any irregularities.
PSA blood test
There is controversy about using the PSA test to look for prostate cancer in people with no symptoms of the disease. On the one hand, the PSA test is useful for detecting early-stage prostate cancer, especially in those with many risk factors, which helps some get the treatment they need before the cancer grows and spreads. On the other hand, PSA screening may find very-slow-growing prostate cancers that would never threaten someone’s life. As a result, screening for prostate cancer using PSA may lead to treatments that are not needed, which can cause side effects and seriously affect a person’s quality of life.
ASCO recommends that people with no symptoms of prostate cancer and who are expected to live less than 10 years do not receive PSA screening. For those expected to live longer than 10 years, ASCO recommends that they talk with their doctor to find out if the test is appropriate for them.
Other organizations have different recommendations for screening:
Also Check: Life Extension Ultra Prostate Formula
What Do My Psa Test Results Mean
Once your test results are back, your healthcare provider will let you know if any additional testing is recommended. PSA levels can vary over time for several reasons unrelated to prostate cancer . So, if you have a borderline PSA, your provider may simply recommend another PSA test in six months or so.
Screening For Prostate Cancer
There is no national screening programme for prostate cancer in the UK. This is because there isnt a reliable test that can pick up prostate cancer that needs treatment at an early stage.
Overall research has shown that current tests dont reduce the number of men dying from prostate cancer. Research is going on to find a new test. Or see if the current test is more effective if used in a different way and can find the cancers that need treatment more accurately.
Read Also: Does Riding A Bike Affect Your Prostate
Prostate Cancer: Advancements In Screenings
You may know thatprostate canceris one of the most common cancer types in men. The good news is that thereare many treatment and management options, even if the cancer is caught ata later stage.
What you may not know: There are several options when it comes toprostate cancer screening. After considering multiple factors, your doctor may recommend theprostate-specific antigen test, and/or one of the newer screeningtests that are now available.
Johns Hopkins urologistChristian Pavlovich, M.D., explains what you should know.
Also Check: Prostate Massage Therapy For Erectile Dysfunction
What Is A Prostate Cancer Screening Like
A prostate cancer screening can be conducted in one of two ways. The first, a PSA test, is a simple blood draw. The second is a brief rectal exam that takes less than 30 seconds to perform.
âFor a screening, if a patient comes and asks for a prostate cancer screening, it begins with a blood test,â said Ehdaie. âItâs a small vial of blood, and then a medical history and physical examination. In the physical examination there will be a digital rectal examination in which the physicianâs finger is inserted into the rectum to feel the prostate.â
Also Check: How To Reverse Prostate Problems
Schedule Your Prostate Exam Today
At Northern Inyo Healthcare District, our urology services focus on the urinary tract and system, including the kidneys and bladder, as well as reproductive organs. Our expert team treats a full range of conditions and performs surgery at our hospital if necessary with our state-of-the-art da Vinci Xi Surgical System.
To stay on top of your prostate health, schedule a prostate exam with our Rural Health Clinic today by calling 760-873-2849.
What To Expect During The Exam
You can get a prostate exam easily and quickly at your doctors office. Generally, for cancer screenings, your doctor will take a simple blood test.
Your doctor might also choose to perform a DRE. Before performing this exam, your doctor will ask you to change into a gown, removing your clothing from the waist down.
During a DRE, your doctor will ask you to bend over at the waist or lie on the exam table in a fetal position, with your knees to your chest. They will then insert a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum.
Your doctor will feel for anything abnormal, such as bumps or hard or soft areas that might indicate a problem. Your doctor may also be able to feel if your prostate is enlarged.
A digital rectal exam can be uncomfortable, especially if you have hemorrhoids, but isnt overly painful. It will last only a couple of minutes.
A DRE is one of your doctors tools that can help them detect several prostate and rectal problems, including:
- prostate cancer
Your doctor will be able to tell immediately if there are any areas of concern that may warrant further testing.
The results of a DRE exam are either normal or abnormal, but doctors typically rely on several different tests to help them make a prostate cancer diagnosis.
If your doctor feels something abnormal during the DRE, they will probably recommend getting a PSA blood test, if you havent done so already.
- transrectal ultrasound
Read Also: Best Prostate Cancer Centers In Us
Don’t Miss: First Line Treatment For Prostate Cancer
What Are Some Of The Limitations And Potential Harms Of The Psa Test For Prostate Cancer Screening
Detecting prostate cancer early may not reduce the chance of dying from prostate cancer. When used in screening, the PSA test can help detect small tumors. Having a small tumor found and treated may not, however, reduce the chance of dying from prostate cancer. That is because many tumors found through PSA testing grow so slowly that they are unlikely to be life threatening. Detecting such tumors is called overdiagnosis, and treating them is called overtreatment.
Overtreatment exposes a person unnecessarily to the potential complications associated with prostate surgery and radiation therapy. These include urinary , gastrointestinal , and sexual side effects .
In addition, finding cancer early may not help someone who has a fast-growing or aggressive prostate tumor that may have spread to other parts of the body before being detected.
The PSA test may give false-positive results. A false-positive test result occurs when the PSA level is elevated but no cancer is actually present. A false-positive test result may create anxiety and lead to additional medical procedures, such as a prostate biopsy, that can be harmful. Possible side effects of biopsies include serious infections, pain, and bleeding.
False-positive test results are common with PSA screening only about 25% of people who have a prostate biopsy due to an elevated PSA level are found to have prostate cancer when a biopsy is done .
Information For Well Men Aged 50 And Over
You can refer to the infographic above and direct patients to the information sheet for well men aged 50 and over for a summary of the potential benefits and risks of PSA testing.
The information sheet for well men includes the above infographic, which explains the PSA test. It also includes a list of the potential advantages and disadvantages of the PSA test for men to consider when making a decision.
The Office for Health Improvement and Disparities created this information on behalf of the NHS.
Don’t Miss: Does Prostate Cancer Cause Low White Blood Cell Count
When Should I Have A Prostate Check
Generally, if you aged 50 years or older and have any urinary symptoms, you should let your doctor know. They will discuss with you whether or not you should have a prostate check.
Symptoms include:
- poor flow of urine
- trouble stopping peeing
- dribbling after you are done peeing
- needing to pee more often, at night or urgently
- trouble starting peeing
- pain when peeing
- blood in your pee.
If you have no symptoms, it is recommended that you get checked if you:
- you are a man aged 5070 years old but dont have any family history
- you are a man aged 4070 years old and your father or brother has had prostate cancer
- you are a man aged more than 70 years old and you have family history of prostate cancer or you have had an abnormal PSA test previously, and you have a life expectancy of more than 10 years.
Having a prostate check is your decision. The tests for prostate cancer can be uncomfortable but they may reduce your chance of being harmed or dying from prostate cancer.
If your test results suggest you are at risk of cancer, you will need to decide whether to have further testing and possibly treatment. In making this decision, you will need to consider whether your quality of life will be better living with a slow growing cancer than having treatments, which may cause you more harm than the cancer ever will.
Your doctor can help you weigh up the benefits and risks of being tested, by taking into consideration factors such as your age and family history.
What Is The Psa Test
Prostate-specific antigen, or PSA, is a protein produced by normal, as well as malignant, cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. For this test, a blood sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are usually reported as nanograms of PSA per milliliter of blood.
The blood level of PSA is often elevated in people with prostate cancer, and the PSA test was originally approved by the FDA in 1986 to monitor the progression of prostate cancer in men who had already been diagnosed with the disease. In 1994, FDA approved the PSA test to be used in conjunction with a digital rectal exam to aid in the detection of prostate cancer in men 50 years and older. Until about 2008, many doctors and professional organizations had encouraged yearly PSA screening for prostate cancer beginning at age 50.
PSA testing is also often used by health care providers for individuals who report prostate symptoms to help determine the nature of the problem.
In addition to prostate cancer, several benign conditions can cause a persons PSA level to rise, particularly prostatitis and benign prostatic hyperplasia . There is no evidence that either condition leads to prostate cancer, but someone can have one or both of these conditions and develop prostate cancer as well.
Read Also: Prognosis For Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Should You Know Your Psa Level
Instead of a national screening programme, there is an informed choice programme, called prostate cancer risk management, for healthy men aged 50 or over who ask their GP about PSA testing. It aims to give men good information on the pros and cons of a PSA test.
If you’re aged 50 or over and decide to have your PSA levels tested after talking to a GP, they can arrange for it to be carried out free on the NHS.
If results show you have a raised level of PSA, the GP may suggest further tests.
Getting The Results Of The Biopsy
Your biopsy samples will be sent to a lab, where they will be looked at with a microscope to see if they contain cancer cells. Getting the results usually takes at least 1 to 3 days, but it can sometimes take longer. The results might be reported as:
- Positive for cancer: Cancer cells were seen in the biopsy samples.
- Negative for cancer: No cancer cells were seen in the biopsy samples.
- Suspicious: Something abnormal was seen, but it might not be cancer.
If the biopsy is negative
If the prostate biopsy results are negative , and the chance that you have prostate cancer isnt very high based on your PSA level and other tests, you might not need any more tests, other than repeat PSA tests sometime later.
But even if many samples are taken, biopsies can still sometimes miss a cancer if none of the biopsy needles pass through it. This is known as a false-negative result. If your doctor still strongly suspects you have prostate cancer , your doctor might suggest:
- Getting other lab tests to help get a better idea of whether or not you might have prostate cancer. Examples of such tests include the Prostate Health Index , 4Kscore test, PCA3 tests , and ConfirmMDx. These tests are discussed in Whats New in Prostate Cancer Research?
- Getting a repeat prostate biopsy. This might include getting additional samples of parts of the prostate not biopsied the first time, or using imaging tests such as MRI to look more closely for abnormal areas to target.
Prostate cancer grade
Gleason score
Recommended Reading: Surgery After Radiation For Prostate Cancer
