What Can I Do To Lower My Changes Of Getting An Infection
It is important for you to lower your chances of getting an infection to keep your doctor from stopping or delaying your chemotherapy treatment. There are many simple things that you can do to lower your risk of getting an infection during your chemotherapy treatment.
Plan For Lowering Your Chance of Getting An Infection
- If you have animals, is there someone who can help you take care of them during your treatment?
- What plans will you make if you watch young children and one of them gets sick during your chemotherapy treatment?
- How do you get in touch with your doctor or health care team if you need help?
Evaluation Of Patients With Leukocytosis
LYRAD K. RILEY, MD, and JEDDA RUPERT, MD, Eglin Air Force Base Family Medicine Residency, Eglin Air Force Base, Florida
Am Fam Physician. 2015 Dec 1 92:1004-1011.
Leukocytosis, often defined as an elevated white blood cell count greater than 11,000 per mm3 in nonpregnant adults, is a relatively common finding with a wide differential. It is important for clinicians to be able to distinguish malignant from non-malignant etiologies, and to differentiate between the most common nonmalignant causes of leukocytosis.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Leukocytosis greater than 100,000 per mm3 is almost always caused by leukemias or myeloproliferative disorders.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
|
Leukocytosis is not a reliable indicator of postpartum bacterial infection. |
||
|
Patients with leukocytosis and no other signs of systemic inflammatory response syndrome do not require blood cultures. |
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence B = inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, go to .
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Leukocytosis greater than 100,000 per mm3 is almost always caused by leukemias or myeloproliferative disorders.
What Can Cause A Low Platelet Count
There are several common causes, including:
Chemotherapy. Some types of cancer medications, such as chemotherapy, damage bone marrow. This is the tissue inside your bones where your body makes platelets. A low platelet count from chemotherapy is usually temporary. It is rare that chemotherapy permanently damages bone marrow cells.
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy does not usually cause a low platelet count. But your platelet levels may go down if you receive a large amount of radiation therapy to your pelvis or if you have radiation therapy and chemotherapy at the same time.
Antibodies. Your body makes proteins called antibodies. They destroy substances that may harm you, such as bacteria and viruses. But sometimes the body makes antibodies that destroy healthy platelets.
Specific types of cancer. Certain cancers such as leukemia or lymphoma can lower your platelet count. The abnormal cells in these cancers can crowd out healthy cells in the bone marrow, where platelets are made.Less common causes of a low platelet count include:
Cancer that spreads to the bone. Some cancers that spreads to the bone may cause a low platelet count. The cancer cells in the bones can make it difficult for the bone marrow inside of bones to make platelets.
Don’t Miss: Prostate Medicine Side Effects
Topic #: White Blood Cell Growth Factors For Preventing Infection
Background
White blood cell growth factors, also called hematopoietic colony-stimulating factors , are proteins that help the body make white blood cells. White blood cells help fight infection. Many cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, damage white blood cells. This can cause neutropenia, a very low level of white blood cells that increases the risk of getting an infection. When neutropenia occurs with a fever, it is called febrile neutropenia and may be a sign of an infection. Infections can be very serious for people with cancer because they often do not have enough white blood cells to fight the infection on their own and will usually need to be treated in the hospital with antibiotics. CSFs increase levels of white blood cells to help a person avoid infection. However, most patients receiving chemotherapy will not need CSFs. This is because most chemotherapy is only associated with less severe neutropenia, and the risk of severe neutropenia can usually be predicted ahead of time.
Recommendation
ASCO recommends that CSFs are used in the following situations:
- When the risk of febrile neutropenia from chemotherapy is more than 20% and another treatment that works as well is not available.
- For patients receiving chemotherapy with less than a 20% risk of febrile neutropenia if their individual risk is increased because of age, medical history, or other reasons related to the cancer.
What this means for patients
Questions to ask your doctor
For More Information
Blood Transfusions To Treat Anemia
A blood cell transfusion is a safe and a common way to treat anemia in people with cancer. It can help the patient feel better and helps oxygen get to vital organs. While blood transfusions can help symptoms very quickly, sometimes the relief is temporary depending on the cause of anemia.
Whether a blood transfusion might be needed depends on how severe your symptoms are and your hemoglobin level. A transfusion might be done if your hemoglobin level reaches a certain number or if your symptoms get too bothersome
A blood transfusion requires careful matching of donated blood to the recipients blood. Blood products are tested to be sure they are safe and the same kind of blood type as the recipient. But, receiving a blood transfusion also has some risks
Don’t Miss: Flomax No Ejaculation
What Can I Do To Prevent Neutropenia
Since white blood cells are destroyed as a side effect of chemotherapy, there is nothing specifically that you can do to prevent neutropenia from occurring. Nonetheless, there are several things that you can do to reduce your risk of getting an infection when your white blood cells are low:
Perform excellent daily personal hygiene.
- Wash your hands frequently, especially before eating and after using the bathroom.
- Use alcohol-free, antiseptic mouthwashes daily.
- Do not cut or pick at cuticles. Use a cuticle cream instead. Even if you have a manicure, only cuticle cream should be used.
- Use a deodorant rather than an antiperspirant. Antiperspirants block sweat glands and, therefore, may promote infection.
- When menstruating, use sanitary napkins rather than tampons, which may promote infection in a neutropenic patient.
Avoid situations that will increase your chance of getting an infection.
- Stay away from people who are ill.
- Avoid contact with anyone who has recently been vaccinated, including infants and children.
- Avoid crowds as much as possible. When going to places where there are often a lot of people , try going at off-peak times, when they are not as crowded.
Use extra precautions to decrease the chance of injury and infection.
If you cut or scrape the skin, clean the area immediately with soap and water and bandage as necessary.
Effects Of Cancer Drugs On Blood Cells
Some types of cancer drugs can lower the number of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets in your blood for some time. Drugs that can cause this include some chemotherapy drugs and some targeted cancer drugs.
Developing blood cells multiply all the time as they mature in the bone marrow and are then released into the blood. Some cancer drugs can slow the production of blood cells by the bone marrow, so they are not released as quickly into the blood. Then the number of circulating blood cells goes down.
Read Also: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
White Blood Cell Count Is Positively Associated With Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Department of Urology, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Suita, Japan
Department of Urology, Osaka General Medical Center, Osaka, Japan
Correspondence:
Department of Urology, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Suita, Japan
Department of Urology, Osaka General Medical Center, Osaka, Japan
Correspondence:Get access to the full version of this article.You previously purchased this article through ReadCube.
Institutional Login
Log in to Wiley Online Library
If you have previously obtained access with your personal account, please log in.
- View the article PDF and any associated supplements and figures for a period of 48 hours.
- Article can not be printed.
- Article can not be downloaded.
- Article can not be redistributed.
- Unlimited viewing of the article PDF and any associated supplements and figures.
- Article can not be printed.
- Article can not be downloaded.
- Article can not be redistributed.
- Unlimited viewing of the article/chapter PDF and any associated supplements and figures.
- Article/chapter can be printed.
To determine whether low-grade systemic inflammation is associated with prostatic enlargement/benign prostatic hyperplasia.
How May My Low White Blood Cell Count Be Treated
During your chemotherapy treatment your doctor will ask you to have blood tests. These blood tests tell your doctor how your body is doing. When you have a blood test, a nurse or technician will take a small amount of blood from your arm with a needle. The blood tests will tell your doctor if you have a low white blood cell count. A low white blood count is also called neutropenia . If your white blood cell count is too low, your doctor may stop your chemotherapy until your white blood cell count is higher. The good news is that the low white blood cell count caused by your chemotherapy is treatable.
The most common treatment for a low white blood cell count is to take a medicine that tells your body to make more white blood cells. These medicines are called colony stimulating factors . These medicines are usually given to you one to three days after your chemotherapy treatment. Depending on which CSF your doctor uses, you may take the medicine every day for up to two weeks.
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
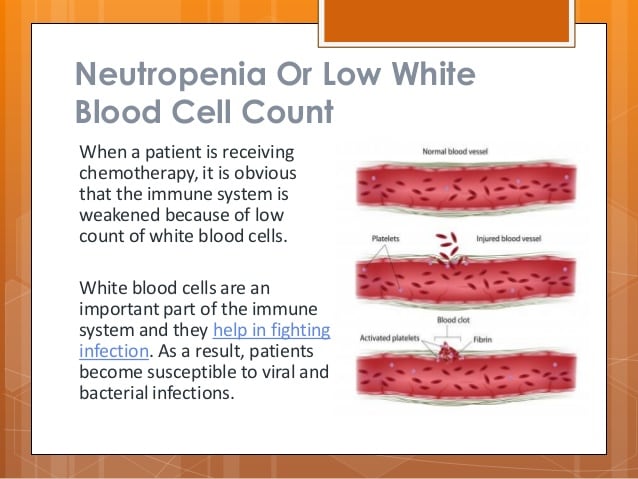
Low White Blood Cell Counts
A lowered level of immunity is called immunosuppression. Certain diseases, including cancer, and certain treatments, including chemotherapy and radiation therapy, can cause some people to have immunosuppression. This is usually referred to as having a low white blood cell count, but you might hear other words to describe it too.
Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression
Metastatic spinal cord compression happens when cancer cells grow in or near to the spine and press on the spinal cord. MSCC isnt common, but you need to be aware of the risk if your prostate cancer has spread to your bones or has a high risk of spreading to your bones. The risk of MSCC is highest if the cancer has already spread to the spine. Speak to your doctor or nurse for more information about your risk.
MSCC can cause any of the following symptoms.
- Pain or soreness in your lower, middle or upper back or neck. The pain may be severe or get worse over time. It might get worse when you cough, sneeze, lift or strain, or go to the toilet. It might get worse when you are lying down. It may wake you at night or stop you from sleeping.
- A narrow band of pain around your abdomen or chest that can move towards your lower back, buttocks or legs.
- Pain that moves down your arms or legs.
- Weakness in your arms or legs, or difficulty standing or walking. You might feel unsteady on your feet or feel as if your legs are giving way. Some people say they feel clumsy.
- Numbness or tingling in your legs, arms, fingers, toes, buttocks, stomach area or chest, that doesnt go away.
- Problems controlling your bladder or bowel. You might not be able to empty your bladder or bowel, or you might have no control over emptying them.
Dont wait
It is very important to seek medical advice immediately if you think you might have MSCC.
Read more about metastatic spinal cord compression .
Read Also: Do Females Have A Prostate
What Are White Blood Cells
There are several types of white blood cells , also called leukocytes, and each can be affected differently by cancer and its treatments. There are five types of white blood cells:
- Neutrophils attack viruses and bacteria.
- Eosinophils fight bacteria, parasites, and mount immune responses to allergens.
- Basophils create generic immune responses and play a role in conditions like asthma.
- Lymphocytes help defend and fight against infection. There are two main types of lymphocytes: T-cells and B-cells. T-cells target infectious invaders, while B-cells create antibodies to prevent future infections.
- Monocytes clean up wastes and dead cells in the body.
Cancer can lead to a high or low WBC count, depending on the type of cancer, which type of white blood cell is affected, and where the cancer is in your body.
Early Warning Signs Of Leukemia
Leukemia symptoms often vary depending on the type of leukemia diagnosed. Some symptoms, like night sweats, fever, fatigue and achiness, resemble flu-like symptoms. Unlike symptoms of the flu, which generally subside as you get better, leukemia symptoms generally last longer than two weeks, and may include sudden weight loss, bone and joint pain and easy bleeding or bruising. Other early warning signs of leukemia include:
- Fever, chills
- Petechiae
- Unintended weight loss
Chronic myelogenous leukemia may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, when it does cause symptoms, they may include:
- Unintended weight loss
- Night sweats
- Fever Pain or fullness below the left ribs
Because some conditions occur as side effects of the disease, the following may be signs of leukemia:
Anemia: A low red blood cell count. Red blood cells carry oxygen around the body. This condition may contribute to weakness, fatigue or shortness of breath.
Leukopenia: A low white blood cell count. A decrease in the production of functional leukocytes weakens the body’s immune defense, which may make you more prone to infections.
Thrombocytopenia: A low blood platelet count. Platelets are the blood cells responsible for blood clotting. A shortage of blood platelets may lead to easy bruising or bleeding.
When leukemia results in thrombocytopenia, symptoms may include bleeding from the gums and nose. In women, thrombocytopenia can result in heavy or abnormally long menstruation.
Also Check: Zinc And Prostate Cancer
What Will I Learn By Reading This
When you have chemotherapy to control your prostate cancer, you may have side effects or unwanted changes in your body. Side effects are different from person to person, and may be different from one treatment to the next. Some people have no or very mild side effects. The good news is that there are ways to deal with most of the side effects. You will learn:
- What an infection is
- Why chemotherapy raises your chance of getting an infection
- How your doctor will lower your chance of getting an infection
- Things you can do to help lower your chance of getting an infection
- When to call your doctor
It is important for you to learn how to manage the side effects you may have from chemotherapy so that you can keep doing as many of your normal activities as possible.
What Tests Should I Request To Confirm My Clinical Dx In Addition What Follow
A urinalysis should be performed on every patient with LUTS. The absence of nitrite, leukocyte esterase, and white blood cells on urinalysis essentially rules out a urinary tract infection. However, if a urinary tract infection is suspected, urine culture should be performed to characterize the infectious agent. In those patients without urinary tract infections, a digital rectal examination and serum PSA assay are indicated.
PSA is a kallikrein-like serine protease produced almost exclusively by the epithelial cells of the prostate. It is measured in sera by means of immunometric assay. Levels greater than 10 ng/mL are highly suggestive of prostate cancer, whereas levels less than 2.5 ng/mL are highly suggestive of the absence of the disease. When serum PSA levels are between 2.5 and 10 ng/mL, the measurement of free PSA and the computation of the derived index free/total PSA, are recommended.
Free/Total PSA
The majority of serum immunoreactive PSA is covalently bound to endogenous prostate inhibitors, mainly alpha-1-antichymotrypsin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, and protease C inhibitor. A small fraction of unbound immunoreactive PSA is present in sera, and this fraction is called free PSA . The free/total PSA ratio is reduced in patients with prostate cancer. A value for this ratio below 10% in cases with tPSA between 2.5 and 10 ng/mL is suggestive of prostate cancer.
Transrectal Ultrasound Guided Biopsy
TRUS is recommended in the following conditions:
Also Check: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
What About Anemia After Radiation Therapy
A study at Beth Israel Medical Center and St. Luke’s-Roosevelt Hospital Center in New York City found that 51 percent of men and 64 percent of women had anemia at the end of radiation treatment for cancer .
Vitamin D may protect against the development of cancers of the skin as a result of radiation injury , and many people benefit from supplementation.
Omega-3 essential fatty acids may likewise protect against the development of new cancers as a result of exposure to radiation . But that doesn’t mean that more is always better. You really don’t need more than 10,000 IU of vitamin D per day, and taking more than 10 g of fish oil can produce fatty acid byproducts that actually undo the benefits of lower doses.
You will notice that there isn’t a long list of healthy foods people should eat after radiation or chemotherapy for iron deficiency treatment. That’s because eating any kind of food tends to be a chore after cancer treatment. You will get better results with targeted iron therapies, either from your doctor or the very best iron supplements, with eating as best you can while you recover.
Differentiation By Type Of White Blood Cell
Changes in the normal distribution of types of WBCs can indicate specific causes of leukocytosis .8 Although the differential of the major types of WBCs is important for evaluating the cause of leukocytosis, it is sometimes helpful to think in terms of absolute, rather than relative, leukopenias and leukocytoses. To calculate the absolute cell count, the total leukocyte count is multiplied by the differential percentage. For example, with a normal WBC count of 10,000 per mm3 and an elevated monocyte percentage of 12, the absolute monocyte count is 12% or 0.12 times the WBC count of 10,000 per mm3, yielding 1,200 per mm3 , which is abnormally elevated.
Normal White Blood Cell Distribution
Neutrophils
| White blood cell line | Normal percentage of total leukocyte count |
|---|
Normal White Blood Cell Distribution
Neutrophils
| White blood cell line | Normal percentage of total leukocyte count |
|---|---|
|
0.5 to 1 |
Information from reference 8.
Patient characteristics
note: After patient characteristics, causes are listed in approximate order of frequency.
CRP = C-reactive protein WBC = white blood cell.
Information from references 1 through 7, 9, and 10.
Patient characteristics
note: After patient characteristics, causes are listed in approximate order of frequency.
CRP = C-reactive protein WBC = white blood cell.
Information from references 1 through 7, 9, and 10.
Selected Conditions Associated with Elevations in Certain White Blood Cell Types
Basophils
Basophils
You May Like: Flomax Ejaculatory Dysfunction
