Causes Of Malignant Neoplasm Cancer
The abnormal growth of cells in the human body can be linked to various causal factors. One or more of these factors may be at play, and the exact cause can be determined only after elaborate medical tests are performed on the patient. The main factors that can lead to a cancerous growth of cells in the human body are as follows:
Gene Mutations Mutation or changes in the DNA sequence of one or more cells in the human body may lead to cancer. The cells may be located at any part of the body. When the DNA sequencing is changed, the cells start behaving differently than what they are supposed to do. Though it is not necessary that a mutation will definitely trigger cancerous growth, yet if the changes in the sequence instruct the cells to rapidly multiply without the ability to stop, it may lead to malignant neoplasia. All new cells thus produced will be mutated ones and they, too, can grow uncontrollably, thus leading to a quick growth of the tumor.
Smoking Smoking tobacco in any form can lead to cancer. Tobacco contains various complex chemical compounds amongst which atleast 70 chemicals are known to be carcinogenic, i.e., induced cancerous growth in the body. When dried tobacco is burned, the smoke is inhaled by the smoker and those around them, thus allowing the harmful chemicals to enter the body. These carcinogens, then, may affect the genome of the person and trigger neoplasia.
Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast
Breast tumors are classified by several factors including the size of the tumor and the stage that it has reached when it is detected. Breast tumors are measured from stage 0 through stage 4, with stage 4 tumors being the most advanced. The grade of the tumor is also looked at and this measures how the cells have differentiated themselves. Breast cancer is caused by the development of malignant cells in the breast. The malignant cells originate in the lining of the milk glands or ducts of the breast , defining this malignancy as a cancer.
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for prostate cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages.
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside the prostate.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the prostate to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to parts of the body farther from the prostate, such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
Don’t Miss: What Is Robotic Prostate Surgery
Prostate Cancer Stages And Other Ways To Assess Risk
After a man is diagnosed with prostate cancer, doctors will try to figure out if it has spread, and if so, how far. This process is called staging. The stage of a prostate cancer describes how much cancer is in the body. It helps determine how serious the cancer is and how best to treat it. Doctors also use a cancers stage when talking about survival statistics.
The stage is based on tests described in Tests to Diagnose and Stage Prostate Cancer, including the blood PSA level and prostate biopsy results.
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates
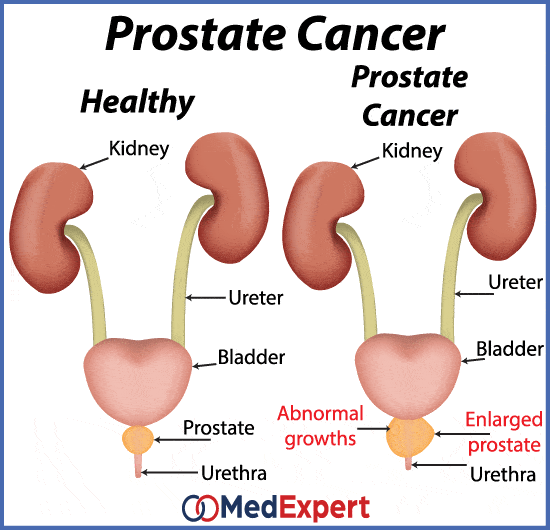
The good news about prostate cancer is that it usually grows slowly, and 9 out of 10 cases are found in the early stages. Overall, the 5-year relative survival rate is 100% for men with disease confined to the prostate or nearby tissues. Many men live much longer. When the disease has spread to distant areas, that figure drops to 31%. But these numbers are based on men diagnosed at least 5 years ago. The outlook may be better for men diagnosed and treated today.
Also Check: How Do You Know If You Have Prostate Cancer
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma and flat non-invasive carcinoma . In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded the bladder wall.
This early stage of bladder cancer is most often treated with transurethral resection with fulguration followed by intravesical therapy within 24 hours.
Recommended Reading: Florida Bladder Institute Patient Portal
Overview Of The Staging System
After a thorough assessment by your oncologist, your cancer will be assigned a stage between I and IV. Prostate cancer stages are based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system. Using the TNM system, your oncologist:
- Examines the tumor
- Determines if the cancer has spread to any lymph nodes
- Assesses whether the cancer has metastasized
- Considers the prostate-specific antigen level from blood testing
- Assigns a grade group based on how abnormal the cancer appears under a microscope
With this information in mind, you can better understand how stages are assigned and what they mean for patients in general.
You May Like: What Are The Effects Of Removing The Prostate
Malignant Neoplasm Of Prostate Definition
The only other thing I was drinking in the first 6 months after my diagnosis was green tea. I would drink about 4 glasses of green tea daily to go along with the increased water intake. I wasnt putting any other liquid into my body for the first 6 months. This was a big help in starting my road to recovery.
Once I started feeling better then I added organic soy milk to my diet as well. Soy milk isnt much like regular milk but once you get used to it then its not bad at all. To this day these are the only 3 liquids I have in my diet. To recap the 3 liquids I drink today are purified water,green tea,& organic soy milk. I put no other liquids into my body period.
Now, I want to chat a little more about meat & other aspects of a proper diet. As I said we dont need meat to live. I thought cutting or limiting meat in my diet would be to hard to accomplish. Well again my thinking was wrong. Was it easy? No! However, after a couple weeks then things were starting to get easier. I didnt cut all meats out of my diet but I did cut certain meats & eat moderate amounts of all others.
One meat that needs to be completely cut or at least very minimized is red meat . Too much Red meat consumption is not good for prostate health. I was eating a lot of fast food burgers & also red meat at home. I will say to at least cut red meat completely out of your diet until you get your prostate health back.
What Is C61 Malignant Neoplasm Of Prostate
4.2/5Malignant neoplasm of prostate C61
A tumor can be cancerous or benign. A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. This is because many prostate tumors do not spread quickly to other parts of the body. Some prostate cancers grow very slowly and may not cause symptoms or problems for years or ever.
Also Know, what is the code for prostate cancer? Prostate cancer is assigned to ICD-9-CM diagnosis code 185. Carcinoma in situ of the prostate is classified to code 233.4, and a benign neoplasm of the prostate goes to code 222.2.
Beside above, what is a malignant neoplasm mean?
A malignant neoplasm is a cancerous tumor, an abnormal growth that can grow uncontrolled and spread to other parts of the body.
What is metastatic prostate cancer?
If your prostate cancer spreads to other parts of your body, your doctor may tell you that itâs âmetastaticâ or that your cancer has âmetastasized.â Most often, prostate cancer spreads to the bones or lymph nodes. Itâs also common for it to spread to the liver or lungs.
You May Like: Is Drinking Tea Bad For Your Prostate
Looking For More Of An Introduction
If you would like more of an introduction, explore this related item. Please note that this link will take you to another section on Cancer.Net.
-
ASCO Answers Fact Sheet:Read a 1-page fact sheet that offers an introduction to bladder cancer. This free fact sheet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
Also Check: Can Anxiety Cause Overactive Bladder
Survival By Tumor Grade
One way cancer is staged is by looking at the grade of cancer. Grade refers to how cancer cells look like under a microscope.
Traditionally for prostate cancer, this has been done using the Gleason Score, which was developed in the 1960s. Under this system, cancerous cells are categorized on a scale from 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are considered normal prostate tissues, while cells in the grade 5 range have mutated to such an extent they no longer resemble normal cells.
In determining a Gleason score, a pathologist will examine a biopsy sample under a microscope and give a Gleason grade using the above scale to the most predominant pattern displayed, then a second grade to the pattern that is the second most predominant. Those two grades are then added to form the overall Gleason score .
In theory, Gleason scores could range from 2 to 10, but pathologists today rarely give a score between 2 and 5 and are more likely to be in the range of 6 to 10 with 6 being the lowest grade of prostate cancer.
Under the Gleason Score system, a 6 is considered low grade, 7 is intermediate and scores of 8, 9, or 10 are considered high-grade cancers.
The higher the Gleason score, the more likely it is the prostate cancer will grow and spread quickly.
However, there have been some issues with the Gleason system, and a new grading system, to act as an extension of the Gleason system, has been developed.
Under this system Gleason scores are now categorized into grade groups:
You May Like: What Does Stage 2 Prostate Cancer Mean
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment or comes back after treatment , treatment options will depend on where and how much the cancer has spread, what treatments have already been used, and the patients overall health and desire for more treatment. Its important to understand the goal of any further treatment if its to try to cure the cancer, to slow its growth, or to help relieve symptoms as well as the likely benefits and risks.
For instance, non-invasive bladder cancer often comes back in the bladder. The new cancer may be found either in the same place as the original cancer or in other parts of the bladder. These tumors are often treated the same way as the first tumor. But if the cancer keeps coming back, a cystectomy may be needed. For some non-invasive tumors that keep growing even with BCG treatment, and where a cystectomy is not an option, immunotherapy with pembrolizumab might be recommended.
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy, might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
Staging Of Prostate Cancer
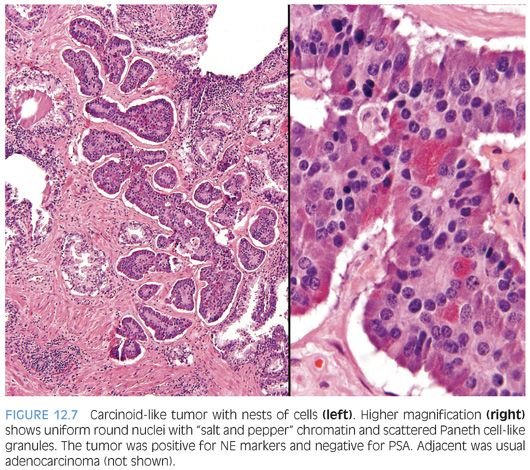
Doctors will use the results of your prostate examination, biopsy and scans to identify the stage of your prostate cancer .
The stage of the cancer will determine which types of treatments will be necessary.
If prostate cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, the chances of survival are generally good.
Don’t Miss: Pi Rads 5 Prostate Cancer
Effects On Pituitary System
commonly develops after radiation therapy for sellar and parasellar neoplasms, extrasellar brain tumours, head and neck tumours, and following whole body irradiation for systemic malignancies. Radiation-induced hypopituitarism mainly affects and . In contrast, and deficiencies are the least common among people with radiation-induced hypopituitarism. Changes in -secretion is usually mild, and vasopressin deficiency appears to be very rare as a consequence of radiation.
Also Check: How Is Prostate Removal Performed
Adenocarcinoma With Glomeruloid Features
Prostatic adenocarcinoma with glomeruloid features is characterized by intraluminal ball-like clusters of cancer cells, reminiscent of renal glomeruli . Glomeruloid structures in the prostate represent an uncommon but distinctive pattern of growth that is specific for malignancy. Glomeruloid features can be a useful diagnostic clue for malignancy, particularly in some challenging needle biopsy specimens. This pattern of growth is usually seen in high-grade adenocarcinoma, often with extraprostatic extension. Glomeruloid features have not been observed in any benign or premalignant lesions, including hyperplasia and intraepithelial neoplasia.116
Ming Zhou, … Jonathan I. Epstein, in, 2007
Recommended Reading: When Should Guys Get Their Prostate Checked
Determining Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Clinically significant prostate cancer is frequently categorized according to three main prognostic factors as defined by Stamey and Epstein :
- Gleason score 7 or greater
- Extraprostatic tumor extension
- Tumor volume on whole-mount prostatectomy > 0.5 cm3 .
This definition is derived from the seminal work of Hanahan and Weinberg . These lesions exhibit more malignant behaviour and are more likely to warrant treatment compared to smaller, less aggressive tumours that can be inconsequential . The parameters used to define clinically significant prostate cancer aid in prognostication of prostate cancer. However, these parameters are not used in isolation for clinical decision making where further patient characteristics including comorbidities, age, performance status and patient choice will further contribute.
Nanoknife Is A Pioneering Treatment For Prostate Cancer The First Nerve Sparing Prostate Cancer Treatment
Unlike traditional prostate cancer treatments, NanoKnife kills the prostate cancer cells instead of removing or irradiating the entire prostate. Its a one time two hour procedure, at most. Not weeks. Not months. Youre clear in days, with no side effects no incontinence, no impotence.*
Talk to us here at Vitus and youre talking to the worlds leading experts in using NanoKnife for treating prostate cancer, with over 1000 mentreated successfully.
*No incontinence in any of the patients we have treated with NanoKnife. No impotence in 90-95%.
Recommended Reading: How Long Do Prostate Cancer Patients Live
Psma Expression On Pre
Increased PSMA expression on tumor tissue obtained from biopsy at time point of initial diagnosis is significantly associated with the likelihood of disease recurrence. During the observation period, 79 out of 235 patients developed disease recurrence following RPE. The frequency of disease recurrence was 16.7, 25.7, 39.2, and 60.7% for patients exhibiting no, low, medium or high PSMA expression on pre-operative biopsy, respectively. Kaplan-Meier curve illustrates reduced recurrence free survival with increasing PSMA expression . The 5-year-PSA-recurrence free survival rates are 88.2, 74.2, 67.7, and 26.8% for patients exhibiting no, low, medium or high PSMA expression on pre-operative biopsy, respectively . Compared to PSMA-negative tumors, low, medium and high PSMA expression is associated with 1.940-, 2.893-, and 6.900-fold incidence of developing disease recurrence following RPE, respectively . Multivariate Cox-regression adjusting PSMA expression to iPSA blood level at time of diagnosis and grade group on biopsy was used to investigate the potential to predict disease recurrence independently from other prognostic marker. High PSMA expression on biopsy remained significant in multivariate analysis predicting a 4.024-fold increased risk of disease recurrence in relation to PSMA negative tumors independently from other established prognostic factors .
Patient Discussion About Prostate Cancer
Q. breating air that has tetrachloroethene in it how does it affect you if u have prostate cancer the air in my building has been determined to have Tetrachloroethylene in it i have just been diagnosed with prostate cancer
Q. What does treatment for prostate cancer consist of, and does it affect a maleâs ability to have sex? A very close friend of ours has been diagnosed with prostate cancer and we were wondering what his treatment options might be.If the prostate gland is removed, does that eliminate the ability to have sex?
Q. Rising PSA to 10 with two negative biospies? Expect cancer? 67 yrs old in good health otherwise.
Read Also: Laser Prostate Surgery For Bph
You May Like: What Are The Early Signs Of Prostate Cancer
> > > All Natural Technique Fixes Enlarged Prostate Watch Here< <
You add the alternative treatments I have used/use then I feel these are the things needed in order to manage prostate problems. This total program may not help all men but I feel it will help most men. It takes determination,dedication,& discipline to follow this program. Im not making any shortcuts or trying butter things here either. Malignant Neoplasm of Prostate Definition
If you want your health back & keep that health then youd better get ready for that drive. It takes years for our prostate to get in bad health & sometimes it takes a long time to get it back. If you make that determination & drive yourself to get better then it can happen. Its not going to happen overnight for sure. I suffered off & on for 18 months but now for the past 6 months or so I can honestly say I have no symptoms for prostate problems. Article Source: http://EzineArticles.com/2610529
While these Non Objective treatments have had varying levels of success, Washington University scientists who have spent over 15 years studying volumes of clinical research discovered a solution that FORCES your enlarged prostate to go back to a healthy size.
All without resorting to prescription drugs, risky surgeries, or continuous injectionsMalignant Neoplasm of Prostate Definition
And the solution is surprisingly simple we can protect ourselves without risky medication:
Do This and automatically reduce prostate inflammation Like 12k People Did.
What Are The Risk Factors For Bladder Cancer
Some factors increase the risk of bladder cancer:
- Cigarette smoking is the biggest risk factor it more than doubles the risk. Pipe and cigar smoking and exposure to second-hand smoking may also increase ones risk.
- Prior radiation exposure is the next most common risk factor .
- Certain chemotherapy drugs also increase the risk of bladder cancer.
- Environmental exposures increase the risk of bladder cancer. People who work with chemicals, such as aromatic amines are at risk. Extensive exposure to rubber, leather, some textiles, paint, and hairdressing supplies, typically related to occupational exposure, also appears to increase the risk.
- Infection with a parasite known as Schistosoma haematobium, which is more common in developing countries and the Middle East.
- People who have frequent infections of the bladder, bladder stones, or other diseases of the urinary tract, or who have chronic need for a catheter in the bladder, may be at higher risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Patients with a previous bladder cancer are at increased risk to form new or recurrent bladder tumors.
Other risk factors include diets high in fried meats and animal fats, and older age. In addition, men have a three-fold higher risk than women.
Read Also: Us Task Force Prostate Cancer Screening
