Possible Side Effects Of Ebrt
Some of the side effects from EBRT are the same as those from surgery, while others are different.
Bowel problems: Radiation can irritate the rectum and cause a condition called radiation proctitis. This can lead to diarrhea, sometimes with blood in the stool, and rectal leakage. Most of these problems go away over time, but in rare cases normal bowel function does not return. To help lessen bowel problems, you may be told to follow a special diet during radiation therapy to help limit bowel movement during treatment. Sometimes a balloon-like device or gel is put between the rectum and the prostate before treatment to act like a spacer to lessen the amount of radiation that reaches the rectum.
Urinary problems: Radiation can irritate the bladder and lead to a condition called radiation cystitis. You might need to urinate more often, have a burning sensation while you urinate, and/or find blood in your urine. Urinary problems usually improve over time, but in some men they never go away.
Some men develop urinary incontinence after treatment, which means they cant control their urine or have leakage or dribbling. As described in the surgery section, there are different levels and types of incontinence. Overall, this side effect occurs less often with radiation therapy than after surgery. The risk is low at first, but it goes up each year for several years after treatment.
What Is Prostate Cancer
Check out this factsheet for a summary of the video.
Prostate cancer starts in the cells of the prostate. A cancerous tumour consists of cancer cells that can grow into nearby tissue and destroy it. The tumour can also spread to other parts of the body.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in Canadian men. It is most common in older men. It is more common in Black men than in white men, and it is less common in Asian men. Trans women and non-binary people who were assigned male at birth can also get prostate cancer.
The prostate is usually about the size of a walnut in younger men but can change as you age and grow larger in older men.
Prostate cancer usually grows slowly and can often be completely removed or successfully managed when it is diagnosed before it has spread outside of the prostate. Older men with prostate cancer often die of other causes. Adenocarcinoma of the prostate is the most common type of prostate cancer. It accounts for 95% of all prostate cancers.
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy
IMRT, an advanced form of 3D-CRT therapy, is the most common type of external beam radiation therapy for prostate cancer. It uses a computer-driven machine that moves around the patient as it delivers radiation. Along with shaping the beams and aiming them at the prostate from several angles, the intensity of the beams can be adjusted to limit the doses of radiation reaching nearby normal tissues. This lets doctors deliver an even higher radiation dose to the cancer.
Some newer radiation machines have imaging scanners built into them. This advance, known as image guided radiation therapy , lets the doctor take pictures of the prostate just before giving the radiation to make minor adjustments in aiming. This appears to help deliver the radiation even more precisely and results in fewer side effects.
A variation of IMRT is called volumetric modulated arc therapy . It uses a machine that delivers radiation quickly as it rotates once around the body. This allows each treatment to be given over just a few minutes. Although this can be more convenient for the patient, it hasnt yet been shown to be more effective than regular IMRT.
Don’t Miss: Are Eggs Good For Prostate Health
Transitional Cell Prostate Cancer
This is also known as urothelial carcinoma. This cancer starts in the cells that line the urethra .
Studies of men with transitional cell prostate cancer show that PSA levels can be low or high. More research is needed before we can know whether PSA tests can help to diagnose transitional cell prostate cancer.
Men with this cancer often have difficulty urinating and find blood in their urine. This is because the cancer grows around the urethra , causing it to narrow. So transitional cell carcinoma is often diagnosed when men have surgery called transurethral resection of the prostate to treat their urinary problems. Tissue removed during surgery is looked at under the microscope to confirm you have transitional cell prostate cancer. Youll also need scans to see if your cancer has spread.
If the cancer has not spread outside the prostate , then you may be offered surgery and radiotherapy.
If the cancer has spread to areas just outside the prostate or to more distant areas of the body such as the bones then chemotherapy and radiotherapy may be an option.
In the UK, docetaxel is the standard chemotherapy drug for men with advanced prostate cancer that is no longer responding to hormone therapy. But if you have transitional cell prostate cancer you may have other types of chemotherapy, called carboplatin or cisplatin chemotherapy. If you have cisplatin chemotherapy, you will probably have it alongside another chemotherapy drug called gemcitabine.
Study Identifies Five Different Types Of Prostate Cancer
For the first time, scientists have discovered prostate cancer can be categorized into five different types a finding that may prove to be game-changing, according to a new study.
The findings, published in the journal EBioMedicine, may have important clinical implication for the future. Doctors can now hope to identify which tumors are present in patients body and if they are likely to spread aggressively and grow.
This new knowledge could open up the path to more tailored cancer treatments.
Previously, prostate cancer could not be separated into subgroups. Due to this, treatments for the disease can often be inconsistent in effectiveness due to the wide range of reactions from patients.
Prof. Malcolm Mason, from Cancer Research UK, describes the difficulties of treating prostate cancer. He explains:
The challenge in treating prostate cancer is that it can either behave like a pussycat growing slowly and unlikely to cause problems in a mans lifetime or a tiger spreading aggressively and requiring urgent treatment. But at the moment we have no reliable way to distinguish them.
This means that some men may get treatment they do not need, he continues, causing unnecessary side effects, while others might benefit from more intensive treatment.
Prof. Mason says the findings could be game-changing if the same results are achieved in larger clinical trials. He explains:
Read Also: Can Enlarged Prostate Cause Retrograde Ejaculation
Diagnosing Rare Prostate Cancers
Rarer prostate cancers can be harder to diagnose. For example, some dont cause your prostate specific antigen level to rise. This means theyre not always picked up by a PSA test. Because of this, some rare cancers may not be diagnosed until they have already spread outside the prostate. Read more about the PSA test and other tests used to diagnose prostate cancer.
Some rare prostate cancers may only be picked up after having a biopsy to check for prostate cancer, or surgery called transurethral resection of the prostate to treat an enlarged prostate. The tissue removed during the biopsy or TURP is looked under a microscope to see if you have common prostate cancer or a rare type of prostate cancer. Rare cancers arent always given a Gleason score after a biopsy. This is because they can behave differently to common prostate cancer and cant be measured in the same way.
Because rare cancer can be aggressive and spread outside the prostate, you will probably have more tests to see if they have spread. These include:
What Are The Possible Treatment Options For Prostate Cancer
Staging is not the only information that doctors need. Symptoms and the patients age, life expectancy, co-existing health conditions and personal preferences may also be considered when deciding on treatment. Doctors use a general guideline for treatment based on stage groups.
Stage I prostate cancer:
Also Check: Can A Man Have Intercourse After Prostate Removal
It Is Hoped Treatments Can Attack Bacteria And Slow Down Development Of Disease
Researchers have identified five types of bacteria that are linked to aggressive prostate cancer. PA
Researchers have identified five types of bacteria that are linked to aggressive prostate cancer.
The bacteria was common in urine and tissue samples from men with the condition, a study found.
It is hoped the findings could help to pave the way for treatments that could attack this bacteria and slow or prevent the development of aggressive disease.
Scientists do not yet know how people pick up the bacteria, or whether they are causing the disease.
We already know of some strong associations between infections and cancer,” said project lead Prof Colin Cooper, from the University of East Anglias Norwich Medical School.
For example, the presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the digestive tract can lead to stomach ulcers and is associated with stomach cancer, and some types of the HPV virus can cause cervical cancer.
We wanted to find out whether bacteria could be linked to the way prostate cancer grows and spreads.
While prostate cancer is responsible for a large proportion of all male cancer deaths, it is more commonly a disease men die with rather than from.
And little is known about what causes some prostate cancers to become more aggressive than others.
We now have evidence that certain bacteria are involved in this and are part of the puzzle.
Signet Ring Cell Prostate Cancer
You might also hear this called signet cell prostate cancer or signet ring cell adenocarcinoma. Signet ring cell cancer can be very aggressive and spread to other parts of the body.
Like common prostate cancer, signet ring cell prostate cancer can produce high levels of PSA. This means a PSA test can be used to help diagnose signet ring cell prostate cancer. But a biopsy is needed to confirm it is a signet ring cell cancer.
If your biopsy shows that you have signet ring cell cancer, you may need further tests to check whether it started in your prostate or somewhere else. If your cancer started in another part of the body, it will affect the type of treatment you have. For example, if the cancer spread to the prostate from your stomach, you will be offered treatment for stomach cancer, not prostate cancer.
Your treatment will depend on how much the cancer has grown and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. You may be offered:
- or a combination of these treatments.
Your doctor or nurse will tell you what treatment options are available to you.
Don’t Miss: Is There Sex After Prostate Cancer Surgery
How Prostate Cancer Is Treated
In cancer care, different types of doctorsincluding medical oncologists, surgeons, and radiation oncologistsoften work together to create an overall treatment plan that may combine different types of treatments to treat the cancer. This is called a multidisciplinary team. Cancer care teams include a variety of other health care professionals, such as palliative care experts, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, oncology nurses, social workers, pharmacists, counselors, dietitians, physical therapists, and others.
The common types of treatments used for prostate cancer are described below. Your care plan may also include treatment for symptoms and side effects, an important part of cancer care.
Treatment options and recommendations depend on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, possible side effects, and the patients preferences and overall health.
Cancer treatment can affect older adults in different ways. More information on the specific effects of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy on older patients can be found another section of this website.
Because most prostate cancers are found in the early stages when they are growing slowly, you usually do not have to rush to make treatment decisions. During this time, it is important to talk with your doctor about the risks and benefits of all your treatment options and when treatment should begin. This discussion should also address the current state of the cancer:
Soft Tissue Prostate Cancer
Sarcomas comprise less than 0.1 percent of all primary prostate cancer cases, and develops in soft tissues. Soft tissue includes muscles and nerves. Although bones connect and support bodily structures, they are not considered soft tissue. Since soft tissue can be found all over the body, these cancers can develop and spread to just about anywhere. Although sarcomas can grow in the lymphatic vessels, blood vessels, and smooth muscles of the prostate, the most common place to find these once they break away and spread is in the lungs. The two most common prostate sarcomas include leiomyosarcomas and rhabdomyosarcomas, which can affect younger men between ages 35 and 60, however, extremely rare cases have been found in children. Prostate sarcomas are hard to detect and usually do not change PSA levels.3,5,6
Read Also: How To Perform Prostate Exam
Screening For Prostate Cancer
There are no tests available with sufficient accuracy to screen populations of men for early signs of prostate cancer. However, early detection and treatment can significantly improve prostate cancer survival.
The test most commonly used to aid early detection of prostate cancer is the prostate specific antigen blood test. This is not a diagnostic test as it can only indicate changes in the prostate. If you are concerned about prostate cancer you should talk to your doctor and make an informed choice about whether to have one of the tests designed to find early signs of prostate cancer, in view of the potential risks and benefits.
There are no proven measures to prevent prostate cancer.
Risk Factors You Cant Control
Age: The risk of developing prostate cancer increases with age. One in 10,000 men younger than 40 will be diagnosed with prostate cancer, but one in 15 men in their 60s will be diagnosed with the disease.
Family history: Being born with a gene mutation is one of the unavoidable risks of prostate cancer. Two of them include the BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations. BRCA and other inherited mutations, including HOXB13 and DNA mismatch repair genes, may explain why prostate cancer runs in families. Having a father or brother with prostate cancer may double a mans risk, especially if that relative was diagnosed before age 55.
Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia :
Race: Studies show that African-American men are about 70 percent more likely to develop prostate cancer in their lifetime than Caucasian or Hispanic men.
Also Check: Why Do Men Have A Prostate
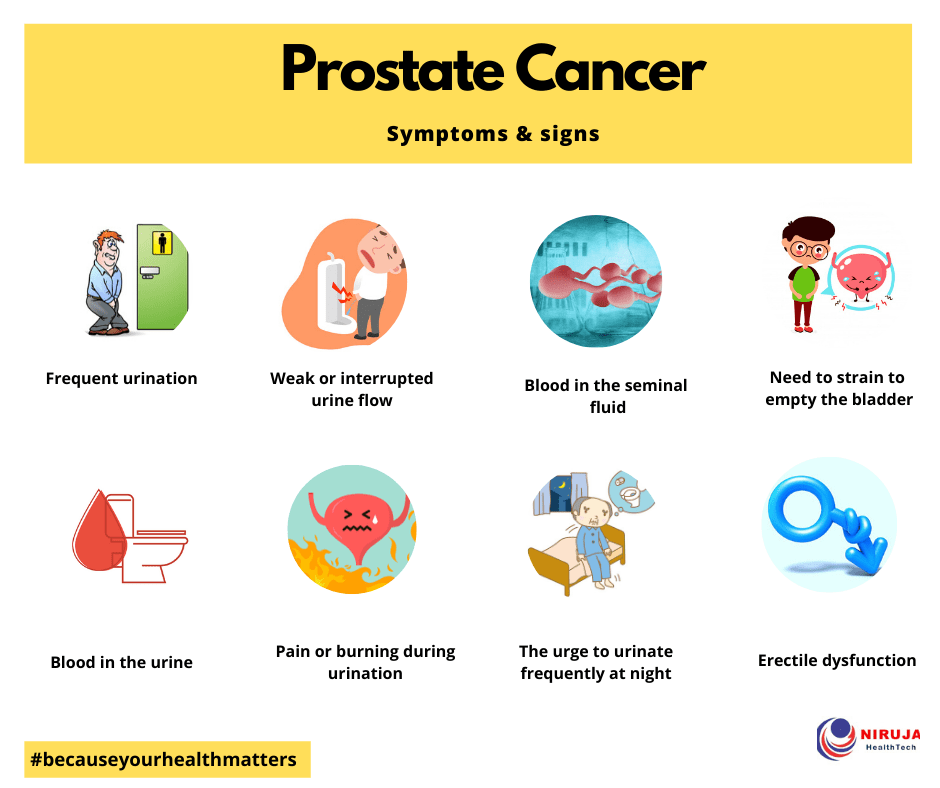
Advanced Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Men with advanced prostate cancer may experience additional symptoms. Thats because the cancer has spread from the prostate to other parts of the body, such as the bones or lymph nodes.
Signs of metastatic prostate cancer may include:
- Swelling in legs or pelvic area
- Numbness or pain in the hips, legs or feet
- Bone pain that persists or leads to fractures
A wide range of treatment options are available for managing advanced cancer. These treatments kill cancer cells, but they may also help patients manage pain.
Prostate cancer treatment: The care you need is one call away
Your multidisciplinary team will work with you to develop a personalized plan to treat your prostate cancer in a way that fits your individual needs and goals.
Basic Information About Prostate Cancer
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. When cancer starts in the prostate, it is called prostate cancer. Except for skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most common cancer in American men.
Many men with prostate cancerespecially those with tumors that have not spread beyond the prostatedie of other causes without ever having any symptoms from the cancer. Overall, about 96% of men who are diagnosed with prostate cancer are still alive five years later.
Cancer screening means looking for cancer before it causes symptoms. There is no standard test to screen for prostate cancer. Two tests that are commonly used to screen for prostate cancer are a prostate specific antigen test and a digital rectal examination .
Different types of treatment are available for prostate cancer. You and your doctor will decide which treatment is right for you.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Don’t Miss: Prostate Cancer Gleason Score 7 Life Expectancy
Genetic Testing For Prostate Cancer
You may hear a lot about genetics or genomics. Both terms are related to genes and cell DNA, but they are different. These tests are being used to learn more about the DNA of cancer cells, and link DNA mutations with treatments. In the future, genetic testing may be the first step doctors take when diagnosing prostate cancer.
About The Prostate And Prostate Cancer
The prostate gland, which grows during puberty, is considered an organ and is made up of several dozen lobules or saclike glands, held together with connective prostate tissue and muscle between them. The glands are called exocrine glands, because they secrete liquid to outside the body.
An enlarged prostate, called benign prostatic hyperplasia , is common in men over the age of 40 and may obstruct the urinary tract. The abnormal prostate cell growth in BPH is not cancerous and doesnt increase your risk of getting prostate cancer. However, symptoms for BPH and prostate cancer can be similar.
A condition called prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia , where prostate gland cells look abnormal when examined under a microscope, may be connected to an increased risk of prostate cancer. Prostate cancer is often caught by a doctor performing a digital rectal exam , through a prostate-specific antigen blood test, through a prostate biopsy or with a CT scan.
Another condition, prostatitis, is the inflammation of the prostate. While not cancerous, it may cause higher PSA levels in the blood.
When prostate cancer is found, pathologists stage the disease using a Gleason score, which grades the extent and arrangement of the cell mutations. For instance, a Gleason score of 6, the lowest possible, indicates a low-grade tumor, while cancers with scores of 9 or 10 are considered high-grade or the most aggressive and most likely to spread.
Also Check: Can The Prostate Be Checked During A Colonoscopy
