Index To Diseases And Injuries
The Index to Diseases and Injuries is an alphabetical listing of medical terms, with each term mapped to one or more ICD-10 code. The following references for the code C61 are found in the index:
- – Adenocarcinoma – See Also: Neoplasm, malignant, by site
- – Cystadenocarcinoma – See: Neoplasm, malignant, by site
- – endometrioid – See: Neoplasm, malignant, by site
- – male – C61
After Prostate Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Prostate Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within theprostate or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The results of the tests used to diagnoseprostate cancer are often also used to stage the disease. In prostate cancer, staging tests may not be done unless the patient has symptoms or signs that the cancer has spread, such as bone pain, a high PSA level, or a high Gleason score.
The following tests and procedures also may be used in the staging process:
Symptoms Of Malignant Neoplasm Cancer
Unlike other ailments, the symptoms or indicative signs of cancer vary widely depending on a variety of factors like the cancer type, cancer stage, etc. Not only that, the symptoms vary from individual to individual and may also be totally absent until cancer has reached a very advanced stage. However, in case of critical cancers like brain cancer, the symptoms may start exhibiting at the very early stages. Though several symptoms are cancer-type specific, yet an uncontrolled growth of cells leads to certain common problems that may be considered as the typical cancer symptoms which may be indicative of malignant neoplasm. Some symptoms and signs that you need to look out for are:
- Unusual bleeding
- Hoarse voice caused due to continued coughing
- Appetite loss or weight loss
- Continued feelings of vomiting, nausea, and fatigue
- Pain in one or more body parts that occurs intermittently and is usually worse
- Intermittent fevers for no obvious reason
- Recurring infections
- Changes in moles and warts
Don’t Miss: Prostate Health Beta Plus Side Effects
About The Prostate And Prostate Cancer
The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system and produces fluid that mixes with semen during ejaculation to help sperm travel. The prostate is a walnut-sized, rubbery organ that surrounds the urethrathe urinary duct that carries urine from the bladder out of the bodyand sits directly below the bladder.
The prostate gland, which grows during puberty, is considered an organ and is made up of several dozen lobules or saclike glands, held together with connective prostate tissue and muscle between them. The glands are called exocrine glands, because they secrete liquid to outside the body.
An enlarged prostate, called benign prostatic hyperplasia , is common in men over the age of 40 and may obstruct the urinary tract. The abnormal prostate cell growth in BPH is not cancerous and doesnt increase your risk of getting prostate cancer. However, symptoms for BPH and prostate cancer can be similar.
A condition called prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia , where prostate gland cells look abnormal when examined under a microscope, may be connected to an increased risk of prostate cancer. Prostate cancer is often caught by a doctor performing a digital rectal exam , through a prostate-specific antigen blood test, through a prostate biopsy or with a CT scan.
Another condition, prostatitis, is the inflammation of the prostate. While not cancerous, it may cause higher PSA levels in the blood.
Early Stage Prostate Cancer
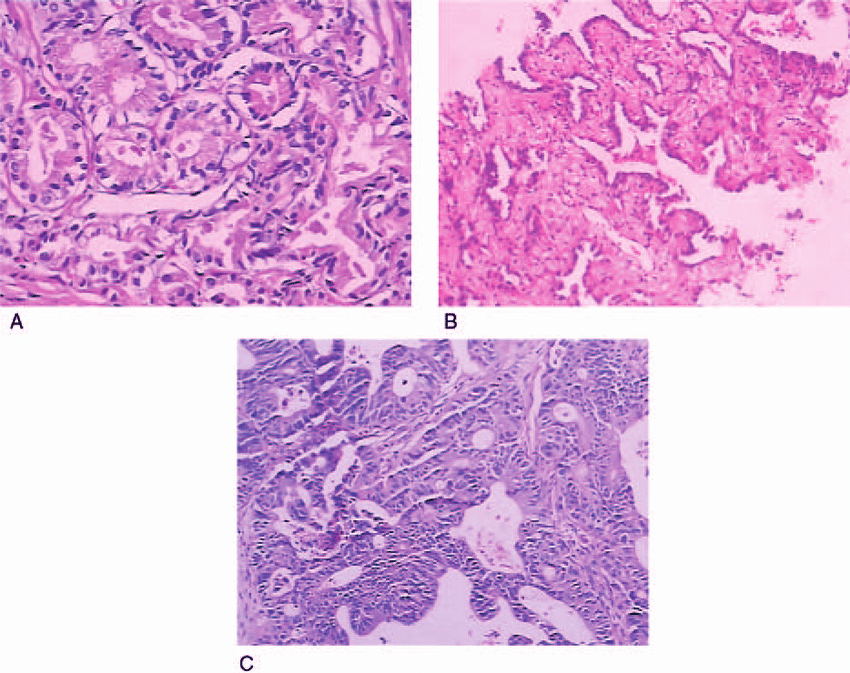
If the cancer is small and localized, a doctor may recommend:
Watchful waiting or monitoring
The doctor may check PSA blood levels regularly but take no immediate action.
Prostate cancer grows slowly, and the risk of side effects may outweigh the need for immediate treatment.
Surgery
A surgeon may carry out a prostatectomy. They can remove the prostate gland using either laparoscopic or open surgery.
Radiation therapy
Options include:
Brachytherapy: A doctor will implant radioactive seeds into the prostate to deliver targeted radiation treatment.
Conformal radiation therapy: This targets a specific area, minimizing the risk to healthy tissue. Another type, called intensity modulated radiation therapy, uses beams with variable intensity.
Treatment will depend on various factors. A doctor will discuss the best option for the individual.
Read Also: Cialis For Prostatitis
What Is The Prognosis Of Malignant Neoplasm Of Prostate
The overall prognosis of a patient with Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate depends on the age, overall health of the patient, and stage of the disease process. In majority of the cases where the disease is diagnosed early the prognosis is extremely good. Since this is a slow growing tumor, even if the diagnosis is made a bit late with adequate treatments the prognosis for the patient overall is fair to good post treatment of Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate.
| Written, Edited or Reviewed By:Pramod Kerkar, M.D., FFARCSI, DA Pain Assist Inc.This article does not provide medical advice. See disclaimerLast Modified On: January 2, 2018 |
Active Surveillance Of Prostate Cancer
Active surveillance is a management option for localized that can be offered to appropriate patients who would also be candidates for aggressive local therapies , with the intent to intervene if the disease progresses. Active surveillance should not be confused with , another observational strategy for men that would not be candidates for curative therapy because of a limited life expectancy. Active surveillance offers men with a prostate cancer that is thought to have a low risk of causing harm in the absence of treatment, a chance to delay or avoid aggressive treatment and its associated side effects.While prostate cancer is the most common non cutaneous cancer and second leading cause of cancer-related death in American men, it is conservatively estimated that approximately 100,000 men per year in the United States who would be eligible for conservative treatment through active surveillance, undergo unnecessary treatments. The management of localized prostate cancer is controversial and men with localized disease diagnosed today often undergo treatments with significant side effects that will not improve overall health outcomes. The 2011 NIH State-of-the-Science Conference Statement on the “Role of active surveillance in the management of men with localized prostate cancer” pointed out the many unanswered questions about observational strategies for prostate cancer that require further research and clarification. These included:
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Talk With Your Doctor
Prostate cancer is a risk for all men as they age, but if its caught and treated early, the outlook is generally very good. So as you get older, be sure to have open conversations with your doctor about your risk.
If you have any symptoms you think might be prostate cancer, talk to your doctor right away. And even if you dont have symptoms, consider adopting a healthy lifestyle to decrease your risk.
Malignant And Benign Neoplasm
A malignant, or cancerous, tumor, on the other hand, is innately dangerous because its cells can divide uncontrollably and produce virtually immortal daughter cells. Malignant tumor cells can penetrate and destroy adjacent tissue, and can metastasize, or travel through the circulation to distant parts of the body and form new tumors. If the cells are not cancerous, the tumor is benign. It wont invade nearby tissues or spread to other areas of the body . A benign tumor is less worrisome unless it is pressing on nearby tissues, nerves, or blood vessels and causing damage. Fibroids in the uterus or lipomas are examples of benign tumors.
You May Like: Perineural Invasion Prostate Cancer
What Is Malignant Neoplasm
Simply explained, malignant neoplasm or cancer is the uncontrollable, abnormal growth of cells within the human body. Such cells are commonly known as tumor cells, malignant cells or cancer cells. These cells are quite different in characteristics as compared to normal cells and can attack different body parts, organs, vessels, etc. This abnormal cell growth can be triggered by a number of factors and can occur at almost any area of the body. Moreover, the cells can also travel to other areas of the body and induce uncontrolled growth in those areas.
Functional Outcomes And Quality Of Life After Treatment For Localized Prostate Cancer
At 15 years after treatment of localized prostate cancer diagnosed in 1994-1995, declines in urinary, sexual, and bowel function were common. These functional declines in quality of life occur to a significantly greater extent among those that undergo treatment for prostate cancer as compared to a normative aging population without a diagnosis of prostate cancer, and symptom distress is more common among men with prostate cancer that are treated compared to those not treated. In a contemporary study of quality of life after treatment for localized prostate cancer, the authors reported that a substantial proportion of men did not return to baseline function in the domains of bowel, sexual, and urinary function that changes in quality of life domains were treatment specific and that patient and partner outcome satisfaction were closely associated with changes in quality of life after treatment. Thus, treatment for prostate cancer commonly results in quality of life changes that affect both the patient and his partner.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Prostate Cancer That Has Spread To Bones
Effects On Pituitary System
commonly develops after radiation therapy for sellar and parasellar neoplasms, extrasellar brain tumours, head and neck tumours, and following whole body irradiation for systemic malignancies. Radiation-induced hypopituitarism mainly affects and . In contrast, and deficiencies are the least common among people with radiation-induced hypopituitarism. Changes in -secretion is usually mild, and vasopressin deficiency appears to be very rare as a consequence of radiation.
How Is Malignant Neoplasm Of Prostate Treated
As Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate are a very slow growing tumors, a diagnosis is not made until the patient is in his 70s. In such conditions, the treatment option is to just observe through frequent blood work checking for levels of PSA.
In cases of younger patients, the treatment approach depends on the extent or stage of the disease and includes radiation therapy which may involve external beam radiation. Another option is implantation of radioactive seeds in the prostate, and proton therapy.
There are also surgical options available for treatment of Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate. These include radical prostatectomy in which the tumor is removed completely either through an open technique or utilizing robotic approach.
Hormone therapy is also used as a treatment for Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate. This therapy is aimed at decreasing the levels of testosterone which facilitates growth of tumor
Chemotherapy. This is followed by chemotherapy to kill any cancer cells that may have been left behind to complete the treatment for Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate.
You May Like: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Prostate Cancer
Because prostate cancer tends to grow slowly, most men die from something other than the disease. Early detection is key to better outcomes. Almost all men 97% to 98% diagnosed with localized cancer that hasnt spread outside of the prostate live at least five years after diagnosis. When metastatic cancer has spread outside of the gland, one-third of men continue to survive after five years.
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if prostate cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually prostate cancer cells. The disease is metastatic prostate cancer, not bone cancer.
Denosumab, a monoclonal antibody, may be used to preventbone metastases.
Recommended Reading: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast
Breast tumors are classified by several factors including the size of the tumor and the stage that it has reached when it is detected. Breast tumors are measured from stage 0 through stage 4, with stage 4 tumors being the most advanced. The grade of the tumor is also looked at and this measures how the cells have differentiated themselves. Breast cancer is caused by the development of malignant cells in the breast. The malignant cells originate in the lining of the milk glands or ducts of the breast , defining this malignancy as a cancer.
Can Prostate Cancer Be Prevented
There are no clear prevention strategies for prostate cancer. There is some conflicting evidence that a healthy diet composed of low fat, high vegetables and fruits may help reduce your risk of prostate cancer. Routine screening, with PSA blood test and physical exam, is important to detect prostate cancer at an early stage. A healthy diet and regular exercise are also critical in maintaining good health and preventing disease in general.
Read Also: How To Stimulate Prostate Gland
Neoplasm Of Breast Prostate Colon Skin
Learn all about neoplasm of breast, prostate, colon and skin. A tumor is an abnormal growth of cells that serves no purpose. A benign tumor is not a malignant tumor, which is cancer. It does not invade nearby tissue or spread to other parts of the body the way cancer can. In most cases, the outlook with benign tumors is very good. But benign tumors can be serious if they press on vital structures such as blood vessels or nerves.
Tumors are of two types, benign or malignant. A benign tumor is not considered cancer. It is slow growing, does not spread or invade surrounding tissue, and once it is removed, doesnt usually recur. A malignant tumor, on the other hand, is cancer. It invades surrounding tissue and spreads to other parts of the body. If the cancer cells have spread to the surrounding tissues, even after the malignant tumor is removed, it generally recurs.
An abnormal tissue that grows by cellular proliferation more rapidly than normal and continues to grow after the stimuli that initiated the new growth cease is called a neoplasm. Neoplasms show partial or complete lack of structural organization and functional coordination with the normal tissue, and usually form a distinct mass of tissue that may be either benign or malignant .
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have prostate cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get prostate cancer?
- What is my Gleason score? What is my Grade Group? What do these numbers mean for me?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the prostate gland?
- What is the best treatment for the stage of prostate cancer I have?
- If I choose active surveillance, what can I expect? What signs of cancer should I look out for?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Is my family at risk for developing prostate cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Prostate cancer is a common cancer that affects males. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and remain in the prostate gland. For a small number, the disease can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. Men with slow-growing prostate cancers may choose active surveillance. With this approach, you can postpone, and sometimes completely forego, treatments. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for you based on your Gleason score and Group Grade.
You May Like: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Are There Any New Developments In The Treatment Of Prostate Cancer
Doctors often successfully treat prostate cancer. Sometimes, however, the disease returns . An FDA-approved radiotracer for PET/CT called Axumin® helps detect and locate cancer that recurs following radiation therapy or surgery.
Conventional imaging, such as MRI or ultrasound, cannot locate recurring prostate cancer when it is small. PET/CT with Axumin® can detect recurring cancer when PSA levels are low and when the cancer is small.
Identifying the exact location and extent of the disease at an early state is vital. It allows doctors to specifically target the cancer and limit exposure to healthy tissues.
Prostate-specific membrane antigen is a protein that helps develop prostate cancer. A PSMA scan uses PET imaging and a radiotracer to locate recurrent cancer. Doctors are studying Lutetium-177 PSMA therapy in clinical trials for use in treating prostate cancer. Neither of these procedures has FDA approval yet. For more information about the clinical trials, visit .
History Of Untreated Prostate Cancer
The course of prostate cancer in the absence of treatment has been evaluated both in observational studies and randomized trials. Most of the evidence on the outcomes of men that are not treated for prostate cancer comes from those diagnosed in the era prior to when the disease was diagnosed at a more advanced state.
You May Like: Prostate 5xl
Factors Influencing Health Status And Contact With Health Servicesnote
