Annual Report On Prostate Diseases
Most men eventually develop some type of prostate problem, and when they do there are usually no easy solutions. More than a primer on prostate conditions, this Special Health Report, the Annual Report on Prostate Diseases, includes roundtable discussions with experts at the forefront of prostate research, interviews with men about their treatment decisions, and the latest thinking on complementary therapies. This report will provide you with the information you need to understand the current controversies, avoid common pitfalls, and work with your doctor to make informed choices about your prostate health.
Thanks for visiting. Dont miss your FREE gift.
The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness, is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School
Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health, plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise, pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School
Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight lossfrom exercises to build a stronger core to advice on treating cataracts. PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts.
BONUS! Sign up now and get a FREE copy of theBest Diets for Cognitive Fitness
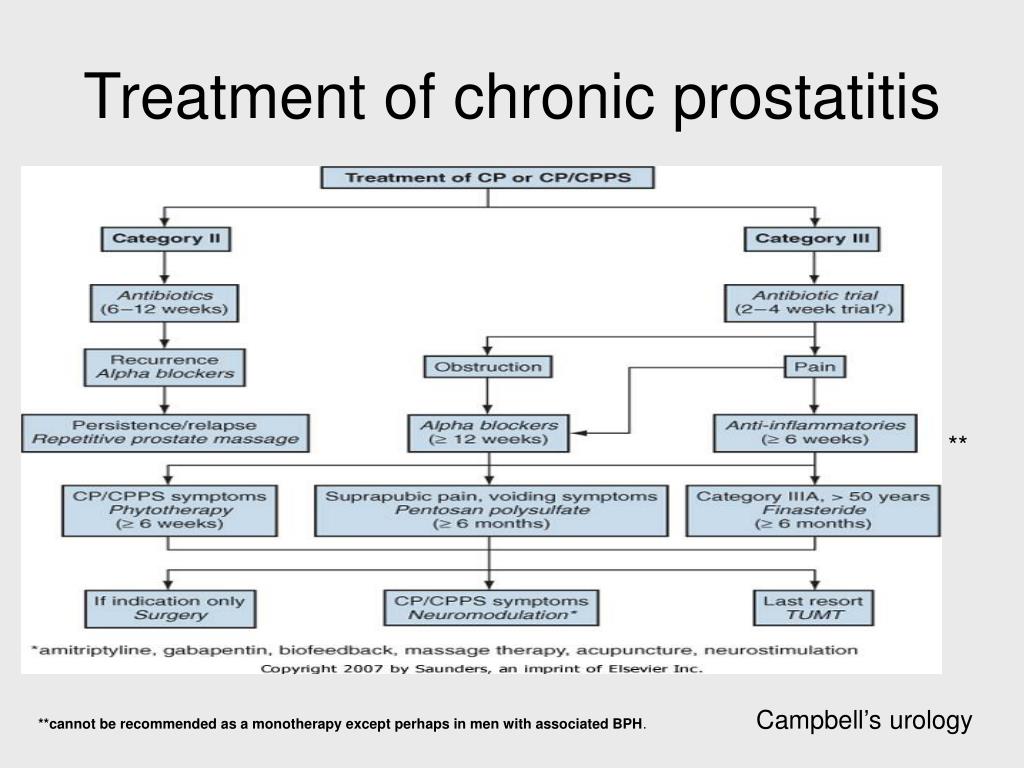
Chronic Prostatitis: Approaches For Best Management
Department of Urology, Dongguk University School of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea.
Corresponding Author: Kyung Seop Lee. Department of Urology, Dongguk University Gyeongju Hospital, Dongguk University School of Medicine, 87, Dongdae-ro, Gyeongju, 780-350, Korea. TEL: +82-54-770-8266, FAX: +82-54-770-8121,
How Is Prostatitis Treated
The treatment is based on the cause. Your doctor may do a rectal exam and test urine samples to find out the cause.
An antibiotic is used to treat prostatitis that is caused by an infection. Some antibiotics that might be used are trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxin. You might have to take antibiotics for several weeks or even a few months. If prostatitis is severe, you might have to go to a hospital for treatment with fluids and antibiotics.
Don’t Miss: Are There Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
How is it treated?
Treatment varies from man to man just like CPPS does. The treatments will help to control your symptoms and might even get rid of your CPPS completely. But CPPS could return weeks, months or even years later. You may have to try a few things until you find something that works well for you. Youll probably try more than one of the following:
- treatment for pain
- other treatments.
Each person will respond to treatments differently. If one doesnt work, you should be able to try something else. Your treatment may be managed by your GP or by a urologist at the hospital. You may also see a specialist nurse, or a sexual health specialist.
Medicines
There is some evidence that certain medicines can help improve prostatitis symptoms. Your GP or urologist may prescribe one or a combination of the following medicines.
All medicines carry a risk of side effects. Ask your doctor for more information about the different treatments, and whether they might be suitable for you.
Names of medicines
Medicines often have two different names a scientific or generic name and a brand name. For example, the alpha-blocker tablet tamsulosin is the scientific or generic name for the drug. Flomaxtra® and Diffundox® are examples of different brand names. The brand name is given to the drug by the company that makes it. Ask your doctor or nurse if you have any questions about your medicines, or speak to our Specialist Nurses.
Counselling
Exercises and physical activity
Treating Bacterial Prostatitis By Type

Bacterial infection can cause two types of prostatitisacute and chronic .
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
The main treatment for acute bacterial prostatitis is the use of antibiotics to kill the bacteria. Depending on the antibiotic and the type of bacteria, this treatment can last anywhere from several weeks to a few months. Escherichia coli infections are one of the most common causes, with this species of bacteria found in 65 to 80 percent of cases.
Severe infections may require hospitalization for monitoring and additional antibiotics. In addition, the infection can cause the prostate to grow bigger and block the urethra, the tube that removes urine from the body. Such blockages are especially important to treat so as to prevent urine from backing up in the urinary tract and damaging the kidneys.
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
With chronic bacterial prostatitis, bacteria can linger in the prostate even after treatment about 5 percent of men with acute bacterial prostatitis end up with the chronic type. E. coli has been implicated in chronic prostatitis, too, as has a species of Corynebacterium. When these bacteria hang around, they can also cause occasional urinary tract infections.
Also Check: Green Tea Prostate Cancer Prevention
How Do You Treat The Chronic Prostatitis
Azithromycin is the drug of choice for chronic prostatitis. Givea loading dose of one gram then 500 mg twice a day for two to threeweeks. For men less than 60 Kg weight, you should give 750 mg perday. You have to give tablet serratiopeptidase 10 mg three times aday for the same period or three more days. Tablet Satronidazole300 mg twice a day should be added to cover the anaerobic bacteria.The drug has to be given for about two weeks. You can give tabletCiprofloxacin 500 to 750 mg twice a day for three weeks instead ofAzithromycin. Some multivitamin preparation should be given twice aday. Daily cleansing of the prostate gland by way of ejaculationwill greatly help to cure the chronic prostatitis. This is notnecessary and is not possible for elderly men, who are not activesexually.
How Are Bacterial Forms Of Prostatitis Managed Or Treated
Antibiotics can kill bacteria that cause bacterial types of prostatitis. Men with acute bacterial prostatitis may need 14 to 30 days of antibiotics, starting with IV antibiotics in the hospital. Rarely, men need surgery to drain an abscess on the prostate.
Treating chronic bacterial prostatitis is challenging. You may need up to three months of antibiotics to sterilize the prostate. If the prostate cant be sterilized, low-dose antibiotics can be used long term to prevent recurrences. Some men need surgery to remove prostate stones or scar tissue in the urethra. Rarely, surgeons remove part or all of the prostate gland .
You May Like: Aneros Helix Trident Prostate Massager
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of prostatitis, such as pelvic pain, difficulty or pain when peeing, or painful ejaculation.
They’ll ask about the problems you’re having and examine your tummy.
You may also have a rectal examination. This is where a doctor inserts a gloved finger into your bottom to feel for anything unusual. You may have some discomfort during this examination if your prostate is swollen or tender.
Your urine will usually be tested for signs of infection, and you may be referred to a specialist for further tests to rule out other conditions.
See a GP straight away if you get sudden and severe symptoms of prostatitis.
You may have acute prostatitis, which needs to be assessed and treated quickly because it can cause serious problems, such as suddenly being unable to pee.
If you have persistent symptoms , you may be referred to a doctor who specialises in urinary problems .
What Are The Risk Factors For Chronic Nonbacterial Prostatitis
The cause of chronic nonbacterial prostatitis is unknown. This makes it difficult to predict who is at risk for this condition. However, research into the cause is ongoing. Once a cause is discovered, doctors will be able to identify risk factors and target treatment.
request a urine sample to look for infection.
During a prostate exam, your doctor will insert a lubricated, gloved finger into your rectum. They do this so they can feel for a tender, soft, or swollen prostate, which indicates inflammation or infection. Depending on the results of your exam, your doctor may perform the following:
- prostate ultrasound
- tests to rule out a sexually transmitted infection
- studies to evaluate urine flow
- further evaluation of the urinary tract
Don’t Miss: What Is The Prostate For
What Research Is Being Done
Researchers are trying to find out more about prostatitis so that they can develop better treatments.
Theyre looking into the causes of CPPS and why it affects men differently. This includes looking at the genes involved. A better understanding of the causes will mean that, in the future, treatments can be tailored to suit each man.
Theyre also looking into different treatments. These include a number of medicines, botox, surgery, and using small electrical currents to reduce pain.
Another area of research is looking at ways to help men live with CPPS, such as cognitive behavioural therapy , and ways men can take more control themselves such as with diet and supplements.
At the moment, most of the research is happening in other countries, but if youre interested in taking part in a clinical trial, mention this to your doctor. There might be trials you can join in the future.
Diagnosing Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
To make a diagnosis, your doctor will review your medical history and perform a physical exam to look for swollen lymph nodes near the groin or fluid discharge from the urethra.
Your doctor will also perform a digital rectal exam to examine the prostate. During this test, they will insert a lubricated and gloved finger into your rectum to look for signs of infection, such as a soft or enlarged prostate.
Your doctor may also use the following tests and techniques:
Antibiotics are the main course of treatment for this condition. Theyre usually taken for 4 to 12 weeks. For many people, treatment will last for 6 weeks.
First-line treatment is typically a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, such as ciprofloxacin , ofloxacin, or levofloxacin.
However, fluoroquinolones can increase your risk for a ruptured Achilles tendon, which is why they are no longer considered a preferred treatment.
Other commonly prescribed antibiotics include:
- sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim , another first-line treatment
- tetracycline antibiotics, such as doxycycline or azithromycin
Tetracyclines are commonly used in cases where a doctor identifies or suspects chlamydia or mycoplasma genitalium. Like chlamydia, mycoplasma genitalium is an STI.
The antibiotic that youre prescribed will ultimately depend on which bacterium is causing your prostatitis.
You May Like: What Is The Best Medicine For Prostate
How Can I Clean My Prostate
10 diet & exercise tips for prostate health Eat at least five servings of fruits and vegetables every day. Choose whole-grain bread instead of white bread and choose whole-grain pasta and cereals. Limit your consumption of red meat, including beef, pork, lamb, and goat, and processed meats, such as bologna and hot dogs.
When To Seek Medical Care
A person may have urinary symptoms unrelated to prostatitis that are caused by bladder problems, UTIs, or benign prostatic hyperplasia. Symptoms of prostatitis also can signal more serious conditions, including prostate cancer.
Men with symptoms of prostatitis should see a health care provider.
Men with the following symptoms should seek immediate medical care:
- complete inability to urinate
Recommended Reading: Rezum Steam Treatment For Prostate
How To Manage An Enlarged Prostate
About half of intact male dogs will develop some form of prostate disease by the age of 5, and 95% by the age of 9. And even neutered dogs are not spared from this. Male dogs of any size, from middle-aged to senior, can experience an enlarged prostate.
Heres what you need to watch for and what you can do if your dog experiences prostate problems.
Symptoms Of Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Bacterial infections in the prostate can be very painful.
The symptoms begin slowly and last 3 months or longer. Seek medical attention if you have any of the following symptoms:
Serious complications can arise if an infection isnt properly treated. Complications include:
- urinary retention, which is an inability to urinate
- , which occurs when bacteria spread into the bloodstream
- a prostate abscess, which is a collection of pus that causes inflammation
A bacterial infection causes chronic bacterial prostatitis. Even when the primary symptoms of infection have been treated, bacteria may continue to thrive in the prostate.
Causes of infection include:
- sexually transmitted infections , such as chlamydia and gonorrhea
- E. coli after having an infection of the testicles, urethritis , or a UTI
Certain factors put people at risk for developing this condition, such as:
Don’t Miss: What Os The Function Of The Prostate
Treating Prostatitis Not Caused By Infection
Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis, also known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome , is inflammation of the prostate without any detectable infection. The cause is unknown, making it difficult to treat.
Even though no bacteria are implicated in this kind of prostatitis, a physician will sometimes prescribe antibiotics in case there is a hidden infection. Most often, however, therapy involves treating the symptoms. Options include:
- Over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen or naproxen
- Soaking in a hot bath
- Medications such as phenazopyridine , oxybutynin, or tolterodine to help with frequent, urgent, or painful urination
- Psychological counseling to help with the ongoing pain
When To Seek Medical Care For Prostate Infections
Contact a doctor for any of the following symptoms. These symptoms are even more significant if accompanied with high fever and chills:
- Urinary burning or pain
- Difficulty or pain when starting urination
- Pain in the genital area
- Pain with ejaculation
Doctors usually diagnose and treat prostate infections on an outpatient basis. If a person develops high fever with chills or a new onset of difficulty in urinating, seek medical care immediately or go to a hospitals emergency department because the infection may be spreading to other areas of the body.
Don’t Miss: What Causes A Man To Have Prostate Problems
How Do Doctors Diagnose A Prostate Infection
The diagnosis of both acute and chronic prostate infections begins with the history of the symptoms described above, the physical exam, including the digital exam of the prostate and often confirmed by culture and identification of the infecting organism.
Acute bacterial prostatitis diagnosis
- Usually an enlarged, firm, and tender prostate is enough to make a presumptive diagnosis and start treatment .
- Because there is usually a low level of bacteria in urine, the doctor will perform a urinalysis to quantitate and identify infecting bacteria by urine culture.
- If the person has symptoms suggesting the infection has spread outside the prostate , blood cultures and other blood tests are likely to be ordered.
- If a spread of the infection is suspected, a doctor will often perform an ultrasound to help confirm the diagnosis and to rule out an abscess. If this ultrasound is not available, the doctor may perform a CT scan or MRI of the pelvis.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis diagnosis
One of two tests are sometimes performed to help with the diagnosis:
The classic test is a Meares-Stamey 3-glass test. Three separate urine samples are collected and examined during this test. The last sample is taken after prostatic massage.
Premassage and postmassage test
Men with recurrent urinary tract infections should have ultrasound imaging of their upper urinary tract and a plain abdominal X-ray or an intravenous urography to exclude a possible structural problem or a kidney stone.
How Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treated
Patients who have mild symptoms may not require treatment other than continued observation to make sure their condition doesnt get worse. This approach is sometimes called watchful waiting or surveillance. There are a number of treatment options available if your symptoms are severe.
Medications
Finasteride and dutasteride work by decreasing the production of the hormone dihydrotestosterone , which affects the growth of the prostate gland. These appear to be most beneficial for men with larger prostates.
Drugs that relax the muscle in the prostate are more commonly used. These include terazosin , doxazosin , tamsulosin , alfuzosin , and silodosin . The most common side effects are lightheadedness, weakness and retrograde ejaculation.
Medications are sometimes combined to help treat symptoms and improve the flow of urine. One such medication is dutasteride and tamsulosin .
Surgery
Several different types of surgery can be used to remove the prostate tissue that blocks the flow of urine, including:
Minimally invasive treatments
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/10/2020.
References
You May Like: Foods That Irritate The Prostate
Also Check: What Is The Latest Prostate Surgery Technique
You Dont Have To Put Up With Symptoms Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Thanks To These Treatment Options
You may find the symptoms of an enlarged prostate unpleasantfrequent urination is among the most commonbut do they require treatment? It depends on the severity of your symptoms. Up to one-third of mild benign prostatic hyperplasia cases clear up without any treatment at all, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases .
If your enlarged prostate symptoms are more severe, or they cause frequent urinary tract infections or other complications, work with a urologist for relief. These are some of your options to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia:
- Use of an electrical current to vaporize tissue
- Heating tissue directly with needles
- Heating tissue indirectly with microwave energy
- Using a laser or focused ultrasound to destroy tissue
- Using a stent to keep the urethra open
Traditional surgical techniques include cutting away prostate tissue, making incisions in the bladder neck to relieve pressure in the gland, or completely removing the tissue .
Drug and surgical treatments for enlarged prostate come with potential side effects, including a small risk for erectile dysfunction. Be sure to discuss possible side effects with your healthcare provider as you weigh the benefits of different BPH treatments.
Recommended
Also Check: Vitamin D And Prostate Cancer Prevention And Treatment
Quick Answer: How Do You Treat Nonbacterial Prostatitis

Treatment Long-term antibiotics to make sure that the prostatitis is not caused by bacteria. Drugs called alpha-adrenergic blockers help relax the muscles of the prostate gland. Aspirin, ibuprofen, and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , which may relieve symptoms for some men.
Recommended Reading: How To Lower The Risk Of Prostate Cancer
