Treatments For Symptom Relief
The preferred treatment regimen for chronic bacterial prostatitis is a combination of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs .
Although NSAIDs can provide relief from the pain of prostatitis, theyre primarily used to reduce inflammation.
Other medications you may receive are:
- stool softeners to avoid constipation
- alpha-blocker medications, such as tamsulosin , to help treat urinary retention
Certain home remedies may be able to ease your symptoms too. Home remedies include:
- warm baths
- avoiding alcohol, caffeine, citrus juices, and hot and spicy food
Symptoms Of Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Bacterial infections in the prostate can be very painful.
The symptoms begin slowly and last 3 months or longer. Seek medical attention if you have any of the following symptoms:
Serious complications can arise if an infection isnt properly treated. Complications include:
- urinary retention, which is an inability to urinate
- , which occurs when bacteria spread into the bloodstream
- a prostate abscess, which is a collection of pus that causes inflammation
A bacterial infection causes chronic bacterial prostatitis. Even when the primary symptoms of infection have been treated, bacteria may continue to thrive in the prostate.
Causes of infection include:
- sexually transmitted infections , such as chlamydia and gonorrhea
- E. coli after having an infection of the testicles, urethritis , or a UTI
Certain factors put people at risk for developing this condition, such as:
Is Prostatitis A Sexually Transmitted Disease
Yes, prostatitis can be contracted through sex, so the more sexual partners a man has, the higher his odds of developing the condition. 34567
Interestingly, Trichomonas vaginalis, a parasite and STD, has been found in prostate biopsies of men with prostatitis, and although it seems that E. Coli is a much more regular culprit, the prostates susceptibility to Trichomonas vaginalis colonization has been linked to zinc levels. The prostate is the number one home for zinc in a mans body, and when levels get low, studies have shown these types of pathogens can take a greater foothold.
Mineral deficiencies are common in the U.S., which means supplementing with small amounts of zinc to see whether conditions improve could be worthwhile. As far as food is concerned, pumpkin seeds and oysters are both high in zinc.
As an added benefit, zinc supplementation has also shown some promise in maintaining the cell lining of the gut, which can prevent or help to heal leaky gut, a condition that often accompanies prostatitis, and that is marked by a breakdown of the epithelial wall of the gut lining, which allows pathogens and undigested food particles to enter the blood stream. 89 I will touch more on leaky gut later in this post.
Don’t Miss: How To Get To A Man’s Prostate
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Could my symptoms be caused by something other than prostatitis?
- How do I know if an STD caused my prostatitis?
- How long do I need to take medicine?
- Are there any side effects from treatment?
- Should I avoid having sex while I have prostatitis?
- Is there anything I can do to avoid getting prostatitis again?
Are There Any Risk Factors For Prostatitis
Any man can develop prostatitis, but as with many medical conditions, some men are at higher risk than others. Risk factors for developing prostatitis include:
- Being under the age of 50
- Having a , or an infection in the urethra or the epididymis, the tube that carries semen
- Trauma to the pelvic region, such as an injury from cycling
- Previous episodes of prostatitis
- Having a urinary catheter to drain urine from your bladder
- HIV/AIDS
You May Like: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
Treating Prostatitis: Any Cause For Optimism
Michael P. OLeary, M.D., M.P.H., looks at what may be ahead
Prostatitis gets little press, but its an all-too-common genitourinary condition in men. It accounts for about 1.8 million visits to the doctors office in the United States each year. Depending on how you define the term, 9% to 16% of men experience prostatitis. Its also an equal opportunity disorder. Unlike benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer, which predominantly affect older men, prostatitis affects men of all ages.
Despite its commonness, little is known about what sparks prostatitis or, more importantly, how to treat it. Frustrated patients visit one doctor after another in search of a remedy, but they usually leave disappointed. Relative to other prostate conditions, little research has been conducted on prostatitis. But a few bright spots may be emerging.
Clinical Presentation And Diagnostic Evaluation
ABP typically presents abruptly with voiding symptoms and distressing but poorly localized pain and is often associated with systemic findings . Clinicians should enquire about urogenital disorders, recent genitourinary instrumentation, and new sexual contacts. Only 5% of men with ABP develop CBP, and 2% develop a prostatic abscess. CBP usually presents with more-prolonged urogenital symptoms. The hallmark is relapsing UTI , but <50% of patients with CBP have this history . Between symptomatic UTIs, patients may be asymptomatic, despite ongoing prostatic infection.
Physical examination should include obtaining vital signs and examining the lower abdomen , back , genitalia, and rectum. Digital prostate palpation in ABP can cause discomfort and can potentially induce bacteremia but is safe if done gently. In ABP, the gland is typically tender, swollen, and warm, whereas in CBP, there may be some tenderness, softening , firm induration, or nodularity.
Don’t Miss: Can No Sex Cause Prostate Problems
What Are The Symptoms Of Prostatitis
Each type of prostatitis has a range of symptoms that vary depending on the cause and may not be the same for every man. Many symptoms are similar to those of other conditions.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. The main symptoms of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome can include pain or discomfort lasting 3 or more months in one or more of the following areas:
- between the scrotum and anus
- the central lower abdomen
- the scrotum
- the lower back
Pain during or after ejaculation is another common symptom. A man with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome may have pain spread out around the pelvic area or may have pain in one or more areas at the same time. The pain may come and go and appear suddenly or gradually. Other symptoms may include
- pain in the urethra during or after urination.
- pain in the penis during or after urination.
- urinary frequencyurination eight or more times a day. The bladder begins to contract even when it contains small amounts of urine, causing more frequent urination.
- urinary urgencythe inability to delay urination.
- a weak or an interrupted urine stream.
Acute bacterial prostatitis. The symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis come on suddenly and are severe. Men should seek immediate medical care. Symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis may include
What Do We Mean By A Prostate Infection
Prostate Infection, also known as Prostatitis, is an infection in and around the prostate gland. This occurs when the prostate gland and the area around it gets inflamed. This is usually caused by bacteria which may have infiltrated the body through other causes. The prostate gland is located between the bladder and the base of the penis. The prostate gland also has the urethra passing through it which carries urine from the bladder to the penis.
Some Prostate Infections tend to cause no symptoms whatsoever; however there are some forms of prostate Infections which can cause potentially serious symptoms and require immediate medical attention. There are basically two types of Prostate Infections of which one is acute bacterial prostate infection and the other is chronic bacterial prostate infection.
The Acute form of prostate infection causes sudden onset of symptoms which are severe in intensity and require emergent medical attention while the chronic form of prostate infection has symptoms which are mild in intensity and develop gradually over a period of time.
Recommended Reading: Does Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
Does Prostatitis Cause Cancer
Although prostatitis can cause you trouble, it does not cause cancer. There is a blood test some doctors use for prostate cancer called the prostate-specific antigen test . If you have prostatitis, your PSA level might go up. This does not mean you have cancer. Your doctor will treat your prostatitis and may check your PSA level again.
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
Causative Pathogens In Prostatitis
Aerobic gram-negative bacilli are the predominant pathogens in bacterial prostatitis. E. coli cause 50%80% of cases; other pathogens include Enterobacteriaceae , Enterococcus species , and nonfermenting gram-negative bacilli . Some debate the role of gram-positive organisms other than enterococci , but most accept Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species as pathogens . The increasing prevalence of gram-positive pathogens may represent changing disease epidemiology or acceptance of their pathogenicity by health care providers. Limited data suggest that obligate anaerobes may rarely cause chronic prostatitis .
Some cases of prostatitis are caused by atypical pathogens . A large prospective study of men with chronic prostatitis found that 74% had an infectious etiology; the most common isolates were Chlamydia trachomatis and Trichomonas vaginalis , whereas 5% of patients had infection due to Ureaplasma urealyticum . Classical bacterial uropathogens were found in 20% of patients, and more patients with these pathogens, compared with patients with nonbacterial pathogens, had prostatic specimens with leukocytes . Other possible prostatitis pathogens include Mycoplasma genitalium, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, various fungi, and several viruses .
You May Like: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
What Is A Prostate Infection
A prostate infection occurs when your prostate and the surrounding area become inflamed. The prostate is about the size of a walnut. Its located between the bladder and the base of the penis. The tube that moves urine from the bladder to the penis runs through the center of your prostate. The urethra also moves semen from the sex glands to the penis.
Several types of infections can affect the prostate. Some men with prostatitis experience no symptoms at all, while others report many, including intense pain.
Prostatitis: Frequently Asked Questions
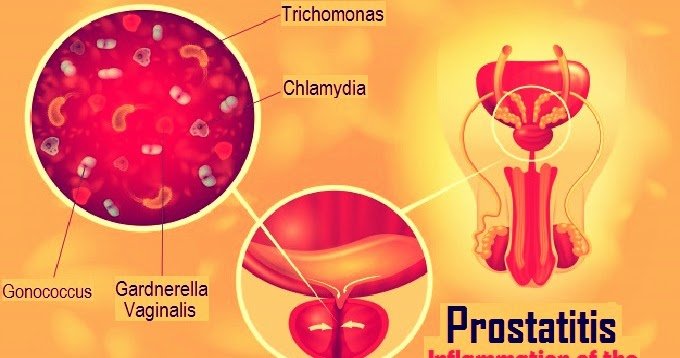
Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland, a walnut-sized gland found just below your bladder. Its a fairly common problem that affects over 8% of men. Prostatitis can be acute or chronic, which can last for weeks, maybe months. Get answers to common prostatitis questions, such as what causes it, how its diagnosed, and treatments.
Don’t Miss: Can Prostate Issues Cause Erectile Dysfunction
How Is Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Managed Or Treated
Prostatitis treatments vary depending on the cause and type. Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis doesnt require treatment.
For chronic pelvic pain syndrome , your healthcare provider may use a system called UPOINT to classify symptoms into six categories. Your provider uses multiple treatments at the same time to treat only the symptoms youre experiencing.
Approximately 80% of men with CPPS improve with the UPOINT system. The system focuses on these symptoms and treatments:
- Urinary: Medications, such as tamsulosin and alfuzosin , relax muscles around the prostate and bladder to improve urine flow.
- Psychosocial: Stress management can help. Some men benefit from counseling or medications for anxiety, depression and catastrophizing .
- Organ: Quercetin and bee pollen supplements may relieve a swollen, inflamed prostate gland.
- Infection:Antibiotics kill infection-causing bacteria.
- Neurologic: Prescription pain medicines, such as amitriptyline and gabapentin , relieve neurogenic pain. This pain can include fibromyalgia or pain that extends into the legs, arms or back.
- Tenderness: Pelvic floor physical therapy may include myofascial release . This therapy can reduce or eliminate muscle spasms.
Alternative Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment For Prostatitis With Out Recurrence
This Treatment Is Mostly used for the Patients Suffering From CPPS / Prostatitis which is Prescribed by Dr.Ming Depending on the Disease Severity & Patients Condition . In which the Herbal Oral Medication is Provided to the Patients For a Duration Prescribed according to the Doctor , Depending on the Severity of the Disease .The Traditional Chinese Medicine Called Nanke Pills Can easily Treat Prostatitis with No Recurring again which is seen in large number of patients , This Herbal Medication Increases the Blood Circulation , eliminates the Damp Heat , Decreases the Inflammation , fights against the Bacterial Infections , Increase immunity & disease resistance power in the body which why the Treatment with Nanke Pills Are very successful among large number of patients .
Please contact Dr.Ming with your Disease History & Symptoms , Test Reports If Available for the best Treatment for the Prostatitis .
Thank You! Your message has been sent successfully. We will Get back to you With in 24-48 Hours .We are off on Weekends , If you sent us message on week ends we will Get back to you On Monday .
Also Check: How To Cum From Prostate
Top Supplements For Prostatitis
| Antibiotic group combined with natural supplements saw most reduction in symptoms | Serenoa repens, lactobacillus sporogens and arbutin show better control and recurrence rate than antibiotics alone | |||
| Nettles, saw palmetto, curcumin, and quercetin blend with antibiotic prulifloxacin | Serenoa repens associated with Urtica dioica and curcumin and quercitin extracts are able to improve the efficacy of prulifloxacin in bacterial prostatitis patients | 14 days | Nearly 90% of patients who took prulifloxacin with natural treatments had reduced symptoms; after 6 months, all patients in this group had no recurrence of the disease | The association of S. repens, U. dioica, quercitin and curcumin extracts is able to improve the clinical efficacy of prulifloxacin in patients affected by CBP |
Will Chronic Prostatitis Go Away By Itself
When people talk about chronic prostatitis, they are talking about chronic nonbacterial prostatitis actually, the other name of this prostatitis is chronic pelvic pain syndrome, the most common form of prostatitis.
- Shop 1-3, Nan Hu Xin Cheng, Wenchang Road, Hongshan District, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China
Q&A
Also Check: What Happens After Prostate Surgery
What Tests Diagnose Prostatitis What Are Prostate
Prostatitis is usually diagnosed by analyzing a urine sample and undergoing an examination of your prostate gland by your health care practitioner. This examination involves a digital rectal examination to palpate the prostate gland and feel for abnormalities of the gland. Occasionally, the physician may also collect and test a sample of the prostatic fluid.
Sometimes a prostate massage is performed to compare samples of the prostatic fluid both before and after this intervention has been performed. To perform this procedure, the doctor will stroke/massage the prostate gland during the digital rectal examination. Because there is the concern that this procedure can release bacteria into the bloodstream, this test is contraindicated in cases of acute bacterial prostatitis.
Additional tests that may be obtained include a complete blood count , an electrolyte panel, blood cultures, a swab of urethral discharge if present, and sometimes a prostate-specific antigen level. The PSA test, which is used as a screening test for prostate cancer, may also be elevated with prostatitis.
Other tests that may also be obtained include urodynamic tests , ultrasound imaging, computed tomography imaging, cystoscopy, and a prostate biopsy.
If recurring episodes of urinary tract infections and prostatitis occur, see your doctor for a more detailed evaluation of your genitourinary system for anatomic abnormalities, which may make you more prone to infections.
What Triggers Prostatitis
Prostatitis can be caused by bacteria that leak into the prostate gland from the urinary tract and from direct extension or lymphatic spread from the rectum. It can also result from various sexually transmitted organisms such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, or HIV.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Prostatitis
Is Prostatitis Curable
Acute prostatitis may go away quickly but chronic prostatitis can last a long time or go away and return. If you have prostatitis caused by a bacterial infection, it can be treated with . If the prostatitis is caused by nerve irritation or damage, it may not go away.
Additional prostatitis treatment options include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
Your doctor may also recommend you increase your fluid intake, but limit alcohol and caffeine consumption, as well as spicy or acidic foods. Sitting for prolonged periods may also irritate the prostate.
Rarely, surgery is needed for chronic prostatitis to remove scar tissue causing the irritation.
How Is It Treated
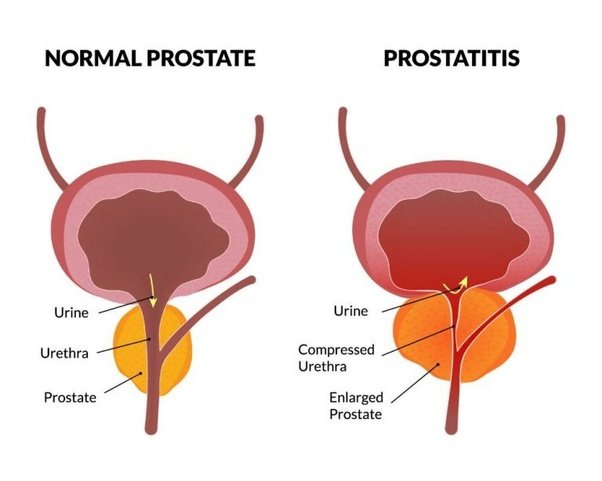
Treating chronic nonbacterial prostatitis is difficult, and is typically hard to cure. Some men however do respond well to treatment. In some cases, symptoms can return and may last for a long time. Treatment methods generally focus on managing symptoms to reduce pain and discomfort. Common treatments include:
- antibiotics
- medications to relax the prostate muscles called alpha-adrenergic blockers
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen to reduce swelling
- stool softeners to prevent constipation
You May Like: Can A Ct Scan Detect Prostate Cancer
The Role Of Leaky Gut
In addition to the retention of urine, the prostate can become infected due to a break down in the intestinal lining, sometimes called leaky gut.
Leaky gut is characterized by bacteria, toxins, and even undigested food, which are all meant to stay within the digestive system, leaking out into the blood stream where these invaders have the potential to cause autoimmune like reactions in some people.11
For example, men who give up gluten sometimes find that their prostate issues go away.
Presumably, this happens because gluten increases the production of zonulin, a protein that is responsible for breaking down the intracellular tight junctions that form the gut wall. 12 Removing gluten reduces levels of zonulin, which allows the gut to heal, stopping the release of irritants that had previously reached the blood stream where they can cause autoimmune reactions.
As a practical matter, this will overlap with the anti-fungal protocol above, but stop eating gluten for a month and see if the condition improves. There are multiple anecdotal stories online about men healing prostate issues by cutting out gluten.
The point here is that a low-grade infection of the prostate can come from places you may not expect, including the gut.
How Bad Is Prostatitis Pain
Acute prostatitis pain, which may be severe, in or around your penis, testicles, anus, lower abdomen or lower back pooing can be painful. pain when peeing, needing to pee frequently , problems starting or stop-start peeing, an urgent need to pee and, sometimes, blood in your urine.
Don’t Miss: Is Masturbation Good For Your Prostate
What Is The Prognosis For Prostatitis Does It Increase The Risk Of Developing Prostate Cancer
Prostatitis caused by bacterial illness often can be treated with antibiotics, or the condition can be chronic that recurs and requires long-term medical attention.
- Acute bacterial prostatitis can often be treated very successfully and has a very good prognosis.
- Chronic prostatitis, and especially chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, can often lead to long-term symptoms and discomfort if treatment is unsuccessful. It is important to have close follow-up and continued care by either your primary care doctor or a urologist.
- Prostatitis does not increase your risk of developing prostate cancer.
What Causes Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a type of infective prostatitis. It is caused by a persistent infection with a germ of the prostate gland. A man with chronic bacterial prostatitis will usually have had recurring urine infections. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is usually caused by the same type of germs that causes the urine infections. The prostate gland can harbour infection and therefore recurring infections can occur. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is not a sexually transmitted infection.
Read Also: How To Stimulate Prostate Gland
How Long Can Nonbacterial Prostatitis Last
does
. Likewise, does nonbacterial prostatitis go away?
The symptoms of chronic bacterial prostatitis are often less severe than those of acute bacterial prostatitis. A person who has previously had an acute infection might notice that their symptoms get better, but do not go away. Some people with chronic bacterial prostatitis may find that the infection persists.
One may also ask, what are the symptoms of nonbacterial prostatitis?
- difficulty urinating or straining to urinate.
- frequent or urgent need to urinate.
- blood in semen.
- pain or burning with urination.
- pain with bowel movement.
- pain with ejaculation.
Considering this, how long can a flare up of prostatitis last?
Your symptoms may last a long time, although they may ‘come and go’ or vary in severity. Painkillers can keep discomfort to a minimum. Most men diagnosed with chronic prostatitis/CPPS tend to have an improvement in their symptoms over the following six months.
What causes chronic nonbacterial prostatitis?
Possible causes of nonbacterial prostatitis include: A past bacterial prostatitis infection. Bicycle riding. Less common types of bacteria.
Diagnosing Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
To make a diagnosis, your doctor will review your medical history and perform a physical exam to look for swollen lymph nodes near the groin or fluid discharge from the urethra.
Your doctor will also perform a digital rectal exam to examine the prostate. During this test, they will insert a lubricated and gloved finger into your rectum to look for signs of infection, such as a soft or enlarged prostate.
Your doctor may also use the following tests and techniques:
Antibiotics are the main course of treatment for this condition. Theyre usually taken for 4 to 12 weeks. For many people, treatment will last for 6 weeks.
First-line treatment is typically a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, such as ciprofloxacin , ofloxacin, or levofloxacin.
However, fluoroquinolones can increase your risk for a ruptured Achilles tendon, which is why they are no longer considered a preferred treatment.
Other commonly prescribed antibiotics include:
- sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim , another first-line treatment
- tetracycline antibiotics, such as doxycycline or azithromycin
Tetracyclines are commonly used in cases where a doctor identifies or suspects chlamydia or mycoplasma genitalium. Like chlamydia, mycoplasma genitalium is an STI.
The antibiotic that youre prescribed will ultimately depend on which bacterium is causing your prostatitis.
Read Also: How Do They Test For Prostate Infection
Who Is More Likely To Develop Prostatitis
The factors that affect a mans chances of developing prostatitis differ depending on the type.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Men with nerve damage in the lower urinary tract due to surgery or trauma may be more likely to develop chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Psychological stress may also increase a mans chances of developing the condition.
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis. Men with lower UTIs may be more likely to develop bacterial prostatitis. UTIs that recur or are difficult to treat may lead to chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis And Pelvic Pain Syndrome
In most chronic bacterial prostatitis cases, we can use antibiotics. It is different in patients with pelvic pain syndrome. They only benefit from antibiotics if there is any evidence of inflammation. In these cases, antibiotic therapy should be extensive. It usually takes 4 to 6 weeks until the patient is cured. Patients can alleviate their symptoms with alpha-blockers, analgesics , and other medications throughout this time. When you start feeling better is variable between one patient and the other. In some patients, chronic prostatitis becomes a recurrent problem. If your prostatitis is chronic with acute exacerbations, the time it takes for antibiotics to work depends on many factors. So, ask your doctor in these cases to have a more accurate grasp of what to expect in your case.
Recommended Reading: How To Stop Leaking After Prostate Surgery
What Is The Prostate Gland What Does It Look Like
The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system, and it is a walnut-sized gland found in men that is located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine and semen exit the body. Its main function is to produce seminal fluid in order to transport sperm through the urethra.
