What Is The Life Expectancy For Stage 4 Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer life expectancy is determined using five-year survival rates. This is the percentage of people who may still be alive five years after being diagnosed.
The five-year survival rate for men with localized prostate cancer, where there is no evidence of cancer spreading outside the prostate, and regional prostate cancer, when cancer has migrated outside the prostate to adjacent structures or lymph nodes exclusively, is approximately 100 percent.
When prostate cancer reaches stage 4 and has spread to other organs such as the lungs, liver, or bones, the five-year survival rate falls below 30%. At stage 4, prostate cancer is unlikely to be cured, although with effective therapy, many people can live for several years. The patients life expectancy is determined by the precise characteristics of his cancer.
However, thanks to routine screening procedures, prostate cancer is often discovered early, before it has spread to other organs, and it is usually not fatal. When diagnosed early, there are several treatment options available, as well as a good likelihood of a cure.
Is Metastatic Cancer Always Terminal
This cancer stage has high mortality risk. However, in most cases, stage 4 or metastatic cancer is not always terminal. It is all depending on the spread area and case. On the other hand, it is also the stage where more advanced and aggressive treatment is necessary to kill the cancer cell.
Terminal cancer refers to a cancer case that is impossible to cure. This case mostly will result in the death of the patient. Therefore, the treatment for terminal cancer is only to control the spread and ease the patients pain. The curing process is difficult to do. So, it is the period when doctors and patients families prepare for the worst.
Despite its obvious result, the medical world still sets the standard for the patients survival likelihood. And, to learn more about that matter, you can continue reading. We will start talking about our main topic here, the stage 4 cancer life expectancy.
Us Cancer Statistics Data Visualizations Tool
The Data Visualizations tool makes it easy for anyone to explore and use the latest official federal government cancer data from United States Cancer Statistics. It includes the latest cancer data covering the U.S. population.
See how the rates of new prostate cancers or prostate cancer deaths changed over time for the entire United States and individual states.Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
CDC.gov Privacy Settings
We take your privacy seriously. You can review and change the way we collect information below.
These cookies allow us to count visits and traffic sources so we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to know which pages are the most and least popular and see how visitors move around the site. All information these cookies collect is aggregated and therefore anonymous. If you do not allow these cookies we will not know when you have visited our site, and will not be able to monitor its performance.
Read Also: What Is Better For Prostate Cancer Surgery Or Radiation
Cods More Than 5 Years After Metastatic Pc Diagnosis
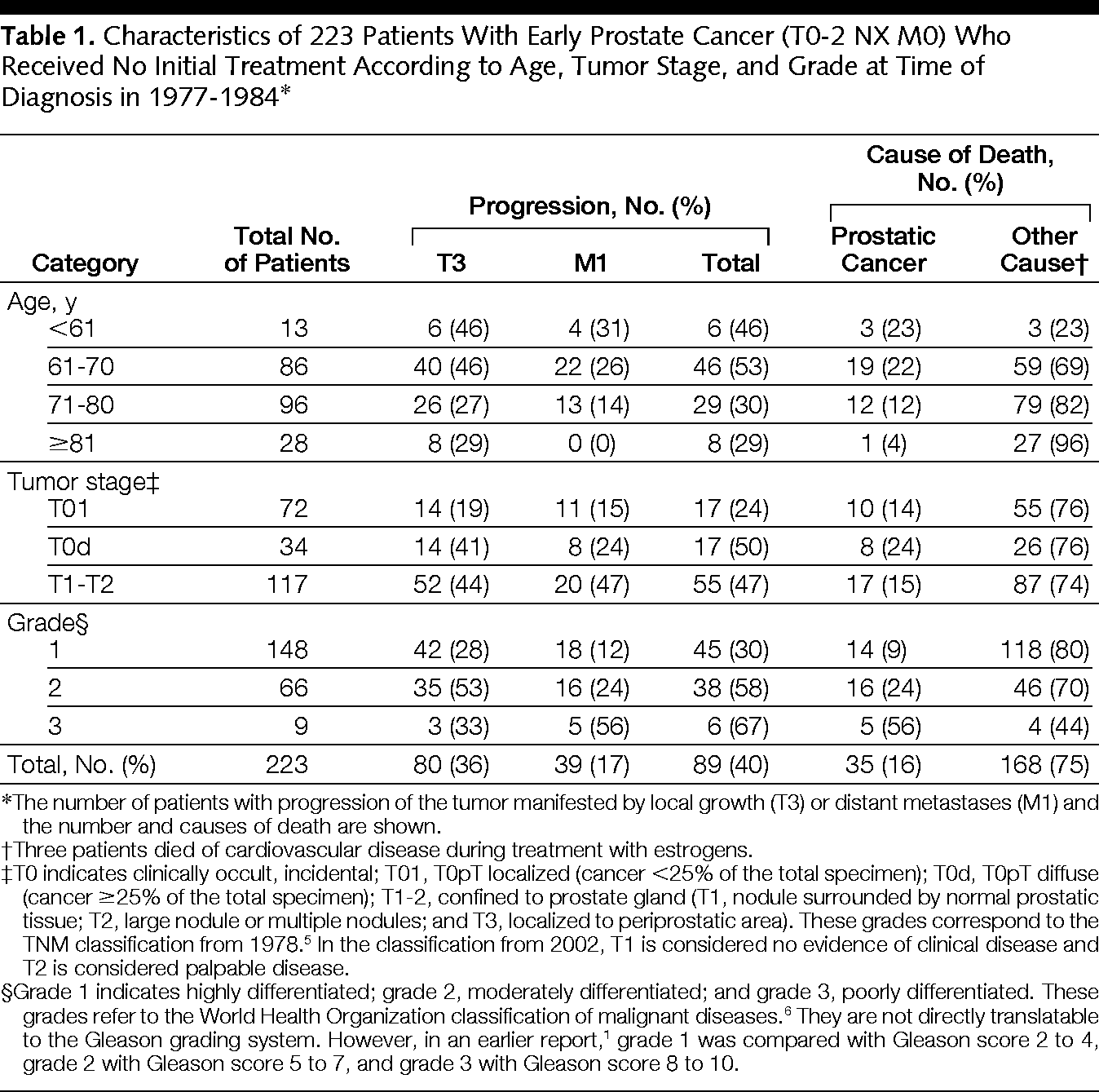
A total of 1573 men with metastatic PC died more than 5 years after their cancer diagnosis, of whom 1048 died of metastatic PC, 126 died of nonprostate cancers, and 399 died of noncancer causes. The most common noncancer COD was cardiovascular disease , followed by cerebrovascular disease and COPD . Among men with metastatic PC, the overall risk of death more than 5 years after diagnosis was significantly greater than that in the general US male population .
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates: What They Mean
As cancer diagnoses go, prostate cancer is often a less serious one. Prostate cancer is frequently slow-growing and slow to spread. For many men, prostate cancer is less serious than their other medical conditions.
For these reasons, and possibly because of earlier detection of low-grade prostate cancers, prostate cancer has one of the highest survival rates of any type of cancer. WebMD takes a look at prostate cancer survival rates and what they mean to you.
You May Like: What Vitamins Are Good For Prostate Cancer
Stages Of Prostate Cancer
In order to determine the stage of a patients prostate cancer, most doctors start by using the TNM staging system, which helps describe different aspects of the cancers growth.
- T the T category measures the size and extent of the Tumor
- N the N category measures whether and how far the cancer has spread to the Lymph Nodes
- M the M category whether the cancer has spread to other organs in the body (a process called Metastasis
The score for each of these categories is determined based on a pre-determined set of criteria. Your doctor cannot feel or see the tumor with a score of T1. A score of T3 means that the tumor has begun to grow outside of the prostate.
After calculating the TNM categories, doctors will combine the TNM score with the patients Gleason score and PSA levels assigning of a specific stage to the patients cancer.
Prostate cancer prognosis and survival rates can help give patients an idea of their chances of surviving the disease based on the stage and time of diagnosis. While some patients may find this information helpful, others may not want to know.
Stage Iv Cancer Life Expectancy
The five-year relative survival rate for prostate cancer that has spread to distant organs is 28%. This means about 28% of the patients with stage 4 prostate cancer will live for five years.
According to certain studies, about 98% men with low or intermediate grade prostate cancer will live for more than five years. However, only 67% men with end stage prostate cancer will live for more than five years.
End stage prostate cancer life expectancy is normally less than five years. It may vary according to the age and overall health of the patient, the type of treatment, and the extent and location of metastases , etc.
Studies show that the five-year survival rate for prostate cancer without bone metastasis is 56%. For prostate cancer with bone metastasis, it is only 3%.
The five-year survival rate for prostate cancer with bone metastasis and skeletal involvement is unfortunately less than 1%.
Usually, at stage IV, doctors assure life only for three years. The life expectancy not only depends on the treatment, but also on the physical and mental health of the patient. Patients who are loved and cared by their family members can fight the disease courageously. Those with strong will power live longer. There are examples of patients who have lived for eight years, or even further. Some recent studies show that a prostatectomy, even in late stage prostate cancer, can double or triple the life expectancy of a patient . But more studies are required to prove this fact.
Recommended Reading: Pelvic Floor Exercises After Prostate Surgery
Gleason Score Vs Grade Groups
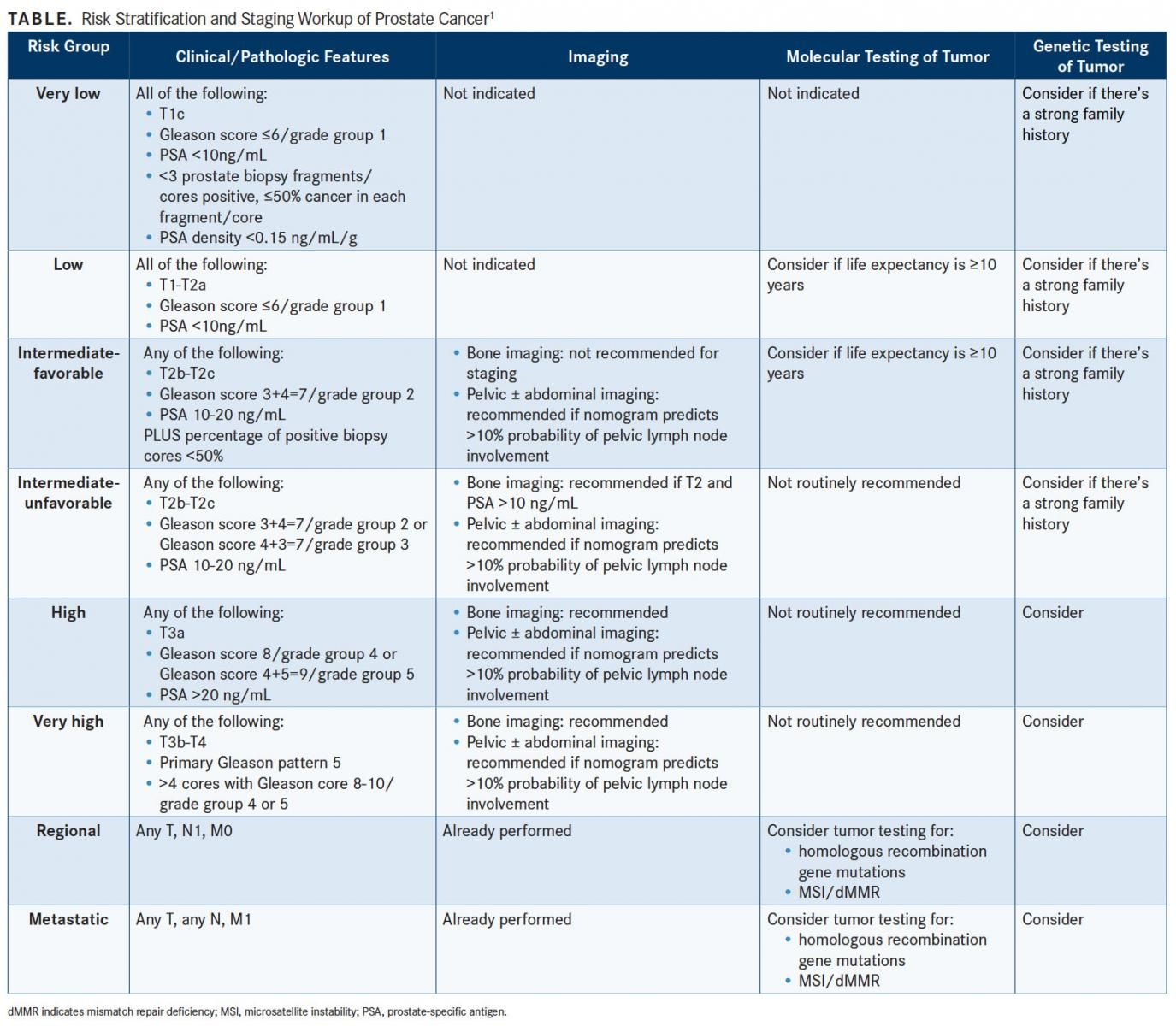
The International Society of Urological Pathology released a revised prostate cancer grading system in 2014. The grade group system seeks to simplify Gleason scores and give a more accurate diagnosis.
One of the major problems with the Gleason score is that some scores can be made up in different ways. For example, a score of 7 can mean:
- 3 + 4. The 3 pattern is the most common in the biopsy and 4 is the second most common. This pattern is considered favorable intermediate risk.
- 4 + 3. The 4 pattern is the most common in the biopsy and 3 is the second most common. This pattern is considered unfavorable and may mean local or metastatic spread.
So, although both situations give a Gleason score of 7, they actually have very different prognoses.
Heres an overview of how the two grading systems compare:
| Cancer grade | |
|---|---|
| grade group 5 | 910 |
Not all hospitals have switched to the grade group system. Many hospitals give both grade group and Gleason scores to avoid confusion until grade groups become more widely used.
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer Life Expectancy
The five year survival rate for stage 1 prostate cancer is 100%, but stage 4 prostate cancer life expectancy is not very encouraging. While providing information on late stage prostate cancer life expectancy, this HealthHearty article also describes what is meant by staging and grading of prostate cancer.
The five year survival rate for stage 1 prostate cancer is 100%, but stage 4 prostate cancer life expectancy is not very encouraging. While providing information on late stage prostate cancer life expectancy, this HealthHearty article also describes what is meant by staging and grading of prostate cancer.
Statistics show that more and more men are being diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Various tests like PSA test, DRE test, ultrasound sonography, etc., help diagnose the cancer. Staging and grading of cancer not only help design the treatment but they also help determine how well the cancer may respond to the treatment. Staging, generally, is concerned with the spread of cancer. The Gleason grading system involves classification of cancer cells. It helps determine aggressiveness of the cells and their likelihood of spreading.
Don’t Miss: Qué Alimentos Son Perjudiciales Para La Prostata
What Is Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer that affects the prostate gland in men. Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer deaths for men in the US.
Growth in the prostate can be of two types
Prostate cancer starts in the prostate gland and may spread to the nearby areas: lymph nodes, organs, or bones in other parts of the body.
You May Like: Elevated Prostate Specific Antigen Icd 10
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer Substages
Stage 4 prostate cancer is classified into substages, and the subcategory the oncologist assigns helps guide the treatment options:
- Stage 4A: Cancer cells have been found in nearby lymph nodes and may have spread into local tissue.
- Stage 4B: Cancer has spread to areas farther away from the prostate, such as distant lymph nodes or bones.
Recommended Reading: Can Zantac Cause Prostate Cancer
Survival By Tumor Grade
One way cancer is staged is by looking at the grade of cancer. Grade refers to how cancer cells look like under a microscope.
Traditionally for prostate cancer, this has been done using the Gleason Score, which was developed in the 1960s. Under this system, cancerous cells are categorized on a scale from 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are considered normal prostate tissues, while cells in the grade 5 range have mutated to such an extent they no longer resemble normal cells.
In determining a Gleason score, a pathologist will examine a biopsy sample under a microscope and give a Gleason grade using the above scale to the most predominant pattern displayed, then a second grade to the pattern that is the second most predominant. Those two grades are then added to form the overall Gleason score .
In theory, Gleason scores could range from 2 to 10, but pathologists today rarely give a score between 2 and 5 and are more likely to be in the range of 6 to 10 with 6 being the lowest grade of prostate cancer.
Under the Gleason Score system, a 6 is considered low grade, 7 is intermediate and scores of 8, 9, or 10 are considered high-grade cancers.
The higher the Gleason score, the more likely it is the prostate cancer will grow and spread quickly.
However, there have been some issues with the Gleason system, and a new grading system, to act as an extension of the Gleason system, has been developed.
Under this system Gleason scores are now categorized into grade groups:
Latest Prostate Cancer Data
Prostate cancer is the 2nd most commonly occurring cancer in men and the 4th most common cancer overall. There were more than 1.4 million new cases of prostate cancer in 2020.
The 10 countries with the highest rates of prostate cancer and the highest number of deaths from prostate cancer in 2020 are shown in the tables below.
ASR = age-standardised rates. These are a summary measure of the rate of disease that a population would have if it had a standard age structure. Standardisation is necessary when comparing populations that differ with respect to age because age has a powerful influence on the risk of dying from cancer.
Also Check: How To Check For Prostate Cancer At Home
How To Make The Right Treatment Decision
Current expert guidelines for treatment of localized prostate carcinoma recommend potentially curative therapy for patients whose life expectancy is at least 10 years., Patients with limited life expectancy are more likely to die from health conditions other than prostate cancer. Men with a life expectancy of more than 10 years are more likely to die from progressive prostate cancer. This 10-year rule enjoys broad acceptance among urologists and radiation oncologists.,
Conservative management proved to be an acceptable treatment option for men with low-grade Gleason scores, clinically localized disease, and life expectancies of less than 10 years. Increasing age was described as a risk factor for receiving inadequate treatment for prostate cancer. Thus, older men have been shown to receive potentially curative therapy less often than younger men., Radical prostatectomy is preferred treatment in men younger than 70 years, whereas radiation therapy is applied predominantly in patients older than 70 years. Conservative therapy such as watchful waiting or androgen deprivation by luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogs is preferentially applied in men older than 80 years. Watchful waiting or hormonal therapy is used to treat 82% of men older than 80 years.
Read Also: Does Cialis Shrink The Prostate
Metastatic Prostate Cancer Symptoms
With metastatic prostate cancer, the patient may notice different symptoms than those generally associated with other stages of the disease. Some of the most frequently occurring stage 4 prostate cancer symptoms include:
- Bone pain, particularly in the pelvis, ribs, skull and spine
- Unexplained weight loss
- General feeling of being unwell
- Changes in urinary habits, such as needing to go more often
- Cough, breathlessness or other changes involving the lungs and chest
Not everyone with metastatic prostate cancer will experience each of these symptoms, but patients should speak with their care teams if they notice any such changes.
Read Also: Cutting Edge Prostate Cancer Treatment
Read Also: How To Check For Prostate Cancer
Study Design And Data Source
In this retrospective cohort study,24 we used SEER*Stat software, version 8.3.5,25 to access the 2018 version of the SEER 18 registries, which included 27.8% of the general US population from January 1, 2000, to December 31, 2016.26 Data were analyzed from February 2 to July 28, 2020. SEER data are anonymized, and use of the data is considered as nonhuman participant research. Thus, institutional review board approval and informed consent were not needed. The study followed the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology reporting guideline.
Survival Rates For Prostate Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. These rates cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Ask your doctor, who is familiar with your situation, how these numbers may apply to you.
Recommended Reading: Can You Milk Your Prostate
Treatments To Help Manage Symptoms
Advanced prostate cancer can cause symptoms, such as bone pain. Speak to your doctor or nurse if you have symptoms there are treatments available to help manage them. The treatments above may help to delay or relieve some symptoms. There are also specific treatments to help manage symptoms you may hear these called palliative treatments. They include:
This is the team of health professionals involved in your care. It is likely to include:
- a specialist nurse
What Are Next Steps
Bone metastasis have a profound effect on the long-term outlook for prostate cancer. But its important to remember that the numbers are only statistics.
The good news is that life expectancy for advanced prostate cancer continues to increase. New treatments and therapies offer both longer life and better quality of life. Speak to your doctor about your treatment options and long-term outlook.
Everyones cancer experience is different. You may find support through sharing your treatment plan with friends and family. Or you can turn to local community groups or online forums like Male Care for advice and reassurance.
You May Like: Problems Caused By Enlarged Prostate
Who Gets This Cancer
Prostate cancer occurs only in men, and it is more common in older men than younger men. It is more likely to occur in men with a family history of prostate cancer and men of African American descent. The rate of new cases of prostate cancer was 112.7 per 100,000 men per year based on 20152019 cases, age-adjusted.
Rate of New Cases per 100,000 Persons by Race/Ethnicity: Prostate Cancer
Males
SEER 22 20152019, All Races, Males
