Take The Next Step Today
Request your free consultation with Dr. Sperling, and well work together to make the best diagnostic and treatment plan for you.
;NOTE: This content is solely for purposes of information and does not substitute for diagnostic or medical advice. Talk to your doctor if you have health concerns or questions of a personal medical nature.
Positron Emission Tomography Scan
A PET scan is similar to a bone scan, in that a slightly radioactive substance is injected into the blood, which can then be detected with a special camera. But PET scans use different tracers that collect mainly in cancer cells. The most common tracer for standard PET scans is FDG, which is a type of sugar. Unfortunately, this type of PET scan isnt very useful in finding prostate cancer cells in the body.
However, newer tracers, such as fluciclovine F18, sodium fluoride F18, and choline C11, have been found to be better at detecting prostate cancer cells.
Other newer tracers, such as Ga 68 PSMA-11 and 18F-DCFPyl , attach to prostate-specific membrane antigen , a protein that is often found in large amounts on prostate cancer cells. Tests using these types of tracers are sometimes referred to as PSMA PET scans.
These newer types of PET scans are most often used if its not clear if prostate cancer has spread. For example, one of these tests might be done if the results of a bone scan arent clear, or if a man has a rising PSA level after initial treatment but its not clear where the cancer is in the body.
The pictures from a PET scan arent as detailed as MRI or CT scan images, but they can often show areas of cancer anywhere in the body. Some machines can do a PET scan and either an MRI or a CT scan at the same time, which can give more detail about areas that show up on the PET scan.;
The Best Prostate Cancer Screening And Detection Tool Is The 3t Mri
To date, the newer versions of the 3T MRI are the most reliable devices for screening and detecting the 15% or so of potentially deadly high-grade prostate cancers. Unlike the current standard screening and detection methods, the 3T MRI evaluates the WHOLE of the prostate, can ignore the bogus G6 cancer and, based upon imaging details in a properly conducted study, able to identify reliably with PIRADS 4 and 5 features, almost all high-grade cancer anywhere within the prostate. Any high-grade areas identified can then be targeted for needle biopsy under real-time 3T MRI for confirmation of disease as only these particular prostate cancers demand detection and treatment. However, because imaging studies are highly insensitive and, high-grade cells can reside in the bone marrow for many years undetected, treatment of some apparently localized high-grade prostate cancers can lead to a semblance of cure, especially when only followed for a few years.Joe Busch MD, prostate MRI specialist, Chattanooga, Tennessee www.drcradiology.com/
Also Check: How Is Prostate Size Measured
Which Patients Might Benefit
When is MRI recommended for men with prostate cancer?
Men who are most commonly referred to our center have had a prostate biopsy that reveals cancer, but some other aspect of the diagnostic workup raises questions about the extent or aggressiveness of the cancer. For instance, maybe the PSA level or biopsy indicates that cancer is aggressive, but nothing can be felt on a digital rectal exam. In this type of situation, an MRI can help to resolve the issue.
So youre trying to provide some additional information that might affect a treatment decision?
Exactly.
What are some other situations where MRI is helpful?
One of the more useful applications of MRI is in locating cancer that has not shown up on a biopsy. This can be very helpful to a man who has not yet been diagnosed with prostate cancer despite having an elevated PSA and continued biopsies that come back as being negative, meaning there is no evidence of cancer. The urologist thinks that cancer is present, but cant find it based upon the biopsy results. Often men are referred to us after they have several negative biopsies. We can use MRI to advise the urologist where to target the biopsy needle, so that the doctor samples the area where we have the highest degree of suspicion that cancer exists.
How do you answer critics who have not kept up with developments in this field and remember MRI of the prostate as being no better than a coin flip, and who believe that this may be a total waste of time and energy?
The Highly Unreliable Psa
Although marketed as potentially life-saving, the PSA blood test is associated with a very high false positive rate; leads to the detection of mainly non-lethal diseases; is NOT cancer-specific; its limits of normal are artificial; is commonly NOT the same result on repeat studies as it fluctuates normally; can be artificially raised or lowered by several processes without a cancer being present; often rises with age as the prostate grows; is normally high with big prostates and, MOST IMPORTANTLY, commonly fails to indicate the 15 per cent or so of potentially lethal high-grade prostate cancers with significant amounts of pattern 4 and or, 5 disease as these cancers often make little or no PSA. Furthermore, should an elevated PSA lead to a significant prostate cancer being detected, the elevated PSA is commonly caused by the enlarged benign portion of the prostate and NOT the cancer.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does A Prostate Biopsy Take
Prostate Mri Can Help You Avoid Unnecessary Biopsy
Prostate biopsies are used to confirm cancer in high-risk patients suspected to have aggressive prostate cancer. Uncomfortable and invasive, men undergoing the procedure are extremely prone to complications like antibiotic-resistant infections and sepsis. Its estimated that 18% of patients experience some sort of complication, while as many as 4% develop an infection requiring hospital care.
27% of the one million prostate biopsies performed each year are unnecessary.
Typically, a biopsy will be recommended to a patient for one of two reasons: they tested high for levels of the PSA protein, or, the results from a digital rectal exam show they may have prostate cancer. The issue here is that PSA tests are not always accurate.
A males PSA level can be affected by a number of other factors, such as recent sexual activity, an enlarged prostate, and prostatitis. Even a long bicycle ride can cause levels to spike. This leaves a lot of room for false-positives – which lead to unnecessary biopsies.
Potential Disadvantages Of Mri
The primary disadvantage of adoption of an mpMRI-based approach for prostate cancer screening is the associated cost which is considerably higher than a serum PSA test at a population-based level. However, the per-individual costs for a prostate MRI are similar to those for colonoscopy, the recommended screening test for colorectal cancer . In addition, in many jurisdictions, the cost of mpMRI is equivalent or marginally higher than genomic tests with the added advantage of providing biopsy guidance. Further, compared to ongoing PSA-based screening, mpMRI-based prostate cancer screening offers the opportunity to significantly reduce the cost and morbidity of prostate cancer screening by reducing the number of biopsies performed and reducing the diagnosis of clinically insignificant prostate cancer, thus reducing overtreatment. In addition, compared to abandoning prostate cancer screening entirely, mpMRI-based prostate cancer screening offers the opportunity to diagnose clinically significant disease while it is localized and amenable to prostate-directed treatments. Such treatment has been shown to decrease progression to metastatic disease , which carries significant cost and morbidity . Should mpMRI be proven to be a better screening instrument than serum PSA from further studies, comprehensive cost-related studies will be required to determine the feasibility of mpMRI screening for prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: How To Stimulate Prostate Gland
The Tricky Prostate Cancer Label
The all-inclusive prostate cancer label leaves the public with the impression that all prostate cancers are potentially lethal. Unfortunately, this very deceptive generic prostate cancer label includes both the bogus Gleason 6 and real prostate cancers. Even worse, this confusion allows predatory urologists to game the cancer label and imply that pseudo-cancers like the Gleason 6 are real and use falsehoods and scare tactics to bully patients into unneeded treatments for profiteering. Easily done since the only thing these vulnerable patients hear is the terrorizing cancer word.
When To Consider A Prostate Mri
Studies indicate that MRI may be helpful in the following situations. The best images are obtained when using an endorectal coil.
- You have a PSA that continues to increase, but an ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy does not reveal cancer; an MRI may be able to better pinpoint a suspicious area for a more targeted biopsy and increase the likelihood of finding cancer if it is there.
- Different elements of your diagnostic workup are in conflict ; an MRI can better determine size of the tumor and whether it has extended beyond the capsule.
- For large palpable tumors, MRI can rule out cancer that extends beyond the prostate itself.
- If your PSA rises following prostate cancer treatment, MRI can be used to identify any cancerous tissue in the periprostatic bed , which indicates a local recurrence.
- MRI may provide better guidance about where to target radiation therapy.
Don’t Miss: What Happens To The Prostate Later In Life
Pilot Study To Examining The Feasibility Of Mri Prostate Cancer Screening
In contrast to previously described approaches, the use of mpMRI in an otherwise unselected population is relatively untested. We recently conducted a pilot study assessing the feasibility of mpMRI as an initial prostate cancer screening test . Following a newspaper based call for volunteers, 319 men agreed to participate in this study. Of these, 120 were eligible, 50 were enrolled due to limitations in funding, and 47 completed the study protocol. Serum PSA testing, mpMRI, digital rectal examination, and systematic prostate biopsies were performed on all men. Prostate cancer was identified in 18 of 47 men . MpMRI significantly outperformed PSA in the prediction of prostate cancer. In multivariable analyses including age, digital rectal examination findings, PSA and MRI score, mpMRI was the only significant predictor for the presence of prostate cancer . These findings were even stronger when we sought to predict only clinically significant prostate cancer .
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computer’s clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
Also Check: How Long Can You Live With Prostate Cancer Without Treatment
How We Screen For Prostate Cancer Now
Most prostate cancers are first detected when a patient is found to have an elevated prostate-specific antigen , which is a blood test used for prostate cancer screening. The prostate is a walnut-sized gland that produces the fluid in semen. PSA is a protein made in the prostate, and elevated levels often are found in men with prostate cancer.
There has been some controversy about when men should get PSA tests, but we follow the guidelines of the American Urological Association, which recommend patients and their doctors discuss the test at age:
- 55-69 for men at average risk
- 40-54 for men at higher risk for prostate cancer, such as black men and men with a family history of prostate cancer
- 70 and older for men in excellent health with a 10- to 15-year life expectancy
While a PSA test can give us a clue that something may be wrong, it isnt fool-proof. For example, the test can be elevated in patients who have benign enlargement of their prostate or prostatic inflammation. In such cases, the abnormal PSA test can lead to an unnecessary biopsy.
If your PSA levels are elevated, well likely perform a transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy to gather small samples of the prostate to examine in the lab. We use a transrectal ultrasound to visualize the prostate. Then we insert a small needle into the gland to remove about 12 samples from different parts of the prostate.
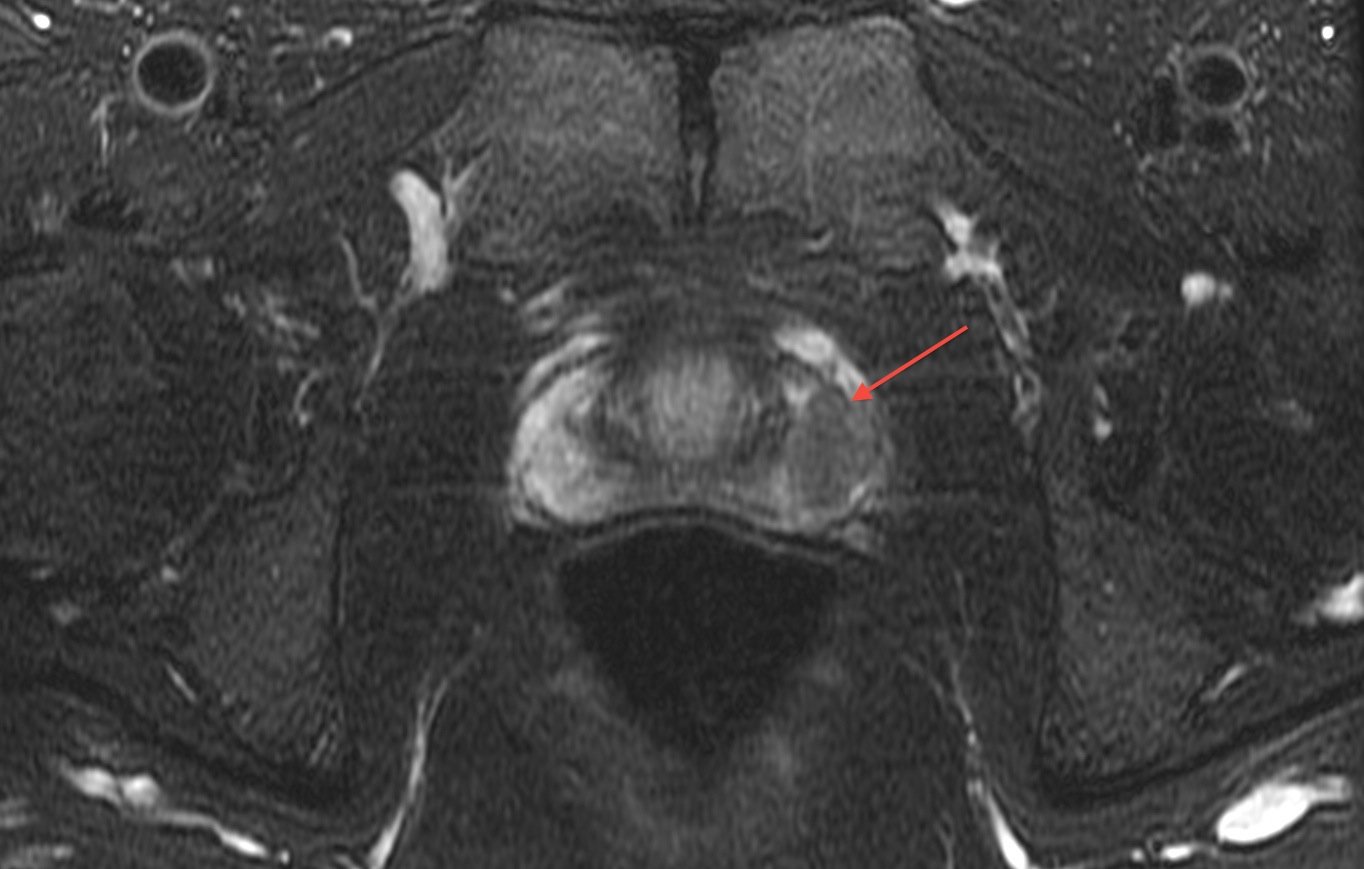
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of The Prostate
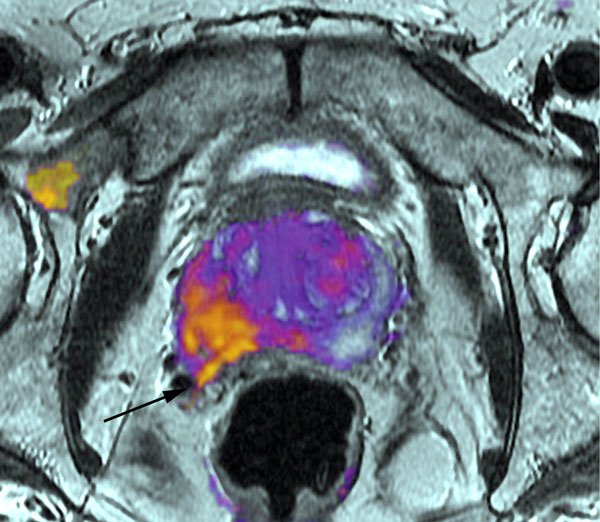
Multiparametric prostate magnetic resonance imaging has an increasingly large role in the early detection and staging of prostate cancer. MRI was initially used as a staging test in patients with prostate cancer for assessment of direct extra-prostatic extension. Significant variability in diagnostic performance, limited ability to detect microscopic disease, and inability to localize the tumor within the gland itself limited its adoption . Since that time, and in particular with the addition of diffusion weighted imaging allowing visualization of tumor within the prostate, there has been a migration in the use of MRI earlier in the disease process, and to direct biopsy .
Recently Salami et al. compared the performance of the PCPT risk calculator and mpMRI in the prediction of clinically significant prostate cancer, among men with an abnormal PSA . Prior to biopsy, MRI significantly outperformed the nomogram in identifying patients with clinically significant disease who may benefit from diagnosis and treatment. Thus, as the PCPT risk calculator is used in the initial screening phases for prostate cancer, it is reasonable to examine whether MRI might prove a better screening test.
Read Also: Can You Really Milk A Prostate
How Is The Procedure Performed
MRI exams may be done on an outpatient basis.
You will be positioned on the moveable exam table. Straps and bolsters may be used to help you stay still and maintain your position.
Devices that contain coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves may be placed around or next to the area of the body being scanned.
MRI exams generally include multiple runs , some of which may last several minutes.
Your exam may use an endorectal coil. If so, a nurse or doctor will place a disposable cover over the coil. They will lubricate the assembly and insert the coil a short distance into your rectum. After insertion, the doctor inflates the circular balloon that sits around the coil and holds it in place during the exam. When the exam is complete, the doctor deflates the balloon and removes the coil.
If a contrast material is used, a doctor, nurse or technologist;will insert an intravenous;catheter into a vein in your hand or arm that will be used to inject the contrast material.
You will be placed into the magnet of the MRI unit. The technologist will perform the exam while working at a computer outside of the room.
If a contrast material is used during the exam, it will be injected into the intravenous line after an initial series of scans. More images will be taken during or following the injection.
When the exam is complete, you may be asked to wait while the radiologist checks the images in case more are needed.
Your IV line will be removed after the exam is over.
Preparing For Your Mri Scan
Before you go to your appointment, or when you arrive, you fill in a safety checklist. This asks about:
- any operations youve had
- whether you have any metal implants or other metals in your body
An MRI scan uses strong magnetism which could affect any metal in your body. This;includes:
- pacemakers or an implantable defibrillator
- surgical clips, pins or plates
- cochlear implants
- metal fragments anywhere in your body for example from an injury, dental fillings and bridges
You can still have an MRI scan if you have some metals in your body, but your doctor and radiographer decide if its safe for you. Tell the scanner staff about any metals in your body.
Some people feel claustrophobic or closed in when theyre having an MRI scan. Contact the department before your test if youre likely to feel like this. The hospital;staff can take extra care to make sure youre comfortable and that you understand whats going on. Your doctor can give you medicine to help you relax if you need to.
The radiographers let you know whether you need to empty your bowels of any poo or gas before having the scan. In some departments you might be given an enema. An enema is a liquid filled pouch that has a nozzle that you can put into your back passage and it helps to empty your bowels.;
Don’t Miss: How Often Should You Test For Prostate Cancer
Potential Advantages Of Mri
Radiologist expertise may also significantly influence the diagnostic characteristics of MRI. In a cohort of 101 patients, Branger et al. showed that a negative MRI could not exclude the presence of clinically significant cancer . However, experienced radiologists can exclude significant volumes of Gleason score â¥7 prostate cancer with a negative predictive value exceeding 95% .
Much of the data supporting the potential role for screening MRI is drawn not from the use of MRI in the screening setting but extrapolation from reports among patients with abnormal PSA test results. Thus, further research is required.
Biopsy During Surgery To Treat Prostate Cancer
If there is more than a very small chance that the cancer might have spread , the surgeon may remove lymph nodes in the pelvis during the same operation as the removal of the prostate, which is known as a radical prostatectomy .
The lymph nodes and the prostate are then sent to the lab to be looked at. The lab results are usually available several days after surgery.
Don’t Miss: Will A Blood Test Show Prostate Cancer
