What Are The Complications Of Prostatitis
Men with acute bacterial prostatitis may develop . This widespread inflammation can be life-threatening. It requires immediate medical treatment.
Antibiotics can cause an upset stomach. Men with chronic bacterial prostatitis may need lots of antibiotics to treat recurring infections. Some people develop antibiotic resistance, making treatment ineffective.
Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis can lower sperm count, affecting fertility.
Pain Or Burning During Urination
The urinary tract becomes inflamed and swelling, as well as the prostate. This leads to an overactivation of nerve terminals. They become irritated, and any additional impulse will be translated into pain. Then, urination can feel burning or painful, as if the patient had a urinary infection. Infected urine and prostatitis have in common this symptom, and sometimes it can be a bit difficult to differentiate them.
Painful urination is often attributed to urinary infections. It is often found as a symptom in patients with recurrent urinary tract infections. If thats the case and doctors prescribe antibiotics, the symptoms will be solved in bacterial prostatitis. But in nonbacterial prostatitis, antibiotics are unlikely to resolve the problem.
What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Prostatitis
Antibiotics can cure acute bacterial prostatitis. These medications also ease chronic bacterial prostatitis symptoms in approximately 30% to 60% of men. Up to 80% of men with chronic pelvic pain syndrome feel better after receiving appropriate treatments for their symptoms using the UPOINT system. Men with asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis dont need treatment.
You May Like: Can You Get Prostate Cancer From Asbestos
How Is Prostate Infection Treated
Treatment depends on the type of prostatitis. Prostatitis is a treatable condition. Even if the problem cannot be cured, patients may usually get relief from their symptoms by following the recommended treatment.
Treatments include the following:
- Anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen or paracetmol
- Antibiotic medications may be initially started for 7-14 days; however, they may be taken longer for severe conditions.
- Alpha-blocking agents may improve the urinary stream and often reduce the other voiding symptoms in patients with chronic prostatitis. Alpha-blocking agents include Flomax or Uroxatral for patients with voiding symptoms and those who do not empty their bladders well.
- Other treatments for severe noninfectious prostatitis include the drugsProscar , terazosin, and doxazosin. These drugs relax the muscles of the prostate and bladder to improve urine flow and reduce symptoms.
Facts You Should Know About Prostate Infections
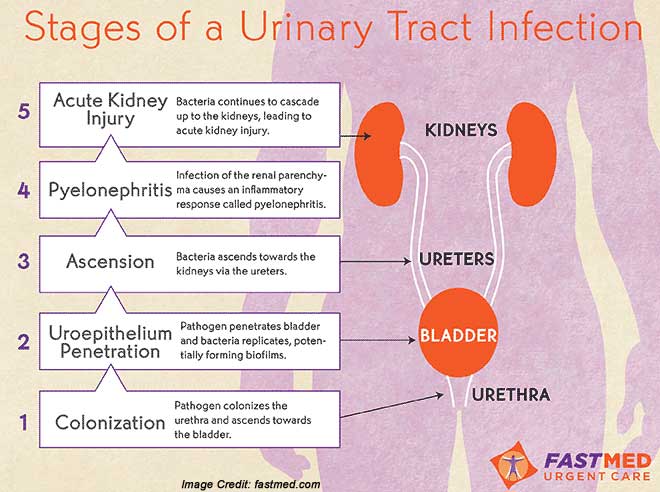
- Prostate infections comprise only small percentage of all men with prostatitis. This small percentage is comprised of acute and chronic prostatic infections.
- E. coli;and other Gram-negative bacteria cause most acute and chronic prostatic infections.
- Prostatic infection symptoms include groin pain, dysuria, pain with ejaculation, reduced urine output; and may include fever, malaise, and periodic recurrence of symptoms even after treatment.
- Seek medical care if symptoms develop, emergency care if fever or inability to urinate occurs.
- Diagnosis of prostate infections or prostatitis is made by identifying the agent infecting the prostate.
- Treatment of prostate infections or prostatitis is usually antibiotics; chronic infectious prostatitis may require long-term antibiotic treatment, and severe infections may require hospitalization with IV antibiotics.
- Home care is limited to pain reduction. Men with a prostate infection or prostatitis need medical care.
- Follow-up is important to confirm adequate treatment results or to plan additional treatment if the infection reoccurs.
- Some prostate infections cannot be prevented, but reducing the risk of groin trauma or injury, avoiding sexually transmitted diseases, and staying well hydrated are ways to reduce the chance of getting infectious prostatitis.
- The prognosis of acute infectious prostatitis is usually good, but chronic infectious prostatitis is only fair because it is difficult to cure.
Also Check: What Is The Function Of The Prostate Gland
Drug Therapy And Other Alternative Treatments
You must know that there is no therapy, which could be applied at home conditions. You could use anti-inflammatory drugs, like ibuprofen, acetaminophen, naproxen and etc to relieve pain or chills. Thats why you must seek medical assistance as soon as possible.
What you can do to help your prostate, you must avoid bicycling, jogging and even horse riding. These activities irritate the gland and every person who has experienced an infection of the prostate must avoid.
Is Prostate infection the first signal of prostate cancer?
Many people worry about the possibility of getting a prostate cancer is not increased if you undergo an infection of the prostate. There is not data that supports this false belief.
Warning Symptoms Of Prostatitis
Prostate cancer is one of the main concerns in older adult males.
The incidence of prostate problems increases as we age. But theres a prostate problem that appears in young and older patients.
Prostatitis can be widespread in adult males. It is actually more common in patients younger than 50 years old. But older patients with prostate problems may also develop prostatitis. For example, prostatitis can be a complication of a transrectal prostate biopsy.
Thats why males should know about prostatitis regardless of their age. In this article, we are going to review this prostate problem and its warning signs.
We are also giving you a few recommendations about what you can do if you have these symptoms.
Read Also: Can Zytiga Cure Prostate Cancer
How Is Acute Prostatitis Diagnosed
Your doctor will likely start by asking questions about your medical history. Theyll also conduct a physical examination.
Theyll probably conduct a digital rectal examination . During this procedure, theyll gently insert a gloved and lubricated finger into your rectum. Your prostate is located in front of your rectum, where your doctor can easily feel it. If you have acute bacterial prostatitis, it will likely be swollen and tender.
During a DRE, your doctor may also massage your prostate to squeeze a small amount of fluid into your urethra. They can collect a sample of this fluid for testing. Laboratory technicians can check it for signs of infection
Your doctor may also feel the lymph nodes in your groin, which may be enlarged and tender.
They may also conduct or order additional tests, such as:
- a blood culture to rule out bacteria in your blood
- a urinalysis or a urine culture to test your urine for blood, white cells, or bacteria
- a urethral swab to test for gonorrhea or chlamydia
- urodynamic tests to learn if you have problems emptying your bladder
- a cystoscopy to examine the inside of your urethra and bladder for signs of infection
What Is The Prostate Gland
The prostate is a gland that lies just below a man’s urinary bladder. It surrounds the urethra like a donut and is in front of the rectum. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the bladder, through the penis and out of the body. Your doctor may check your prostate by putting a finger into your rectum to feel the back of your prostate gland.
The prostate gland makes a fluid that provides nutrients for sperm. This fluid makes up most of the ejaculate fluid. We do not yet know all of the ways the prostate gland works.
You May Like: When Should You Have A Prostate Biopsy
What Are The Remedies For Prostate Infection
The common remedies of prostate infection include:
Warm baths called sitz baths
Local heat therapy with hot water bottles or heating pads
Physical therapy:
- Kegel exercises: Tightening and relaxing the muscles that hold urine in the bladder and hold the bladder in its proper position. These are also called pelvic muscle exercises.
- Myofascial release: Pressing and stretching, sometimes with cooling and warming, of the muscles and soft tissues in the lower back, pelvic region, and upper legs. It is also known as myofascial trigger point release.
Phytotherapy: Plant extracts such as quercetin, bee pollen, and saw palmetto may help in relieve symptoms.
Avoiding food that triggers symptoms such as caffeine, spicy foods, and alcohol
Using a cushion if you will be sitting for a long time
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of prostatitis, such as pelvic pain, difficulty or pain when peeing, or painful ejaculation.
They’ll ask about the problems you’re having and examine your tummy.
You may also have;a rectal examination. This is where a doctor inserts a gloved finger into your bottom to feel for anything unusual. You may have some discomfort during this examination if your prostate is swollen or tender.
Your urine will usually be tested for signs of infection, and you may be referred to a specialist for further tests to rule out other conditions.
See a GP straight away if you get sudden and severe symptoms of prostatitis.
You may have acute prostatitis, which needs to be assessed and treated quickly because it can cause serious problems, such as suddenly being unable to pee.
If you have persistent symptoms , you may be referred to a doctor who specialises in urinary problems .
You May Like: What Is The Best Over The Counter Prostate Medicine
Signs And Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancers are found early, through screening. Early prostate cancer usually causes no symptoms. More advanced prostate cancers can sometimes cause symptoms, such as:
- Problems urinating, including a slow or weak urinary stream or the need to urinate more often, especially at night
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Trouble getting an erection
- Pain in the hips, back , chest , or other areas from cancer that has spread to bones
- Weakness or numbness in the legs or feet, or even loss of bladder or bowel control from cancer pressing on the spinal cord
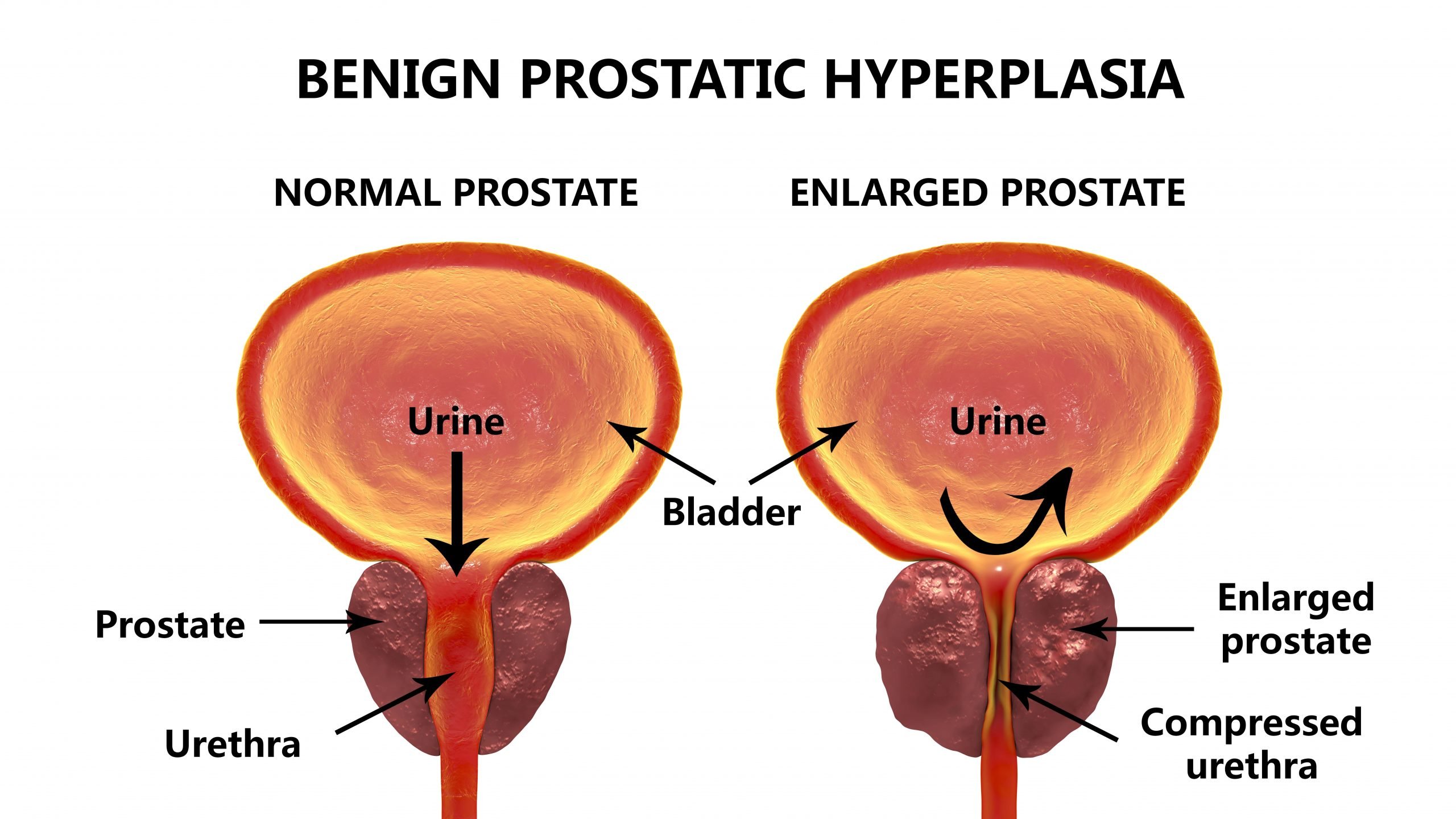
Most of these problems are more likely to be caused by something other than prostate cancer. For example, trouble urinating is much more often caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia , a non-cancerous growth of the prostate. Still, its important to tell your health care provider if you have any of these symptoms so that the cause can be found and treated, if needed. Some men might need more tests to check for prostate cancer.
What Causes Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a type of infective prostatitis. It is caused by a persistent infection with a germ of the prostate gland. A man with chronic bacterial prostatitis will usually have had recurring urine infections. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is usually caused by the same type of germs that causes the urine infections. The prostate gland can harbour infection and therefore recurring infections can occur. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is not a sexually transmitted infection.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Maximum Size Of Prostate
What Causes Chronic Prostatitis/chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
Chronic prostatitis/CPPS is a persistent discomfort or pain that you feel in your lower pelvic region – mainly at the base of your penis and around your anus. It is usually diagnosed if you have had pain for at least three months within the previous six months. The cause of this type of chronic prostatitis is not fully understood.
Symptoms Of Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Bacterial infections in the prostate can be very painful.
The symptoms begin slowly and last 3 months or longer. Seek medical attention if you have any of the following symptoms:
Serious complications can arise if an infection isnt properly treated. Complications include:
- urinary retention, which is an inability to urinate
- , which occurs when bacteria spread into the bloodstream
- a prostate abscess, which is a collection of pus that causes inflammation
A bacterial infection causes chronic bacterial prostatitis. Even when the primary symptoms of infection have been treated, bacteria may continue to thrive in the prostate.
Causes of infection include:
- sexually transmitted infections , such as chlamydia and gonorrhea
- E. coli after having an infection of the testicles, urethritis , or a UTI
Certain factors put people at risk for developing this condition, such as:
You May Like: Can You Shrink An Enlarged Prostate
When To Seek Medical Care
A person may have urinary symptoms unrelated to prostatitis that are caused by bladder problems, UTIs, or benign prostatic hyperplasia. Symptoms of prostatitis also can signal more serious conditions, including prostate cancer.
Men with symptoms of prostatitis should see a health care provider.
Men with the following symptoms should seek immediate medical care:
- complete inability to urinate
- great discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen and urinary tract
How Do Doctors Diagnose A Prostate Infection
The diagnosis of both acute and chronic prostate infections begins with the history of the symptoms described above, the physical exam, including the digital exam of the prostate and often confirmed by culture and identification of the infecting organism.
Acute bacterial prostatitis diagnosis
- Usually an enlarged, firm, and tender prostate is enough to make a presumptive diagnosis and start treatment .
- Because there is usually a low level of bacteria in urine, the doctor will perform a urinalysis to quantitate and identify infecting bacteria by urine culture.
- If the person has symptoms suggesting the infection has spread outside the prostate , blood cultures and other blood tests are likely to be ordered.
- If a spread of the infection is suspected, a doctor will often perform an ultrasound to help confirm the diagnosis and to rule out an abscess. If this ultrasound is not available, the doctor may perform a CT scan or MRI of the pelvis.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis diagnosis
One of two tests are sometimes performed to help with the diagnosis:
The classic test is a Meares-Stamey 3-glass test. Three separate urine samples are collected and examined during this test. The last sample is taken after prostatic massage.
Premassage and postmassage test
Men with recurrent urinary tract infections should have ultrasound imaging of their upper urinary tract and a plain abdominal X-ray or an intravenous urography to exclude a possible structural problem or a kidney stone.
Also Check: What Causes A Man To Have Prostate Problems
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: Diagnosis And Management
TIMOTHY J. COKER, MD, and DANIEL M. DIERFELDT, DO, Ehrling Bergquist Family Medicine Residency Program, Offutt Air Force Base, Nebraska
Am Fam Physician.;2016;Jan;15;93:114-120.
;Patient information: A handout on this topic is available at .
Acute bacterial prostatitis is an acute infection of the prostate gland that causes urinary tract symptoms and pelvic pain in men.1 It is estimated to comprise up to 10% of all prostatitis diagnoses, and its incidence peaks in persons 20 to 40 years of age and in persons older than 70 years.2 Most cases can be diagnosed with a convincing history and physical examination.3 Although prostatitis-like symptoms have a combined prevalence of 8.2% in men, the incidence and prevalence of acute bacterial prostatitis are unknown.4
Is There More Than One Type Of Prostatitis
The main types of prostatitis are bacterial prostatitis and non-bacterial prostatitis.
Bacterial prostatitis
Bacterial prostatitis is an infection caused by bacteria. Its the easiest kind of prostatitis to diagnose and treat, although it can become serious if not dealt with quickly.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is the least common form of prostatitis, but if the infection is not dealt with it can be life-threatening.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is when bacterial prostatitis comes back again and again. Its caused by an underlying problem in the prostate, such as prostate stones or an enlarged prostate , which attract bacteria. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is also a common cause of repeated urinary tract infections , which are infections in the urinary system.
Non-bacterial prostatitis
Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis is when the prostate is inflamed, but there isnt any bacteria present. We dont yet understand this form of prostatitis very well, although we know that they dont cause urinary tract infections. Symptoms can disappear and come back later, and are often made worse by stress.
Also Check: How To Milk A Man’s Prostate
Causes Of Prostate Infection
Prostate infection is the most common pathology related to men of all ages, from young to old ones. Therefore, every man in the world must be familiar with its concept, what it is and what to do to handle his situation. However, in most cases the help of a doctor is necessary.
If you;want to have presonalised health answer for as little as 5 usd from a real doctor;
First of all, from anatomical point of view, the prostate gland is located in every man only. It is part of mens reproductive system and plays important part in the secretion of fluids, which help the transportation of the sperm. The gland is located below the bladder.
What Causes Prostatitis
The causes of prostatitis differ depending on the type.
Chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. The exact cause of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome is unknown. Researchers believe a microorganism, though not a bacterial infection, may cause the condition. This type of prostatitis may relate to chemicals in the urine, the immune systems response to a previous urinary tract infection , or nerve damage in the pelvic area.
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis. A bacterial infection of the prostate causes bacterial prostatitis. The acute type happens suddenly and lasts a short time, while the chronic type develops slowly and lasts a long time, often years. The infection may occur when bacteria travel from the urethra into the prostate.
Also Check: Does Having Sex Help An Enlarged Prostate
What Is Prostate Cancer
In prostate cancer, normal cells undergo a transformation in which they not only grow and multiply without normal controls, but they also change in their microscopic appearance and can invade adjacent tissues. Prostate cancer cells form into malignant tumors or masses, which then overwhelm surrounding tissues by invading their space and taking vital oxygen and nutrients. Cancer cells from these tumors can eventually invade remote organs via the bloodstream and the lymphatic system. This process of invading and spreading to other organs is called metastasis. Common metastatic locations where prostate cancer cells may eventually be found include pelvic lymph nodes, and bones. The lungs and the liver may also show deposits of, or metastases from, prostate cancer, but that is less common.
Almost all prostate cancers arise from the glandular cells in the prostate. Cancer arising from a glandular cell in any organ in the body is known as adenocarcinoma. Therefore, the most common type of prostate cancer is an adenocarcinoma. The most common non-adenocarcinoma is transitional cell carcinoma. Other rare types include small cell carcinoma and sarcoma of the prostate.
Older men commonly have an enlarged prostate, caused by a benign condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia . Prostate gland cells simply keep growing in number in the prostate gland in BPH. BPH can cause urinary symptoms but is not a form of prostate cancer .
