Medication For Urinary Problems
Your doctor may suggest various medications to help ease your urinary problems, including:
- medications to reduce the tone of the muscles of the urethra and prostate to minimise any constriction to urine flow caused when these muscles contract
- medication to reduce the size of the prostate gland. These medications work by blocking the action of male hormones produced by the prostate gland
- medications to relax the bladder, making unwanted contractions less likely and reducing the symptoms of urgency and frequency of urination
- the over-the-counter preparation ‘saw palmetto’ is sometimes used. This may help some men, especially if frequent urination at night is a problem.
However, recent reviews of the evidence for using saw palmetto as a treatment for mild or moderate urinary symptoms did not show any improvement, compared to no treatment, in men with BPH.;
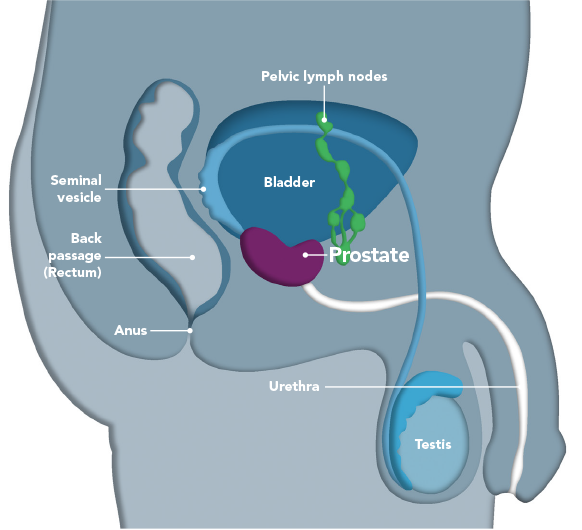
What Does My Prostate Do
It is a small gland that is part of the male reproductive system. It’s supposed to be about the shape and size of a walnut.
It rests below your bladder and in front of your rectum. It surrounds part of the urethra, the tube in your penis that carries pee from your bladder.
The prostate helps make some of the fluid in semen, which carries sperm from your testicles when you ejaculate.
Symptoms Of Prostate Disease
In its earliest stages, prostate disease may or may not be associated with symptoms. The symptoms of prostate disease depend on the condition, but may include:
- difficulties urinating, such as trouble starting the flow of urine
- the urge to urinate often, particularly at night
- feeling as though the bladder can’t be fully emptied
- painful urination
- blood in the urine or blood coming from the urethra independent of urination.
Blood in the urine is often due to causes not related to the prostate. Always see your doctor if you find blood in your urine.
Also Check: How To Reduce Prostate Size
Prostate Volume And Bph Prevalence: Comparison To Industrial Populations
Compared to TRUS from multiple industrial populations including 1,240 Caucasian German men , 3,924 Caucasian Dutch men , 472 Caucasian Scottish men , and 631 Caucasian U.S. men , the Tsimane have significantly smaller prostate volumes controlling for age and height, and a shallower rate of change with age controlling for height .
The overall age standardized prevalence of BPH among men age 40 80 was 28.4% compared to 60.8% of U.S. men of the same age . For Tsimane men aged 60 80, an age standardized 31.7% presented with BPH, compared with 76.0% of U.S. men aged 60 80 . Only 0.56% of this sample achieved prostate volumes greater than 40 cc compared to approximately 20% of U.S. males .
Tsimane Prevalence of BPH by Age and U.S. Prevalence of Histologic BPH from Berry et al.
| Tsimane .; |
|---|
Questions You May Want To Consider Asking Your Doctor Include:
- What type of prostate problem do I have?
- Is more testing needed and what will it tell me?
- If I decide on watchful waiting, what changes in my symptoms should I look for and how often should I be tested?
- What type of treatment do you recommend for my prostate problem?
- For men like me, has this treatment worked?
- How soon would I need to start treatment and how long would it last?
- Do I need medicine and how long would I need to take it before seeing improvement in my symptoms?
- What are the side effects of the medicine?
- Are there other medicines that could interfere with this medication?
- If I need surgery, what are the benefits and risks?
- Would I have any side effects from surgery that could affect my quality of life?
- Are these side effects temporary or permanent?
- How long is recovery time after surgery?
- Will I be able to fully return to normal?
- How will this affect my sex life?
- How often should I visit the doctor to monitor my condition?
Related Resources
Don’t Miss: Can Prostate Issues Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Cause Of Urinary Problems As Men Age
Many men experience urinary symptoms as they age, which may be caused by inflammation of the prostate gland .;In older men, symptoms may be due to a blockage in the tubes due to a benign enlargement of the prostate gland . The most common symptom is difficulty emptying your bladder. Urinary symptoms may become bothersome enough that they require treatment.;Not all urinary symptoms are due to changes to the prostate. Also, some men have enlarged prostates and yet experience few, if any, symptoms.;
Enlarged Prostate Treatments In The Pipeline
Researchers continue to investigate new therapies for enlarged prostates. âAnother category of drugs is under development,â says Slawin. âWeâve come a long way in treating BPH. Itâs no longer the life-threatening disease it once was. Now, in treatment, weâre working on quality of life issuesââ¬Ã¦ reducing side effects of treatment.â
Also being studied is a procedure called water-induced thermotherapy , an experimental procedure that involves destroying excess prostate tissue utilizing heated water and an air-filled balloon, which protects normal prostate tissue. The procedure is performed with only local anesthesia. Results may not be fully apparent for three to four months. However, preliminary studies examining WIT have shown positive results, with a near doubling in urine flow. However, the American Urological Association has not thus far endorsed WIT as a viable treatment option for symptoms of BPH.
Donât Miss: How To Stimulate Prostate Gland
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Prostate Cancer That Has Spread To Bones
What Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasiaalso called BPHis a condition in men in which the prostate gland is enlarged and not cancerous. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is also called benign prostatic hypertrophy or benign prostatic obstruction.
The prostate goes through two main growth periods as a man ages. The first occurs early in puberty, when the prostate doubles in size. The second phase of growth begins around age 25 and continues during most of a mans life. Benign prostatic hyperplasia often occurs with the second growth phase.
As the prostate enlarges, the gland presses against and pinches the urethra. The bladder wall becomes thicker. Eventually, the bladder may weaken and lose the ability to empty completely, leaving some urine in the bladder. The narrowing of the urethra and urinary retentionthe inability to empty the bladder completelycause many of the problems associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Symptoms Of Urinary Problems
Urinary symptoms commonly experienced with prostate problems include:
- the need to urinate frequently during the night
- urinating more often during the day
- urinary urgency the urge to urinate can be so strong and sudden that you may not reach the toilet in time
- the urine stream is slow to start
- urine dribbling for some time after finishing urination
- a sensation that the bladder isn’t fully emptied after urination
- lack of force to the urine flow, which makes directing the stream difficult
- the sensation of needing to go again soon after urinating.
Although these symptoms often do not need treatment, see your doctor if they are causing you difficulty, as they can be successfully treated.
You May Like: Can No Sex Cause Prostate Problems
Your Prostate Has Four Areas
The prostate gland contains four areas, or zones.
The peripheral zone is the largest segment, containing about 75% of the glands in the prostate. Most prostate cancer occurs in the peripheral zone and is the site where most needle biopsies are taken. The peripheral zone contains the majority of the prostatic tissue.
The central zone of the prostate gland is the area that surrounds the ejaculatory ducts. Less than 5% of prostate cancers originate here. However, if prostate cancer does originate here, it is more aggressive and can metastasize to the seminal vesicles.
The transition zone surrounds the urethra in the place where it enters the prostate. This part of the prostate grows in adult men and is responsible for BPH, or the enlarged prostate. Around 20% of cancers originate here.
The fourth zone is the anterior fibromuscular storma.
What Causes Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The cause of benign prostatic hyperplasia is not well understood; however, it occurs mainly in older men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia does not develop in men whose testicles were removed before puberty. For this reason, some researchers believe factors related to aging and the testicles may cause benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Throughout their lives, men produce testosterone, a male hormone, and small amounts of estrogen, a female hormone. As men age, the amount of active testosterone in their blood decreases, which leaves a higher proportion of estrogen. Scientific studies have suggested that benign prostatic hyperplasia may occur because the higher proportion of estrogen within the prostate increases the activity of substances that promote prostate cell growth.
Another theory focuses on dihydrotestosterone , a male hormone that plays a role in prostate development and growth. Some research has indicated that even with a drop in blood testosterone levels, older men continue to produce and accumulate high levels of DHT in the prostate. This accumulation of DHT may encourage prostate cells to continue to grow. Scientists have noted that men who do not produce DHT do not develop benign prostatic hyperplasia.
You May Like: What Are The Manifestations Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The Prostate Gland: Mans Center Of Gravity
The prostate gland is a mysterious male reproductive organ that can be a source of curiosity, anxiety, fear and potential trouble. Since this gland is a midline organ nestled deep within the pelvis, I like to think of it as mans center of gravity.
Where exactly is the prostate gland?
The prostate gland is located behind the pubic bone and is attached to the bladder and the urethra . The rectum is directly behind the prostate . The prostate is situated at the crossroads of the urinary and reproductive tracts and completely surrounds the urethra, allowing its many ducts to drain into the urethra. The relationship between the prostate and the urethra can potentially be the source of problems for the older male. When a man ages, the prostate gland gradually enlarges. This prostate enlargement can constrict and block the urethra, giving rise to bothersome urinary symptoms.
What is the prostate, what purpose does it serve, and how does it function?
The prostate is a male reproductive gland that produces prostate fluid, a nutrient and energy vehicle for sperm. The prostate consists of glandular and fibro-muscular tissue enclosed by a capsule of collagen, elastin and smooth muscle. The glandular tissue contains the secretory cells that produce the prostate fluid.
What are the zones of the prostate gland?
Curious facts about the prostate:
The Prostate Is Responsible For Producing The Fluid That Makes Up Semen Filtering Sperm And Maintaining An Erection
You may be aware that prostate gland performs some functions but do you know everything this busy gland does? Although it is just a small gland the size of a walnut the prostate is responsible for keeping the male reproductive system on task.
The prostate prevents urine from mixing with sperm when a man ejaculates
Located in front of the rectum and just below the bladder surrounding the urethra, it completes various functions over the course of the day to keep the male reproductive system up and running. These include:
Also Check: Can An Ultrasound Detect Prostate Cancer
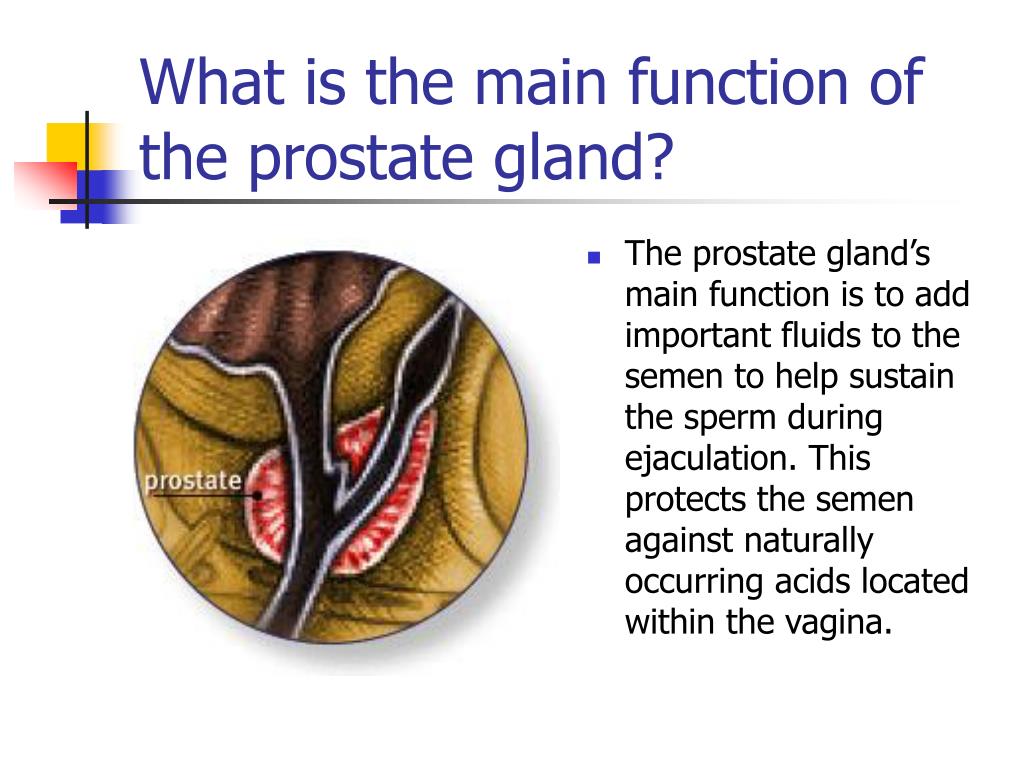
What Is The Main Function Of The Prostate Gland
The main function of the prostate gland is to secrete an alkaline fluid that comprises approximately 70% of the seminal volume. The secretions produce lubrication and nutrition for the sperm. The alkaline fluid in the ejaculate results in liquefaction of the seminal plug and helps to neutralize the acidic vaginal environment.
The prostatic urethra is a conduit for semen and prevents retrograde ejaculation by closing off the bladder neck during sexual climax. Ejaculation involves a coordinated contraction of many different components, including the smooth muscles of the seminal vesicles, vasa deferentia, ejaculatory ducts, and the ischiocavernosus and bulbocavernosus muscles.
Problems With Enlarged Prostate Gland
Benign enlargement of the prostate gland is more common as men get older. It can cause troublesome symptoms, although it doesnt always.
The urethra passes through the prostate gland, so men may have problems urinating if the enlarged gland restricts the flow of urine. If the flow stops completely, a catheter is required to empty the bladder. It is rare for this form of acute urinary retention to cause kidney damage.
An enlarged prostate doesn’t always cause urinary problems. Studies indicate that the size of a man’s prostate gland has little influence on the type or severity of his urination problems. BPH is just one possible cause of urinary symptoms.;
Another cause of urinary symptoms can be changes to the muscular wall of the bladder, which may cause spasms of the bladder or weaken the bladder, causing problems passing urine.
Also Check: How To Tell Prostate Cancer
Diagnosis Of Prostate Disease
Prostate disease is diagnosed using a variety of tests, including:
- physical examination, including digital rectal examination , where the doctor inserts a gloved finger into your rectum to check the size of your prostate
- blood test for prostate specific antigen
- mid-stream urine tests to look for infection or blood in the urine
- ultrasound scans and urinary flow studies
- biopsies of the prostate.
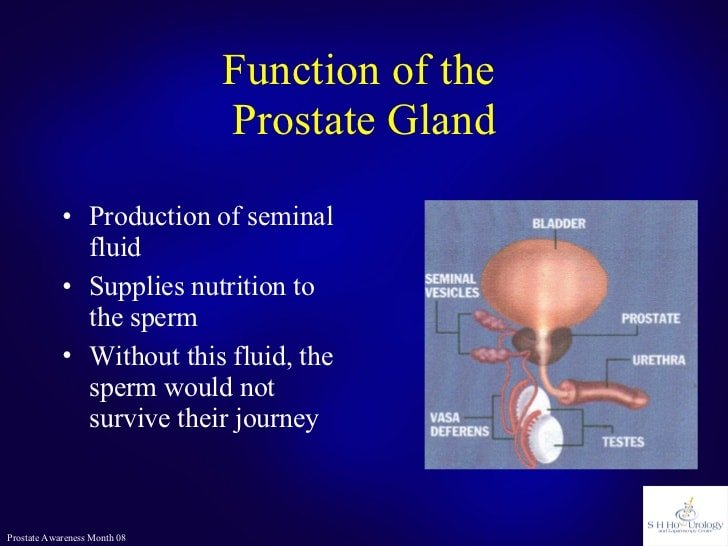
Function Of The Prostate Gland
As part of the male reproductive system, the prostate glands main job;is to secrete a slightly alkaline fluid that forms part of the seminal fluid. This is the fluid that carries sperm. During a man’s orgasm, the muscular glands of the prostate help to propel the prostate fluid, and sperm that was made in the testicles, into the urethra. The semen then leaves the body out of the tip of the penis during ejaculation.
Online Medical Reviewer:Online Medical Reviewer:Online Medical Reviewer:Date Last Reviewed:
Don’t Miss: Can You Ejaculate With An Enlarged Prostate
Blood And Lymphatic Vessels
The prostate receives blood through the inferior vesical artery, internal pudendal artery, and middle rectal arteries. These vessels enter the prostate on its outer posterior surface where it meets the bladder, and travel forward to the apex of the prostate. Both the inferior vesical and the middle rectal arteries often arise together directly from the internal iliac arteries. On entering the bladder, the inferior vesical artery splits into a urethral branch, supplying the urethral prostate; and a capsular branch, which travels around the capsule and has smaller branches which perforate into the prostate.
The veins of the prostate form a network the prostatic venous plexus, primarily around its front and outer surface. This network also receives blood from the deep dorsal vein of the penis, and is connected via branches to the vesical plexus and internal pudendal veins. Veins drain into the vesical and then internal iliac veins.
The lymphatic drainage of the prostate depends on the positioning of the area. Vessels surrounding the vas deferens, some of the vessels in the seminal vesicle, and a vessel from the posterior surface of the prostate drain into the external iliac lymph nodes. Some of the seminal vesicle vessels, prostatic vessels, and vessels from the anterior prostate drain into internal iliac lymph nodes. Vessels of the prostate itself also drain into the obturator and sacral lymph nodes.
-
Microscopic glands of the prostate
What A High Psa Level Means If Its Not Prostate Cancer
Other important components of prostatic fluid include an enzyme called prostatic acid phosphatase, citric acid, zinc, spermine and prostatic inhibin .
During an orgasm, prostate muscles squeeze the gland’s stored fluid into the urethra, where it mixes with the sperm cells and other semen components.
This expulsive process also helps propel the semen out of the body during ejaculation.
You May Like: How To Have A Prostate Orgasim
How Common Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is the most common prostate problem for men older than age 50. In 2010, as many as 14 million men in the United States had lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia.1 Although benign prostatic hyperplasia rarely causes symptoms before age 40, the occurrence and symptoms increase with age. Benign prostatic hyperplasia affects about 50 percent of men between the ages of 51 and 60 and up to 90 percent of men older than 80.2
Prostatitis: A Common Prostate Problem In Younger Men
Prostatitis, or prostate inflammation, is the most common prostatic and urinary tract problem for men under age 50, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases . It accounts for 2 million doctor visits in the United States each year.
There are several types of prostatitis.
Prostatitis caused by bacteria is known as bacterial prostatitis, and it can cause an acute or chronic infection.
Recommended Reading: Can Exercise Reduce Prostate Size
Treatment For Prostate Disease
Treatment for prostatitis may include antibacterial drugs and supportive treatments, depending on the type of prostatitis.Treatment for BPH may include medications to relax the smooth muscle of the gland or to shrink the size of the prostate, and surgery to produce a permanently widened channel in the part of the urethra that passes through the prostate.Treatment for prostate cancer is tailored to suit individual circumstances. The nature of the cancer, other health problems the person may have, and their wishes will all be taken into account.Management approaches for prostate cancer include:
- active surveillance
- surgery for example, prostatectomy
- radiotherapy
- ablative treatments such as high-intensity focused ultrasound and NanoKnife®
- hormone treatment
- chemotherapy
Urinary Tract Infections In Men: Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment
Nonbacteria microbes may cause a different type of chronic prostatitis, known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome, which may also develop as a result of chemicals in the urine, a;urinary tract infection, or pelvic nerve damage.
Affecting 10 to 15 percent of the U.S. male population, chronic pelvic pain syndrome is the most common type of prostatitis,;but also the least understood.
Symptoms vary depending on the type of prostatitis, but can include urination problems, pain , fever, and body aches, among other things.
Some people develop asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis, in which the prostate is inflamed but doesn’t produce any symptoms or require treatment.
Bacterial prostatitis is most often treated with antibiotics. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome may require drugs, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
Over time, prostatitis may cause sexual dysfunction, abscesses in the prostate, inflammation of nearby reproductive organs, and infection of the bloodstream.
Learn More About Prostate Problems and Complications
Don’t Miss: How Do They Test For Prostate Infection
