Survival Statistics For Prostate Cancer
Survival statistics for prostate cancer are very general estimates and must be interpreted very carefully. Because these statistics are based on the experience of groups of people, they cannot be used to predict a particular person’s chances of survival. In general, most men diagnosed with prostate cancer do not die from the disease itself and will die from other causes.
There are many different ways to measure and report cancer survival statistics. Your doctor can explain the statistics for prostate cancer and what they mean to you.
Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prognosis
Prostate cancer prognosis varies from person to person, as every situation is different. Five-year relative survival rates are categorized by the type of cancer: localized, regional and distant.
According to the American Cancer Society, localized cancer has a five-year relative survival rate of more than 99 percent. For regional cancer , the five-year relative survival rate is also more than 99 percent.
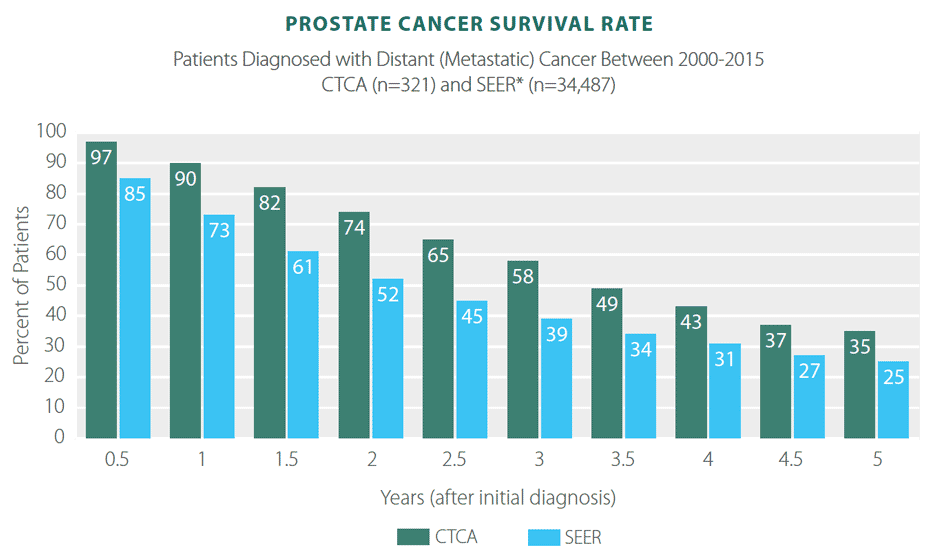
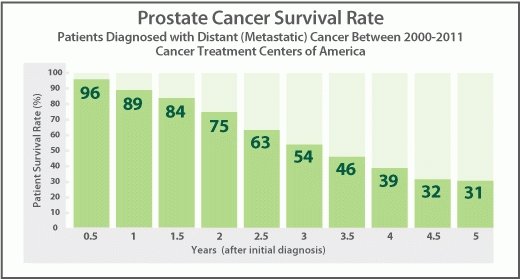
For distant cancer , the five-year relative survival rate drops to 31 percent.
Prostate Cancer Survival By Age
Five-year survival for prostate cancer shows an unusual pattern with age: survival gradually increases from 91% in men aged 15-49 and peaks at 94% in 60-69 year olds survival falls thereafter, reaching its lowest point of 66% in 80-99 year olds patients diagnosed with prostate cancer in England during 2009-2013. The higher survival in men in their sixties is likely to be associated with higher rates of PSA testing in this age group.
Prostate Cancer , Five-Year Net Survival by Age, Men, England, 2009-2013
Don’t Miss: Hip Pain And Prostate Cancer
Keeping Health Insurance And Copies Of Your Medical Records
Even after treatment, its very important to keep health insurance. Tests and doctor visits cost a lot, and although no one wants to think of their cancer coming back, this could happen.
At some point after your cancer treatment, you might find yourself seeing a new doctor who doesnt know your medical history. Its important to keep copies of your medical records to give your new doctor the details of your diagnosis and treatment.
Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
In stage 2, the tumor is still confined to your prostate and hasnt spread to lymph nodes or other parts of your body. A doctor may or may not be able to feel the tumor during a prostate exam, and it may appear on ultrasound imaging. The survival rate is still .
The PSA score for stage 2 is less than 20 ng/mL.
Stage 2 cancer is further divided into three phases depending on the grade group and Gleason scores:
- Grade group: 1
- Gleason score: 6 or less
Also Check: What Causes Prostate To Swell
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for prostate cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages.
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside the prostate.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the prostate to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to parts of the body farther from the prostate, such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
What Influences Survival Rates
There are many factors to consider when talking about survival rates. All of these can influence survival, especially in men undergoing advanced prostate cancer. Below is a list of factors that influence survival rates:
- Stage of cancer: this is described by doctors using the TNM system . Doctors use scans and diagnostic results to determine important values. Such as, how large a tumor is and where it is. If the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes and has the cancer spread to other parts of the body . Together those values are combined to see what stage the cancer is. The scale has five stages.1-2 on the TNM scale refers to localized prostate cancer that has yet to spread. Stage 3 means the cancer has spread to nearby areas or lymph nodes. Stage 4 involves cancer spreading to organs far from its origin point.
- Age: Age is an important factor in the likelihood of developing prostate cancer. It has less to do with survival rates.
- Race: Survival rates are impacted by disparities in healthcare access, which lead to late diagnosis. This then has an effect on survival rates. In the United States, Black men have the highest incidence of prostate cancer among all other ethnic groups.
Recommended Reading: What Organs Does Prostate Cancer Spread To
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of prostate cancer is 90%, it means that men who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as men who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Survival Of Prostate Cancer
Survival depends on many factors. No one can tell you exactly how long you will live.
Below are general statistics based on large groups of people. Remember, they cant tell you what will happen in your individual case.
Survival for prostate cancer is generally good, particularly if you are diagnosed early.
Recommended Reading: Can Prostate Cause Frequent Urination
Differences Among Risk Groups
Men with PCa have been classified into low-, intermediate- and high-risk Groups for tumor recurrence and disease specific mortality, based on PSA level, clinical or pathological staging and GS. High-risk patients have PSA level 20ng/mL or GS 8 or clinical/pathological stage T2c . Lymph-node positive and PSM have also been reported as poor prognosis factors.
Risk Group classification predicts biochemical and clinical progression as well as PCa specific mortality and overall survival. The risk of disease progression in these groups has been validated for patients submited to RP in many studies. In patients from Mayo Clinic, BCR rates were 2.3 and 3.3-fold greater in high and intermediate-risk in comparison with low-risk patients, respectively. In those patients, mortality rates in high and intermediate-risk patients were greater than 11 and 6-fold over low-risk men .
Therefore, it is crutial to understand the role of each clinical and pathologic feature in PCa BCR and disease progression.
Dont Miss: Can You Be Asleep During A Prostate Biopsy
Towards A Meaningful Definition Of High
In the United States, approximately 238,590 men were expected to be diagnosed with prostate cancer in 2013, and 29,720 prostate cancer patients were anticipated to die of their disease in 2013.2 Many of the patients who die of prostate cancer present initially with tumours seemingly confined to the gland this arguably represents true high-risk disease and new approaches are needed for these patients. By current estimates, high-risk disease accounts for 15% of all prostate cancer diagnoses3. The limitations of determining risk based on the T, N, M classification, which does not include Gleason score or PSA, have long been recognized. An important first step toward a more reliable schema was first proposed by DAmico et al.,4 using an endpoint of PSA failure and defining high-risk as a clinical T stage cT2c, a Gleason score 8, or a PSA > 20 ng/mL this definition has been adopted by the American Urological Association .5 The Radiation Therapy Oncology Group developed the first classification which associated specific baseline factors with overall survival and cause-specific survival, arguably more relevant measures. High risk in the RTOG classification includes 1) Gleason 8, or 2) Gleason =7 plus either cT3 or node-positive PSA adds little to this model for the prediction of cause-specific survival or overall survival.6 When combining the RTOG model with the Kattan nomogram, the ability to predict prostate cancerspecific survival is improved.7
Read Also: What Does A Swollen Prostate Feel Like
Survival By Tumor Grade
One way cancer is staged is by looking at the grade of cancer. Grade refers to how cancer cells look like under a microscope.
Traditionally for prostate cancer, this has been done using the Gleason Score, which was developed in the 1960s. Under this system, cancerous cells are categorized on a scale from 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are considered normal prostate tissues, while cells in the grade 5 range have mutated to such an extent they no longer resemble normal cells.
In determining a Gleason score, a pathologist will examine a biopsy sample under a microscope and give a Gleason grade using the above scale to the most predominant pattern displayed, then a second grade to the pattern that is the second most predominant. Those two grades are then added to form the overall Gleason score .
In theory, Gleason scores could range from 2 to 10, but pathologists today rarely give a score between 2 and 5 and are more likely to be in the range of 6 to 10 with 6 being the lowest grade of prostate cancer.
Under the Gleason Score system, a 6 is considered low grade, 7 is intermediate and scores of 8, 9, or 10 are considered high-grade cancers.
The higher the Gleason score, the more likely it is the prostate cancer will grow and spread quickly.
However, there have been some issues with the Gleason system, and a new grading system, to act as an extension of the Gleason system, has been developed.
Under this system Gleason scores are now categorized into grade groups:
Additional Ui Design And Readability Adjustments
Read Also: What Is Prostate Removal Called
What Is The Survival Rate For Prostate Cancer
The average five-year survival rate for prostate cancer is very optimistic: 98%. This means it is relatively unlikely that a man diagnosed with prostate cancer will die from the disease.
This high survival rate is largely attributable to the fact that most prostate cancers are detected before the prostate cancer spreads to other organsin other words, when it is localized. Prostate cancer is detected at these earlier stages with regular screenings, which is why its so important for men to begin screening for prostate cancer at age 50.
That being said, there are aggressive prostate cancers that may decrease the chance of survival. The chances of survival dramatically decrease if the cancer has the opportunity to spread to further areas of the body.
How Is Prostate Cancer Staged
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer that develops in men and is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in American men, behind lung cancer and just ahead of colorectal cancer. The prognosis for prostate cancer, as with any cancer, depends on how advanced the cancer has become, according to established stage designations.
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized gland present only in men, found in the pelvis below the bladder. The prostate gland wraps around the urethra and lies in front of the rectum. The prostate gland secretes part of the liquid portion of the semen, or seminal fluid, which carries sperm made by the testes. The fluid is essential to reproduction.
The term to stage a cancer means to describe the evident extent of the cancer in the body at the time that the cancer is first diagnosed.
- Clinical staging of prostate cancer is based on the pathology results, physical examination, PSA, and if appropriate, radiologic studies.
- The stage of a cancer helps doctors understand the extent of the cancer and plan cancer treatment.
- Knowing the overall results of the different treatments of similarly staged prostate cancers can help the doctor and patient make important decisions about choices of treatment to recommend or to accept.
You May Like: How To Tell If You Have Prostate Cancer
How To Understand The Gleason Score
For instance, if the Gleason Score is written 4+3=7, this means 4 is the grade assigned to the most cancerous cells, while 3 is the grade of the next largest section of the tumor. Together they make up the total Gleason Score, in this instance 7.
A Gleason Score of 6 is considered low-grade. It describes cancer cells that resemble the normal cells and, therefore, the cancer is slow-growing.
A Gleason Score of 7 is considered an intermediate grade, with a medium risk of aggressive cancer. In this case, it is very important to know what is the primary grade . If the primary grade is 3 and the secondary grade is 4, the cancer is not that likely to spread so quickly or cause important problems while a Gleason Score of 7, with the primary grade of 4 and the secondary grade of 3 is more likely to be more aggressive and high-risk.
Consider asking about your primary Gleason Grade, especially when your Gleason Score is 7 and the Gleason Grades are not specified.
A Gleason score of 8-10 is considered to be high-risk. Cancers are likely to spread more quickly and be more aggressive.
For a better understanding of your particular situation, do not hesitate to contact a urologist!
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
Doctors describe the growth and spread of prostate cancer in stages. Doctors use these stages as guides when choosing treatment options or offering prognoses to their patients.
Prostate cancer staging is based on a number of different factors, including prostate cancer screening tests such as a digital rectal exam or prostate-specific antigen test and imaging studies like bones scans, MRIs, CT scans, and trans-rectal ultrasounds.
You May Like: How Many People Die From Prostate Cancer
To Treat Or Not To Treat
Up until now, with a few notable exceptions, doctors have myopically focused on treating prostate cancer, says Adami. They are willing to spend tens of thousands of dollars on chemotherapy that has minimal effects on cancer mortality, often with substantial side effects. But we ignore entirely the fact that large groups of prostate cancer patients die from other causes that actually are preventable.
Among older patients especially, that activity can take the form of vigorous walking. Recently, Mucci has spearheaded an intervention with Adami and other colleagues in Sweden, Iceland, and Ireland in which men walk in groups with a nurse three times a week. In a pilot study, researchers found improvements in just 12 weeks in body weight, blood pressure, sleep, urinary function, and mental health.
Scientists at HSPH are also searching for genetic and lifestyle markers that help predict how aggressive a patients prostate cancer will be. For example, an ongoing project led by Mucci and Adami draws on detailed cancer registries in Nordic countries, including an analysis of 300,000 twins, to tease out the relative contribution of different genes to prostate cancer incidence and survival.
is a Boston-based journalist and author of The Coke Machine: The Dirty Truth Behind the Worlds Favorite Soft Drink.
Browser And Assistive Technology Compatibility
We aim to support the widest array of browsers and assistive technologies as possible, so our users can choose the best fitting tools for them, with as few limitations as possible. Therefore, we have worked very hard to be able to support all major systems that comprise over 95% of the user market share including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, Opera and Microsoft Edge, JAWS and NVDA , both for Windows and for MAC users.
Also Check: Are Eggs Bad For Prostate
Survival By Disease Progression
The extent prostate cancer has progressed can influence survival rates.
Prostate-specific antigen is a protein produced by cells of the prostate gland by normal and malignant cells. In men with prostate cancer, blood levels of PSA are often elevated.
Doctors can use PSA as a marker to better understand the progression of prostate cancer and the resulting prognosis.
One way doctors assess the progression of the disease is through PSA doubling time. This refers to the number of months it takes for PSA to double.
One study suggests a short doubling time means a poorer prognosis for patients with stage IV prostate cancer. Median survival was 16.5 months for those with a PSA doubling time lower than 45 days compared with 26 months for patients with a longer PSA doubling time.
Whether or not the cancer has metastasized and spread to other areas of the body outside the prostate can also influence survival. In distant or stage IV prostate cancer, when cancer has spread from the prostate to other organs like the liver or lungs, the five-year survival rate is 31% compared with localized cancer, which has a five-year survival rate of nearly 100%.
Nomogram Predicting Model And Validation
The predicting model of nomograms was built with the factors in the multivariate Cox analysis . The C-index of this nomogram was 0.773, indicating a good discrimination ability of this model. Five- and 10-year calibration curves also revealed good agreement between the actual observation and the nomogram prediction.
Figure 3Figure 4
Dont Miss: How Do You Keep Your Prostate Healthy
Also Check: What Causes Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
